kdump is a Linux kernel crash dump mechanism that allows you to capture memory dump information when a kernel crash, such as a kernel panic, occurs in the operating system. This helps you analyze the cause of the crash. kdump requires an amount of reserved memory, which is called crashkernel memory, to ensure that sufficient memory is available to store kernel dump information even in the event of an operating system crash. This topic describes how to view and change the size of reserved memory on a Linux Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance.
View the size of reserved memory in the operating system
To allow kdump to use reserved memory, you must add the crashkernel parameter to the GRand Unified Bootloader (GRUB) configuration file and specify the size of reserved memory for each memory segment.
By default, the GRUB configuration file is stored in the /etc/default/grub directory. In Alibaba Cloud Linux 3, the GRUB configuration file is stored in the /usr/share/alinux-base-setup/cmdline directory.
When the operating system starts, GRUB passes the crashkernel parameter from the configuration file to the kernel to notify the kernel of the amount of memory that must be reserved for kdump on startup. You can view the /proc/cmdline file at system runtime to check whether the crashkernel parameter functions as expected.
Run the following command to check whether the crashkernel parameter is enabled:
cat /proc/cmdlineThe following command output includes the configuration of the
crashkernelparameter, which indicates that the crashkernel parameter is enabled.
Run the following command to view the size of reserved memory:
cat /sys/kernel/kexec_crash_sizeThe following command output is returned, which indicates the size of reserved memory. Unit: bytes.
In this example, 201326592 is returned, which indicates that 192 MB of memory is reserved.
Release the reserved memory and disable kdump
If you do not need to enable kdump for your instance and want to return the reserved memory address space to the operating system to prevent resource waste, perform the following operations to release the reserved memory and disable kdump.
If you release the reserved memory and disable kdump, the operating system may be unable to collect kernel crash information when the operating system fails. As a result, you cannot identify and fix kernel-related issues at the earliest opportunity. This affects the service continuity and stability of the instance. Proceed with caution.
Alibaba Cloud Linux and CentOS
Back up the GRUB configuration file.
Run the following command in Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 or CentOS:
sudo cp /etc/default/grub /etc/default/grub.bakRun the following command in Alibaba Cloud Linux 3:
sudo cp /usr/share/alinux-base-setup/cmdline /usr/share/alinux-base-setup/cmdline.bak
Delete the configuration of the
crashkernelparameter from the GRUB configuration file and save the file.Run the following command in Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 or CentOS:
sudo vim /etc/default/grub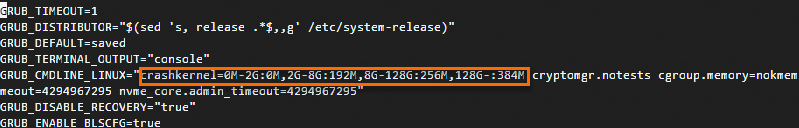
Find the
crashkernelparameter on theGRUB_CMDLINE_LINUXline and delete thecrashkernel=0M-2G:0M,2G-8G:192M,8G-128G:256M,128G-:384Mconfiguration. Press theEsckey, enter:wq, and then press the Enter key to save and close the configuration file.Run the following command in Alibaba Cloud Linux 3:
sudo vim /usr/share/alinux-base-setup/cmdline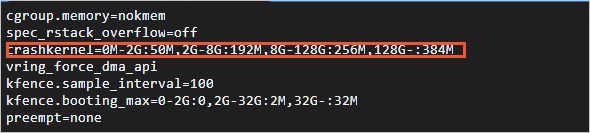
Delete the
crashkernel=0M-2G:0M,2G-8G:192M,8G-128G:256M,128G-:384Mline from the configuration file. Press theEsckey, enter:wq, and then press the Enter key to save and close the configuration file.
Run the following command to update the GRUB configurations:
sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfgNoteIn distributions that are based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) 9, such as CentOS Stream 9, AlmaLinux 9, and Rocky Linux 9, run the
sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg --update-bls-cmdlinecommand to update the GRUB configurations.Run the following commands to disable and stop kdump:
sudo systemctl disable kdump sudo systemctl stop kdumpRun the following command to restart the operating system for the changes to take effect:
sudo rebootView the status of kdump and the crashkernel parameter to check whether the changes take effect.
Run the following command to view the status of kdump. If kdump is in the
inactive (dead)state,kdumpis disabled.sudo systemctl status kdump
Run the following command to obtain the GRUB configuration file of the instance and check whether the configuration of the crashkernel parameter is deleted:
cat /proc/cmdline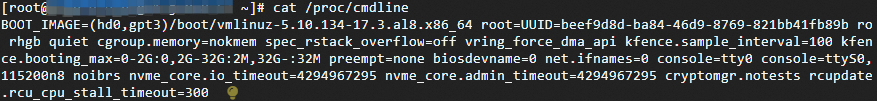
Ubuntu and Debian
Run the following command to back up the GRUB configuration file:
sudo cp /etc/default/grub /etc/default/grub.bakRun the following command to delete the configuration of the
crashkernelparameter from the GRUB configuration file and save the file:sudo vim /etc/default/grub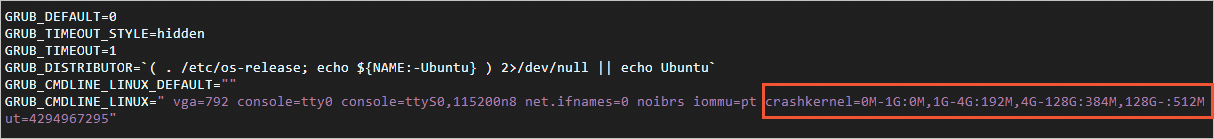
Find the
crashkernelparameter on theGRUB_CMDLINE_LINUXline and delete thecrashkernel=0M-2G:0M,2G-8G:192M,8G-128G:256M,128G-:384Mconfiguration. Press theEsckey, enter:wq, and then press the Enter key to save and close the configuration file.Run the following command to update the GRUB configurations:
sudo update-grub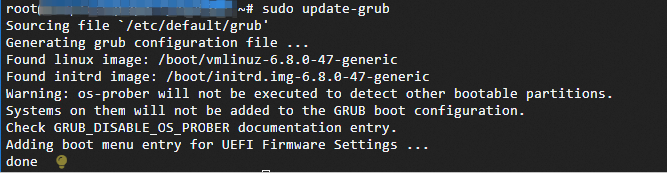
Run the following commands to disable and stop kdump:
sudo systemctl disable kdump-tools sudo systemctl stop kdump-toolsRun the following command to restart the operating system for the changes to take effect:
sudo rebootView the status of kdump and the crashkernel parameter to check whether the changes take effect.
Run the following command to view the status of kdump. If kdump is in the
inactive (dead)state,kdumpis disabled.sudo systemctl status kdump
Run the following command to obtain the GRUB configuration file of the instance and check whether the configuration of the crashkernel parameter is deleted:
cat /proc/cmdline
Enable memory reservation and kdump
If you want to use kdump to capture memory dump information of your instance, perform the following operations to add the configuration of the crashkernel parameter and enable kdump.
Alibaba Cloud Linux and CentOS
Back up the GRUB configuration file.
Run the following command in Alibaba Cloud Linux 3:
sudo cp /usr/share/alinux-base-setup/cmdline /usr/share/alinux-base-setup/cmdline.bakRun the following command in Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 or CentOS:
sudo cp /etc/default/grub /etc/default/grub.bak
Add the configuration of the
crashkernelparameter to the GRUB configuration file and save the file.Run the following command in Alibaba Cloud Linux 3:
sudo vim /usr/share/alinux-base-setup/cmdline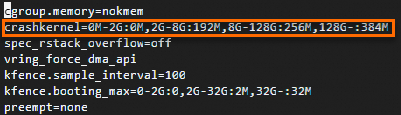
Add the
crashkernel=0M-2G:0M,2G-8G:192M,8G-128G:256M,128G-:384Mconfiguration to the configuration file. Press theEsckey, enter:wq, and then press the Enter key to save and close the configuration file.Run the following command in Alibaba Cloud Linux 2 or CentOS:
sudo vim /etc/default/grub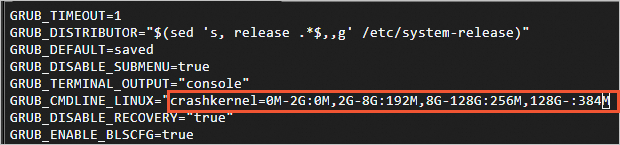
Find the
crashkernelparameter on theGRUB_CMDLINE_LINUXline and add thecrashkernel=0M-2G:0M,2G-8G:192M,8G-128G:256M,128G-:384Mconfiguration to the configuration file. Press theEsckey, enter:wq, and then press the Enter key to save and close the configuration file.
Run the following command to update the GRUB configurations:
sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfgNoteIn distributions that are based on RHEL 9, such as CentOS Stream 9, AlmaLinux 9, and Rocky Linux 9, run the
sudo grub2-mkconfig -o /boot/grub2/grub.cfg --update-bls-cmdlinecommand to update the GRUB configurations.Run the following command to enable kdump:
sudo systemctl enable kdumpRun the following command to restart the operating system for the changes to take effect:
sudo rebootView the status of kdump and the crashkernel parameter to check whether the changes take effect.
Run the following command to view the status of kdump. If kdump is in the
active (exited)state,kdumpis enabled.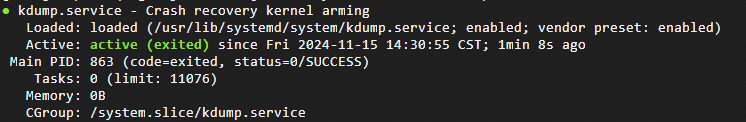
Run the following command to obtain the GRUB configuration file of the instance and check whether the configuration of the crashkernel parameter is added:
cat /proc/cmdline
Ubuntu and Debian
Run the following command to back up the GRUB configuration file:
sudo cp /etc/default/grub /etc/default/grub.bakRun the following command to add the configuration of the
crashkernelparameter to the GRUB configuration file and save the file:sudo vim /etc/default/grub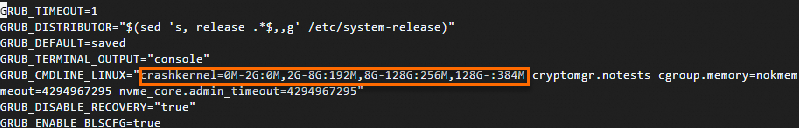
Add the
crashkernel=0M-2G:0M,2G-8G:192M,8G-128G:256M,128G-:384Mconfiguration to theGRUB_CMDLINE_LINUXline. Press theEsckey, enter:wq, and then press the Enter key to save and close the configuration file.Run the following command to update the GRUB configurations:
sudo update-grubRun the following commands to enable and start kdump:
sudo systemctl enable kdump-tools sudo systemctl start kdump-toolsRun the following command to restart the operating system for the changes to take effect:
sudo rebootView the status of kdump and the crashkernel parameter to check whether the changes take effect.
Run the following command to view the status of kdump. If kdump is in the
active (exited)state,kdumpis enabled.
Run the following command to obtain the GRUB configuration file of the instance and check whether the configuration of the crashkernel parameter is added:
cat /proc/cmdline