You can use the always-confidential database feature to ensure data security of Alibaba Cloud databases. If you enable the always-confidential database feature for a PolarDB for PostgreSQL (Compatible with Oracle) cluster, you can encrypt sensitive data columns in tables. This ensures that sensitive data in the columns is transmitted, computed, and stored as ciphertext.
Background information
As authorities enhance the supervision for data security and personal sensitive information protection, atomic data security capabilities can no longer meet the supervision requirements. If you want to meet the requirements of national regulations and industry standards, you must ensure the security of data throughout its lifecycle. However, traditional third-party security hardening and client-side encryption have disadvantages in terms of cost reduction, restructuring, and performance optimization. In response to these challenges, the always-confidential database feature was developed and has received widespread recognition in the industry. You can use the always-confidential database feature to resolve data security issues in various scenarios.
What is the always-confidential database feature?
The always-confidential database feature is jointly developed by the Database and Storage Lab of Alibaba DAMO Academy and the Alibaba Cloud database team. The feature uses advanced technologies to minimize the impact of potential data risks that are caused by unexpected events, such as human errors and platform management issues. The feature prevents any personnel who are not the data owner, such as the application service providers, from accessing your plaintext data and protects against data leaks in the cloud. The feature ensures that your data remains secure from unauthorized access by developers and operations & maintenance (O&M) personnel, and protects your database account information from being compromised.
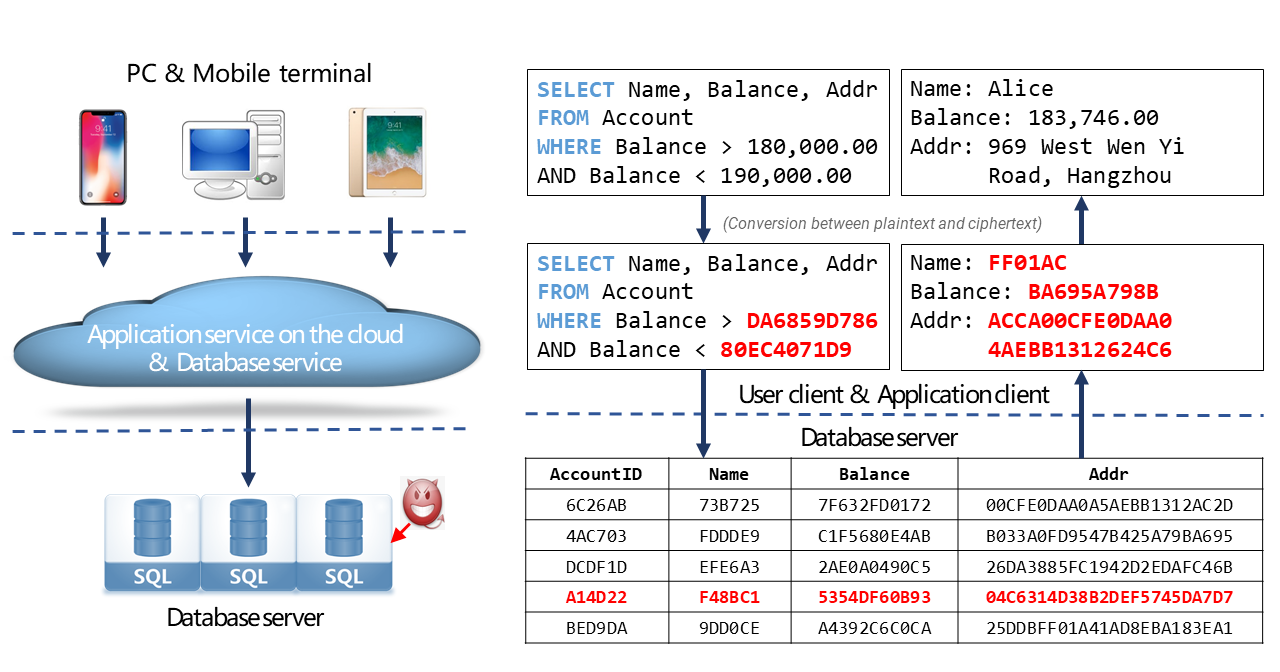
The always-confidential database feature offers confidential computing capabilities, which allow database transactions, queries, and analytics to be performed on ciphertext data within an untrusted server environment after the data has been encrypted on the user side (client side). This prevents cloud platform providers, unauthorized users, and management personnel such as database administrators (DBAs) from accessing your plaintext data. This also ensures that your data is available but invisible to all database users. The always-confidential database feature defends against external and internal threats in an efficient manner, protects your data throughout its lifecycle, and helps you privatize your cloud data.
How does the always-confidential database feature ensure that my data is not leaked on the cloud?
You encrypt your data on the client side by using your key and send the data to the PolarDB for PostgreSQL database. The PolarDB for PostgreSQL database personnel does not have access to the key. Therefore, the data cannot be decrypted and disclosed to untrusted environments.
How does the always-confidential database feature ensure that database operations can be performed on ciphertext data?
Before database operations are performed on ciphertext data, the client uses remote attestation to check whether the server runs in a trusted execution environment (TEE) and whether the code that is running in the TEE is trusted. If both conditions are met, the client passes the key to the TEE in end-to-end mode. This way, the ciphertext data and key can be processed in the TEE and cannot be accessed by external users.
Scenarios
The always-confidential database feature is developed in a bid to deliver the next-generation database framework and products that come with the capabilities to ensure data confidentiality and integrity. Built on an optimal design and architecture, the always-confidential database feature provides advanced security capabilities without compromising the high stability, high performance, and cost-effectiveness of the database system.
The following section describes several scenarios in which you can use the always-confidential database feature to ensure data security.
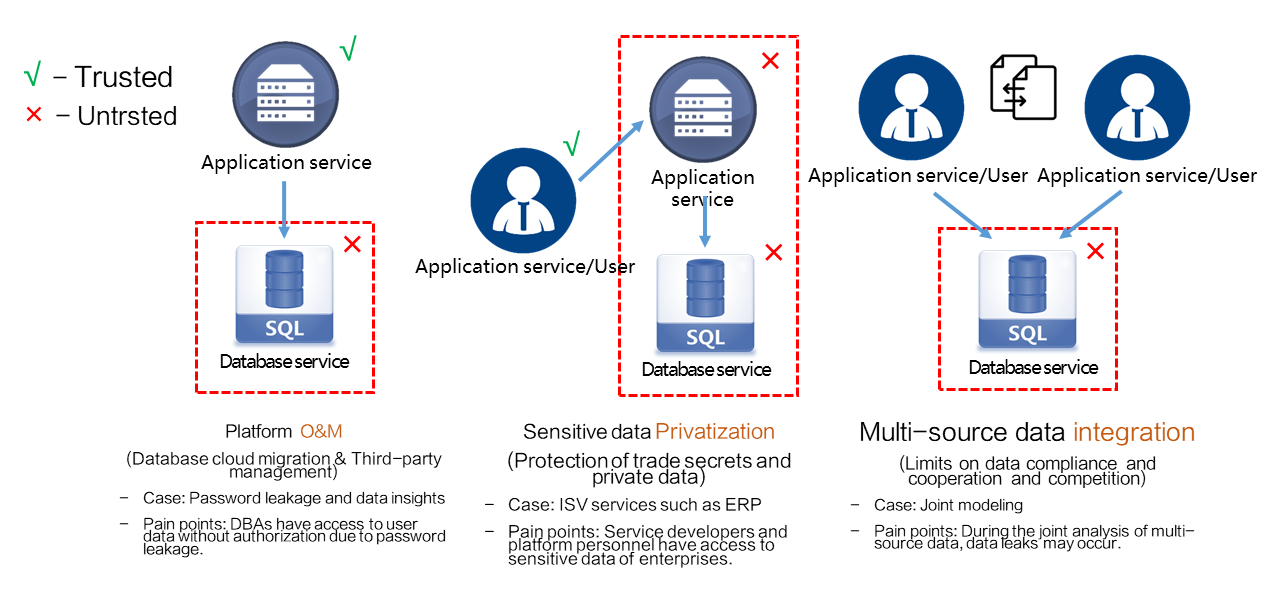
Platform O&M: This scenario involves database service protection in untrusted environments, such as third-party platforms, to ensure data security during O&M. In most cases, data owners are application service providers. They want to prevent their application data from being accessed by unauthorized database service providers and O&M personnel and ensure that their databases are running as expected.
Examples:
If a database is migrated to the cloud, the always-confidential database feature prevents unauthorized cloud platform providers and O&M personnel from accessing the database data.
If a database system is deployed on a server in a data center for application connection, the always-confidential database feature prevents unauthorized O&M personnel from accessing the database data.
Sensitive data compliance: This scenario involves application service protection in untrusted environments, such as third-party platforms, to ensure the security of sensitive user data. In user-oriented scenarios, specific data, such as health data and financial data, is owned by users. They want application services to provide data management and analysis capabilities without accessing plaintext private data.
Examples:
If enterprises use third-party services to manage commercial data, the always-confidential database feature prevents the trade secrets of the enterprises from being obtained by the third-party service providers.
If third-party service providers manage confidential data, such as personally identifiable information (PII) and gene information, the always-confidential database feature helps meet compliance requirements for end-to-end encryption.
Multi-source data integration: This scenario involves the joint analysis of multi-source data. During multi-source data integration and computing, the always-confidential feature prevents unauthorized access to multi-source data. The key used for encryption is available only to the data owners. If specific data needs to be shared with a third party, the always-confidential database feature allows the data owner to share the data without disclosing the key to the third party while meeting compliance requirements.
Examples:
In scenarios such as joint risk control and cross-border services, strict data compliance requirements are imposed. Organizations cannot obtain the plaintext data of each other.
In scenarios such as co-marketing, partners are also competitors. This complicates their relationship and makes it difficult for them to share plaintext data.
Security levels provided by the always-confidential database feature
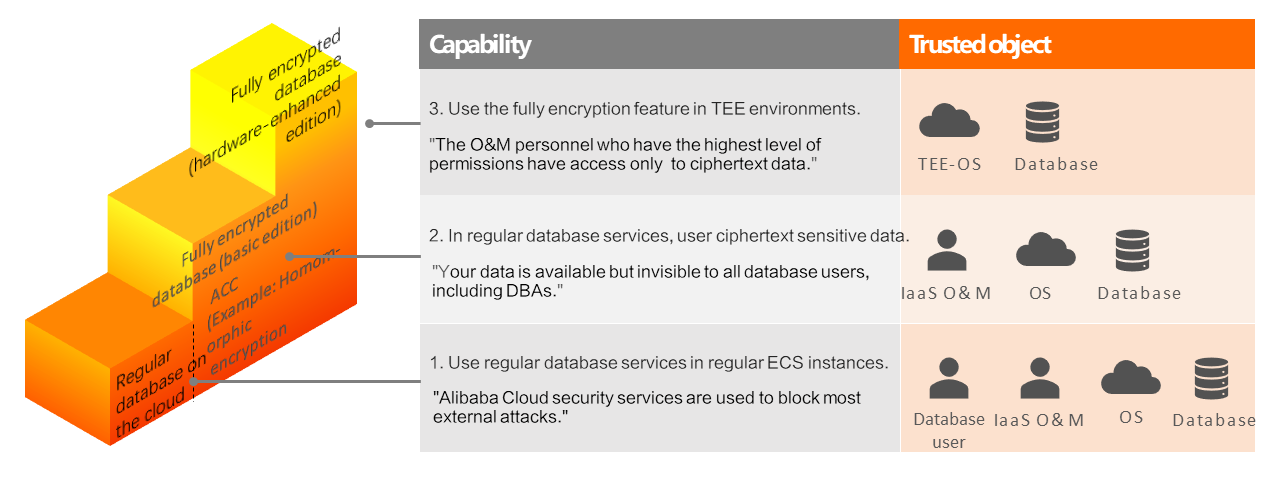
From a security perspective, cloud databases can prevent security threats at the following levels in ascending order:
Regular database in the cloud: This feature is used together with Alibaba Cloud security services to block most external attacks. However, a trust relationship must be built among the operating system, database software, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) O&M personnel, and database users.
Always-confidential database (basic edition): This feature is recommended. This feature is used together with the always-confidential access control module to control the access of database users to data within a database. This prevents unauthorized access and ensures that your data is available but invisible to all database users, including DBAs. You need to trust only the operating system, database software, and IaaS O&M personnel in your database cluster.
Always-confidential database (hardware-enhanced edition): Compared with the always-confidential database (basic edition) feature, this feature uses TEE technologies to allow the always-confidential database (basic edition) feature to run in TEE environments in which all external security threats are isolated. TEE technologies include Intel Software Guard Extensions (SGX), Intel Trust Domain Extensions (TDX), ARM TrustZone, AMD Secure Encrypted Virtualization (SEV), Hygon Commercial Security Version (CSV), and confidential containers. You need to trust only the operating system and database software in your database cluster.
All security levels of the always-confidential database feature have consistent features and advanced cryptographic capabilities such as homomorphic encryption.