Object Storage Service (OSS) provides up to 100 Gbit/s of single-account bandwidth over an internal network in the following regions: China (Shanghai), China (Shenzhen), China (Beijing), and China (Hangzhou). This topic describes how to make full use of the 100 Gbit/s bandwidth of OSS by analyzing key points and providing a case study of using OSS SDK for Go to download an object and test the peak bandwidth. This topic also describes how to use common tools to improve the object concurrent download performance of OSS.
Scenarios
Business scenarios involving large amounts of data, high concurrent access, or extremely high real-time requirements typically require up to 100 Gbit/s of internal network bandwidth. Examples:
Big data analysis and computing: You need to read a large amount of data, such as reading terabytes or even petabytes of data in a single task, which requires high real-time performance. To improve computing efficiency, the data reading speed must be fast enough to avoid performance bottlenecks.
AI training dataset loading: The training dataset may contain petabytes of data, which requires high throughput. When multiple training nodes load data at the same time, the total bandwidth may reach 100 Gbit/s.
Data backup and restoration: If the amount of data is large, backup and restoration operations, such as full data backups, involve petabytes of data. If you need to complete the backup and restoration operations within a short period of time, the bandwidth may reach 100 Gbit/s.
High-performance scientific computing: A scientific computing task may process petabytes of data or even larger datasets. Multiple research teams may access the same data at the same time, resulting in high concurrent access and high bandwidth requirements. To support real-time analysis and team collaboration, data transmission must be accelerated.
Key points
To use up to 100 Gbit/s of bandwidth, you must first select an appropriate Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance type to set the upper bandwidth limit. Second, if you want to store data on disks, you must select high-performance disks to improve efficiency. In addition, we recommend that you access data over a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) to improve access speed. If you require concurrent downloads, you can use appropriate optimization techniques to leverage the download bandwidth.
Network receiving capability
If you installed the OSS client on an ECS instance, the data download speed is limited by the network speed of the ECS instance. The Alibaba Cloud model with the strongest network capability can provide 160 Gbit/s of bandwidth. If you deploy multiple instances in a cluster, the total bandwidth can reach 100 Gbit/s when the client is concurrently accessed. If you deploy only a single instance, we recommend that you use network-enhanced instance families or instance families with high clock speeds. The latter performs better when they receive a large number of data packets.
Take note that a single elastic network interface (ENI) supports up to 100 Gbit/s of bandwidth based on the instance specifications. If the bandwidth of a single instance exceeds 100 Gbit/s, ECS requires you to bind multiple ENIs. For more information, see Elastic Network Interfaces.
Disk I/O
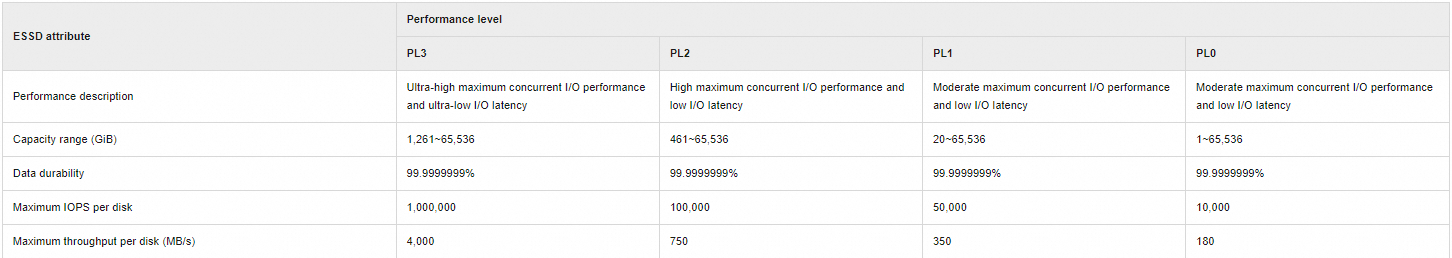
After the data is downloaded to the local computer, if you want to store the data on disks, the download speed is limited by the disk performance. By default, tools such as ossutil and ossfs store data on disks. In this case, you can use high-performance disks or memory disks to improve the download speed, as shown in the following figure.
Although an Enterprise SSD (ESSD) can achieve a throughput of 32 Gbit/s, a memory disk has a significantly better performance. To reach the maximum download bandwidth, do not store data on disks. For more information about how to use ossfs to prevent data from being stored on disks and improve data read performance, see Performance optimization in read-only scenarios.
Use a VPC
The Alibaba Cloud internal network is optimized for network data requests. When you use a VPC endpoint, the network is more stable than the Internet. To reach the maximum download bandwidth, you must use a VPC.
Your ECS instances run in your VPC. OSS provides a unified internal domain name that can be accessed by any customer over a VPC. Example: oss-cn-beijing-internal.aliyuncs.com. The data flow between ECS and OSS passes through Server Load Balancer (SLB), and requests are sent to the backend distributed cluster. This evenly distributes data requests across the cluster and grants OSS powerful high-concurrency processing capabilities.

Concurrent download
OSS uses the HTTP protocol to transmit data. Due to the performance limitations of a single HTTP request, concurrent download is used to accelerate data download. For example, you can split an object into multiple ranges so that each request accesses only one range to reach the maximum download bandwidth. You are charged based on the number of API operations. A greater number of ranges mean a greater number of API operations, and a greater number of ranges do not guarantee the peak download speed during the single-stream data downloads. For more information about how to use common tools for concurrent download, see Optimize concurrent download by using common tools.

Use cases
To test the download capability of the maximum bandwidth, we built a Go language test program to download a 100 GB binary bin object from OSS. We designed a special data processing strategy to avoid storing data on disks, which means that the data is read once and then discarded. At the same time, the large object is split into multiple ranges, and the range size and the amount of concurrent data are configured as adjustable parameters. You can easily adjust these parameters to reach the maximum download bandwidth.
Test environment
Instance type | vCPU | Memory (GiB) | Network baseline/burst bandwidth (Gbit/s) | Packet forwarding rate (PPS) | Number of connections | NIC queues | ENI | Private IPv4/IPv6 addresses per ENI | Number of disks that can be attached | Disk baseline/burst IOPS | Disk baseline/burst bandwidth (Gbit/s) |
ecs.hfg8i.32xlarge | 128 | 512 | 100/none | 30 million | 4 million | 64 | 15 | 50/50 | 64 | 900,000/none | 64/none |
Test procedure
Configure environment variables.
export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID=<ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID> export OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET=<ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET>Sample code:
package main import ( "context" "flag" "fmt" "io" "log" "time" "github.com/aliyun/alibabacloud-oss-go-sdk-v2/oss" "github.com/aliyun/alibabacloud-oss-go-sdk-v2/oss/credentials" ) // Specify the global variables to store the command line parameters. var ( region string // The region in which the bucket is located. endpoint string // The endpoint of the bucket in which the bucket is located. bucketName string // The name of the bucket. objectName string // The name of the object. chunkSize int64 // The size of the chunk. Unit: bytes. prefetchNum int // The number of chunks to be prefetched. ) // Initialize the function to parse command line parameters. func init() { flag.StringVar(®ion, "region", "", "The region in which the bucket is located.") flag.StringVar(&endpoint, "endpoint", "", "The domain names that other services can use to access OSS.") flag.StringVar(&bucketName, "bucket", "", "The `name` of the bucket.") flag.StringVar(&objectName, "object", "", "The `name` of the object.") flag.Int64Var(&chunkSize, "chunk-size", 0, "The chunk size, in bytes") flag.IntVar(&prefetchNum, "prefetch-num", 0, "The prefetch number") } func main() { // Parse the command line parameters. flag.Parse() // Check whether the required parameters are specified. if len(bucketName) == 0 { flag.PrintDefaults() log.Fatalf("invalid parameters, bucket name required") } if len(region) == 0 { flag.PrintDefaults() log.Fatalf("invalid parameters, region required") } // Configure the OSSClient instance. cfg := oss.LoadDefaultConfig(). WithCredentialsProvider(credentials.NewEnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider()). // Use credentials in environment variables. WithRegion(region) // Specify the region. // If a custom endpoint is provided, specify the endpoint. if len(endpoint) > 0 { cfg.WithEndpoint(endpoint) } // Create the OSSClient instance. client := oss.NewClient(cfg) // Open the OSS object. f, err := client.OpenFile(context.TODO(), bucketName, objectName, func(oo *oss.OpenOptions) { oo.EnablePrefetch = true // Enable the prefetch mode. oo.ChunkSize = chunkSize // Specify the size of the chunk. oo.PrefetchNum=prefetchNum // Specify the number of chunks to be prefetched. oo.PrefetchThreshold=int64 (0) // Specify the prefetch threshold. }) if err != nil { log.Fatalf("open fail, err:%v", err) } // Record the start time. startTick := time.Now().UnixNano() / 1000 / 1000 // Read and discard the content of the file used to test the reading speed. written, err := io.Copy(io.Discard, f) // Record the end time. endTick := time.Now().UnixNano() / 1000 / 1000 if err != nil { log.Fatalf("copy fail, err:%v", err) } // Calculate the reading speed. Unit: MiB/s. speed := float64(written/1024/1024) / float64((endTick-startTick)/1000) // Display the average reading speed. fmt.Printf("average speed:%.2f(MiB/s)\n", speed) }Start the test program.
go run down_object.go -bucket yourbucket -endpoint oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com -object 100GB.file -region cn-hangzhou -chunk-size 419430400 -prefetch-num 256
Test conclusions
In the preceding process, we adjust the concurrency and chunk size to observe changes in the download duration and peak download bandwidth. In general, we recommend that you set the concurrency to 1 to 4 times the number of the cores and set the chunk size to the FileSize/Concurrency value. The chunk size cannot be less than 2 MB. The shortest download duration can be achieved and the peak download bandwidth reaches 100 Gbit/s based on the parameter configurations.
No. | Concurrency | Chunk size (MB) | Peak bandwidth (Gbit/s) | E2E (s) |
1 | 128 | 800 | 100 | 16.321 |
2 | 256 | 400 | 100 | 14.881 |
3 | 512 | 200 | 100 | 15.349 |
4 | 1024 | 100 | 100 | 19.129 |
Optimize concurrent downloads by using common tools
The following section describes the methods for optimizing the download performance of OSS objects by using common tools.
ossutil
Parameter description
Parameter
Description
--bigfile-threshold
The object size threshold for using resumable download. Default value: 104857600 (100 MB). Valid values: 0 to 9223372036854775807. Unit: bytes.
--range
The byte range of the object to download. Bytes are numbered starting from 0.
You can specify a range. For example, 3-9 indicates a range from byte 3 to byte 9, which includes byte 3 and byte 9.
You can specify the range from which the download starts. For example, 3- indicates a range from byte 3 to the end of the object, which includes byte 3.
You can specify the range from which the download ends. For example, -9 indicates a range from byte 0 to byte 9, which includes byte 9.
--parallel
The number of concurrent operations to perform on a single object. Valid values: 1 to 10000. By default, ossutil automatically sets a value for this option based on the operation type and object size.
--part-size
The part size. Unit: bytes. Valid values: 2097152 to 16777216 (2 to 16 MB). In most cases, if the number of CPU cores is large, you can set a small part size. If the number of CPU cores is small, you can increase the part size appropriately.
Example
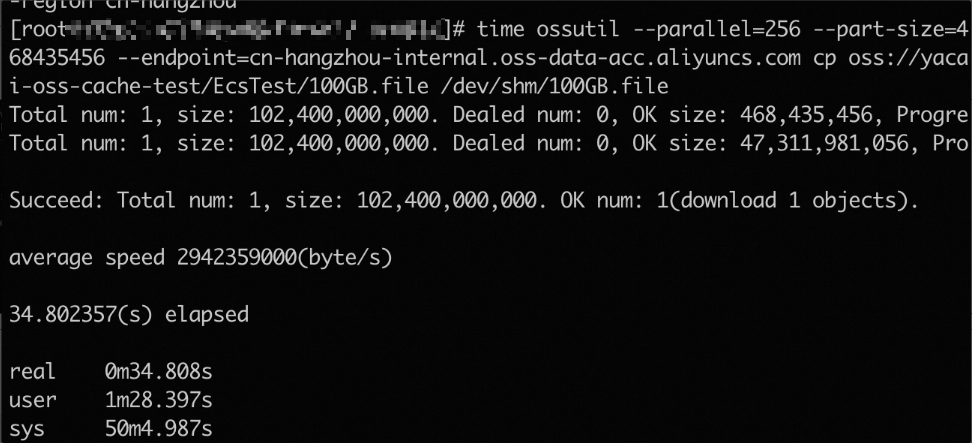
Run the following command to set the concurrency to 256 and the part size to 468435456 to download the
100GB.fileobject from the destination bucket to the/dev/shmdirectory and record the download duration.time ossutil --parallel=256 --part-size=468435456 --endpoint=oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com cp oss://cache-test/EcsTest/100GB.file /dev/shm/100GB.filePerformance description
The average end-to-end speed is 2.94 GB/s (about 24 Gbit/s).
ossfs
Parameter description
Parameter
Description
parallel_count
The number of parts that can be concurrently downloaded when multipart upload is used to upload a large object. Default value: 5.
multipart_size
The part size in MB when multipart upload is used to upload data. Default value: 10. This parameter limits the maximum size of the object that you can upload. When multipart upload is used, the maximum number of parts that an object can be split into is 10,000. By default, the maximum size of the object that can be uploaded is 100 GB. You can change the value of this option to upload a larger object.
direct_read
Enables the direct read mode. By default, ossfs uses the disk storage capacity to store temporary data uploaded or downloaded. You can specify this option to directly read data from OSS instead of the local disk. This option is disabled by default. You can use -odirect_read to enable the direct read mode.
NoteDirect reads are interrupted when a write, rename, or truncate operation is performed on the object being read. In this case, the object exits the direct read mode and must be reopened.
direct_read_prefetch_chunks
The number of chunks that can be prefetched to the memory. This option can be used to optimize sequential read performance. Default value: 32.
This option takes effect only if the -odirect_read option is specified.
direct_read_chunk_size
The amount of data that can be directly read from OSS in a single read request. Unit: MB. Default value: 4. Valid values: 1 to 32.
This option takes effect only if the -odirect_read option is specified.
ensure_diskfree
The size of the reserved disk capacity, which is used to prevent the disk capacity from being fully occupied and affecting other applications to write data. By default, the disk capacity is not reserved. Unit: MB.
For example, if you want to set the ossfs reserved disk capacity to 1024 MB, you can specify
-oensure_diskfree=1024.free_space_ratio
The minimum remaining disk space ratio that you want to reserve. For example, if the disk space is 50 GB and you set -o free_space_ratio to 20, 10 GB (50 GB x 20% = 10 GB) is reserved.
max_stat_cache_size
The maximum number of files whose metadata can be stored in metadata caches. By default, the metadata of up to 100,000 objects can be cached. If a directory contains a large number of objects, you can modify this option to improve the object listing performance of the Is command. To disable metadata caching, you can set this option to 0.
stat_cache_expire
The validity period of the object metadata cache. Unit: seconds. Default value: 900.
readdir_optimize
Specifies whether to use cache optimization. Default value: false.
If you specify the parameter, ossfs does not send a HeadObject request to obtain the object metadata, such as
gidanduid, when you run the ls command. The HeadObject request is sent only if the size of the accessed object is 0. However, a specific number of HeadObject requests may still be sent due to reasons such as permission checks. Specify the parameter based on the application characteristics. To use cache optimization, specify the-oreaddir_optimizeparameter.Examples
NoteWe recommend that you modify the parameters based on the CPU processing capability and network bandwidth.
Default read mode: Mount a bucket named cache-test to the /mnt/cache-test folder on your computer, set the number of parts that can be concurrently downloaded to 128, and set each part to 32 MB in size.
ossfs cache-test /mnt/cache-test -ourl=http://oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com -oparallel_count=128 -omultipart_size=32Direct read mode: Mount a bucket named cache-test to the /mnt/cache-test folder on your computer, enable direct read mode, set the number of prefetched chunks to 128, and set each chunk to 32 MB in size.
ossfs cache-test /mnt/cache-test -ourl=http://oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com -odirect_read -odirect_read_prefetch_chunks=128 -odirect_read_chunk_size=32
Performance description
In default read mode, ossfs downloads data to the local disk. In direct read mode, data is stored in the memory, which accelerates access, but consumes more memory.
NoteIn direct read mode, ossfs manages downloaded data in chunks. The size of each chunk is 4 MB by default and can be changed by using the direct_read_chunk_size parameter. In the memory, ossfs retains the data within the following range: [The current chunk - 1, The current chunk + direct_read_prefetch_chunks]. Determine whether to use the direct read mode based on the memory size, especially the page cache. In most cases, the direct read mode is suitable for scenarios in which the page cache capacity is insufficient. For example, if the total memory of your computer is 16 GB and the page cache can consume 6 GB, you can use the direct read mode when the object size exceeds 6 GB. For more information, see Direct read mode.
Mode
Concurrency
Chunk size (MB)
Peak bandwidth (Gbit/s)
E2E bandwidth (Gbit/s)
E2E duration (s)
Default read mode
128
32
24
11.3
72.01
Direct read mode
128
32
24
16.1
50.9
Optimization for model object reading:
Model object size (GB)
Default read mode (Duration: s; maximum memory: 6 GB)
Hybrid read mode (Duration: s)
Hybrid read mode (Duration: s; data retention: [-32, +32])
1
8.19
8.20
8.56
2.4
24.5
20.43
20.02
5
26.5
22.3
19.89
5.5
22.8
23.1
22.98
8.5
106.0
36.6
36.00
12.6
154.6
42.1
41.9
Python SDK
In AI model training scenarios, OSS SDK for Python accesses the backend storage service in serial mode by default. By using the multi-threaded transformation of Python's concurrent library, the bandwidth is significantly improved.
Prerequisites
The size of model objects is about 5.6 GB, and the specification of the test machine is ECS48vCPU, with 16 Gbit/s of bandwidth and 180 GB of memory.
Example
import oss2 import time import os import threading from io import BytesIO # Configure parameters. OSS_CONFIG = { "bucket_endpoint": os.environ.get('OSS_BUCKET_ENDPOINT', 'oss-cn-hangzhou-internal.aliyuncs.com'), # The default endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. "bucket_name": os.environ.get('OSS_BUCKET_NAME', 'bucket_name'), # The name of the bucket. "access_key_id": os.environ['ACCESS_KEY_ID], # The AccessKey ID of the RAM user. "access_key_secret": os.environ['ACCESS_KEY_SECRET] # The AccessKey secret of the RAM user. } # Initialize the bucket. def __bucket__(): auth = oss2.Auth(OSS_CONFIG["access_key_id"], OSS_CONFIG["access_key_secret"]) return oss2.Bucket( auth, OSS_CONFIG["bucket_endpoint"], OSS_CONFIG["bucket_name"], enable_crc=False ) # Query the size of the model objects. def __get_object_size(object_name): simplifiedmeta = __bucket__().get_object_meta(object_name) return int(simplifiedmeta.headers['Content-Length']) # Query the last modified time of the model objects. def get_remote_model_mmtime(model_name): return __bucket__().head_object(model_name).last_modified # List the model objects. def list_remote_models(ext_filter=('.ckpt',)): # Specify the default extension filter. dir_prefix = "" output = [] for obj in oss2.ObjectIteratorV2( __bucket__(), prefix=dir_prefix, delimiter='/', start_after=dir_prefix, fetch_owner=False ): if not obj.is_prefix(): _, ext = os.path.splitext(obj.key) if ext.lower() in ext_filter: output.append(obj.key) return output # Download the multipart download thread function by chunk. def __range_get(object_name, buffer, offset, start, end, read_chunk_size, progress_callback, total_bytes): chunk_size = int(read_chunk_size) with __bucket__().get_object(object_name, byte_range=(start, end)) as object_stream: s = start while True: chunk = object_stream.read(chunk_size) if not chunk: break buffer.seek(s - offset) buffer.write(chunk) s += len(chunk) # Calculate the number of downloaded bytes and call the download progress callback function. if progress_callback: progress_callback(s - start, total_bytes) # Read the model objects and specify optional progress callback parameters. def read_remote_model( checkpoint_file, start=0, size=-1, read_chunk_size=2*1024*1024, # 2MB part_size=256*1024*1024, # 256MB progress_callback=None # The download progress callback. ): time_start = time.time() buffer = BytesIO() obj_size = __get_object_size(checkpoint_file) end = (obj_size if size == -1 else start + size) - 1 s = start tasks = [] # Calculate the progress. total_bytes = end - start + 1 downloaded_bytes = 0 while s <= end: current_end = min(s + part_size - 1, end) task = threading.Thread( target=__range_get, args=(checkpoint_file, buffer, start, s, current_end, read_chunk_size, progress_callback, total_bytes) ) tasks.append(task) task.start() s += part_size for task in tasks: task.join() time_end = time.time() # Display the total download of the objects. print(f"Downloaded {checkpoint_file} in {time_end - time_start:.2f} seconds.") # Calculate and display the size of the downloaded objects. Unit: GB. file_size_gb = obj_size / (1024 * 1024 * 1024) print(f"Total downloaded file size: {file_size_gb:.2f} GB") buffer.seek(0) return buffer # Specify the download progress callback function. def show_progress(downloaded, total): progress = (downloaded / total) * 100 print(f"Progress: {progress:.2f}%", end="\r") # Call the download progress callback function. if __name__ == "__main__": # Use the list_remote_models method to list the model objects. models = list_remote_models() print("Remote models:", models) if models: # Download the first model object. first_model = models[0] buffer = read_remote_model(first_model, progress_callback=show_progress) print(f"\nDownloaded {first_model} to buffer.")Conclusion
Version
OSS duration (s)
OSS average bandwidth (Mbit/s)
OSS peak bandwidth (Mbit/s)
OSS SDK for Python (serial mode)
109
53
100
OSS SDK for Python (concurrent download mode)
11.1
516
600
From the preceding results, OSS SDK for Python (concurrent download mode) consumes approximately 0.2% of the duration consumed by OSS SDK for Python (serial mode), the average and peak bandwidth of OSS SDK for Python (concurrent download mode) is about 9.7 times and 6 times of that of OSS SDK for Python (serial mode), respectively. When you use OSS SDK for Python to train AI models, the concurrent download mode can greatly improve processing efficiency and bandwidth performance.
Other solutions
In addition to OSS SDK for Python, Alibaba Cloud provides a Python library named osstorchconnector, which is mainly used to efficiently access and store OSS data in PyTorch training tasks. The library has completed a secondary encapsulation of concurrent downloads for users. The following table describes the test results on AI model loading by using osstorchconnector. For more information, see Performance testing.
Item
Description
Test scenario
Model loading and chat Q&A
Model name
gpt3-finnish-3B
Model size
11 GB
Scenario
Chat Q&A
Hardware configurations
High-specification ECS instance: 96 vCPUs, 384 GiB of memory, and 30 Gbit/s of internal bandwidth
Conclusion
The average bandwidth is approximately 10 Gbit/s. OSS can support 10 tasks to load models at the same time.