This topic describes the typical scenario and related operations of generic secret rotation.
Typical scenario
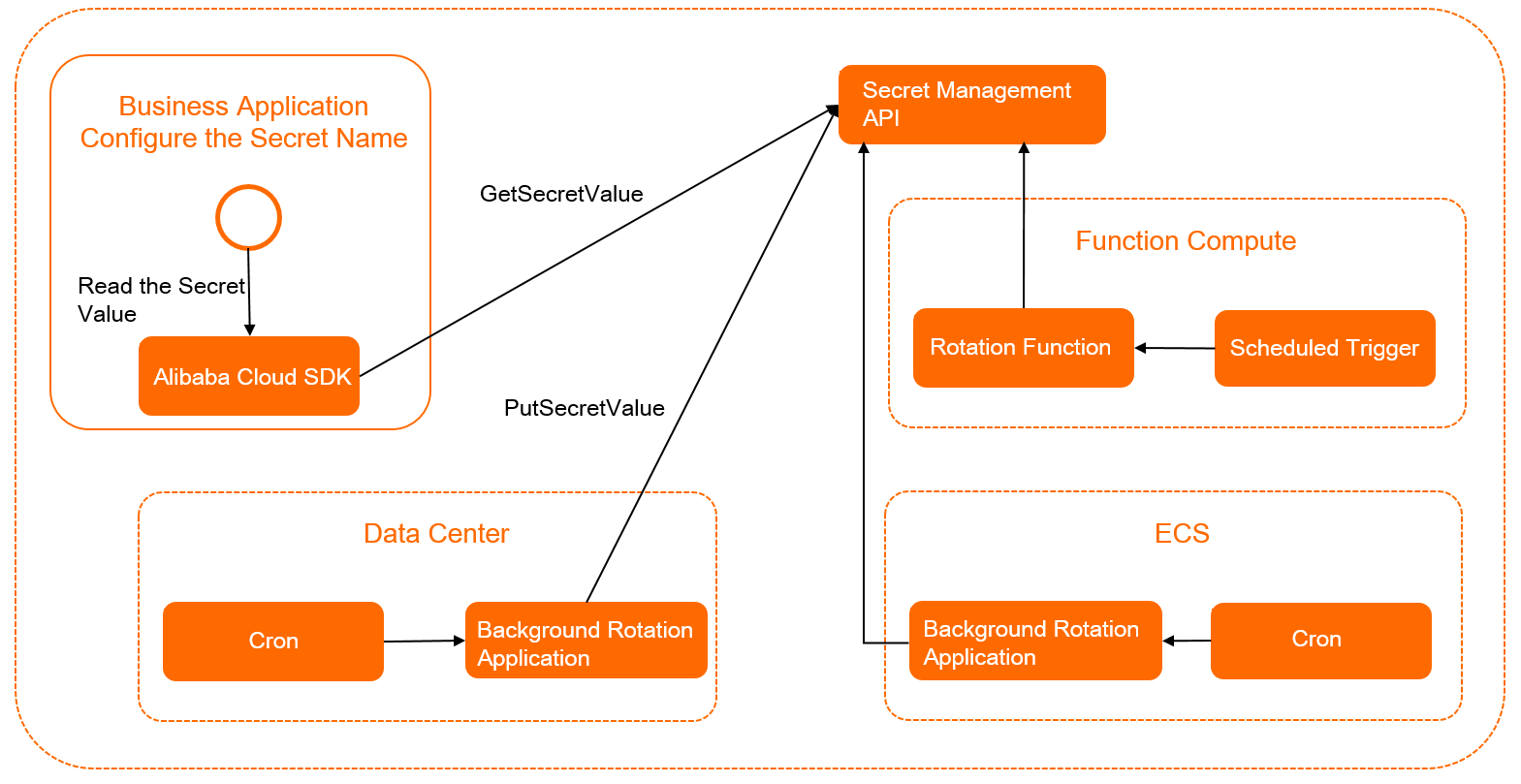
Secret consumers and secret producers can implement secret-related features based on Secrets Manager.
Secrets Manager: manages secrets. For example, Secrets Manager provides API operations that can be used to manage secrets.
Secret consumer: the application that uses secrets. For example, a business application calls the GetSecretValue operation to obtain the latest secret value.
Secret producer: the operations and maintenance (O&M) system or O&M administrator. For example, a data center, an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance, or Function Compute calls the CreateSecret operation to create a secret and calls the PutSecretValue operation to rotate the secret.
Prerequisites
Before you rotate a generic secret, make sure that the following requirements are met:
The initial version of the secret is generated in the O&M system and stored in Secrets Manager. Secrets Manager marks the initial version with ACSCurrent.
The secret value is obtained by the application that needs to use the secret. The application calls the GetSecretValue operation to obtain the secret value. To obtain the secret value, the application needs only to specify the secret name. Secrets Manager returns the secret value of the version marked with ACSCurrent.
Rotate a generic secret by calling a single API operation
Assume that a new secret is generated and takes effect in the system that an application needs to access. You can call a single API operation to store the secret to Secrets Manager and rotate the secret. For example, an OAuth 2.0 system can generate application secrets by itself. You can use Secrets Manager to manage the application secrets. The following process shows how the secret is rotated:
An administrator generates a new application secret in the OAuth 2.0 system.
The administrator uses Alibaba Cloud CLI to store the new application secret to Secrets Manager. This new secret version is marked with ACSCurrent. The mark of the original version is changed from ACSCurrent to ACSPrevious.
aliyun kms PutSecretValue \ --SecretName MyOAuthAppSecret --SecretData sample-app-secret \ --VersionId v2An application calls the GetSecretValue operation to obtain the secret value. Secrets Manager returns the value of the version marked with ACSCurrent. This secret value is the latest application secret value.
Rotate a generic secret by calling multiple API operations
In most cases, a system cannot automatically generate secrets. For example, an ApsaraDB RDS database cannot automatically generate an account, and an ECS instance cannot automatically generate an SSH key. You can create a new secret, store it to Secrets Manager, and then mark the version of the secret with MyPendingLabel. Register the new secret with the system. Then, rotate the version marked with MyPendingLabel to the current version in Secrets Manager.
The following example shows how to use Alibaba Cloud CLI to rotate the username and password of a database that are managed in Secrets Manager.
Call the GetRandomPassword operation to generate a random string as the new password by using the rotation program.
aliyun kms GetRandomPassword --ExcludePunctuation trueKey Management Service (KMS) returns the following results:
{ "RequestId": "e36ca295-6e47-4dfb-9df1-48d19df41545", "RandomPassword": "v2GwsgcuNylyYw9JGJNE5yBViGSi****" }Store the new username and password of the database as a new version of an existing secret.
Run the following command to store the new username and password and mark them with MyPendingLabel. The existing versions marked with ACSCurrent and ACSPrevious remain unchanged.
aliyun kms PutSecretValue \ --SecretName db_cred --SecretData "{\"uname\": \"alice\", \"pwd\": \"v2GwsgcuNylyYw9JGJNE5yBViGSiZ****"}" \ --VersionId v2 \ --VersionStages "[\"MyPendingLabel\"]"Register the new username and password with the database.
Only the secret value of the v2 version in the db_cred secret can be used to access the database.
Mark the new version of the secret with ACSCurrent in Secrets Manager.
aliyun kms UpdateSecretVersionStage \ --SecretName db_cred \ --VersionStage ACSCurrent \ --MoveToVersion v2Call the GetSecretValue operation to obtain the secret value. Secrets Manager returns the value of the version marked with ACSCurrent. This secret value contains the latest username and password of the database.
You can also use a dynamic ApsaraDB RDS secret so that Secrets Manager can automatically rotate the secret. For more information, see Overview of Dynamic ApsaraDB RDS secrets.