Pay-as-you-go is a post-paid billing method where you are charged based on the length of time you retain resources or your actual traffic usage. Compared to the subscription billing method, this billing method is more flexible. It lets you release resources and stop billing immediately when they are no longer needed. This effectively reduces costs from idle resources.
Scenarios
Your business experiences fluctuations or bursts that result in temporary and unpredictable resource usage.
You need to create and delete resources at any time.
Common scenarios include temporary scaling, testing, and e-commerce flash sales.
Billing rules
Pay-as-you-go resources are billed based on two models:
Pay-by-duration: You are charged based on the length of time that you retain resources. This applies to resources such as instance types and disks.
Pay-by-usage: You are charged based on your actual resource usage. This applies to public bandwidth that uses the pay-by-traffic billing method.
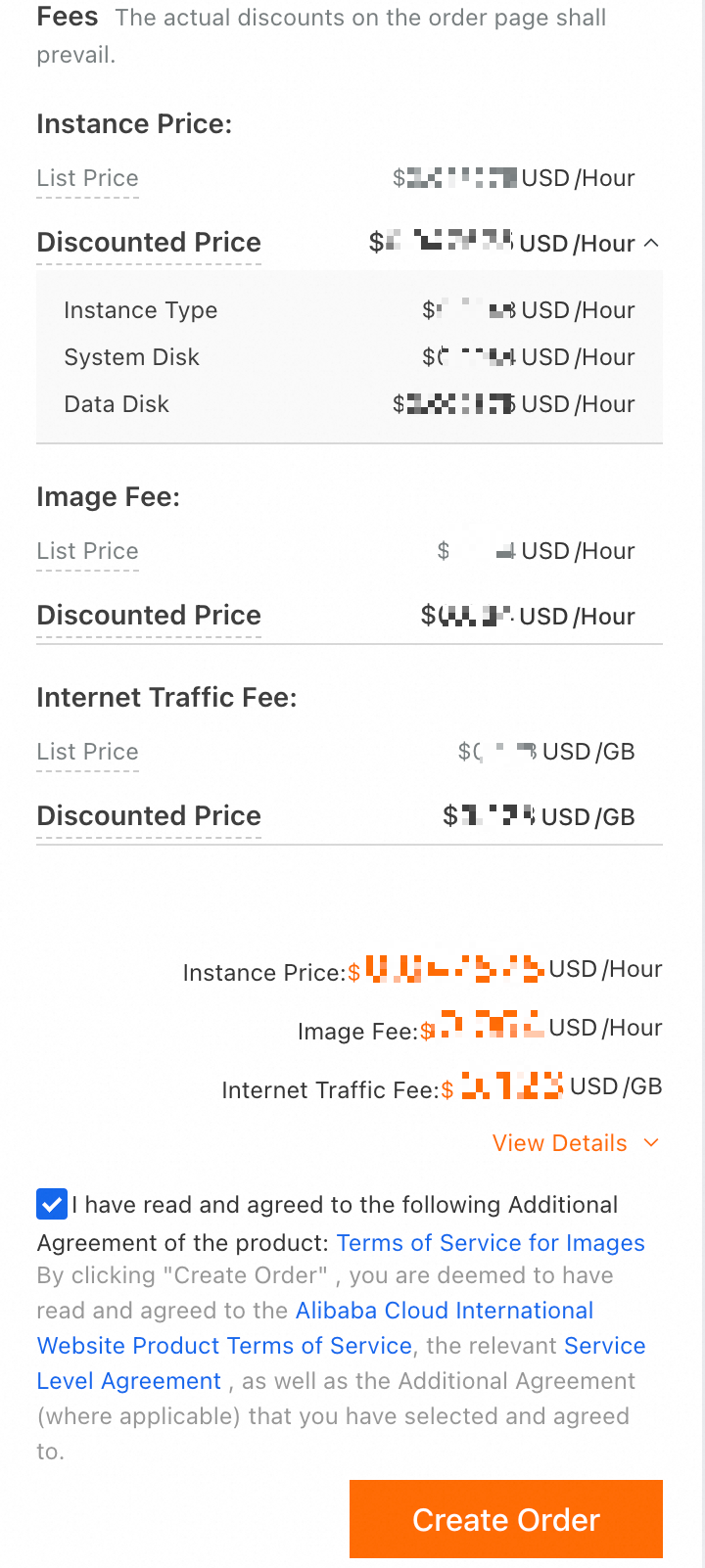
When you purchase a pay-as-you-go ECS instance, you must select an instance type and configure a system disk. You can also configure a paid image, a data disk, and public bandwidth that is billed on a pay-by-traffic basis. On the purchase page, you can view the cost details. The cost breakdown is similar to the one shown in the following figure:
This scenario is an example that illustrates billable items and billing rules. The actual billable items and prices are subject to the information displayed on the purchase page. If the billable items displayed during your purchase differ from those in this example, refer to the billable items and billing rules in the following table based on your actual configuration.
|
|
In addition to the billable items in the example, a pay-as-you-go instance may incur other pay-as-you-go fees based on your configuration. The following table describes the detailed billing rules for pay-as-you-go billable items.
Pay-by-duration
Billable item | Main billing formula | Billing duration |
Instance type fee = Instance type unit price × Billing duration The price for the same instance type may vary between regions. For more information, see the Elastic Compute Service pricing page. | Billing is measured in seconds. It starts when the instance is created and ends when the instance is released. Even if no services are running on the instance, the instance type is still billed until the instance is released. | |
Disk capacity fee = Disk unit price × Disk capacity × Billing duration The capacity of a disk is the provisioned capacity that you specify at the time of purchase. The price for the same type of disk may vary by region. For more information, see Elastic Compute Service pricing page ESSD AutoPL disks are subject to additional fees if you configure provisioned performance or enable performance bursting. For more information, see Elastic Block Storage billing. | Billing is measured in seconds. It starts when the instance is created and ends when the instance is released. | |
Image operating system license fee = Image unit price × Billing duration For the prices of public images, see Image billing. | Billing is measured in seconds. It starts when an instance that uses a paid image is created and ends when the instance is released or its operating system is replaced. | |
Public bandwidth fee (pay-by-bandwidth) = Pay-by-bandwidth unit price × Bandwidth size × Billing duration For public bandwidth prices for different regions, see the Bandwidth tab on the Elastic Compute Service Pricing | Billing is measured in seconds. It starts when the instance is created and ends when the instance is released or the public bandwidth is disabled (the bandwidth is set to 0). If you replace the image after the instance is created, billing for the old image stops and billing for the new image starts. | |
Snapshot storage fee = Snapshot unit price × Snapshot size × Billing duration Alibaba Cloud calculates snapshot fees separately for each region based on the type and size of snapshots that you use. For more information, see the Snapshot tab on the ECS Pricing page | Billing is measured by the hour. It starts when the snapshot is created and ends after the snapshot is deleted. |
Minimum billing duration
For the pay-as-you-go billing method, Alibaba Cloud generates a consumption detail record for each one-hour interval, such as from 00:00:00 to 01:00:00 on January 1, 2025. Each one-hour interval is a billing cycle. If a resource is released within a billing cycle and its actual usage duration is shorter than the minimum billing duration, the resource is billed for the minimum billing duration in that cycle. This applies to resources such as an instance type, disk capacity, public bandwidth (pay-by-bandwidth), or snapshot.
Minimum billing duration for instance types, disk capacity, and public bandwidth (pay-by-bandwidth):
1 vCPU instance: Billed for 10 minutes if used for less than 10 minutes.
2 vCPU instance: Billed for 5 minutes if used for less than 5 minutes.
4 vCPU or more instances: Billed for 2 minutes if used for less than 2 minutes.
Minimum snapshot billing duration: Snapshots are billed for a minimum of one hour.
For a calculation example, see How is the minimum billing duration calculated?
Pay-by-usage
Billable item | Pay-as-you-go billing formula | Unit price | Traffic measurement rule |
Public bandwidth fee (pay-by-traffic) = Outbound data transfer unit price × Traffic | Linear pricing. Public bandwidth prices vary by region. For more information, see the Bandwidth tab on the Elastic Compute Service pricing page. | Measured in bytes. The actual traffic usage is converted to GB and rounded down to six decimal places. |
Bill generation and overdue payments
Billing and settlement process
Until a resource is released, Alibaba Cloud records your resource usage in real time. You can view hourly consumption details on the Bill Details page. After the monthly bill is generated, you can review the usage and price details to verify the cost calculation.
The detailed bill data may be delayed. For more information about usage instructions and field descriptions, see Bill usage instructions.
Pay-as-you-go ECS resources are settled together with other post-paid products in your account. They are billed by the second, and consumption details are generated hourly. A settlement occurs each time the accumulated consumption reaches the deduction threshold.
If your default payment method is a bank card, the deduction threshold is 1,000 USD.
If your default payment method is PayPal or Paytm (India), the deduction threshold varies based on your ECS usage.
The system attempts to deduct fees up to three times: on the due date (T), on day T+7, and on day T+14. If the payment on the due date (T) fails, the payment becomes overdue. The system then makes two more attempts on day T+7 and day T+14. If all three attempts fail, the instance is stopped on day T+15, and billing for the instance also stops. For more information, see Overdue payments for pay-as-you-go resources.
In addition, a final settlement occurs on the first day of the following month to deduct any fees that have accumulated but have not reached the deduction threshold.
Overdue payments
If the available credit in your account (including your Alibaba Cloud account balance and coupons) is less than the bill to be settled, an overdue payment occurs in your account. After a payment becomes overdue, you cannot create new pay-as-you-go resources, and your existing instances are at risk of being stopped and released. The system sends you reminders or notifications. You must settle the overdue bill promptly to avoid any impact on your services.
For information about resource status changes after a payment becomes overdue, see Overdue payments.
Optimize costs
Release idle resources promptly
For pay-as-you-go ECS instances, if economical mode is not enabled, you are still charged for them even after they are manually stopped. If you no longer need an instance to provide services, you can release the instance. After a pay-as-you-go instance is released, it no longer incurs fees. For more information about how to release an instance, see Release an instance.
The data of a released instance is permanently deleted and cannot be recovered. If you still need to save the data, create a snapshot to back up the data before you release the instance. For more information, see Create a snapshot.
Enable economical mode
The following table shows the billing status of various resources when an instance is in the Running, Stopped (Standard), and Stopped (Economical) states. If you do not need to use an instance temporarily, you can enable economical mode to save on resource costs while retaining the instance data. After you enable economical mode for an instance, billing for the instance type, fixed public bandwidth, and image license fees is paused. However, other resources, such as disks and EIPs, continue to be billed.
Billable item | Running | Stopped (Standard) | Economy Mode |
Instance type | |||
Disk (system disk and data disks) capacity | |||
Public bandwidth (pay-by-bandwidth) | |||
Public bandwidth (pay-by-traffic) | Billed based on actual traffic usage | No traffic is generated and no fees are incurred | No traffic is generated and no fees are incurred |
Image operating system license |
Using economical mode may introduce risks when you restart the instance, such as startup failure, public IP address changes, and clearing of CPU credits for burstable performance instances. For more information about the risks, see Risks of economical mode.
Using discount benefits
Savings plans: You can commit to a specific amount of spending over a period of time to receive discounts on pay-as-you-go resources. This plan is suitable for scenarios with stable usage. For more information, see What are savings plans?.
Reserved instances: You can reserve computing resource capacity for a specific region and instance type to receive a discount. This plan is suitable for scenarios with fixed instance types and regions. For more information, see What are reserved instances?.
Switch between billing methods
Change from pay-as-you-go to subscription: If an instance needs to run for a long time, you can convert it to the subscription billing method to receive larger discounts. For more information, see Change from pay-as-you-go to subscription.
Change from subscription to pay-as-you-go: If a long-term task is complete but you still need the instance for temporary use, you can convert it to pay-as-you-go for more flexible cost control. For more information, see Change from subscription to pay-as-you-go.
Set up cost monitoring and alerts
You can set up spending alerts for your pay-as-you-go ECS instances to prevent budget overruns from unexpected high usage. To do this, perform the following steps:
In Message Center, set the recipients for Account Financial Messages.
Log in to the Expenses and Costs console and choose Billing > Bills.
In the upper-right corner of the Bills page, click Configure Daily Bill Alert.
On the settings page, select the Alerting Commodity, enter the Threshold, and click the Add button to add the alert.
For more information, see Set high spending alerts.
FAQ
How is the minimum billing duration calculated?
For the pay-as-you-go billing method, Alibaba Cloud generates a consumption detail record for each one-hour interval, such as from 00:00:00 to 01:00:00 on January 1, 2025. Each one-hour interval is a billing cycle. If the actual billing duration of an instance is shorter than the minimum billing duration within the billing cycle when it is released, the instance is billed for the minimum billing duration in that cycle.
The example instance is configured with only a disk and public bandwidth (pay-by-bandwidth). The instance configuration was not changed before the instance was released.
Scenario | Instance creation and release time | Pay-as-you-go billing duration |
Instance created and released in the same billing cycle | Created: 00:01:00, January 1, 2025 Released: 00:02:00, January 1, 2025 | The actual usage duration of the instance is shorter than the minimum billing duration, so it is billed for the minimum billing duration. The billing duration is as follows:
|
Instance created and released across billing cycles | Created: 00:59:00, January 1, 2025 Released: 02:00:20, January 1, 2025 |
|
Am I charged for a pay-as-you-go ECS instance after it is stopped?
An ECS instance can be in two stopped states. An instance that is stopped due to an overdue payment does not incur fees. Whether you are charged for a manually stopped instance depends on the instance configuration and network type, as described below:
Stopped due to overdue payment: This is an instance that is automatically stopped because your account has an overdue payment. An instance in this state is not billed. After a payment becomes overdue, the instance does not remain in the stopped state indefinitely. For information about resource status changes, see Overdue payments.
Manually stopped: An instance is manually stopped when you change its state to Stopped from the ECS console or by calling the StopInstance API. Billing for a manually stopped instance depends on its network type and whether economical mode is enabled.
If Economical mode is enabled: When an instance is in the Stopped state, billing is paused for its compute resources (vCPUs, GPUs, and memory), operating system license, and fixed public IP address. However, billing for other resources, such as EIPs, continues. Billing for these resources resumes after the instance is started. For more information, see Economical mode.
Economical mode is not enabled: The instance continues to be billed according to the pay-as-you-go billing rules even when it is in the Stopped state.