This topic describes how to handle issues of full-text search in PolarDB for MySQL.
Description
This topic introduces the full-text search in the following ways:
Support for full-text search
Only InnoDB tables in PolarDB for MySQL support full-text indexes.
Full-text search parameters
Execute the following SQL statement to view parameters of full-text search in InnoDB tables:
show global variables like 'innodb_ft%';You can specify the following parameters on the Parameters page in the console. For more information, see Specify cluster and node parameters.
Parameter | Default value | Value range | Description |
innodb_ft_min_token_size | 3 | [0-16] | The minimum token size for full-text indexes in an InnoDB table. |
innodb_ft_max_token_size | 84 | [10-84] | The maximum token size for full-text indexes in an InnoDB table. |
Support for Chinese full-text search
InnoDB tables support Chinese full-text search. You must set the innodb_ft_min_token_size parameter to a value that is smaller than or equal to the minimum length of the word segmentation. Then, recreate a full-text index in the table.
For Chinese full-text search, we recommend that you set the ft_min_word_len parameter to 1. Otherwise, data may not be found.
The following sample code shows how to recreate a full-text index.
CREATE TABLE `my_ft_test_01` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` text, PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
FULLTEXT KEY `idx_ft_name` (`name`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=8 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;Follow these steps to recreate a full-text index:
Execute the following SQL statement to drop an existing full-text index.
alter table my_ft_test_01 drop key idx_ft_name;Execute the following SQL statement to add a full-text index.
alter table my_ft_test_01 add fulltext key idx_ft_name (name);
LIKE statement and full-text search
LIKE statement
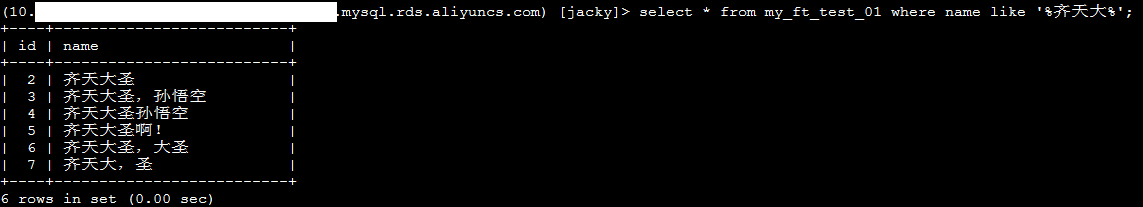
If the size of the table is small and the keyword in the query condition cannot be tokenized, you can use the LIKE operator in the query, as shown in the following figure. However, the query cannot hit the index on the column if you use the LIKE operator in the where clause. As a result, it takes more time to return the result than the queries that use indexes. We recommend that you use the LIKE operator with other query conditions. This allows you to use indexes on other columns to improve the query efficiency.
Full-text search
Full-text search is based on tokens. The returned result differs from that returned by queries using the LIKE operator, as shown in the following figure.
