The following code provides examples of how to configure lifecycle rules using common SDKs. For information about how to configure lifecycle rules using other SDKs, see Overview.
Java
import com.aliyun.oss.*;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.*;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.utils.DateUtil;
import com.aliyun.oss.model.LifecycleRule;
import com.aliyun.oss.model.SetBucketLifecycleRequest;
import com.aliyun.oss.model.StorageClass;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// In this example, the endpoint of the China (Hangzhou) region is used. Specify your actual endpoint.
String endpoint = "https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
// Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = CredentialsProviderFactory.newEnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider();
// Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket.
String bucketName = "examplebucket";
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou.
String region = "cn-hangzhou";
// Create an OSSClient instance.
// Call the shutdown method to release resources when the OSSClient is no longer in use.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4);
OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create()
.endpoint(endpoint)
.credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
.region(region)
.build();
try {
// Create a request by using SetBucketLifecycleRequest.
SetBucketLifecycleRequest request = new SetBucketLifecycleRequest(bucketName);
// Specify the ID of the lifecycle rule.
String ruleId0 = "rule0";
// Specify the prefix that you want the lifecycle rule to match.
String matchPrefix0 = "A0/";
// Specify the tag that you want the lifecycle rule to match.
Map<String, String> matchTags0 = new HashMap<String, String>();
// Specify the key and value of the tag. In the example, the key is set to owner and the value is set to John.
matchTags0.put("owner", "John");
String ruleId1 = "rule1";
String matchPrefix1 = "A1/";
Map<String, String> matchTags1 = new HashMap<String, String>();
matchTags1.put("type", "document");
String ruleId2 = "rule2";
String matchPrefix2 = "A2/";
String ruleId3 = "rule3";
String matchPrefix3 = "A3/";
String ruleId4 = "rule4";
String matchPrefix4 = "A4/";
String ruleId5 = "rule5";
String matchPrefix5 = "A5/";
String ruleId6 = "rule6";
String matchPrefix6 = "A6/";
// Set the expiration time to three days after the last modified time.
LifecycleRule rule = new LifecycleRule(ruleId0, matchPrefix0, LifecycleRule.RuleStatus.Enabled, 3);
rule.setTags(matchTags0);
request.AddLifecycleRule(rule);
// Specify that objects that are created before the specified date expire.
rule = new LifecycleRule(ruleId1, matchPrefix1, LifecycleRule.RuleStatus.Enabled);
rule.setCreatedBeforeDate(DateUtil.parseIso8601Date("2022-10-12T00:00:00.000Z"));
rule.setTags(matchTags1);
request.AddLifecycleRule(rule);
// Specify that parts expire three days after they are last modified.
rule = new LifecycleRule(ruleId2, matchPrefix2, LifecycleRule.RuleStatus.Enabled);
LifecycleRule.AbortMultipartUpload abortMultipartUpload = new LifecycleRule.AbortMultipartUpload();
abortMultipartUpload.setExpirationDays(3);
rule.setAbortMultipartUpload(abortMultipartUpload);
request.AddLifecycleRule(rule);
// Specify that parts that are created before the specific date expire.
rule = new LifecycleRule(ruleId3, matchPrefix3, LifecycleRule.RuleStatus.Enabled);
abortMultipartUpload = new LifecycleRule.AbortMultipartUpload();
abortMultipartUpload.setCreatedBeforeDate(DateUtil.parseIso8601Date("2022-10-12T00:00:00.000Z"));
rule.setAbortMultipartUpload(abortMultipartUpload);
request.AddLifecycleRule(rule);
// Specify that the storage classes of objects are changed to IA 10 days after they are last modified, and to Archive 30 days after they are last modified.
rule = new LifecycleRule(ruleId4, matchPrefix4, LifecycleRule.RuleStatus.Enabled);
List<LifecycleRule.StorageTransition> storageTransitions = new ArrayList<LifecycleRule.StorageTransition>();
LifecycleRule.StorageTransition storageTransition = new LifecycleRule.StorageTransition();
storageTransition.setStorageClass(StorageClass.IA);
storageTransition.setExpirationDays(10);
storageTransitions.add(storageTransition);
storageTransition = new LifecycleRule.StorageTransition();
storageTransition.setStorageClass(StorageClass.Archive);
storageTransition.setExpirationDays(30);
storageTransitions.add(storageTransition);
rule.setStorageTransition(storageTransitions);
request.AddLifecycleRule(rule);
// Specify that the storage classes of objects that are last modified before October 12, 2022 are changed to Archive.
rule = new LifecycleRule(ruleId5, matchPrefix5, LifecycleRule.RuleStatus.Enabled);
storageTransitions = new ArrayList<LifecycleRule.StorageTransition>();
storageTransition = new LifecycleRule.StorageTransition();
storageTransition.setCreatedBeforeDate(DateUtil.parseIso8601Date("2022-10-12T00:00:00.000Z"));
storageTransition.setStorageClass(StorageClass.Archive);
storageTransitions.add(storageTransition);
rule.setStorageTransition(storageTransitions);
request.AddLifecycleRule(rule);
// Specify that rule6 is configured for versioning-enabled buckets.
rule = new LifecycleRule(ruleId6, matchPrefix6, LifecycleRule.RuleStatus.Enabled);
// Specify that the storage classes of objects are changed to Archive 365 days after the objects are last modified.
storageTransitions = new ArrayList<LifecycleRule.StorageTransition>();
storageTransition = new LifecycleRule.StorageTransition();
storageTransition.setStorageClass(StorageClass.Archive);
storageTransition.setExpirationDays(365);
storageTransitions.add(storageTransition);
rule.setStorageTransition(storageTransitions);
// Configure the lifecycle rule to automatically delete expired delete markers.
rule.setExpiredDeleteMarker(true);
// Specify that the storage classes of the previous versions of objects are changed to IA 10 days after the objects are last modified.
LifecycleRule.NoncurrentVersionStorageTransition noncurrentVersionStorageTransition =
new LifecycleRule.NoncurrentVersionStorageTransition().withNoncurrentDays(10).withStrorageClass(StorageClass.IA);
// Specify that the storage classes of the previous versions of objects are changed to Archive 20 days after the objects are last modified.
LifecycleRule.NoncurrentVersionStorageTransition noncurrentVersionStorageTransition2 =
new LifecycleRule.NoncurrentVersionStorageTransition().withNoncurrentDays(20).withStrorageClass(StorageClass.Archive);
// Specify that the previous versions of objects are deleted 30 days after the objects are last modified.
LifecycleRule.NoncurrentVersionExpiration noncurrentVersionExpiration = new LifecycleRule.NoncurrentVersionExpiration().withNoncurrentDays(30);
List<LifecycleRule.NoncurrentVersionStorageTransition> noncurrentVersionStorageTransitions = new ArrayList<LifecycleRule.NoncurrentVersionStorageTransition>();
noncurrentVersionStorageTransitions.add(noncurrentVersionStorageTransition2);
rule.setStorageTransition(storageTransitions);
rule.setNoncurrentVersionExpiration(noncurrentVersionExpiration);
rule.setNoncurrentVersionStorageTransitions(noncurrentVersionStorageTransitions);
request.AddLifecycleRule(rule);
// Initiate a request to configure lifecycle rules.
ossClient.setBucketLifecycle(request);
// Query the lifecycle rules that are configured for the bucket.
List<LifecycleRule> listRules = ossClient.getBucketLifecycle(bucketName);
for(LifecycleRule rules : listRules){
System.out.println("ruleId="+rules.getId()+", matchPrefix="+rules.getPrefix());
}
} catch (OSSException oe) {
System.out.println("Caught an OSSException, which means your request made it to OSS, "
+ "but was rejected with an error response for some reason.");
System.out.println("Error Message:" + oe.getErrorMessage());
System.out.println("Error Code:" + oe.getErrorCode());
System.out.println("Request ID:" + oe.getRequestId());
System.out.println("Host ID:" + oe.getHostId());
} catch (ClientException ce) {
System.out.println("Caught an ClientException, which means the client encountered "
+ "a serious internal problem while trying to communicate with OSS, "
+ "such as not being able to access the network.");
System.out.println("Error Message:" + ce.getMessage());
} finally {
if (ossClient != null) {
ossClient.shutdown();
}
}
}
}
PHP
<?php
if (is_file(__DIR__ . '/../autoload.php')) {
require_once __DIR__ . '/../autoload.php';
}
if (is_file(__DIR__ . '/../vendor/autoload.php')) {
require_once __DIR__ . '/../vendor/autoload.php';
}
use OSS\Credentials\EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider;
use OSS\OssClient;
use OSS\CoreOssException;
use OSS\Model\LifecycleConfig;
use OSS\Model\LifecycleRule;
use OSS\Model\LifecycleAction;
// Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
$provider = new EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider();
// In this example, the endpoint of the China (Hangzhou) region is used. Specify your actual endpoint.
$endpoint = "https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
// Specify the name of the bucket.
$bucket= "examplebucket";
// Specify the rule ID and the prefix contained in the names of the objects that match the rule.
$ruleId0 = "rule0";
$matchPrefix0 = "A0/";
$ruleId1 = "rule1";
$matchPrefix1 = "A1/";
$lifecycleConfig = new LifecycleConfig();
$actions = array();
// Specify that objects expire three days after they are last modified.
$actions[] = new LifecycleAction(OssClient::OSS_LIFECYCLE_EXPIRATION, OssClient::OSS_LIFECYCLE_TIMING_DAYS, 3);
$lifecycleRule = new LifecycleRule($ruleId0, $matchPrefix0, "Enabled", $actions);
$lifecycleConfig->addRule($lifecycleRule);
$actions = array();
// Specify that the objects that are created before the specified date expire.
$actions[] = new LifecycleAction(OssClient::OSS_LIFECYCLE_EXPIRATION, OssClient::OSS_LIFECYCLE_TIMING_DATE, '2022-10-12T00:00:00.000Z');
$lifecycleRule = new LifecycleRule($ruleId1, $matchPrefix1, "Enabled", $actions);
$lifecycleConfig->addRule($lifecycleRule);
try {
$config = array(
"provider" => $provider,
"endpoint" => $endpoint,
"signatureVersion" => OssClient::OSS_SIGNATURE_VERSION_V4,
"region"=> "cn-hangzhou"
);
$ossClient = new OssClient($config);
$ossClient->putBucketLifecycle($bucket, $lifecycleConfig);
} catch (OssException $e) {
printf(__FUNCTION__ . ": FAILED\n");
printf($e->getMessage() . "\n");
return;
}
print(__FUNCTION__ . ": OK" . "\n");
Node.js
const OSS = require('ali-oss')
const client = new OSS({
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to oss-cn-hangzhou.
region: 'yourregion',
// Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
accessKeyId: process.env.OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID,
accessKeySecret: process.env.OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET,
authorizationV4: true,
// Specify the name of the bucket.
bucket: 'yourbucketname'
});
async function getBucketLifecycle () {
try {
const result = await client.getBucketLifecycle('Yourbucketname');
console.log(result.rules); // Query the lifecycle rules.
rules.forEach(rule => {
console.log(rule.id) // Query the rule IDs.
console.log(rule.status) // Query the status of the rules.
console.log(rule.tags) // Query the tags configured in the lifecycle rules.
console.log(rule.expiration.days) // Query the validity period configurations.
console.log(rule.expiration.createdBeforeDate) // Query the expiration date configurations.
// Query the rule for expired parts.
console.log(rule.abortMultipartUpload.days || rule.abortMultipartUpload.createdBeforeDate)
// Query the rule of storage class conversion.
console.log(rule.transition.days || rule.transition.createdBeforeDate) // Query the conversion date configurations.
console.log(rule.transition.storageClass) // Query the configurations used to convert storage classes.
// Query the lifecycle rule to check whether expired delete markers are automatically deleted.
console.log(rule.transition.expiredObjectDeleteMarker)
// Query the configurations used to convert the storage class of previous versions of the objects.
console.log(rule.noncurrentVersionTransition.noncurrentDays) // Query the conversion date configurations for objects of previous versions.
console.log(rule.noncurrentVersionTransition.storageClass) // Query the configurations used to convert the storage classes of previous versions of objects.
})
} catch (e) {
console.log(e);
}
}
getBucketLifecycle();
Python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import oss2
from oss2.credentials import EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider
import datetime
from oss2.models import (LifecycleExpiration, LifecycleRule,
BucketLifecycle,AbortMultipartUpload,
TaggingRule, Tagging, StorageTransition,
NoncurrentVersionStorageTransition,
NoncurrentVersionExpiration)
# Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
auth = oss2.ProviderAuthV4(EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider())
# Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com.
endpoint = "https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com"
# Specify the ID of the region that maps to the endpoint. Example: cn-hangzhou. This parameter is required if you use the signature algorithm V4.
region = "cn-hangzhou"
# Specify the name of the bucket.
bucket = oss2.Bucket(auth, endpoint, "examplebucket", region=region)
# Specify that objects expire three days after they are last modified.
rule1 = LifecycleRule('rule1', 'tests/',
status=LifecycleRule.ENABLED,
expiration=LifecycleExpiration(days=3))
# Specify that objects created before the specified date expire.
rule2 = LifecycleRule('rule2', 'tests2/',
status=LifecycleRule.ENABLED,
expiration = LifecycleExpiration(created_before_date=datetime.date(2023, 12, 12)))
# Specify that the parts expire three days after they are last modified.
rule3 = LifecycleRule('rule3', 'tests3/',
status=LifecycleRule.ENABLED,
abort_multipart_upload=AbortMultipartUpload(days=3))
# Specify that parts created before the specified date expire.
rule4 = LifecycleRule('rule4', 'tests4/',
status=LifecycleRule.ENABLED,
abort_multipart_upload = AbortMultipartUpload(created_before_date=datetime.date(2022, 12, 12)))
# Specify that the storage classes of objects are changed to Infrequent Access (IA) 20 days after they are last modified, and to Archive 30 days after they are last modified.
rule5 = LifecycleRule('rule5', 'tests5/',
status=LifecycleRule.ENABLED,
storage_transitions=[StorageTransition(days=20,storage_class=oss2.BUCKET_STORAGE_CLASS_IA),
StorageTransition(days=30,storage_class=oss2.BUCKET_STORAGE_CLASS_ARCHIVE)])
# Specify the tag that you want the lifecycle rule to match.
tagging_rule = TaggingRule()
tagging_rule.add('key1', 'value1')
tagging_rule.add('key2', 'value2')
tagging = Tagging(tagging_rule)
# Specify that the storage classes of objects are changed to Archive 365 days after they are last modified.
# Compared with the preceding rules, rule6 includes the tag condition to match objects. The rule takes effect for objects whose tagging configurations are key1=value1 and key2=value2.
rule6 = LifecycleRule('rule6', 'tests6/',
status=LifecycleRule.ENABLED,
storage_transitions=[StorageTransition(created_before_date=datetime.date(2022, 12, 12),storage_class=oss2.BUCKET_STORAGE_CLASS_IA)],
tagging = tagging)
# rule7 is a lifecycle rule that applies to a versioning-enabled bucket.
# Specify that the storage classes of objects are changed to Archive 365 days after they are last modified.
# Specify that delete markers are automatically removed when they expire.
# Specify that the storage classes of objects are changed to IA 12 days after they become previous versions.
# Specify that the storage classes of objects are changed to Archive 20 days after they become previous versions.
# Specify that objects are deleted 30 days after they become previous versions.
rule7 = LifecycleRule('rule7', 'tests7/',
status=LifecycleRule.ENABLED,
storage_transitions=[StorageTransition(days=365, storage_class=oss2.BUCKET_STORAGE_CLASS_ARCHIVE)],
expiration=LifecycleExpiration(expired_detete_marker=True),
noncurrent_version_sotrage_transitions =
[NoncurrentVersionStorageTransition(12, oss2.BUCKET_STORAGE_CLASS_IA),
NoncurrentVersionStorageTransition(20, oss2.BUCKET_STORAGE_CLASS_ARCHIVE)],
noncurrent_version_expiration = NoncurrentVersionExpiration(30))
lifecycle = BucketLifecycle([rule1, rule2, rule3, rule4, rule5, rule6, rule7])
bucket.put_bucket_lifecycle(lifecycle)
C#
using Aliyun.OSS;
using Aliyun.OSS.Common;
// Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com.
var endpoint = "https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
// Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
var accessKeyId = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID");
var accessKeySecret = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET");
// Specify the bucket name. Example: examplebucket.
var bucketName = "examplebucket";
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou.
const string region = "cn-hangzhou";
// Create a ClientConfiguration instance and modify the default parameters based on your requirements.
var conf = new ClientConfiguration();
// Use the signature algorithm V4.
conf.SignatureVersion = SignatureVersion.V4;
// Create an OSSClient instance.
var client = new OssClient(endpoint, accessKeyId, accessKeySecret, conf);
client.SetRegion(region);
try
{
var setBucketLifecycleRequest = new SetBucketLifecycleRequest(bucketName);
// Create the first lifecycle rule.
LifecycleRule lcr1 = new LifecycleRule()
{
ID = "delete obsoleted files",
Prefix = "obsoleted/",
Status = RuleStatus.Enabled,
ExpriationDays = 3,
Tags = new Tag[1]
};
// Specify a tag for the rule.
var tag1 = new Tag
{
Key = "project",
Value = "projectone"
};
lcr1.Tags[0] = tag1;
// Create the second lifecycle rule.
LifecycleRule lcr2 = new LifecycleRule()
{
ID = "delete temporary files",
Prefix = "temporary/",
Status = RuleStatus.Enabled,
ExpriationDays = 20,
Tags = new Tag[1]
};
// Specify a tag for the rule.
var tag2 = new Tag
{
Key = "user",
Value = "jsmith"
};
lcr2.Tags[0] = tag2;
// Specify that parts expire 30 days after they are last modified.
lcr2.AbortMultipartUpload = new LifecycleRule.LifeCycleExpiration()
{
Days = 30
};
LifecycleRule lcr3 = new LifecycleRule();
lcr3.ID = "only NoncurrentVersionTransition";
lcr3.Prefix = "test1";
lcr3.Status = RuleStatus.Enabled;
lcr3.NoncurrentVersionTransitions = new LifecycleRule.LifeCycleNoncurrentVersionTransition[2]
{
// Specify that the storage classes of the previous versions of objects are converted to IA 90 days after they are last modified.
new LifecycleRule.LifeCycleNoncurrentVersionTransition(){
StorageClass = StorageClass.IA,
NoncurrentDays = 90
},
// Specify that the storage classes of the previous versions of objects are converted to Archive 180 days after they are last modified.
new LifecycleRule.LifeCycleNoncurrentVersionTransition(){
StorageClass = StorageClass.Archive,
NoncurrentDays = 180
}
};
setBucketLifecycleRequest.AddLifecycleRule(lcr1);
setBucketLifecycleRequest.AddLifecycleRule(lcr2);
setBucketLifecycleRequest.AddLifecycleRule(lcr3);
// Configure lifecycle rules.
client.SetBucketLifecycle(setBucketLifecycleRequest);
Console.WriteLine("Set bucket:{0} Lifecycle succeeded ", bucketName);
}
catch (OssException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed with error code: {0}; Error info: {1}. \nRequestID:{2}\tHostID:{3}",
ex.ErrorCode, ex.Message, ex.RequestId, ex.HostId);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed with error info: {0}", ex.Message);
}
Android-Java
PutBucketLifecycleRequest request = new PutBucketLifecycleRequest();
request.setBucketName("examplebucket");
BucketLifecycleRule rule1 = new BucketLifecycleRule();
// Specify the rule ID and the prefix contained in the names of the objects that match the rule.
rule1.setIdentifier("1");
rule1.setPrefix("A");
// Specify whether to run the lifecycle rule. If this parameter is set to true, OSS periodically runs this rule. If this parameter is set to false, OSS ignores this rule.
rule1.setStatus(true);
// Specify that objects expire 200 days after they are last modified.
rule1.setDays("200");
// Specify that the storage classes of objects are converted to Archive 30 days after they are last modified.
rule1.setArchiveDays("30");
// Specify that parts expire three days after they fail to be uploaded.
rule1.setMultipartDays("3");
// Specify that the storage classes of objects are converted to Infrequent Access (IA) 15 days after they are last modified.
rule1.setIADays("15");
BucketLifecycleRule rule2 = new BucketLifecycleRule();
rule2.setIdentifier("2");
rule2.setPrefix("B");
rule2.setStatus(true);
rule2.setDays("300");
rule2.setArchiveDays("30");
rule2.setMultipartDays("3");
rule2.setIADays("15");
ArrayList<BucketLifecycleRule> lifecycleRules = new ArrayList<BucketLifecycleRule>();
lifecycleRules.add(rule1);
lifecycleRules.add(rule2);
request.setLifecycleRules(lifecycleRules);
OSSAsyncTask task = oss.asyncPutBucketLifecycle(request, new OSSCompletedCallback<PutBucketLifecycleRequest, PutBucketLifecycleResult>() {
@Override
public void onSuccess(PutBucketLifecycleRequest request, PutBucketLifecycleResult result) {
OSSLog.logInfo("code::"+result.getStatusCode());
}
@Override
public void onFailure(PutBucketLifecycleRequest request, ClientException clientException, ServiceException serviceException) {
OSSLog.logError("error: "+serviceException.getRawMessage());
}
});
task.waitUntilFinished();
Go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"github.com/aliyun/aliyun-oss-go-sdk/oss"
)
func main() {
// Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
provider, err := oss.NewEnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error:", err)
os.Exit(-1)
}
// Create an OSSClient instance.
// Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com. Specify the actual endpoint.
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou. Specify the actual region.
clientOptions := []oss.ClientOption{oss.SetCredentialsProvider(&provider)}
clientOptions = append(clientOptions, oss.Region("yourRegion"))
// Specify the version of the signature algorithm.
clientOptions = append(clientOptions, oss.AuthVersion(oss.AuthV4))
client, err := oss.New("yourEndpoint", "", "", clientOptions...)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error:", err)
os.Exit(-1)
}
// Specify the name of the bucket.
bucketName := "examplebucket"
// Configure a lifecycle rule and set ID to rule1. Specify that the objects whose names contain the foo prefix in the bucket expire three days after the objects are last modified.
rule1 := oss.BuildLifecycleRuleByDays("rule1", "foo/", true, 3)
// If an object in a bucket for which versioning is enabled is a delete marker and has no other versions, the delete marker is deleted.
deleteMark := true
expiration := oss.LifecycleExpiration{
ExpiredObjectDeleteMarker: &deleteMark,
}
// Specify that the previous versions of objects are deleted 30 days after they are last modified.
versionExpiration := oss.LifecycleVersionExpiration{
NoncurrentDays: 30,
}
// Specify that the storage classes of the previous versions of objects are converted to Infrequent Access (IA) 10 days after the objects are last modified.
versionTransition := oss.LifecycleVersionTransition{
NoncurrentDays: 10,
StorageClass: "IA",
}
// Configure a lifecycle rule and set ID to rule2.
rule2 := oss.LifecycleRule{
ID: "rule2",
Prefix: "yourObjectPrefix",
Status: "Enabled",
Expiration: &expiration,
NonVersionExpiration: &versionExpiration,
NonVersionTransitions: []oss.LifecycleVersionTransition{
versionTransition,
},
}
// Configure a lifecycle rule and set ID to rule3. This rule takes effect for objects that have the tag whose key is tag1 and value is value1. These objects expire three days after the objects are last modified.
rule3 := oss.LifecycleRule{
ID: "rule3",
Prefix: "",
Status: "Enabled",
Tags: []oss.Tag{
oss.Tag{
Key: "tag1",
Value: "value1",
},
},
Expiration: &oss.LifecycleExpiration{Days: 3},
}
// Configure lifecycle rules.
rules := []oss.LifecycleRule{rule1, rule2, rule3}
err = client.SetBucketLifecycle(bucketName, rules)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Error:", err)
os.Exit(-1)
}
}
C++
#include <alibabacloud/oss/OssClient.h>
using namespace AlibabaCloud::OSS;
int main(void)
{
/* Initialize information about the account used to access OSS. */
/* Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com. */
std::string Endpoint = "yourEndpoint";
/* Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou. */
std::string Region = "yourRegion";
/* Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket. */
std::string BucketName = "examplebucket";
/* Initialize resources such as network resources. */
InitializeSdk();
ClientConfiguration conf;
conf.signatureVersion = SignatureVersionType::V4;
/* Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured. */
auto credentialsProvider = std::make_shared<EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider>();
OssClient client(Endpoint, credentialsProvider, conf);
client.SetRegion(Region);
SetBucketLifecycleRequest request(BucketName);
std::string date("2022-10-12T00:00:00.000Z");
/* Specify the tags of the objects that you want to match the rule. */
Tagging tagging;
tagging.addTag(Tag("key1", "value1"));
tagging.addTag(Tag("key2", "value2"));
/* Specify a lifecycle rule. */
auto rule1 = LifecycleRule();
rule1.setID("rule1");
rule1.setPrefix("test1/");
rule1.setStatus(RuleStatus::Enabled);
rule1.setExpiration(3);
rule1.setTags(tagging.Tags());
/* Specify the expiration date. */
auto rule2 = LifecycleRule();
rule2.setID("rule2");
rule2.setPrefix("test2/");
rule2.setStatus(RuleStatus::Disabled);
rule2.setExpiration(date);
/* Specify that rule3 is enabled for the bucket if versioning is enabled for the bucket. */
auto rule3 = LifecycleRule();
rule3.setID("rule3");
rule3.setPrefix("test3/");
rule3.setStatus(RuleStatus::Disabled);
/* Specify that the storage classes of objects are changed to Archive 365 days after the objects are last modified. */
auto transition = LifeCycleTransition();
transition.Expiration().setDays(365);
transition.setStorageClass(StorageClass::Archive);
rule3.addTransition(transition);
/* Specify that expired delete markers are automatically deleted. */
rule3.setExpiredObjectDeleteMarker(true);
/* Specify that the storage classes of the previous versions of objects are changed to IA 10 days after the objects are last modified. */
auto transition1 = LifeCycleTransition();
transition1.Expiration().setDays(10);
transition1.setStorageClass(StorageClass::IA);
/* Specify that the storage classes of the previous versions of objects are changed to Archive 20 days after the objects are last modified. */
auto transition2 = LifeCycleTransition();
transition2.Expiration().setDays(20);
transition2.setStorageClass(StorageClass::Archive);
/* Specify that previous versions are deleted 30 days after the versions are updated. */
auto expiration = LifeCycleExpiration(30);
rule3.setNoncurrentVersionExpiration(expiration);
LifeCycleTransitionList noncurrentVersionStorageTransitions{transition1, transition2};
rule3.setNoncurrentVersionTransitionList(noncurrentVersionStorageTransitions);
/* Configure the lifecycle rules. */
LifecycleRuleList list{rule1, rule2, rule3};
request.setLifecycleRules(list);
auto outcome = client.SetBucketLifecycle(request);
if (!outcome.isSuccess()) {
/* Handle exceptions. */
std::cout << "SetBucketLifecycle fail" <<
",code:" << outcome.error().Code() <<
",message:" << outcome.error().Message() <<
",requestId:" << outcome.error().RequestId() << std::endl;
return -1;
}
/* Release resources such as network resources. */
ShutdownSdk();
return 0;
}
C
#include "oss_api.h"
#include "aos_http_io.h"
/* Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com. */
const char *endpoint = "yourEndpoint";
/* Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket. */
const char *bucket_name = "examplebucket";
/* Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou. */
const char *region = "yourRegion";
void init_options(oss_request_options_t *options)
{
options->config = oss_config_create(options->pool);
/* Use a char* string to initialize aos_string_t. */
aos_str_set(&options->config->endpoint, endpoint);
/* Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured. */
aos_str_set(&options->config->access_key_id, getenv("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID"));
aos_str_set(&options->config->access_key_secret, getenv("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET"));
// Specify two additional parameters.
aos_str_set(&options->config->region, region);
options->config->signature_version = 4;
/* Specify whether to use CNAME to access OSS. A value of 0 indicates that CNAME is not used. */
options->config->is_cname = 0;
/* Specify network parameters, such as the timeout period. */
options->ctl = aos_http_controller_create(options->pool, 0);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
/* Call the aos_http_io_initialize method in main() to initialize global resources, such as network resources and memory resources. */
if (aos_http_io_initialize(NULL, 0) != AOSE_OK) {
exit(1);
}
/* Create a memory pool to manage memory. aos_pool_t is equivalent to apr_pool_t. The code used to create a memory pool is included in the APR library. */
aos_pool_t *pool;
/* Create a memory pool. The value of the second parameter is NULL. This value indicates that the pool does not inherit other memory pools. */
aos_pool_create(&pool, NULL);
/* Create and initialize options. This parameter includes global configuration information such as endpoint, access_key_id, access_key_secret, is_cname, and curl. */
oss_request_options_t *oss_client_options;
/* Allocate memory resources in the memory pool to the options. */
oss_client_options = oss_request_options_create(pool);
/* Initialize oss_client_options. */
init_options(oss_client_options);
/* Initialize parameters. */
aos_string_t bucket;
aos_table_t *resp_headers = NULL;
aos_status_t *resp_status = NULL;
aos_str_set(&bucket, bucket_name);
aos_list_t lifecycle_rule_list;
aos_str_set(&bucket, bucket_name);
aos_list_init(&lifecycle_rule_list);
/* Specify the validity period. */
oss_lifecycle_rule_content_t *rule_content_days = oss_create_lifecycle_rule_content(pool);
aos_str_set(&rule_content_days->id, "rule-1");
/* Specify the prefix that is contained in the names of the objects that you want to match the rule. */
aos_str_set(&rule_content_days->prefix, "dir1");
aos_str_set(&rule_content_days->status, "Enabled");
rule_content_days->days = 3;
aos_list_add_tail(&rule_content_days->node, &lifecycle_rule_list);
/* Specify the expiration date. */
oss_lifecycle_rule_content_t *rule_content_date = oss_create_lifecycle_rule_content(pool);
aos_str_set(&rule_content_date->id, "rule-2");
aos_str_set(&rule_content_date->prefix, "dir2");
aos_str_set(&rule_content_date->status, "Enabled");
/* The expiration date is displayed in UTC.
aos_str_set(&rule_content_date->date, "2023-10-11T00:00:00.000Z");
aos_list_add_tail(&rule_content_date->node, &lifecycle_rule_list);
/* Configure the lifecycle rule. */
resp_status = oss_put_bucket_lifecycle(oss_client_options, &bucket, &lifecycle_rule_list, &resp_headers);
if (aos_status_is_ok(resp_status)) {
printf("put bucket lifecycle succeeded\n");
} else {
printf("put bucket lifecycle failed, code:%d, error_code:%s, error_msg:%s, request_id:%s\n",
resp_status->code, resp_status->error_code, resp_status->error_msg, resp_status->req_id);
}
/* Release the memory pool to release the memory resources allocated for the request. */
aos_pool_destroy(pool);
/* Release the allocated global resources. */
aos_http_io_deinitialize();
return 0;
}
Ruby
require 'aliyun/oss'
client = Aliyun::OSS::Client.new(
# In this example, the endpoint of the China (Hangzhou) region is used. Specify your actual endpoint.
endpoint: 'https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com',
# Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
access_key_id: ENV['OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID'],
access_key_secret: ENV['OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET']
)
# Specify the bucket name.
bucket = client.get_bucket('examplebucket')
# Configure lifecycle rules.
bucket.lifecycle = [
Aliyun::OSS::LifeCycleRule.new(
:id => 'rule1', :enable => true, :prefix => 'foo/', :expiry => 3),
Aliyun::OSS::LifeCycleRule.new(
:id => 'rule2', :enable => false, :prefix => 'bar/', :expiry => Date.new(2016, 1, 1))
]
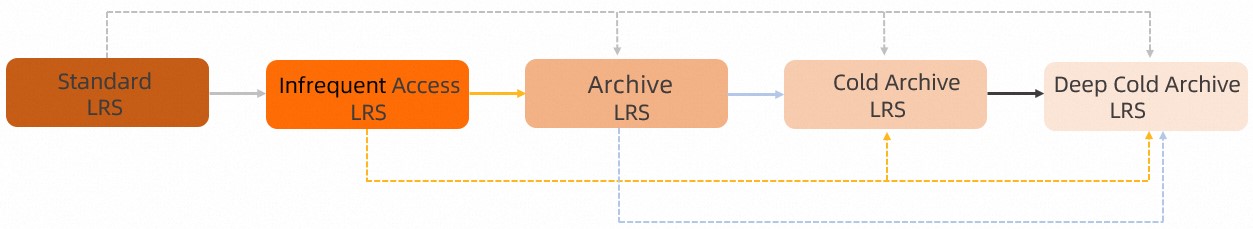
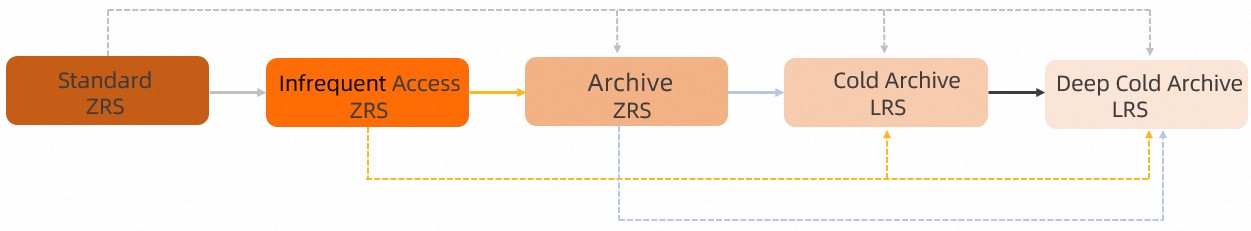
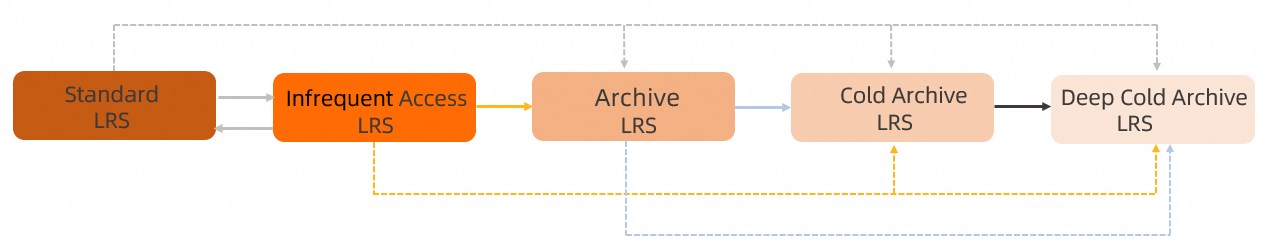
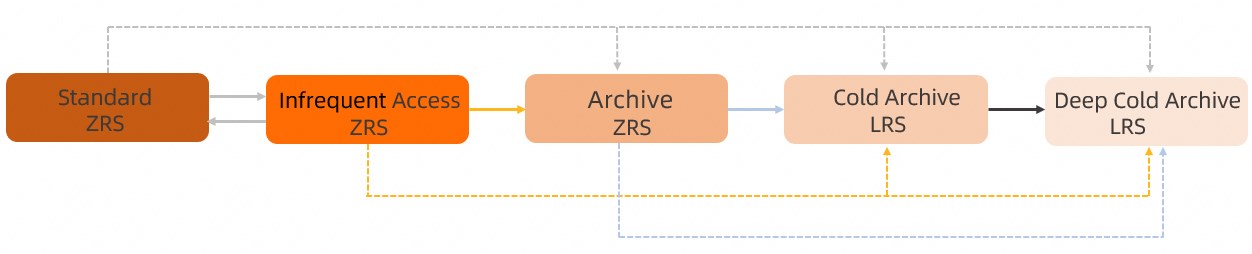
 > Change Storage Class
> Change Storage Class