This topic describes how to manually deploy a Node.js environment on an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance.
Prerequisites
Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 and CentOS 7.x support only Node.js 17.x and earlier versions.
An ECS instance is created and meets the following requirements:
The instance is assigned a public IP address by the system or is associated with an elastic IP address (EIP). For more information, see Enable public bandwidth.
The operating system is Alibaba Cloud Linux 3, Alibaba Cloud Linux 2, CentOS 7.x, Ubuntu 18.x or later, Debian 10.x or later, or Windows.
In the instance's security group, add inbound rules to allow connections on port 22 (for SSH) and port 3389 (for RDP). For enhanced security, we recommend allowing access only from specific IP addresses or ranges, rather than from all IPv4 addresses (0.0.0.0/0). For information about how to add a security group rule, see Add a security group rule.
Linux
This guide uses Node Version Manager (NVM) to deploy Node.js on Linux. NVM offers several advantages over other methods:
It is not limited by system repository versions, which ensures you can install the latest Node.js release.
It automatically configures environment variables, unlike installations from precompiled binaries.
It significantly reduces installation time compared to compiling from source code and requires no specialized skills.
Furthermore, NVM supports managing multiple Node.js versions, installs them in your home directory without requiring sudo permissions, and helps reduce security risks.
Install Node.js
Connect to the instance on which you want to install Node.js. For more information, see Use Workbench to log on to a Linux instance over SSH.
Install the distributed version management system Git.
Alibaba Cloud Linux 2, Alibaba Cloud Linux 3, or CentOS 7.x
sudo yum install git -yUbuntu 18.x and later or Debian 10.x and later
sudo apt update sudo apt install git -y
Use Git to clone the NVM source code into the ~/.nvm directory and check out the latest stable release.
NoteThe source code of NVM may fail to be cloned due to network issues. If a failure occurs, we recommend that you re-clone the source code.
git clone https://gitee.com/mirrors/nvm.git ~/.nvm && cd ~/.nvm && git checkout `git describe --abbrev=0 --tags`Run the following commands in sequence to configure the environment variables of NVM:
sudo sh -c 'echo ". ~/.nvm/nvm.sh" >> /etc/profile' source /etc/profileTo speed up downloads, run the following command to set the Node.js mirror:
export NVM_NODEJS_ORG_MIRROR=https://npmmirror.com/mirrors/nodeRun the following command to check the version of Node.js:
nvm list-remoteInstall multiple Node.js versions.
ImportantAlibaba Cloud Linux 2 and CentOS 7.x only support Node.js 17.x and earlier. If you are using one of these operating systems, replace the version in the following command with a version like
v17.9.1.Install Node.js 23.3.0.
nvm install v23.3.0Install Node.js 22.11.0.
nvm install v22.11.0
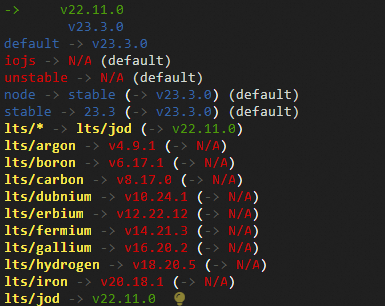
Run the following command to check the installed Node.js versions:
nvm lsIf the following sample command output is returned, v22.11.0 and v23.3.0 are installed and v22.11.0 is being used.
 Note
NoteYou can run the nvm use <Version number> command to switch between the versions of Node.js. For example, to switch to Node.js 23.3.0, run the nvm use v23.3.0 command.
Deploy a test project
Create a test project file named
example.js.Run the following command to go back to the home directory:
cdRun the following command to create the example.js test project file:
touch example.js
Modify the
example.jsproject file.Run the following command to open the
example.jsfile:vim example.jsPress the I key to enter Insert mode and add the following content to the example.js file.
In this example, port 3000 is occupied by the project, and the command output is Hello World. You can configure the project content (res.end) and a port number (const port) based on your business requirements.
const http = require('http'); const hostname = '0.0.0.0'; const port = 3000; const server = http.createServer((req, res) => { res.statusCode = 200; res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain'); res.end('Hello World\n'); }); server.listen(port, hostname, () => { console.log(`Server running at http://${hostname}:${port}/`); });After you add the preceding content, press the Esc key to exit Insert mode. Enter
:wqand press the Enter key to save and close the file.
Run the project in the background:
node ~/example.js &Run the following command to list the ports on which the system is listening:
netstat -tplnIn this example, port 3000 is displayed in the command output, which indicates that the project is running as expected.
Add an inbound rule to a security group of the ECS instance to open the specified port.
In this example, port 3000 is used. For information about how to add rules to a security group, see Add a security group rule.

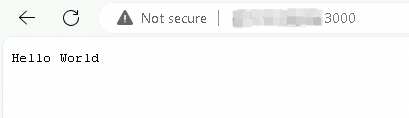
From your local computer or any computer with internet access, open a browser and enter
http://<Public IP address of the instance>:<Port number>in the address bar.In this example, <Port number> is set to 3000. The following page is displayed when you access the project.
Windows
To deploy Node.js on Windows, download the installer from the official website.
Install Node.js
Connect to the instance on which you want to install Node.js. For more information, see Use Workbench to connect to a Windows instance over RDP.
Visit the official website of Node.js and click Download in the top navigation bar.
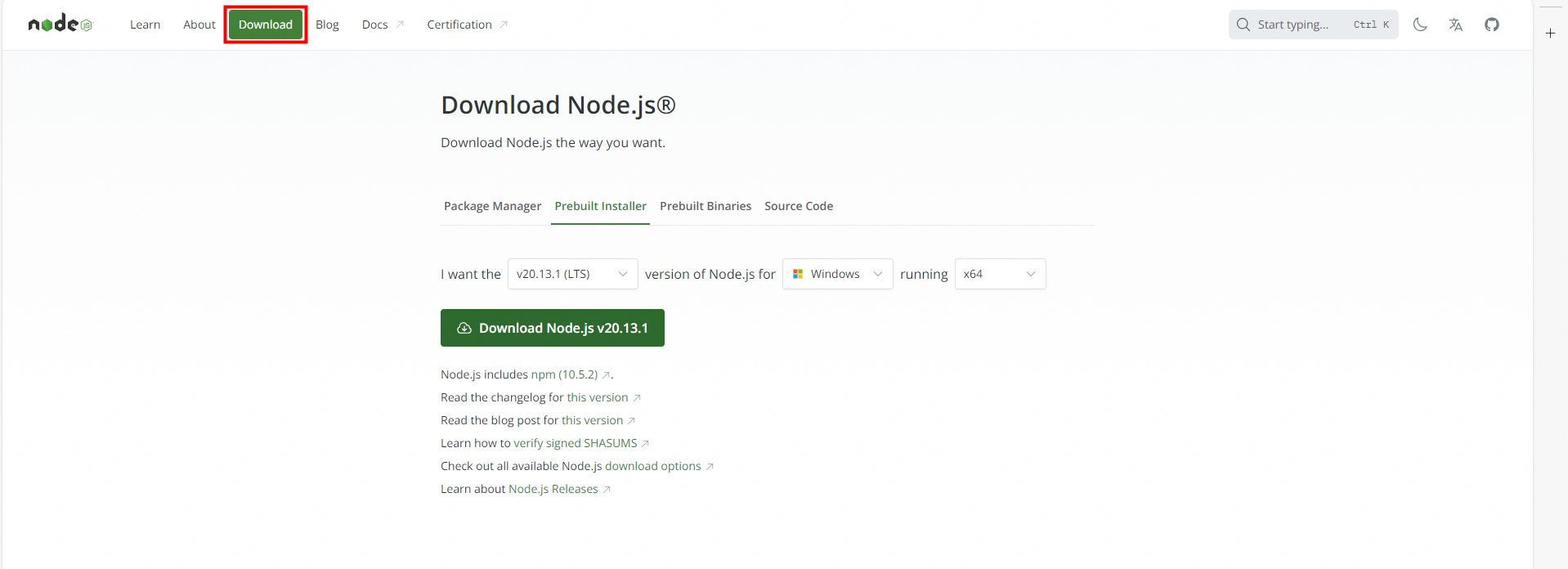
Download the installation package.
The download page provides a variety of installation methods. Each method is suitable for different needs and preferences. In this example, Prebuilt Installer is selected.
NoteWe recommend selecting a Long-Term Support (LTS) version for better stability.
Installation methods
Description
Package Manager
Use the package manager on the operating system such as npm, apt, yum, or brew to install Node.js.
Prebuilt Installer
Use a pre-compiled installation package for your operating system to install Node.js, such as a .msi file for Windows or a .pkg file for macOS. Such a package contains the Node.js runtime and npm, and usually contains some necessary dependencies.
Prebuilt Binaries
Use a Node.js executable file compiled for your platform to install Node.js. No installation wizard is provided. You must manually decompress the package and configure environment variables.
Source Code
Use the source code to install Node.js. After you decompress the package, you must use specific commands or scripts to configure and compile the source code to install Node.js.
Double-click the downloaded installation package and follow the installation wizard to install Node.js.
Open the Command Prompt or PowerShell.
In the Command Prompt window, enter
node -vandnpm -vand press the Enter key. If the output is similar to that in the following figure, Node.js is installed.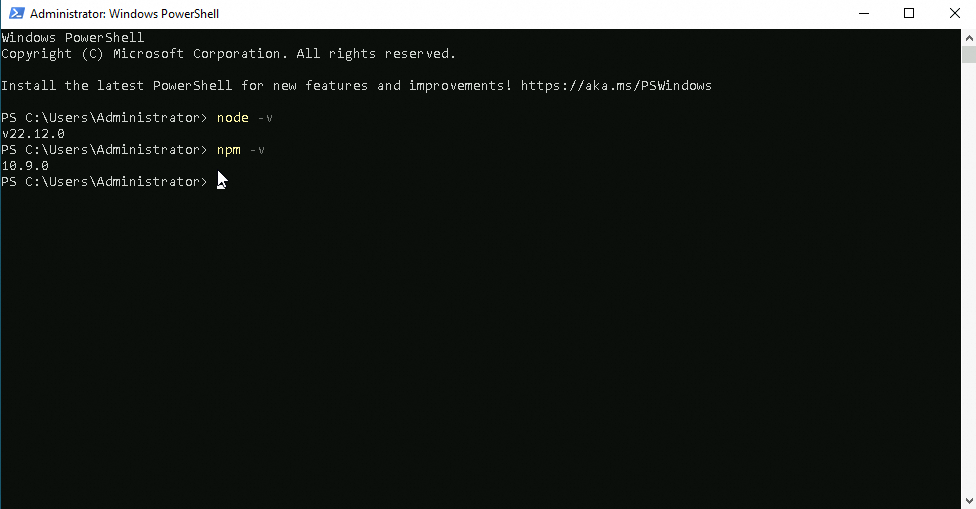
Deploy a test project
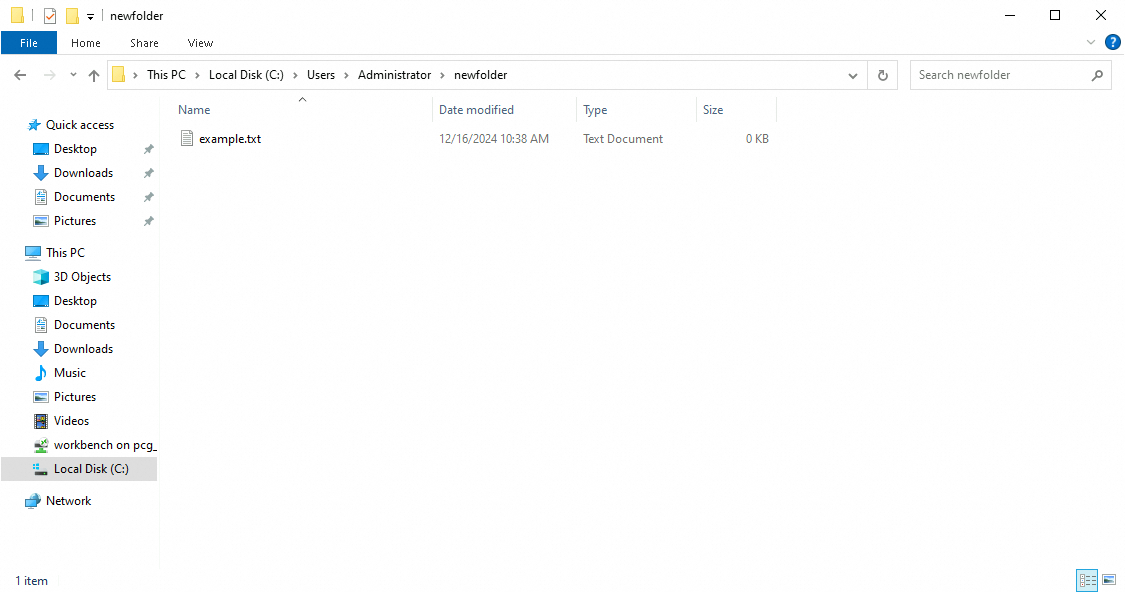
Create a test project folder named newfolder and an example.txt file.
Double-click the example.txt file and copy and paste the following content to the file.
In this example, port 3000 is occupied by the project, and the command output is Hello World. You can configure the project content (res.end) and a port number (const port) based on your business requirements.
const http = require('http'); const hostname = '0.0.0.0'; const port = 3000; const server = http.createServer((req, res) => { // Set the status code to 200. res.statusCode = 200; // Set the content type to plaintext. res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain'); // Add the Cache-Control header to disable caching. res.setHeader('Cache-Control', 'no-store, no-cache, must-revalidate, max-age=0'); // Add the Pragma header to disable caching to be compatible with the old browser. res.setHeader('Pragma', 'no-cache'); // Set the Expires header to a past date, which makes the content immediately expire. Alternatively, specify a specific expiration date, such as 'Expires: Tue, 03 Jul 2001 06:00:00 GMT'. res.setHeader('Expires', '0'); // Send the response body. res.end('Hello World\n'); }); // Listen on the specified port and hostname. server.listen(port, hostname, () => { console.log(`Server running at http://${hostname}:${port}/`); });Rename the example.txt file to example.js.
Go to the project directory and run the npm init command to initialize the project. Enter the project information as prompted to generate a
package.jsonfile.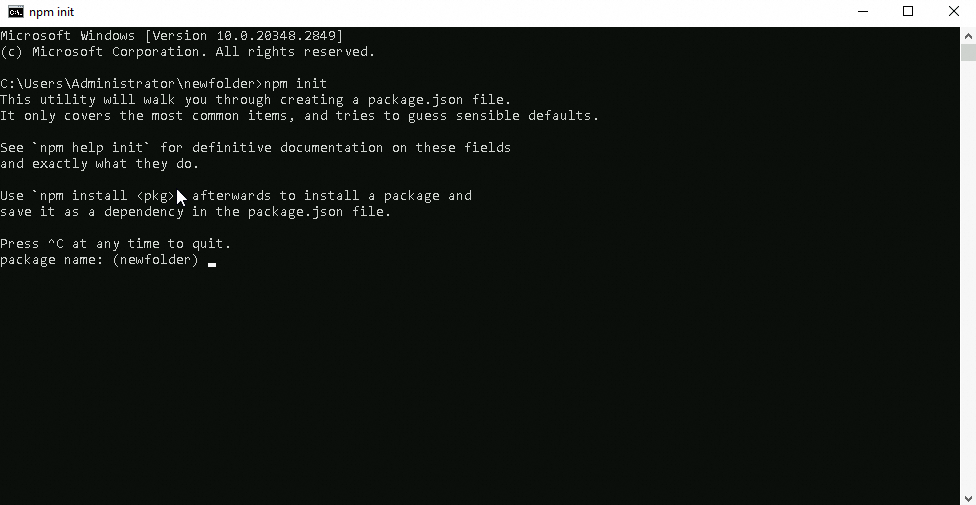
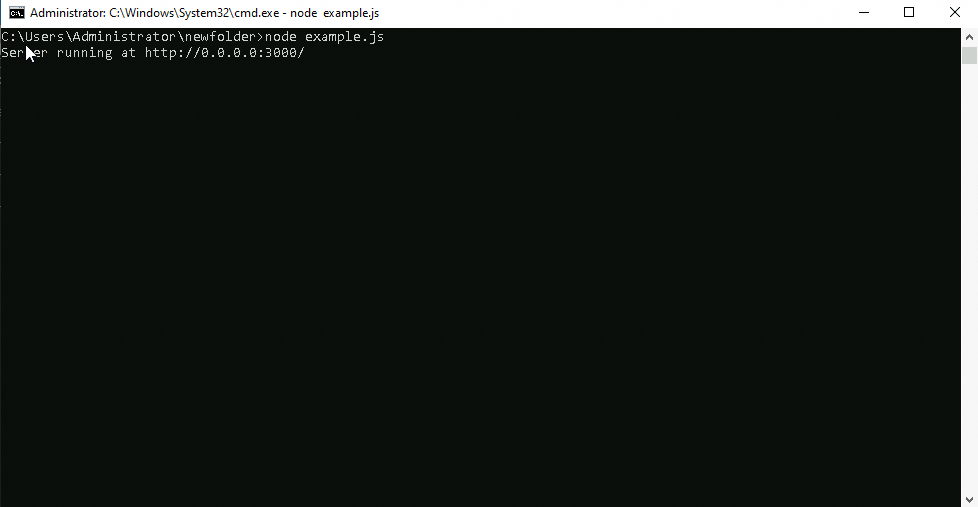
Run the Node.js project by running the node example.js command. After you successfully deploy the Node.js environment, the Node.js server runs and displays relevant information.
Add an inbound security group rule to the security group of the ECS instance to open port 3000 configured in the project. For more information, see Add a security group rule.

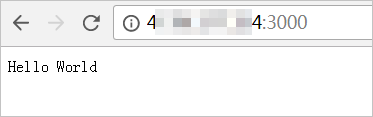
From your local computer or any computer with internet access, open a browser and enter
http://<Public IP address of the ECS instance>:<Project port number>.In this example, <Port number> is set to 3000. The following page is displayed when you access the project.