You can call the PostObject operation to upload files directly from web clients to Object Storage Service (OSS). You can add signature information generated on the application server to secure these uploads and configure an appropriate upload policy to implement upload restrictions that meet your business requirements.
Solution overview
The following figure shows how to generate a signature on an application server and use the signature to upload a file directly from a web client to OSS.

To obtain signature information from the application server and upload data to OSS, perform the following steps:
In this process, temporary access credentials are used. This prevents the AccessKey pair of the application server from being leaked and ensures the security of file uploads.
Prepare OSS resources: You must first create a bucket for storing uploaded data and configure a cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) rule for the bucket to allow cross-origin requests from the web client.
Configure the application server: In this step, you need to call the corresponding operation of Security Token Service (STS) to obtain a pair of temporary access credentials. Then, you use the temporary access credentials and the upload policy preset on the application server to generate a signature and authorize users to upload files within a specific period of time. The preset upload policy includes information such as bucket name, directory path, and expiration time.
Configure the web client: Create an HTML form and use the form to submit the signature and upload the object to OSS.
Demo projects
Java project: server-signed-direct-upload-java.zip
Python project: server-signed-direct-upload-python.zip
Node.js project: server-signed-direct-upload-nodejs.zip
Go project: server-signed-direct-upload-go.zip
PHP project: server-signed-direct-upload-php.zip
Procedure
Step 1: Prepare OSS resources
1. Create a bucket
Create an OSS bucket to store data that is uploaded by the web application from a browser.
Log on to the OSS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Buckets. On the Buckets page, click Create Bucket.
In the Create Bucket panel, configure the parameters described in the following parameters.
Parameter
Sample value
Bucket Name
web-direct-upload
Region
China (Hangzhou)
Click Create.
2. Configure a CORS rule
Configure a CORS rule for the bucket that you created.
On the Buckets page, click the name of the bucket.
In the left-side navigation tree of the page that appears, choose Content Security > CORS. On the CORS page, click Create Rule.
In the Create Rule panel, configure the parameters described in the following table.
Parameter
Sample value
Source
*
Allowed Methods
POST, PUT, and GET
Allowed Headers
*
Click OK.
Step 2: Configure the application server
If you already have an application server available in your deployment, you can skip the preparatory steps and begin directly with the user permission configuration.
Preparations: Create an ECS instance as the application server
Operation 1: Create an ECS instance
On the Custom Launch tab of the instance buy page in the Elastic Compute Service (ECS) console, create or select basic resources required by the ECS instance.
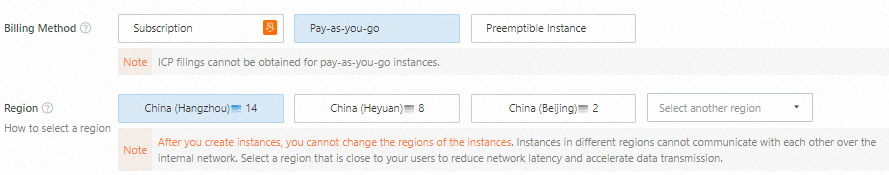
Select a region and a billing method
Select a billing method based on your business requirements. In this example, the Pay-as-you-go billing method is selected.
Select a region based on your network latency requirements. A region located closer to your intended users generally offers lower latency and faster access. In this example, the China (Hangzhou) region is selected.
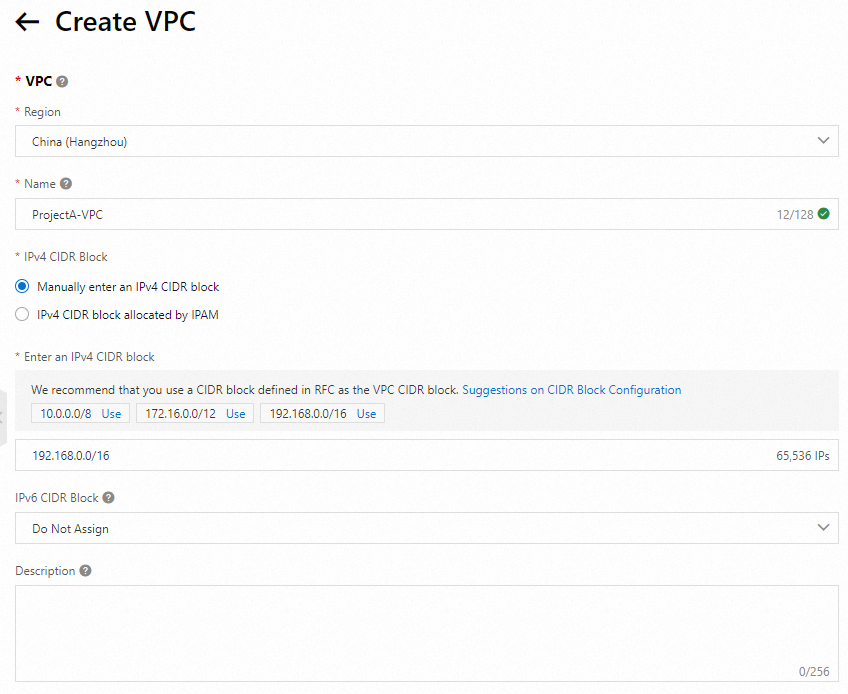
Create a virtual private cloud (VPC) and a vSwitch
When you create a VPC, select the region in which you created the ECS instance and plan CIDR blocks based on your business requirements. In this example, a VPC and a vSwitch are created in the China (Hangzhou) region. After you create a VPC, go back to the Custom Launch tab of the instance buy page in the ECS console, refresh the VPC and vSwitch drop-down lists, and then select the VPC and vSwitch that you created.
NoteYou can also create a vSwitch during VPC creation.

Select an instance type and an image
Select an instance type and an image. The selected image determines the operating system and its version. This example uses the cost-effective
ecs.e-c1m1.largeinstance type and theAlibaba Cloud Linux 3.2104 LTS 64-bitpublic image.
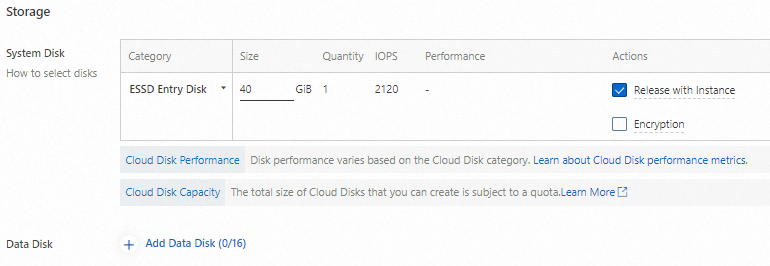
Configure storage
Configure a system disk and data disks for the ECS instance based on your business requirements. Since this demo project deploys a lightweight web application, a system disk alone suffices, and no data disks are configured.
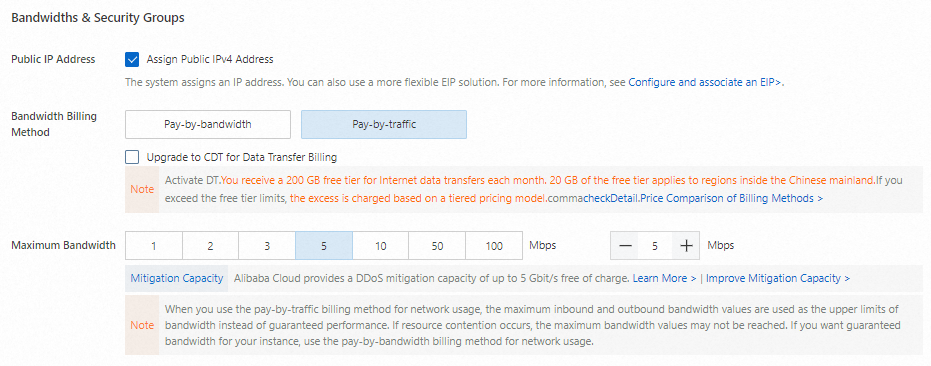
Assign a public IP address
To provide Internet connectivity to the ECS instance, select Assign Public IPv4 Address to assign a public IP address to the instance. Alternatively, you can associate an elastic IP address (EIP) with the ECS instance after you create the instance. For more information, see Associate an EIP with an ECS instance.
NoteIf you do not assign a public IP address to or associate an EIP with the ECS instance, you cannot access the instance over SSH or Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP), or test the web service deployed on the instance over the Internet.
After you select Assign Public IPv4 Address, set Bandwidth Billing Method to specify a billing method for network usage. In this example, the Bandwidth Billing Method parameter is set to Pay-by-traffic. In the pay-by-traffic billing method, you are charged based on the amount of data transferred over the Internet. For more information, see Public bandwidth billing.
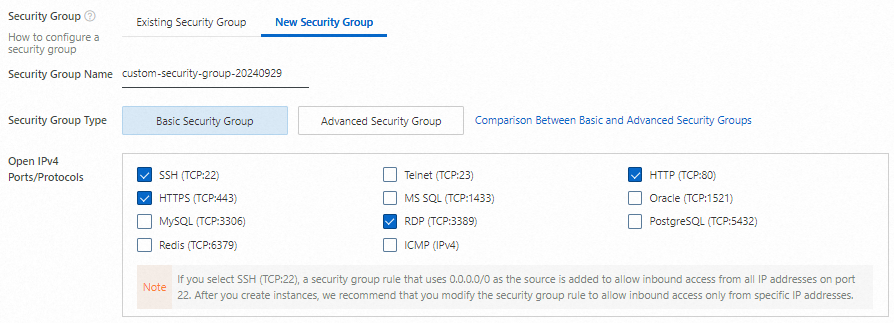
Create a security group
Create a security group for the ECS instance. A security group serves as a virtual firewall that controls inbound and outbound traffic for ECS instances. When you create a security group, open the following ports to allow access to the ECS instance:
Open IPv4 Ports/Protocols: select SSH (TCP:22), RDP (TCP:3389), HTTP (TCP:80), and HTTPS (TCP:443).
NoteThe ports selected for Open IPv4 Ports/Protocols are those that need to be open to the applications that run on the ECS instance.
If SSH (TCP:22) is selected in this process, the security group automatically contains a rule that allows traffic from 0.0.0.0/0, which represents all IP addresses. The rule allows access to the ECS instance from all IP addresses on the specified port. After you create the instance, we recommend that you modify the rule to allow access to the instance from only specific IP addresses. For more information, see Modify a security group rule.
Create a key pair
You can bind key pairs to an ECS instance and use the key pairs as credentials for authenticating your identity when you log on to the instance. After you create a key pair, download the private key of the key pair for subsequent use when you connect to the ECS instance. After you create a key pair, go back to the Custom Launch tab of the instance buy page, refresh the Key Pair drop-down list, and then select the key pair that you created.
rootis the highest-privileged account in the operating system. If you selectrootas the logon username, security risks may arise. We recommend that you selectecs-useras the logon username.NoteAfter you create the key pair, the private key of the key pair is automatically downloaded. View the download history of your browser to check the private key file, which is in the
.pemformat.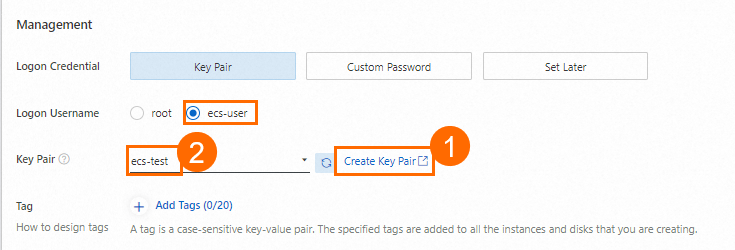
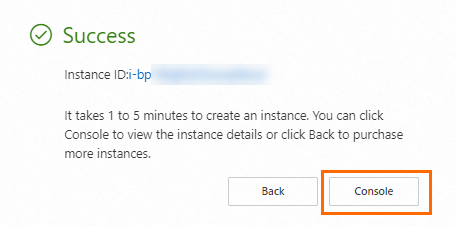
Complete instance creation and view the instance
After you create or select the required resources, click Create Order. In the Success message, click Console to view the created ECS instance. Record the following information for later use:
Instance ID: You can search for the ECS instance by instance ID.
Region and zone: You can search for the ECS instance by region and zone.
Public IP address: You can use the public IP address of the ECS instance to access the web service deployed on the instance.
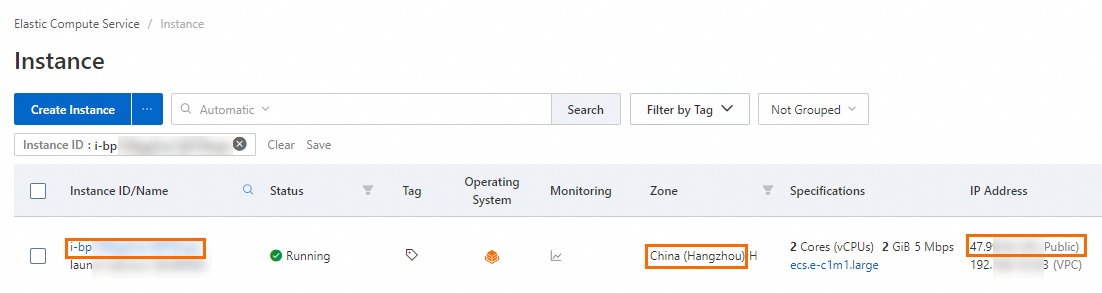
Operation 2: Connect to the ECS instance
On the Instance page in the ECS console, find the ECS instance that you created based on its region and ID. Then, click Connect in the Actions column.
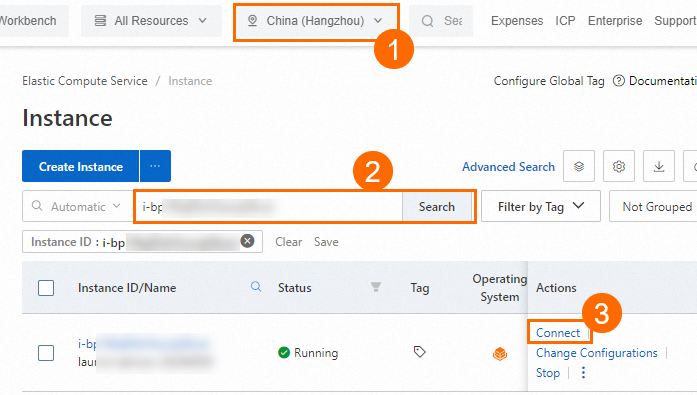
In the Remote connection dialog box, click Sign in now in the Workbench section.
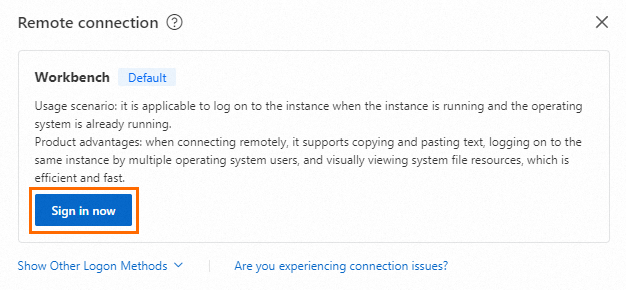
In the Instance Login dialog box, set Connection Method to Terminal Connection and Authentication Method to SSH Key Authentication. Then, enter or upload the private key downloaded when you created the key pair, and Log On to the ECS instance as
ecs-user.- Note
The private key file is automatically downloaded to your on-premises computer when you create the key pair. View the download history of your browser to find the private key file in the
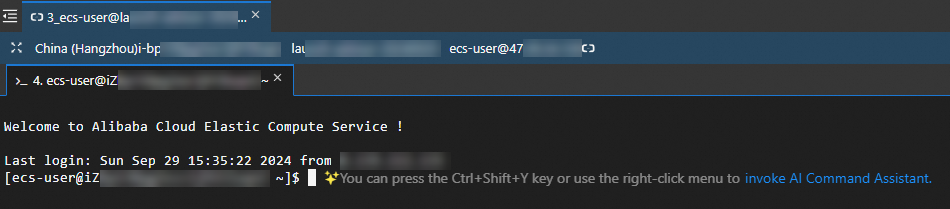
.pemformat. If a page similar to that shown in the following figure appears, you are logged on to the ECS instance.
1. Configure user permissions
We recommend that you grant the required permissions to a RAM user by using the following steps, to prevent failures in uploading files to OSS due to insufficient permission.
Operation 1: Create a RAM user in the RAM console
Create a RAM user and obtain the AccessKey pair of the RAM user. The AccessKey pair is a long-term access credential that is required to access and manage the application.
Log on to the RAM console by using an Alibaba Cloud account or as an account administrator.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Identities > Users.
On the Users page, click Create User.
Configure the Logon Name and Display Name parameters.
In the Access Mode section, select Using permanent AccessKey to access and click OK.
You can obtain the AccessKey secret of a RAM user only when you create the RAM user. You must keep the AccessKey secret secure to prevent credential leaks.
On the page that appears, click Copy in the Actions column to copy the AccessKey pair and paste it into a securely stored file.
Operation 2: Grant the RAM user the permissions to call the AssumeRole operation
Grant the RAM user the permissions to call the AssumeRole operation. This way, the RAM user can obtain temporary access credentials by assuming a RAM role.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Identities > Users.
On the Users page, find the RAM user and click Add Permissions in the Actions column.
In the Policy section of the Grant Permission panel, select the AliyunSTSAssumeRoleAccess policy.
NoteThe AliyunSTSAssumeRoleAccess policy allows a RAM user to call the AssumeRole operation. The policy does not grant the permissions required by the RAM user to obtain temporary access credentials from STS and initiate requests to OSS.
Click Grant permissions.
Operation 3: Create a RAM role in the RAM console
Create a RAM role for the Alibaba Cloud account and obtain the Alibaba Cloud Resource Name (ARN) of the RAM role. The RAM role is assumed by the RAM user later.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Identities > Roles.
Click Create Role and select Cloud Account for the Principal Type parameter.
Select Current Account for Principal Name.
In the dialog box that appears, enter a Role Name and click OK.
On the page that appears, click Copy to save the ARN of the role.
Operation 4: Create a custom policy in the RAM console
Create a custom policy based on the principle of least privilege to grant the RAM role the permissions to upload data only to a specific bucket.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Permissions > Policies.
On the Policies page, click Create Policy.
On the Create Policy page, click JSON. Copy the following sample script and paste it into the code editor. Replace
<BucketName>with the name of the bucket that you created, which isweb-direct-uploadin this example.{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Effect": "Allow", "Action": "oss:PutObject", "Resource": "acs:oss:*:*:<BucketName>/*" } ] }Click OK.
In the Create Policy dialog box, enter the Policy Name and click OK.
Operation 5: Attach the custom policy to the RAM role in the RAM console
Attach the custom policy to the RAM role. This way, the RAM role can provide the required permissions when the RAM role is assumed.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Identities > Roles.
On the Roles page, find the RAM role and click Grant Permission in the Actions column.
In the Grant Permission panel, select Custom Policy, then select the custom policy.
Click Grant permissions.
2. Obtain the temporary access credentials and calculate the signature on the application server
We recommend that you create environment variables to store sensitive information, such as accessKeyId, accessKeySecret, and roleArn, to avoid risks associated with explicitly specifying sensitive information in your code.
Perform the following steps to add environment variables:
Linux
Run the following commands on the CLI to add the configurations of the environment variables to the
~/.bashrcfile:echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID='your-access-key-id'" >> ~/.bashrc echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET='your-access-key-secret'" >> ~/.bashrc echo "export OSS_STS_ROLE_ARN='your-role-arn'" >> ~/.bashrcRun the following command to apply the changes:
source ~/.bashrcRun the following commands to check whether the environment variables take effect:
echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET echo $OSS_STS_ROLE_ARN
macOS
Run the following command in the terminal to view the default Shell type:
echo $SHELLPerform operations based on the default Shell type.
Zsh
Run the following command to add the configurations of the environment variables to the
~/.zshrcfile:echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID='your-access-key-id'" >> ~/.zshrc echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET='your-access-key-secret'" >> ~/.zshrc echo "export OSS_STS_ROLE_ARN='your-role-arn'" >> ~/.zshrcRun the following command to apply the changes:
source ~/.zshrcRun the following commands to check whether the environment variables take effect:
echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET echo $OSS_STS_ROLE_ARN
Bash
Run the following command to add the configurations of the environment variables to the
~/.bash_profilefile:echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID='your-access-key-id'" >> ~/.bash_profile echo "export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET='your-access-key-secret'" >> ~/.bash_profile echo "export OSS_STS_ROLE_ARN='your-role-arn'" >> ~/.bash_profileRun the following command to apply the changes:
source ~/.bash_profileRun the following commands to check whether the environment variables take effect:
echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID echo $OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET echo $OSS_STS_ROLE_ARN
Windows
Run the following command in cmd to create environment variables:
setx OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID "your-access-key-id" setx OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET "your-access-key-secret" setx OSS_STS_ROLE_ARN "your-role-arn"Open a new cmd window.
Run the following command in the new window to check whether the environment variable takes effect:
echo %OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID% echo %OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET% echo %OSS_STS_ROLE_ARN%
You can refer to the following sample code to calculate V4 signatures in PostObject requests on the application server. For information about the policy form field in a PostObject request, see policy.
Java
Add the following dependencies to the Maven project:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.aliyun/credentials-java -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun.oss</groupId>
<artifactId>aliyun-sdk-oss</artifactId>
<version>3.17.4</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun</groupId>
<artifactId>sts20150401</artifactId>
<version>1.1.6</version>
</dependency>You can refer to the following sample code to provide temporary access credentials and calculate signatures that will be used in PostObject requests:
package com.aliyun.oss.web;
import com.aliyun.sts20150401.models.AssumeRoleResponse;
import com.aliyun.sts20150401.models.AssumeRoleResponseBody;
import com.aliyun.tea.TeaException;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.utils.BinaryUtil;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import javax.crypto.Mac;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.time.*;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.*;
@Controller
public class WebController {
// The OSS bucket information. Replace the values with your actual information.
String bucket = "examplebucket";
String region = "cn-hangzhou";
String host = "http://examplebucket.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
// Specify the URL of the application server to which the upload callback request is sent. The URL must use the public domain name. This URL is used for communication between the application server and OSS. After you upload an object, OSS uses the URL to send upload information to the application server.
// The prefix of the names of objects uploaded to OSS.
String upload_dir = "dir";
// The validity period of the temporary credentials. Unit: seconds.
Long expire_time = 3600L;
/**
* The expiration time is calculated based on the specified validity period. Unit: seconds.
* @param seconds: the validity period, in seconds.
* @return: the time string in the ISO 8601 standard. Example: 2014-12-01T12:00:00.000Z.
*/
public static String generateExpiration(long seconds) {
// The current timestamp. Unit: seconds.
long now = Instant.now().getEpochSecond();
// The timestamp for the expiration time.
long expirationTime = now + seconds;
// Convert the timestamp into an Instant object and format it in the ISO 8601 format.
Instant instant = Instant.ofEpochSecond(expirationTime);
// Set the time zone to UTC.
ZoneId zone = ZoneOffset.UTC;
// Convert the Instant object into a ZonedDateTime object.
ZonedDateTime zonedDateTime = instant.atZone(zone);
// Define the date and time format. Example: 2023-12-03T13:00:00.000Z.
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSS'Z'");
// Format the date and time.
String formattedDate = zonedDateTime.format(formatter);
// Return the result.
return formattedDate;
}
// Initialize an StsClient instance.
public static com.aliyun.sts20150401.Client createStsClient() throws Exception {
// If the project code is leaked, the AccessKey pair may be leaked and the security of all resources within your account may be compromised. The following lines are provided only for reference.
// We recommend that you use STS tokens, which provide higher security.
com.aliyun.teaopenapi.models.Config config = new com.aliyun.teaopenapi.models.Config()
// Make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID environment variable is configured.
.setAccessKeyId(System.getenv("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID"))
// Make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variable is configured.
.setAccessKeySecret(System.getenv("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET"));
// Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For more information, visit https://api.alibabacloud.com/product/Sts.
config.endpoint = "sts.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
return new com.aliyun.sts20150401.Client(config);
}
/**
* Obtain an STS token.
* @return AssumeRoleResponseBodyCredentials object.
*/
public static AssumeRoleResponseBody.AssumeRoleResponseBodyCredentials getCredential() throws Exception {
com.aliyun.sts20150401.Client client = WebController.createStsClient();
com.aliyun.sts20150401.models.AssumeRoleRequest assumeRoleRequest = new com.aliyun.sts20150401.models.AssumeRoleRequest()
// Make sure that the OSS_STS_ROLE_ARN environment variable is configured.
.setRoleArn(System.getenv("OSS_STS_ROLE_ARN"))
.setRoleSessionName("yourRoleSessionName");// Specify a custom session name.
com.aliyun.teautil.models.RuntimeOptions runtime = new com.aliyun.teautil.models.RuntimeOptions();
try {
// Write your own code to display the response of the API operation if necessary.
AssumeRoleResponse response = client.assumeRoleWithOptions(assumeRoleRequest, runtime);
// The AccessKey ID, AccessKey secret, and STS token that are required for subsequent operations are included in credentials.
return response.body.credentials;
} catch (TeaException error) {
// Handle exceptions with caution in actual business scenarios, and do not ignore exceptions in your project. In this example, exceptions are printed for demonstration.
// Display the error message.
System.out.println(error.getMessage());
// Display the URL for troubleshooting.
System.out.println(error.getData().get("Recommend"));
com.aliyun.teautil.Common.assertAsString(error.message);
}
// Return a default error response object instead of null.
AssumeRoleResponseBody.AssumeRoleResponseBodyCredentials defaultCredentials = new AssumeRoleResponseBody.AssumeRoleResponseBodyCredentials();
defaultCredentials.accessKeyId = "ERROR_ACCESS_KEY_ID";
defaultCredentials.accessKeySecret = "ERROR_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET";
defaultCredentials.securityToken = "ERROR_SECURITY_TOKEN";
return defaultCredentials;
}
@GetMapping("/get_post_signature_for_oss_upload")
public ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> getPostSignatureForOssUpload() throws Exception {
AssumeRoleResponseBody.AssumeRoleResponseBodyCredentials sts_data = getCredential();
String accesskeyid = sts_data.accessKeyId;
String accesskeysecret = sts_data.accessKeySecret;
String securitytoken = sts_data.securityToken;
// Obtain the current date in the x-oss-credential header. The value is in the yyyyMMdd format.
ZonedDateTime today = ZonedDateTime.now().withZoneSameInstant(java.time.ZoneOffset.UTC);
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyyMMdd");
String date = today.format(formatter);
// Obtain the x-oss-date header.
ZonedDateTime now = ZonedDateTime.now().withZoneSameInstant(java.time.ZoneOffset.UTC);
DateTimeFormatter formatter2 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyyMMdd'T'HHmmss'Z'");
String x_oss_date = now.format(formatter2);
// Step 1: Create a policy.
String x_oss_credential = accesskeyid + "/" + date + "/" + region + "/oss/aliyun_v4_request";
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
Map<String, Object> policy = new HashMap<>();
policy.put("expiration", generateExpiration(expire_time));
List<Object> conditions = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String, String> bucketCondition = new HashMap<>();
bucketCondition.put("bucket", bucket);
conditions.add(bucketCondition);
Map<String, String> securityTokenCondition = new HashMap<>();
securityTokenCondition.put("x-oss-security-token", securitytoken);
conditions.add(securityTokenCondition);
Map<String, String> signatureVersionCondition = new HashMap<>();
signatureVersionCondition.put("x-oss-signature-version", "OSS4-HMAC-SHA256");
conditions.add(signatureVersionCondition);
Map<String, String> credentialCondition = new HashMap<>();
credentialCondition.put("x-oss-credential", x_oss_credential); // Replace the value with your AccessKey ID.
conditions.add(credentialCondition);
Map<String, String> dateCondition = new HashMap<>();
dateCondition.put("x-oss-date", x_oss_date);
conditions.add(dateCondition);
conditions.add(Arrays.asList("content-length-range", 1, 10240000));
conditions.add(Arrays.asList("eq", "$success_action_status", "200"));
conditions.add(Arrays.asList("starts-with", "$key", upload_dir));
policy.put("conditions", conditions);
String jsonPolicy = mapper.writeValueAsString(policy);
// Step 2: Create a string to sign.
String stringToSign = new String(Base64.encodeBase64(jsonPolicy.getBytes()));
// System.out.println("stringToSign: " + stringToSign);
// Step 3: Calculate the signing key.
byte[] dateKey = hmacsha256(("aliyun_v4" + accesskeysecret).getBytes(), date);
byte[] dateRegionKey = hmacsha256(dateKey, region);
byte[] dateRegionServiceKey = hmacsha256(dateRegionKey, "oss");
byte[] signingKey = hmacsha256(dateRegionServiceKey, "aliyun_v4_request");
// System.out.println("signingKey: " + BinaryUtil.toBase64String(signingKey));
// Step 4: Calculate the signature.
byte[] result = hmacsha256(signingKey, stringToSign);
String signature = BinaryUtil.toHex(result);
// System.out.println("signature:" + signature);
Map<String, String> response = new HashMap<>();
// Add data to the Map object.
response.put("version", "OSS4-HMAC-SHA256");
response.put("policy", stringToSign);
response.put("x_oss_credential", x_oss_credential);
response.put("x_oss_date", x_oss_date);
response.put("signature", signature);
response.put("security_token", securitytoken);
response.put("dir", upload_dir);
response.put("host", host);
// Return the ResponseEntity object that includes the 200 OK status code to the web client. Then, the client can perform the PostObject operation.
return ResponseEntity.ok(response);
}
public static byte[] hmacsha256(byte[] key, String data) {
try {
// Initialize SecretKeySpec, set the algorithm to HMAC-SHA256, and use the provided key.
SecretKeySpec secretKeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key, "HmacSHA256");
// Obtain a Mac instance and use the getInstance method to set the algorithm to HMAC-SHA256.
Mac mac = Mac.getInstance("HmacSHA256");
// Use the key to initialize the Mac instance.
mac.init(secretKeySpec);
// Calculate the HMAC value. Use the doFinal method to receive the data to be calculated and return the calculation result as an array.
byte[] hmacBytes = mac.doFinal(data.getBytes());
return hmacBytes;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Failed to calculate HMAC-SHA256", e);
}
}
}Python
Run the following commands to install the dependencies:
pip install flask
pip install alibabacloud_tea_openapi alibabacloud_sts20150401 alibabacloud_credentialsYou can refer to the following sample code to provide temporary access credentials and create an upload policy for calculating a signature to be used in PostObject requests:
from flask import Flask, render_template, jsonify
from alibabacloud_tea_openapi.models import Config
from alibabacloud_sts20150401.client import Client as Sts20150401Client
from alibabacloud_sts20150401 import models as sts_20150401_models
from alibabacloud_credentials.client import Client as CredentialClient
import os
import json
import base64
import hmac
import datetime
import time
import hashlib
app = Flask(__name__)
# Configure the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET, and OSS_STS_ROLE_ARN environment variables.
access_key_id = os.environ.get('OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID')
access_key_secret = os.environ.get('OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET')
role_arn_for_oss_upload = os.environ.get('OSS_STS_ROLE_ARN')
# Specify a session name.
role_session_name = 'yourRoleSessionName'
# Replace the values with your actual information.
bucket = 'examplebucket'
region_id = 'cn-hangzhou'
host = 'http://examplebucket.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com'
# The validity period of the temporary access credentials. Unit: seconds.
expire_time = 3600
# Specify the prefix in the name of the object that you want to upload to OSS.
upload_dir = 'dir'
def hmacsha256(key, data):
"""
The function calculates an HMAC-SHA256 value.
:param key: The key used to calculate the hash value. The key is of the byte type.
:param data: The data whose hash value you want to calculate. The data is of the string type.
:return: The calculated HMAC-SHA256 value. The value is of the byte type.
"""
try:
mac = hmac.new(key, data.encode(), hashlib.sha256)
hmacBytes = mac.digest()
return hmacBytes
except Exception as e:
raise RuntimeError(f"Failed to calculate HMAC-SHA256 due to {e}")
@app.route("/")
def hello_world():
return render_template('index.html')
@app.route('/get_post_signature_for_oss_upload', methods=['GET'])
def generate_upload_params():
# Initialize the configuration.
config = Config(
region_id=region_id,
access_key_id=access_key_id,
access_key_secret=access_key_secret
)
# Create an STS client and obtain temporary access credentials.
sts_client = Sts20150401Client(config=config)
assume_role_request = sts_20150401_models.AssumeRoleRequest(
role_arn=role_arn_for_oss_upload,
role_session_name=role_session_name
)
response = sts_client.assume_role(assume_role_request)
token_data = response.body.credentials.to_map()
# Use the temporary access credentials returned by STS.
temp_access_key_id = token_data['AccessKeyId']
temp_access_key_secret = token_data['AccessKeySecret']
security_token = token_data['SecurityToken']
now = int(time.time())
# Convert the timestamp to a datetime object.
dt_obj = datetime.datetime.utcfromtimestamp(now)
# Set the expiration time to 3 hours later than the current time.
dt_obj_plus_3h = dt_obj + datetime.timedelta(hours=3)
# The request time.
dt_obj_1 = dt_obj.strftime('%Y%m%dT%H%M%S') + 'Z'
# The request date.
dt_obj_2 = dt_obj.strftime('%Y%m%d')
# The expiration time of the request.
expiration_time = dt_obj_plus_3h.strftime('%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.000Z')
# Create a policy and generate a signature.
policy = {
"expiration": expiration_time,
"conditions": [
["eq", "$success_action_status", "200"],
{"x-oss-signature-version": "OSS4-HMAC-SHA256"},
{"x-oss-credential": f"{temp_access_key_id}/{dt_obj_2}/cn-hangzhou/oss/aliyun_v4_request"},
{"x-oss-security-token": security_token},
{"x-oss-date": dt_obj_1},
]
}
print(dt_obj_1)
policy_str = json.dumps(policy).strip()
# Step 2: Create a string to sign.
stringToSign = base64.b64encode(policy_str.encode()).decode()
# Step 3: Calculate the signing key.
dateKey = hmacsha256(("aliyun_v4" + temp_access_key_secret).encode(), dt_obj_2)
dateRegionKey = hmacsha256(dateKey, "cn-hangzhou")
dateRegionServiceKey = hmacsha256(dateRegionKey, "oss")
signingKey = hmacsha256(dateRegionServiceKey, "aliyun_v4_request")
# Step 4: Calculate the signature.
result = hmacsha256(signingKey, stringToSign)
signature = result.hex()
# Specify the response data.
response_data = {
'policy': stringToSign, # The form field.
'x_oss_signature_version': "OSS4-HMAC-SHA256", # The signature version and the algorithm used to calculate the signature. Set the value to OSS4-HMAC-SHA256.
'x_oss_credential': f"{temp_access_key_id}/{dt_obj_2}/cn-hangzhou/oss/aliyun_v4_request", # The parameters used to specify information about the derived key.
'x_oss_date': dt_obj_1, # The request time.
'signature': signature, # The signature description.
'host': host,
'dir': upload_dir,
'security_token': security_token # The STS token.
}
return jsonify(response_data)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(host="127.0.0.1", port=8000) # Listening on public addresses such as 0.0.0.0 requires the implementation of corresponding authentication mechanisms on the server side.Node.js
Run the following command to install the dependency:
npm install ali-oss
npm install @alicloud/credentials
npm install expressYou can refer to the following sample code to provide temporary access credentials and create an upload policy for calculating a signature to be used in PostObject requests:
const express = require('express');
const OSS = require('ali-oss');
const { STS } = require('ali-oss');
const { getCredential } = require('ali-oss/lib/common/signUtils');
const { getStandardRegion } = require('ali-oss/lib/common/utils/getStandardRegion');
const { policy2Str } = require('ali-oss/lib/common/utils/policy2Str');
const app = express();
const PORT = process.env.PORT || 8000; // Specify the port number.
// Specify the directory in which static files are stored.
app.use(express.static('templates'));
const GenerateSignature = async () => {
// Initialize the STS client.
let sts = new STS({
accessKeyId: process.env.OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID, //Obtain the AccessKey ID of the RAM user from the environment variable.
accessKeySecret: process.env.OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET // Obtain the AccessKey secret of the RAM user from the environment variable.
});
// Call the assumeRole operation to obtain temporary access credentials from STS.
const result = await sts.assumeRole(process.env.OSS_STS_ROLE_ARN, '', '3600', 'yourRoleSessionName'); // Obtain the ARN of the RAM role from the environment variable, set the validity period of the temporary access credentials to 3600 seconds, and set the role session name to yourRoleSessionName.
// Get the values of AccessKeyId, AccessKeySecret, and SecurityToken.
const accessKeyId = result.credentials.AccessKeyId;
const accessKeySecret = result.credentials.AccessKeySecret;
const securityToken = result.credentials.SecurityToken;
// Initialize the OSS client instance.
const client = new OSS({
bucket: 'examplebucket', // Replace examplebucket with the actual bucket name.
region: 'cn-hangzhou', // Replace cn-hangzhou with the ID of the region in which the bucket is located.
accessKeyId,
accessKeySecret,
stsToken: securityToken,
refreshSTSTokenInterval: 0,
refreshSTSToken: async () => {
const { accessKeyId, accessKeySecret, securityToken } = await client.getCredential();
return { accessKeyId, accessKeySecret, stsToken: securityToken };
},
});
// Create a Map to store form fields.
const formData = new Map();
// Set the signature expiration time to 10 minutes later than the current time.
const date = new Date();
const expirationDate = new Date(date);
expirationDate.setMinutes(date.getMinutes() + 10);
// Format the date as a UTC time string that conforms to the ISO 8601 standard.
function padTo2Digits(num) {
return num.toString().padStart(2, '0');
}
function formatDateToUTC(date) {
return (
date.getUTCFullYear() +
padTo2Digits(date.getUTCMonth() + 1) +
padTo2Digits(date.getUTCDate()) +
'T' +
padTo2Digits(date.getUTCHours()) +
padTo2Digits(date.getUTCMinutes()) +
padTo2Digits(date.getUTCSeconds()) +
'Z'
);
}
const formattedDate = formatDateToUTC(expirationDate);
// Create x-oss-credential and specify the form data.
const credential = getCredential(formattedDate.split('T')[0], getStandardRegion(client.options.region), client.options.accessKeyId);
formData.set('x_oss_date', formattedDate);
formData.set('x_oss_credential', credential);
formData.set('x_oss_signature_version', 'OSS4-HMAC-SHA256');
// Create a policy.
// The following example policy contains only required fields.
const policy = {
expiration: expirationDate.toISOString(),
conditions: [
{ 'bucket': 'examplebucket'},
{ 'x-oss-credential': credential },
{ 'x-oss-signature-version': 'OSS4-HMAC-SHA256' },
{ 'x-oss-date': formattedDate },
],
};
// If an STS token exists, add it to the policy and form data.
if (client.options.stsToken) {
policy.conditions.push({ 'x-oss-security-token': client.options.stsToken });
formData.set('security_token', client.options.stsToken);
}
// Generate a signature and specify the form data.
const signature = client.signPostObjectPolicyV4(policy, date);
formData.set('policy', Buffer.from(policy2Str(policy), 'utf8').toString('base64'));
formData.set('signature', signature);
// Return the form data.
return {
host: `http://${client.options.bucket}.oss-${client.options.region}.aliyuncs.com`,
policy: Buffer.from(policy2Str(policy), 'utf8').toString('base64'),
x_oss_signature_version: 'OSS4-HMAC-SHA256',
x_oss_credential: credential,
x_oss_date: formattedDate,
signature: signature,
dir: 'user-dir', // Specify the prefix in the name of the object that you want to upload to OSS.
security_token: client.options.stsToken
};
};
app.get('/get_post_signature_for_oss_upload', async (req, res) => {
try {
const result = await GenerateSignature();
res.json(result); // Return the generated signature data.
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error generating signature:', error);
res.status(500).send('Error generating signature');
}
});
app.listen(PORT, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on http://127.0.0.1:${PORT}`); // Listening on public addresses such as 0.0.0.0 requires the implementation of corresponding authentication mechanisms on the server side.
});Go
Run the following command to install the dependency:
go get -u github.com/aliyun/credentials-go
go mod tidyYou can refer to the following sample code to provide temporary access credentials and create an upload policy for calculating a signature to be used in PostObject requests:
package main
import (
"crypto/hmac"
"crypto/sha256"
"encoding/base64"
"encoding/hex"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io"
"hash"
"log"
"net/http"
"os"
"time"
"github.com/aliyun/credentials-go/credentials"
)
// Define the global variables.
var (
region string
bucketName string
product = "oss"
)
// Use the PolicyToken structure to store the generated form data.
type PolicyToken struct {
Policy string `json:"policy"`
SecurityToken string `json:"security_token"`
SignatureVersion string `json:"x_oss_signature_version"`
Credential string `json:"x_oss_credential"`
Date string `json:"x_oss_date"`
Signature string `json:"signature"`
Host string `json:"host"`
Dir string `json:"dir"`
}
func main() {
// Specify the default IP and port strings.
strIPPort := ":8000"
if len(os.Args) == 3 {
strIPPort = fmt.Sprintf("%s:%s", os.Args[1], os.Args[2])
} else if len(os.Args) != 1 {
fmt.Println("Usage : go run test1.go ")
fmt.Println("Usage : go run test1.go ip port ")
fmt.Println("")
os.Exit(0)
}
// Display the IP address and port of the server.
fmt.Printf("server is running on %s \n", strIPPort)
// Register the function that processes the root path requests.
http.HandleFunc("/", handlerRequest)
// Register the function that processes the requests initiated to obtain the signature.
http.HandleFunc("/get_post_signature_for_oss_upload", handleGetPostSignature)
// Start the HTTP server.
err := http.ListenAndServe(strIPPort, nil)
if err != nil {
strError := fmt.Sprintf("http.ListenAndServe failed : %s \n", err.Error())
panic(strError)
}
}
// Use the handlerRequest function to process requests to the root path.
func handlerRequest(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
if r.Method == "GET" {
http.ServeFile(w, r, "templates/index.html")
return
}
http.NotFound(w, r)
}
// Use the handleGetPostSignature function to process the requests initiated to obtain the signature.
func handleGetPostSignature(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
if r.Method == "GET" {
response := getPolicyToken()
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
w.Header().Set("Access-Control-Allow-Origin", "*") // Allow cross-origin requests.
w.Write([]byte(response))
return
}
http.NotFound(w, r)
}
// Use the getPolicyToken function to generate the signature and access credentials required to upload an object.
func getPolicyToken() string {
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located.
region = "cn-hangzhou"
// Specify the bucket.
bucketName = "examplebucket"
// Specify the URL to which the data is uploaded.
host := fmt.Sprintf("https://%s.oss-%s.aliyuncs.com", bucketName, region)
// Specify the directory to which you want to upload the object.
dir := "user-dir"
config := new(credentials.Config).
SetType("ram_role_arn").
SetAccessKeyId(os.Getenv("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID")).
SetAccessKeySecret(os.Getenv("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET")).
SetRoleArn("OSS_STS_ROLE_ARN").
SetRoleSessionName("Role_Session_Name").
SetPolicy("").
SetRoleSessionExpiration(3600)
// Create a credential provider based on the configurations.
provider, err := credentials.NewCredential(config)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("NewCredential fail, err:%v", err)
}
// Obtain access credentials from the credential provider.
cred, err := provider.GetCredential()
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("GetCredential fail, err:%v", err)
}
// Create a policy.
utcTime := time.Now().UTC()
date := utcTime.Format("20060102")
expiration := utcTime.Add(1 * time.Hour)
policyMap := map[string]any{
"expiration": expiration.Format("2006-01-02T15:04:05.000Z"),
"conditions": []any{
map[string]string{"bucket": bucketName},
map[string]string{"x-oss-signature-version": "OSS4-HMAC-SHA256"},
map[string]string{"x-oss-credential": fmt.Sprintf("%v/%v/%v/%v/aliyun_v4_request", *cred.AccessKeyId, date, region, product)},
map[string]string{"x-oss-date": utcTime.Format("20060102T150405Z")},
map[string]string{"x-oss-security-token": *cred.SecurityToken},
},
}
// Convert the format of the policy to JSON.
policy, err := json.Marshal(policyMap)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("json.Marshal fail, err:%v", err)
}
// Create a string to sign.
stringToSign := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString([]byte(policy))
hmacHash := func() hash.Hash { return sha256.New() }
// Create a signing key.
signingKey := "aliyun_v4" + *cred.AccessKeySecret
h1 := hmac.New(hmacHash, []byte(signingKey))
io.WriteString(h1, date)
h1Key := h1.Sum(nil)
h2 := hmac.New(hmacHash, h1Key)
io.WriteString(h2, region)
h2Key := h2.Sum(nil)
h3 := hmac.New(hmacHash, h2Key)
io.WriteString(h3, product)
h3Key := h3.Sum(nil)
h4 := hmac.New(hmacHash, h3Key)
io.WriteString(h4, "aliyun_v4_request")
h4Key := h4.Sum(nil)
// Generate a signature.
h := hmac.New(hmacHash, h4Key)
io.WriteString(h, stringToSign)
signature := hex.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil))
// Create content that will be returned to the frontend form.
policyToken := PolicyToken{
Policy: stringToSign,
SecurityToken: *cred.SecurityToken,
SignatureVersion: "OSS4-HMAC-SHA256",
Credential: fmt.Sprintf("%v/%v/%v/%v/aliyun_v4_request", *cred.AccessKeyId, date, region, product),
Date: utcTime.UTC().Format("20060102T150405Z"),
Signature: signature,
Host: host, // The URL to which the data is uploaded.
Dir: dir, // The directory to which the data is uploaded.
}
response, err := json.Marshal(policyToken)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("json err:", err)
}
return string(response)
}PHP
Run the following command to install the dependency:
composer installYou can refer to the following sample code to provide temporary access credentials and create an upload policy for calculating a signature to be used in PostObject requests:
<?php
// Use Alibaba Cloud SDKs.
require_once __DIR__ . '/vendor/autoload.php';
use AlibabaCloud\Client\AlibabaCloud;
use AlibabaCloud\Client\Exception\ClientException;
use AlibabaCloud\Client\Exception\ServerException;
use AlibabaCloud\Sts\Sts;
// Disable error displaying.
ini_set('display_errors', '0');
$bucket = 'examplebucket'; // Replace the value with your actual bucket name.
$region_id = 'cn-hangzhou'; // Replace the value with the ID of the region in which the bucket is located.
$host = 'http://examplebucket.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com'; // Replace the value with the URL of the bucket.
$expire_time = 3600; // Specify the validity period in seconds.
$upload_dir = 'user-dir'; // Specify the prefix in the object name.
// Calculate the HMAC-SHA256 value.
function hmacsha256($key, $data) {
return hash_hmac('sha256', $data, $key, true);
}
// Process the requests initiated to obtain signatures.
if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] === 'GET' && $_SERVER['REQUEST_URI'] === '/get_post_signature_for_oss_upload') {
AlibabaCloud::accessKeyClient(getenv('OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID'), getenv('OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET'))
->regionId('cn-hangzhou')
->asDefaultClient();
// Create a request to obtain temporary access credentials from STS.
$request = Sts::v20150401()->assumeRole();
// Initiate the STS request and obtain the result.
// Replace <YOUR_ROLE_SESSION_NAME> with a custom session name, such as oss-role-session.
// Replace <YOUR_ROLE_ARN> with the ARN of the RAM role that has the permissions to upload objects to the specified bucket.
$result = $request
->withRoleSessionName('oss-role-session')
->withDurationSeconds(3600)
->withRoleArn(getenv('OSS_STS_ROLE_ARN'))
->request();
// Obtain the credential information in the STS request result.
$tokenData = $result->get('Credentials');
// Construct JSON data from the returned result.
$tempAccessKeyId = $tokenData['AccessKeyId'];
$tempAccessKeySecret = $tokenData['AccessKeySecret'];
$securityToken = $tokenData['SecurityToken'];
$now = time();
$dtObj = gmdate('Ymd\THis\Z', $now);
$dtObj1 = gmdate('Ymd', $now);
$dtObjPlus3h = gmdate('Y-m-d\TH:i:s.u\Z', strtotime('+3 hours', $now));
// Create a policy.
$policy = [
"expiration" => $dtObjPlus3h,
"conditions" => [
["x-oss-signature-version" => "OSS4-HMAC-SHA256"],
["x-oss-credential" => "{$tempAccessKeyId}/{$dtObj1}/cn-hangzhou/oss/aliyun_v4_request"],
["x-oss-security-token" => $securityToken],
["x-oss-date" => $dtObj],
]
];
$policyStr = json_encode($policy);
// Create a string to sign.
$stringToSign = base64_encode($policyStr);
// Calculate the signing key.
$dateKey = hmacsha256(('aliyun_v4' . $tempAccessKeySecret), $dtObj1);
$dateRegionKey = hmacsha256($dateKey, 'cn-hangzhou');
$dateRegionServiceKey = hmacsha256($dateRegionKey, 'oss');
$signingKey = hmacsha256($dateRegionServiceKey, 'aliyun_v4_request');
// Calculate the signature.
$result = hmacsha256($signingKey, $stringToSign);
$signature = bin2hex($result);
// Return the signature data.
$responseData = [
'policy' => $stringToSign,
'x_oss_signature_version' => "OSS4-HMAC-SHA256",
'x_oss_credential' => "{$tempAccessKeyId}/{$dtObj1}/cn-hangzhou/oss/aliyun_v4_request",
'x_oss_date' => $dtObj,
'signature' => $signature,
'host' => $host,
'dir' => $upload_dir,
'security_token' => $securityToken
];
header('Content-Type: application/json');
echo json_encode($responseData);
exit;
}
// Specify the homepage route.
if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] === 'GET' && $_SERVER['REQUEST_URI'] === '/') {
echo file_get_contents(__DIR__ . '/public/index.html');
exit;
}
// Specify other routes.
http_response_code(404);
echo json_encode(['message' => 'Not Found']);
exit;
?>Step 3: Configure the web client
Create and submit a form upload request on the web client
After the web client receives the required information from the application server, you can use the information to construct an HTML form upload request. The request is directly sent to OSS for file upload.
Sample response received by the web client
Receive the temporary access credentials and the upload policy returned to the client from the application server.
{
"dir": "user-dirs",
"host": "http://examplebucket.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com",
"policy": "eyJl****",
"security_token": "CAIS****",
"signature": "9103****",
"x_oss_credential": "STS.NSpW****/20241127/cn-hangzhou/oss/aliyun_v4_request",
"x_oss_date": "20241127T060941Z",
"x_oss_signature_version": "OSS4-HMAC-SHA256"
}The following table describes the fields that are included in the message body.
Field | Description |
dir | The prefix contained in the name of the object. |
host | The URL of the bucket. |
policy | The policy for form upload. For more information, see Policy. |
security_token | The STS token. |
signature | The signature string of the policy. For more information, see POST signature. |
x_oss_credential | The parameters used to specify the derived key. |
x_oss_date | The time when the request was initiated. The time must follow the ISO 8601 standard. Example: |
x_oss_signature_version | The signature version and the algorithm used to calculate the signature. The value is fixed to OSS4-HMAC-SHA256. |
The form request contains file content and parameters returned by the server.
The web client can directly communicate with OSS and upload the file by using the form request.
Except for the file form field, the size of each form field (including key) cannot exceed 8 KB.
By default, an existing object that has the same name as the object that you upload is overwritten. If you do not want to overwrite the existing object, include the x-oss-forbid-overwrite header in the upload request and set the x-oss-forbid-overwrite header to true. This way, if you upload a file whose name is the same as an existing object in the destination path, the upload fails and OSS returns the FileAlreadyExists error code.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh-CN">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Upload Directly to OSS with Signatures from Application Server</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<form>
<div class="mb-3">
<label for="file" class="form-label">Select File:</label>
<input type="file" class="form-control" id="file" name="file" required />
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">Upload</button>
</form>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', function () {
const form = document.querySelector("form");
const fileInput = document.querySelector("#file");
form.addEventListener("submit", (event) => {
event.preventDefault();
const file = fileInput.files[0];
if (!file) {
alert('Select a file to upload. ');
return;
}
const filename = file.name;
fetch("/get_post_signature_for_oss_upload", { method: "GET" })
.then((response) => {
if (!response.ok) {
throw new Error("Failed to obtain the signature.");
}
return response.json();
})
.then((data) => {
let formData = new FormData();
formData.append("success_action_status", "200");
formData.append("policy", data.policy);
formData.append("x-oss-signature", data.signature);
formData.append("x-oss-signature-version", "OSS4-HMAC-SHA256");
formData.append("x-oss-credential", data.x_oss_credential);
formData.append("x-oss-date", data.x_oss_date);
formData.append("key", data.dir + file.name); // The file name.
formData.append("x-oss-security-token", data.security_token);
formData.append("file", file); // The form field "file" must be the last one.
return fetch(data.host, {
method: "POST",
body: formData
});
})
.then((response) => {
if (response.ok) {
console.log("Uploaded.");
alert("File uploaded.");
} else {
console.log("Upload failed with the following response:", response);
alert("Failed to upload the file. Try again later.");
}
})
.catch((error) => {
console.error("An error occurred:", error);
});
});
});
</script>
</body>
</html>The HTML form contains a file input field and a Submit button. You can select a file to upload and submit the form.
When you submit the form, the default form submission is blocked by using JavaScript code, and the signature information required for the upload is obtained from the server by using an Asynchronous JavaScript and XML (AJAX) request.
After you obtain the signature information, construct a
FormDataobject that contains all the required form fields.You can use the
fetchmethod to send a POST request to the URL of the OSS bucket.
If a file is uploaded, the "File uploaded." message is displayed. If a file fails to be uploaded, an error message is displayed.
Verify the result
After you complete the preceding steps, you can access the application server to generate a signature and upload files from a web client to OSS.
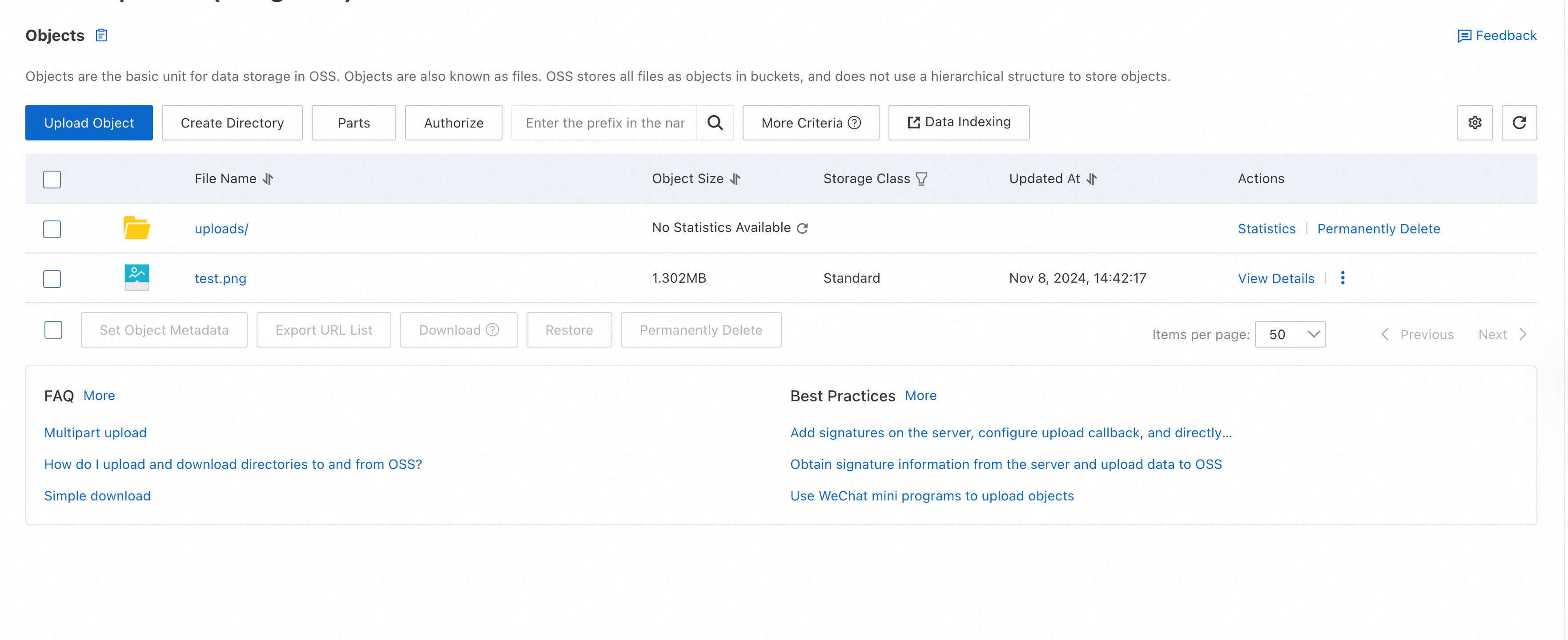
Access the server via the browser, then select and upload the object. The following figure provides an example.
On the Buckets page, click the name of the bucket that you created to store uploaded objects. On the page that appears, view the object that you uploaded from the web client.
Suggested configurations
Restrict file upload permissions and conditions
You can modify the policy part in the sample code to specify intended permissions and conditions for file uploads to OSS from the HTML form. A policy for form uploads defines conditions in JSON format that upload requests must meet to secure file uploads and ensure compliance. For example, you can use conditions to specify the destination bucket for file uploads, object name prefix, expiration time, allowed HTTP methods, file size limit, and file type.
{
"expiration": "2023-12-03T13:00:00.000Z",
"conditions": [
{"bucket": "examplebucket"},
{"x-oss-signature-version": "OSS4-HMAC-SHA256"},
{"x-oss-credential": "AKIDEXAMPLE/20231203/cn-hangzhou/oss/aliyun_v4_request"},
{"x-oss-security-token": "CAIS******"},
{"x-oss-date": "20231203T121212Z"},
["content-length-range", 1, 10],
["eq", "$success_action_status", "201"],
["starts-with", "$key", "user/eric/"],
["in", "$content-type", ["image/jpg", "image/png"]],
["not-in", "$cache-control", ["no-cache"]]
]
}For more information, see Policy
Configure an upload callback
If you want to obtain more information about an uploaded object, such as the object name and size, you can configure an upload callback. This way, information about files is automatically received after the files are uploaded. For more information, see Add signatures on the server, configure upload callbacks, and directly transfer data.
Include the URL of the application server in the sources of the CORS settings
Earlier in the CORS configuration step, we specified the wildcard character * to allow access from all sources. For security reasons, we recommend that you restrict allowed sources. For example, you can specify the URL of your application server as the only allowed source. This way, cross-origin access is only allowed for requests from your application server.
Parameter | Sample value |
Source |
|
Allowed Methods | POST, PUT, and GET |
Allowed Headers | * |
Resource clearup
To build the web application, you created an ECS instance, an OSS bucket, a RAM user, and a RAM role. After you complete verification, you can release these resources to avoid unnecessary charges and eliminate relevant security risks.
Release the ECS instance
If you no longer need the ECS instance that you created, you can release it. After the ECS instance is released, billing for the instance stops, and data on the instance is lost and cannot be restored. To release the ECS instance, perform the following steps:
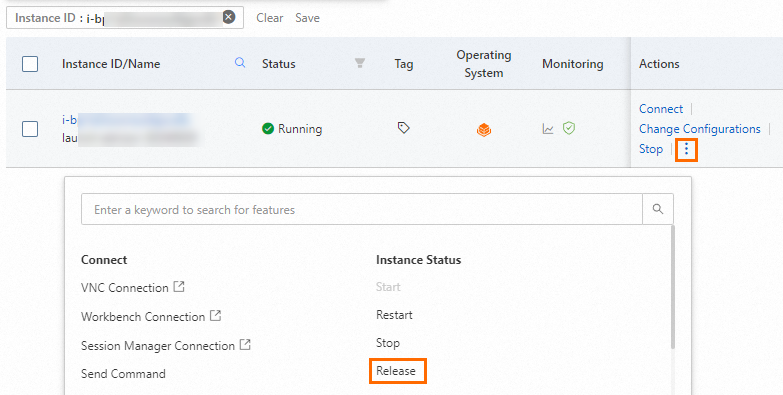
Go to the Instance page in the ECS console, find the ECS instance based on its region and instance ID, and then click the
 icon in the Actions column.
icon in the Actions column. Choose Instance Status > Release.
In the Release dialog box, select Release Now for Release Settings and click Next.
Confirm the associated resources that you want to release, read the notes about data loss risks, select the "I am aware of the instances and their associated resources to be released and understand the data risks" check box, and then click OK.
When the ECS instance is released, the system disk of the instance is released. If a public IP address was assigned to the instance, the IP address is also released.
When the ECS instance is released, the associated security group, vSwitch, and VPC are not released. You are not charged for the security group, vSwitch, or VPC. You can retain or release them based on your business requirements.
If an EIP is associated with the ECS instance, the EIP is retained when the instance is released. You are charged for the EIP. You can retain or release the EIP based on your business requirements.
Delete the bucket
Log on to the OSS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Buckets. On the Buckets page, click the name of the bucket that you want to delete.
Delete all objects in the bucket and then delete the bucket.
In the left-side navigation tree, click Delete Bucket. On the Delete Bucket page, click Delete Bucket and follow the on-screen instructions to complete the delete operation.
Delete the RAM user
Log on to the RAM console as a RAM user who has admin privileges.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Identities > Users.
On the Users page, find the RAM user that you want to delete and click Delete in the Actions column.
You can also select multiple RAM users and click Delete User below the RAM user list to move all the selected RAM users to the recycle bin at the same time.
In the Delete User dialog box, read the statement on the impact of deletion, enter the name of the RAM user, and then click Move to Recycle Bin.
Delete the RAM role
Log on to the RAM console as a RAM user who has admin privileges.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Identities > Roles.
On the Roles page, find the RAM role that you want to delete and click Delete Role in the Actions column.
In the Delete Role dialog box, enter the name of the RAM role and click Delete Role.
NoteIf a policy is attached to the RAM role, the policy is detached when you delete the RAM role.
References
Does this direct upload solution support multipart upload and resumable upload?
No, this solution does not support multipart upload or resumable upload because files in the solution are uploaded by using an HTML form. For information about how to implement multipart upload or resumable upload, see Resumable upload and Multipart upload.
How can I prevent a file upload from overwriting an existing object in the destination OSS path?
If you want to prevent a file upload from overwriting an existing object in the destination OSS path, you can add the x-oss-forbid-overwrite header in the request and set its value to true. For example:
formData.append('x-oss-forbid-overwrite', 'true');