Lindorm Search Engine provides a visual user interface. You can use this interface to access the Lindorm search engine via RESTful APIs. This topic describes how to log on to the user interface (UI) from the Lindorm console and execute read and write operations.
Prerequisites
The service type of the instance must be Lindorm or Lindorm_V2. For more information about how to view the service type, see View product series.
The Lindorm search engine has been activated. For more information, see the Activation Guide.
The IP address of your client must be added to the Lindorm whitelist. For more information, see Configure a whitelist.
ImportantIf your client uses the IPv6 protocol by default, you must disable it. Otherwise, whitelist authentication will fail.
Procedure
Log on to the UI
Log on to the Lindorm console.
In the upper-left corner of the page, select the region where your instance is located.
On the Instances page, click the ID of the target instance or, in the Actions column, click View Instance Details.
In the navigation pane on the left, click Search Engine.
In the UI Access section, click Internet or VPC to log on to the UI.
On the logon page, enter the Default Username and Default Initial Password from the UI Access section.
NoteThe first time you access the UI, you may need to wait for page resources to load.
For your first logon, use the Default Username and Default Initial Password to log on to the search UI. For subsequent logons, use other user accounts created by the default user.
Read and write operations
The syntax for read and write operations is compatible with Elasticsearch (ES) API 7.x.
Open Dev Tools
Click the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the UI to open the sidebar, and then click .
icon in the upper-left corner of the UI to open the sidebar, and then click .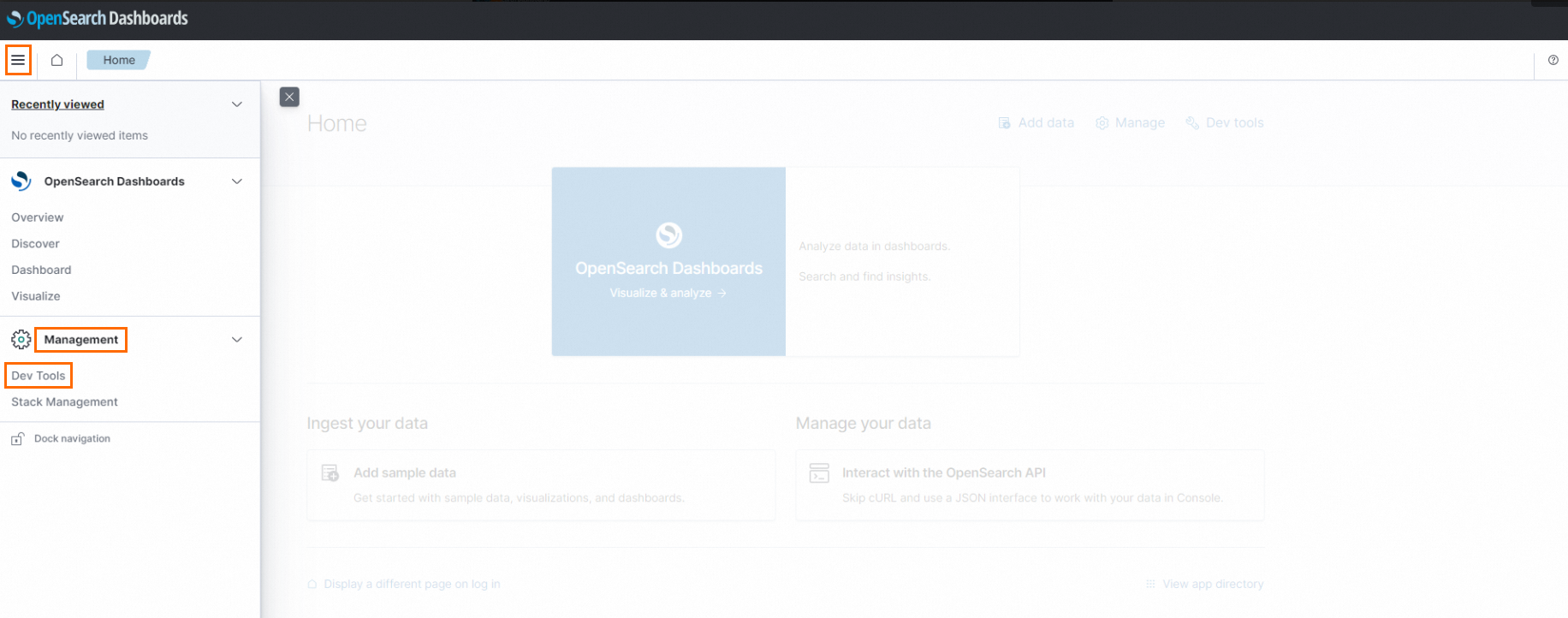
In Dev Tools, you can access the Lindorm search engine via RESTful APIs.
View all created indexes
You can use the cat API to view basic information about all created indexes in the search engine.
Add the v parameter to the path to display column names at the top.
GET /_cat/indices?vReturn value:
health status index uuid pri rep docs.count docs.deleted store.size pri.store.size
green open test2 test2 2 0 0 0 416b 416b
green open test3 test3 2 0 1 0 16.8kb 16.8kb
green open test1 test1 1 0 0 0 208b 208b
green open .kibana_1 .kibana_1 1 0 1 0 5.1kb 5.1kbCreate an index
You can use the Create index API to create an index.
In the request body, you can specify the settings and mappings for the index.
settings: Specifies the configurations of the index, such as the number of shards (`index.number_of_shards`) and the refresh interval (`index.refresh_interval`).
mappings: Specifies the structure of the index, such as the fields in the index and the data type of each field.
PUT /test { "settings": { "index.number_of_shards": 2, "index.refresh_interval": "10s" }, "mappings": { "properties": { "firstName": { "type": "keyword" }, "lastName": { "type": "keyword" } } } }Return value:
{ "acknowledged": true, "shards_acknowledged": true, "index": "test" }
View information about a specific index
You can use the Get index API to view information about a specific index, including its settings and mappings.
GET /testReturn value:
{ "test": { "aliases": {}, "mappings": { "properties": { "firstName": { "type": "keyword" }, "lastName": { "type": "keyword" } } }, "settings": { "index": { "search": { "slowlog": { "level": "DEBUG", "threshold": { "fetch": { "warn": "1s", "trace": "200ms", "debug": "500ms", "info": "800ms" }, "query": { "warn": "10s", "trace": "500ms", "debug": "1s", "info": "5s" } } } }, "refresh_interval": "10s", "indexing": { "slowlog": { "level": "DEBUG", "threshold": { "index": { "warn": "10s", "trace": "500ms", "debug": "2s", "info": "5s" } } } }, "number_of_shards": "2", "provided_name": "test4", "creation_date": "1722418296110", "number_of_replicas": "0", "uuid": "test4", "version": { "created": "136287927" } } } } }To view only the settings or mappings, you can use the Get index settings API or the Get mapping API.
The following example shows how to obtain the settings.
GET /test/_settingsReturn value:
{ "test": { "settings": { "index": { "search": { "slowlog": { "level": "DEBUG", "threshold": { "fetch": { "warn": "1s", "trace": "200ms", "debug": "500ms", "info": "800ms" }, "query": { "warn": "10s", "trace": "500ms", "debug": "1s", "info": "5s" } } } }, "refresh_interval": "10s", "indexing": { "slowlog": { "level": "DEBUG", "threshold": { "index": { "warn": "10s", "trace": "500ms", "debug": "2s", "info": "5s" } } } }, "number_of_shards": "2", "provided_name": "test4", "creation_date": "1722418296110", "number_of_replicas": "0", "uuid": "test4", "version": { "created": "136287927" } } } } }
Update the index configuration
You can use the Update index settings API to update the dynamically modifiable configuration items of an index.
The following example changes the index.refresh_interval setting to 1 s. This sets the interval between when data is written and when it becomes visible to 1 second. The minimum interval is 1 s.
PUT /test/_settings
{
"index": {
"refresh_interval": "1s"
}
}Return value:
{
"acknowledged": true
}Write data to an index
You can use the Index API to write data to an index.
If you use the PUT method, you must specify an id. If a document with the specified id already exists, the existing document is overwritten.
The following example specifies an id of
1:PUT /test/_doc/1 { "firstName": "John", "lastName": "Smith" }Return value:
{ "_index": "test", "_type": "_doc", "_id": "1", "_version": 1, "result": "created", "_shards": { "total": 1, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "_seq_no": 0, "_primary_term": 1 }If you use the POST method, you do not need to specify an id. The Lindorm search engine automatically generates an id for the data.
POST /test/_doc { "firstName": "Frank", "lastName": "Brown" }Return value:
{ "_index": "test", "_type": "_doc", "_id": "b_MsCJEB3g4To6JSOeF6", "_version": 1, "result": "created", "_shards": { "total": 1, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "_seq_no": 0, "_primary_term": 1 }The Lindorm search engine automatically generates an id for the data:
b_MsCJEB3g4To6JSOeF6.Use the Update API to update specific fields of existing data. Include the document id in the path parameter and the
docparameter in the request body.The following example sets the id to
1and updates firstName toLane:POST /test/_update/1 { "doc": { "firstName": "Lane" } }Return value:
{ "_index": "test", "_type": "_doc", "_id": "1", "_version": 2, "result": "updated", "_shards": { "total": 1, "successful": 1, "failed": 0 }, "_seq_no": 1, "_primary_term": 1 }
View index data
You can use the Search API to view the data in an index. You can specify query conditions in the request body.
The following example specifies a lastName of
Smith:GET /test/_search { "query": { "match": { "lastName": "Smith" } } }Return value:
{ "took": 4, "timed_out": false, "_shards": { "total": 2, "successful": 2, "skipped": 0, "failed": 0 }, "hits": { "total": { "value": 1, "relation": "eq" }, "max_score": 0.18232156, "hits": [ { "_index": "test", "_id": "1", "_score": 0.18232156, "_source": { "firstName": "Lane", "lastName": "Smith" } } ] } }You can use the Get API to view the data for a specified id.
The following example specifies an id of
1:GET /test/_doc/1Return value:
{ "_index": "test", "_id": "1", "_version": 2, "_seq_no": 1, "_primary_term": 1, "found": true, "_source": { "firstName": "Lane", "lastName": "Smith" } }
Delete index data
You can use the Delete API to delete data for a specified id from an index.
The following example specifies an id of 1:
DELETE /test/_doc/1Return value:
{
"_index": "test",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 3,
"result": "deleted",
"_shards": {
"total": 1,
"successful": 1,
"failed": 0
},
"_seq_no": 2,
"_primary_term": 1
}A successful return value of 1 indicates that the specified data was successfully deleted.