This topic describes the concepts relating to time and time zones in Linux operating systems. It also describes how to manage them and the differences in clock configurations in some Alibaba Cloud Linux public images.
Background information
The following table describes the basic concepts related to time and time zones in Linux operating systems.
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| clock | Linux has the following clocks:
|
| time standard | Linux has two time standards:
|
Managing time and time zones
- Run the following command on a Linux machine to view the time settings:
timedatectl statusInformation about the time settings of the machine is returned (see the following figure). This information includes the local time, UTC time, RTC time, and time zone of the Linux operating system.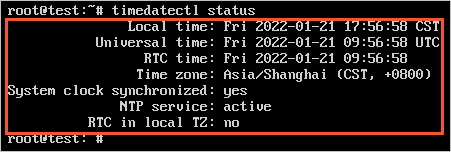
- Run the timedatectl command to set the time standard of the hardware clock.
- Set the time standard of the hardware clock to localtime:
Validation: If you run the timedatectl status command and the value oftimedatectl set-local-rtc 1RTC in local TZisyes, the time standard of the hardware clock is localtime. - Set the time standard of the hardware clock to UTC:
Validation: If you run the timedatectl status command and the value oftimedatectl set-local-rtc 0RTC in local TZisno, the time standard of the hardware clock is UTC.
- Set the time standard of the hardware clock to localtime:
Note The /etc/adjtime file stores the configurations for setting the system clock. When you run the preceding commands, the configurations in the /etc/adjtime file is automatically updated.
Public images in which the Alibaba Cloud RTC uses the UTC time standard
By default, RTC in Alibaba Cloud public images uses the localtime time standard. Note that Alibaba Cloud has changed the default localtime time standard used by RTC to the UTC time standard. In the following public images and their later versions, RTC uses the UTC time standard. For more information about the release of public images whose RTC use the UTC time standard, see the following topics.