The SQL audit feature allows you to query and export various information related to SQL statements, such as databases, states, and runtime.
Prerequisites
You have enabled the SQL Explorer and Stress Testing (New) feature.
If you are a RAM user, you need to first grant permissions to a RAM user (AliyunDRDSReadOnlyWithSQLLogArchiveAccess) or use custom policies to grant a RAM user the permissions to use the search and export features in the SQL Explorer and Audit module before you use the SQL audit feature.
Procedure
Click the Audit tab and select the nodes that you want to audit.
NoteClick Service Settings to set the storage duration of SQL logs.
Set Query Conditions or Enable Advanced Query, and then click Query.
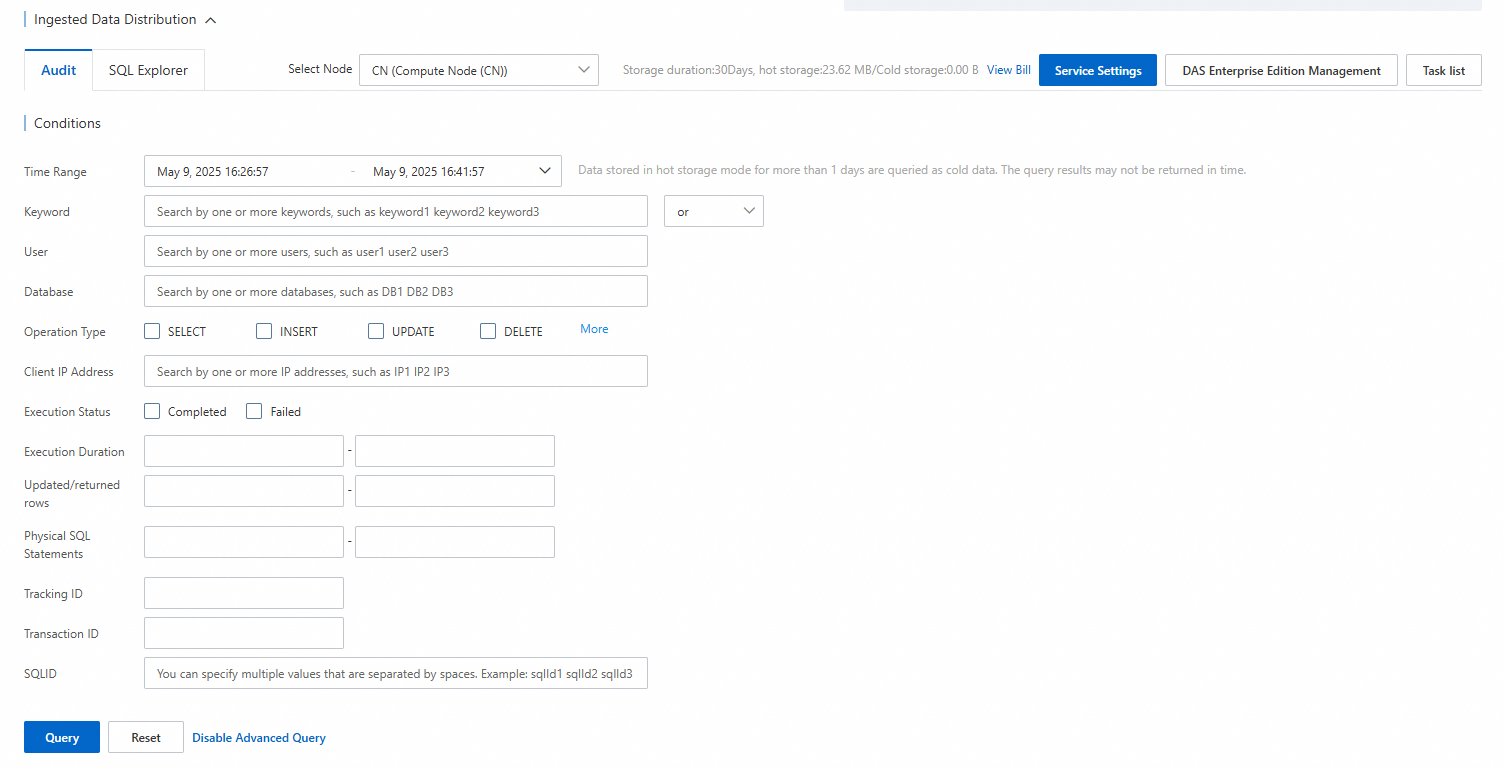
The parameters on the tab:
Parameter
Description
Time Range
The execution duration of the SQL statement.
Keyword
One or more keywords contained in the SQL statement. Separate multiple keywords with spaces (
OR: The filtered SQL statement can be retrieved if it contains one or more of the specified keywords.
AND: The filtered SQL statement can be retrieved only if it contains all the specified keywords.
User
The name of the database account. Multiple database accounts can be filtered together. Separate multiple database account names with spaces (
Database
The database name. Multiple databases can be filtered together. Separate multiple database names with spaces (
Operation Type
Filter by SQL operation type. You can select one or more operation types from SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, LOGIN, LOGOUT, MERGE, ALTER, CREATE, DROP, SET, DESC, REPLACE, CALL, BEGIN, DESCRIBE, ROLLBACK, FLUSH, USE, SHOW, START, COMMIT, RENAME, and TRUNCATE.
Client IP Address
The remote client IP that executes the SQL statement. Separate multiple client IP addresses with spaces (
Execution Status
Filter by whether the SQL execution is successful. You can select both Completed and Failed.
Execution Duration
The SQL execution duration in milliseconds. You can specify a range.
Updated/returned rows
The number of rows updated or returned after the execution. You can specify a range.
Physical SQL Statements
The number of SQL statements actually executed.
Tracking ID
The ID of request between the compute node and the data node. You can obtain it from the query results (log records).
Transaction ID
The transaction ID generated in the execution. You can obtain it from the query results (log records).
SQL ID
The SQL template ID. Separate multiple SQL template IDs with spaces (
(Optional) Click Export, select the required Export Fields to export SQL log records. You can export SQL records for a longer time range by setting the Export Time Range.
NoteClick View Export List to view the list of recent export tasks.