You can use Simple Log Service to record invocation statistics, query and analyze Function Compute invocations that are logged in Simple Log Service in real time, and view monitoring data in a visualized way. You must create your Logstore so that function invocation statistics can be automatically imported to your Logstore in real time. Simple Log Service provides query, analysis, and graphical visualization capabilities with which you can see in real time how functions are invoked and have better control over the service status of Function Compute.
As a result of the refactoring of the Function Compute console, the configuration options related to the log dashboard are no longer available in the new console. The log dashboard features described in this article apply only to the legacy version of the console.
We apologize for any inconvenience this may have caused.
Prerequisites
Collect and import logs
- Log on to the Function Compute console.
- In the top navigation bar, select the region where your Kubernetes cluster is deployed.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Overview.
In the Quick Access section on the Overview page, marked ① in the following figure, click Configure Log Dashboard, marked ② in the following figure.
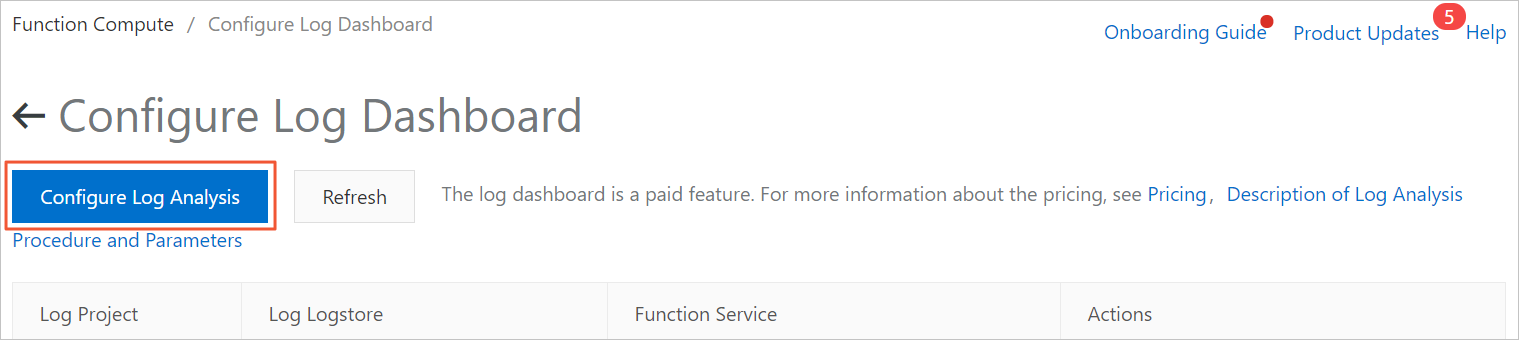
On the Configure Log Dashboard page, click Configure Log Analysis.
In the Custom Log Analysis panel, perform the following operations:
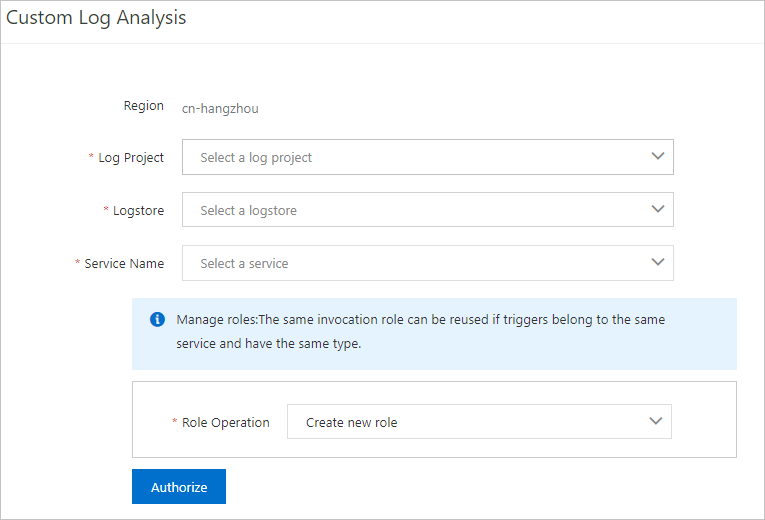
Select a project and a Logstore that reside in the region from the Log Project and Logstore drop-down lists.
Select one or more services that you want to associate with the Logstore.
Select Create new role from the Role Operation drop-down list and click Authorize.
On the Role Templates page, verify the information and click Confirm Authorization Policy.
In the Custom Log Analysis panel, click OK.
Query and analyze logs
On the Configure Log Dashboard page in the Function Compute console, click the Logstore that contains the logs you want to query.
On the details page of the Logstore, execute a query statement to analyze logs. The following examples are provided:
Use the requestID parameter to obtain the details about a request that is called.
requestID:e9870cbd-2ab2-6c78-3486-cd164015b889Query an asynchronous invocation request.
mode:async and operation:InvokeFunctionQuery a request that resulted in an invocation whose duration exceeded 5,000 milliseconds.
operation:InvokeFunction and durationMs > 5000
The following table describes the related parameters.
Parameter
Type
Description
Example
accountID
String
The ID of the account.
188********23420
asyncInvocationFinished
String
Indicates whether the invocation was complete.
true
concurrentCount
Long
The concurrency when the log was created.
10
concurrentReqLimit
Long
The maximum allowed concurrency.
100
durationMs
Double
The time used to execute the function. Unit: milliseconds.
5012.025
errorType
String
The type of the error that occurred.
HandledError
externalServiceVersion
String
The version of the service. For more information, see Manage versions.
1
fcStatus
Long
The internal status code.
200
forwardedFor
String
The original IP address. When an Alibaba Cloud CDN event trigger is used, the IP address is the IP address that calls Function Compute.
200.***. ***.100
functionErrors
Long
Non-system function errors.
0
functionName
String
The name of the function.
ReservedFunction
functionTimeoutInSec
Long
The timeout period for the function. Unit: seconds.
300
host
String
The host for the request.
1234567890.cn-shanghai.fc.aliyun-inc.com
isDarkLaunch
String
Indicates whether an alias or a canary version was used. For more information, see the following topics:
true
ip
String
The IP address of the client that sent the request.
172.***. ***.118
isHTTPS
String
Indicates whether HTTPS was used.
false
isHTTPTrigger
String
Indicates whether the function was triggered by an HTTP trigger.
false
latency
Double
The latency of the function invocation. Unit: milliseconds.
5017.347
maxMemoryUsage
Double
The maximum memory that the instance used. Unit: MB.
17.25
memoryLimitInMB
Long
The maximum memory that the instance can use. Unit: MB.
512
meteredRespSize
Long
The amount of billable traffic. Unit: byte.
0
method
String
The HTTP request method used for the function invocation.
POST
mode
String
The function invocation mode. Valid values:
sync: synchronous
async: asynchronous
sync
operation
String
The log category.
InvokeFunction
path
String
The URL path of the function invocation.
/2016-08-15/services/MeteringService/functions/ReservedFunction/invocations
qualifier
String
The information about the service version used.
The version number or alias.
region
String
The region where the cluster resides.
cn-shanghai
requestID
String
The ID of the request.
e9870cbd-2ab2-6c78-3486-cd164015b889
requestOriginalURI
String
The original Uniform Resource Identifier (URI). After a domain name is bound, the return value of this parameter does not include elements such as
/2016-08-15./2016-08-15/services/MeteringService/functions/ReservedFunction/invocations
requestSize
Long
The size of the request. Unit: byte.
912
resolveQualifierLatency
Long
The time used to parse the service version.
0
responseSize
Long
The size of the response. Unit: byte.
0
runtime
String
The runtime environment of the function.
python2.7
serviceName
String
The name of the service.
test-service-name
status
Long
The HTTP status code received by the client.
200
timestamp
Long
The timestamp when the function began to process the request. Unit: seconds.
1538137847
userAgent
String
The user agent of the requester.
go-sdk-0.1
Use dashboard charts and interpret metrics
- Log on to the Function Compute console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Overview.
In the Quick Access section on the Overview page, marked ① in the following figure, click Configure Log Dashboard, marked ② in the following figure.
On the Configure Log Dashboard page, find the log that you want to analyze and click Analyze Log in the Actions column. The following figure shows the displayed charts.
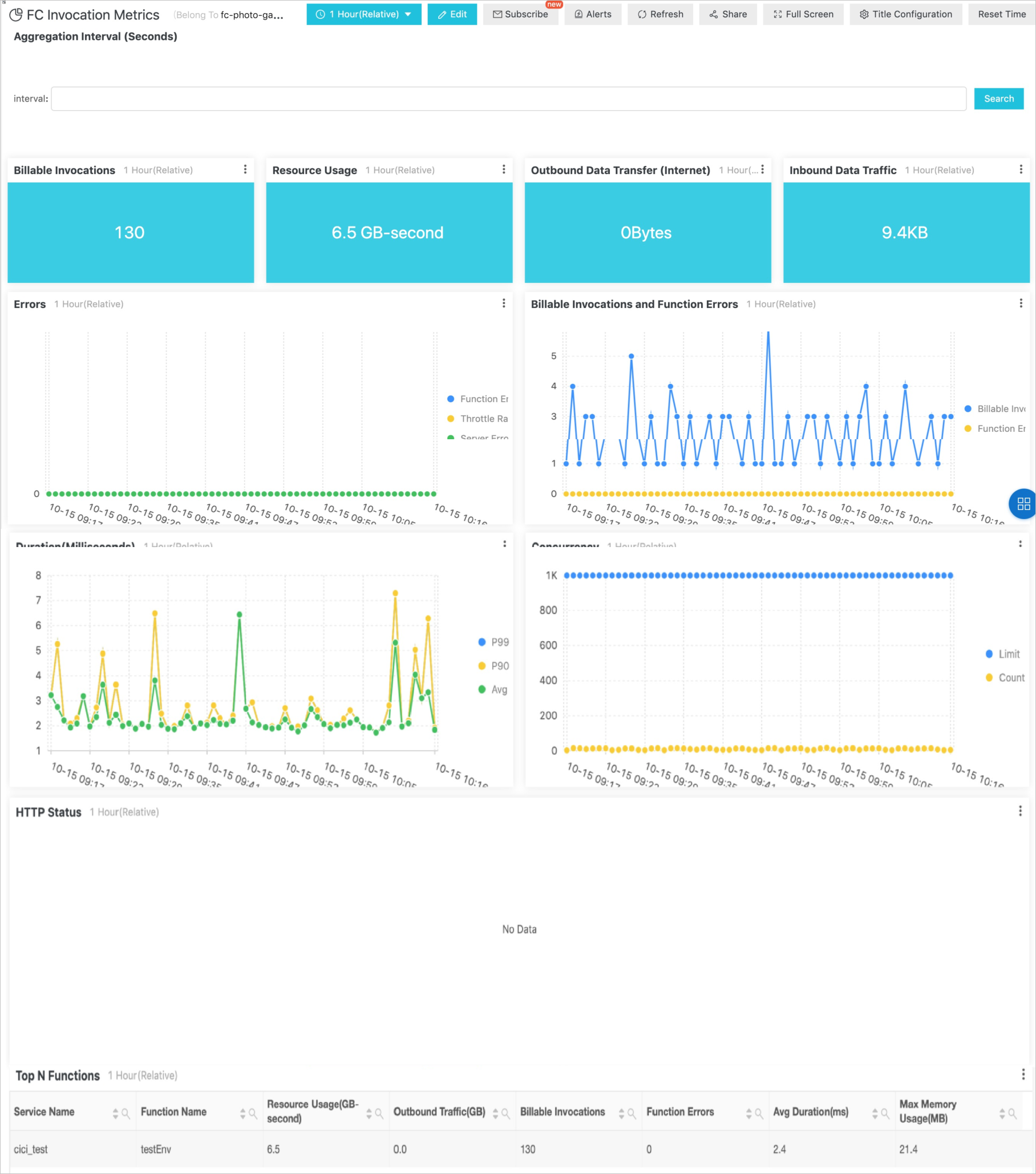
Parameter
Description
Billable Invocations
The number of times your function was executed. This value includes invocations that were successful and invocations that resulted in an internal error.
Resource Usage
The amount of used resources, which is calculated based on the following formula: Memory used by the instance × Time used to execute the function.
Outbound Data Transfer (Internet)
Billable traffic generated by the response of the function. This traffic does not include traffic generated by requests that are initiated from TCP or UDP clients within the function.
Inbound Data Traffic
Inbound traffic generated when the function accepts a request. This traffic is not billable.
Errors
User error rate: the percentage of failures to execute the function that were not caused by the system. These non-system errors include errors in function execution and HTTP client errors 400 to 499, excluding HTTP 429. A value of 0 indicates normal operation.
Throttling error rate: the percentage of failures to execute the function that were caused by throttling. These errors include throttling initiated by Function Compute and throttling that were not caused by exceeding the system quota. Throttling initiated by Function Compute generates the HTTP 503 response, and non-system throttling generates the HTTP 429 response. A value of 0 indicates normal operation.
System error rate: the percentage of failures to execute the function that were caused by Function Compute. These system errors include HTTP server errors 500 to 599, excluding HTTP 503. A value of 0 indicates normal operation.
Billable Invocations and Function Errors
Billable invocations: the number of function invocations that occurred and were billable.
Function errors: the number of function invocations that occurred but failed due to non-system reasons.
Duration (Milliseconds)
Average: the average duration for which functions were executed in a time period.
Concurrency
Concurrency limit: the concurrency quota for your account in the current region.
Actual concurrency: the highest concurrency used in a time period.
HTTP Status
The HTTP status code returned to the client after an HTTP function was executed.
Each status code class shows the number of responses that contain a status code from that class. For example, the Status_4xx class shows the total number of HTTP status codes from 400 to 499 that were returned in a time period.
Top N Functions
By default, functions are sorted by resource usage from large to small.
Resource Usage (GB-second): Memory used by the instance × Time used to execute the function.
Outbound Traffic (GB): billable traffic generated by the response of the function. This traffic does not include traffic generated by requests that are initiated from TCP or UDP clients within the function.
Billable Invocations: the number of times the function was invoked and executed.
Function Errors: the number of function errors.
Max Memory Usage (MB): the maximum amount of memory used by the function.
Customize dashboards
You can use query statements to create new charts. These charts can be added as new dashboards so that you can view them later. For more information, see the following topics:
The following query statements and charts are only for reference. Exercise caution if you decide to use these statements for commercial purposes.
Source analysis of user IP addresses
Access distribution within China
Execute the following query statement and select
map of Chinaas the chart type:operation:InvokeFunction | SELECT ip_to_province(IF(forwardedFor = '', ip, forwardedFor)) AS"Province", approx_distinct(IF(forwardedFor = '', ip, forwardedFor)) AS"Request"GROUP BY"Province"LIMIT 50Access distribution worldwide
Execute the following query statement and select
world mapas the chart type:operation:InvokeFunction | SELECT ip_to_country(IF(forwardedFor = '', ip, forwardedFor)) AS"Country", approx_distinct(IF(forwardedFor = '', ip, forwardedFor)) AS"Request"GROUP BY"Country"LIMIT 50Heatmap
Execute the following query statement and select
heatmapas the chart type:operation:InvokeFunction | SELECT ip_to_geo(IF(forwardedFor = '', ip, forwardedFor)) AS geo, count(1) AS count GROUP BY geo order BY count desc LIMIT 30
User agent ratio
Execute the following query statement and select
pie chartas the chart type:operation:InvokeFunction | SELECT userAgent, COUNT(userAgent) AS count GROUP BY userAgent ORDER BY count DESC LIMIT 20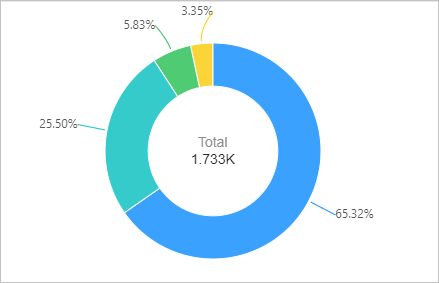
Top 20 URLs to HTTP functions
Execute the following query statement and select
tableas the chart type:operation:InvokeFunction and isHTTPTrigger:true | SELECT requestOriginalURI, COUNT(requestOriginalURI) AS count GROUP BY requestOriginalURI ORDER BY count LIMIT 20
Configure alert rules
You can add a DingTalk chatbot to help you monitor the health status of your functions. The chatbot uses alert rules in Simple Log Service to monitor the health status of your functions. For more information, see Configure an alert rule.