Deployment options
Automated deployment (Terraform): Click Run Now to open Terraform Explorer. You can then run the Terraform code to automatically create and configure a complete environment. This includes an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance, a public IP address, and the necessary security group rules.
Manual deployment: If you prefer to deploy manually to an existing ECS instance, follow the steps below.
Preparations
Enable public access: Assign a fixed public IP address to the instance or bind an Elastic IP (EIP).
Linux: Allow Inbound traffic on TCP ports 22 (Secure Shell) and 8080 (Tomcat).
Windows: Allow Inbound traffic on TCP ports 3389 (RDP) and 8080 (Tomcat).
Manually deploy OpenJDK: Install the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) and development kit on your server.
Procedure
Linux
Step 1: Download and install Tomcat
Log on to the ECS instance.
Go to ECS console - Instances. In the top navigation bar, select the target region and resource group.
Go to the details page of the target instance. Click Connect and select Workbench. Follow the prompts on the page to log on to the terminal.
Download and extract the Tomcat installation package.
This example uses Tomcat v9.0.91. To install a different version, visit the official Tomcat website to find the download URL and replace it in the command.
# Download the Tomcat installation package sudo wget https://archive.apache.org/dist/tomcat/tomcat-9/v9.0.91/bin/apache-tomcat-9.0.91.tar.gz --no-check-certificate # Extract it to the /usr/local/ directory sudo tar -zxvf apache-tomcat-9.0.91.tar.gz -C /usr/local/Create a symbolic link.
This allows you to upgrade Tomcat by changing the target of this link, without altering service configuration files.
sudo ln -s /usr/local/apache-tomcat-9.0.91 /usr/local/tomcat
Step 2: Configure Tomcat as a system service
Configure Tomcat as a systemd service to start automatically at system startup.
Get the JDK path.
sudo readlink -f $(which java)For JDK 8: The correct JDK path is the parent directory of the
jredirectory in the returned path.For JDK 11 or later: The returned path is the correct JDK path.
Create the
tomcat.servicefile.Replace
JDK_PATHwith the path you obtained in the previous step.sudo tee /etc/systemd/system/tomcat.service > /dev/null <<'EOF' [Unit] Description=Apache Tomcat Web Application Container After=network.target [Service] Type=forking Environment="JAVA_HOME=JDK_PATH" Environment="CATALINA_PID=/usr/local/tomcat/temp/tomcat.pid" Environment="CATALINA_HOME=/usr/local/tomcat" Environment="CATALINA_BASE=/usr/local/tomcat" ExecStart=/usr/local/tomcat/bin/startup.sh ExecStop=/usr/local/tomcat/bin/shutdown.sh Restart=on-failure [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target EOFStart the Tomcat service and enable it to start on boot.
# Reload the systemd configuration to apply the new service file sudo systemctl daemon-reload # Start the Tomcat service sudo systemctl start tomcat # Enable the Tomcat service to start on boot sudo systemctl enable tomcat
Step 3: Verify the deployment
Check the service status.
sudo systemctl status tomcatIf the status is
active(running), Tomcat has started successfully.Verify access.
In your local browser's address bar, enter
http://<ECS instance public IP address>:8080. If the Tomcat welcome page appears, the Java web environment is deployed successfully.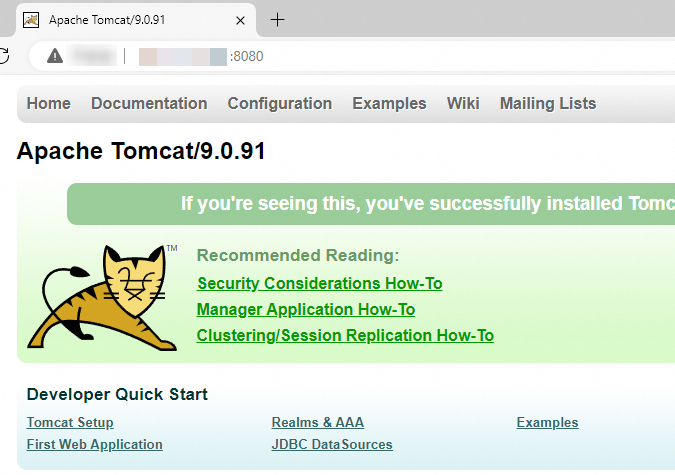
Windows
This example deploys Tomcat 9.0.113 on a 64-bit Windows Server 2022.
Step 1: Install and configure Tomcat
Log on to the ECS instance.
Go to ECS console - Instances. In the top navigation bar, select the target region and resource group.
Go to the details page of the target instance, click Connect, and select Workbench. Set the connection method to Terminal, enter the username and password, and then log on to the graphical terminal page.
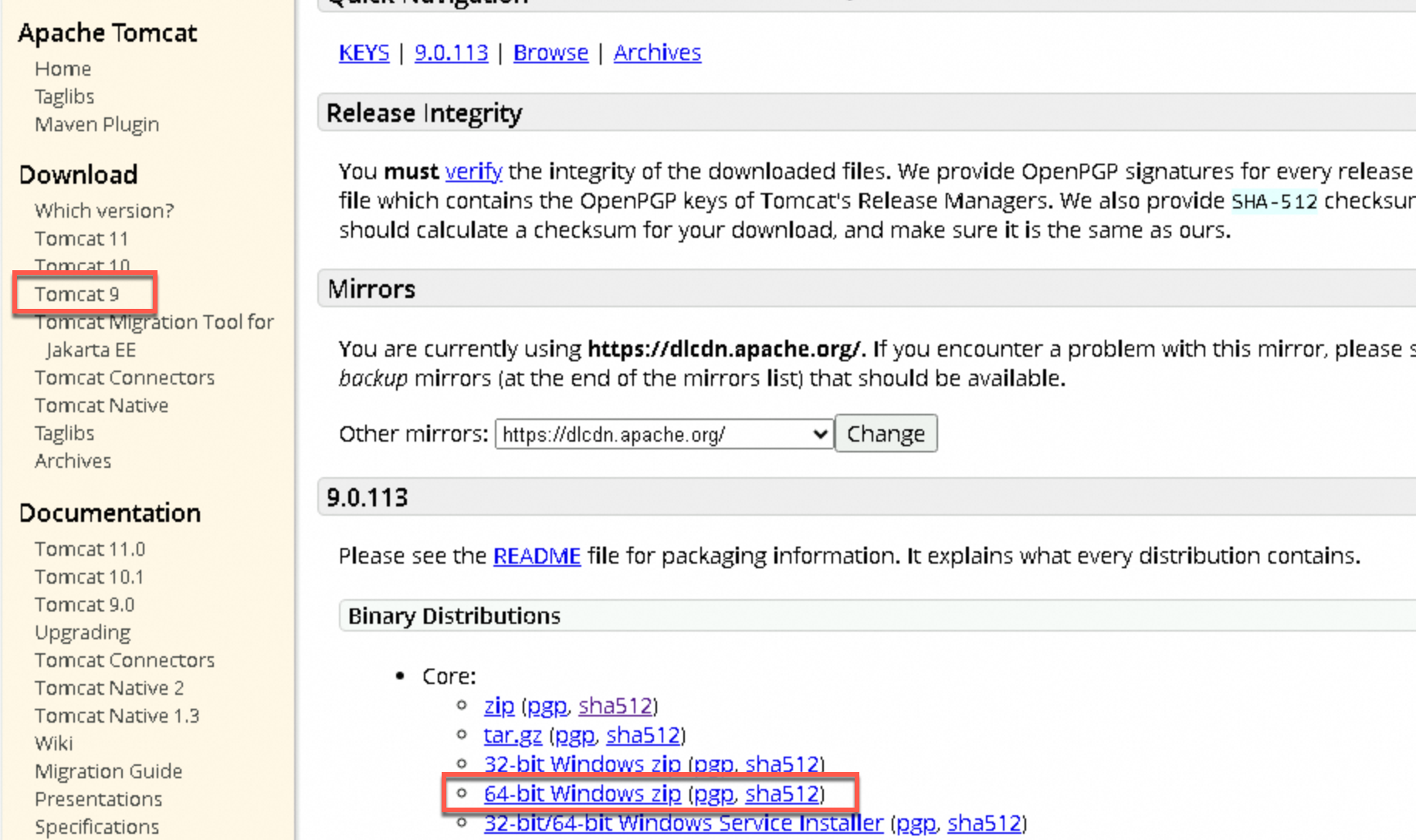
Download Tomcat 9.0.113 and extract it.
To avoid potential path recognition issues, extract the package to a path without non-ASCII characters, such as
C:\Java\apache-tomcat-9.0.113.For other versions, visit the official Tomcat website, select the appropriate version, and download and extract the installation package.
Configure environment variables.
Right-click This PC, and select .
In the System variables section, click New..., create a
CATALINA_HOMEsystem variable, set its value to the Tomcat extraction path, and then click OK.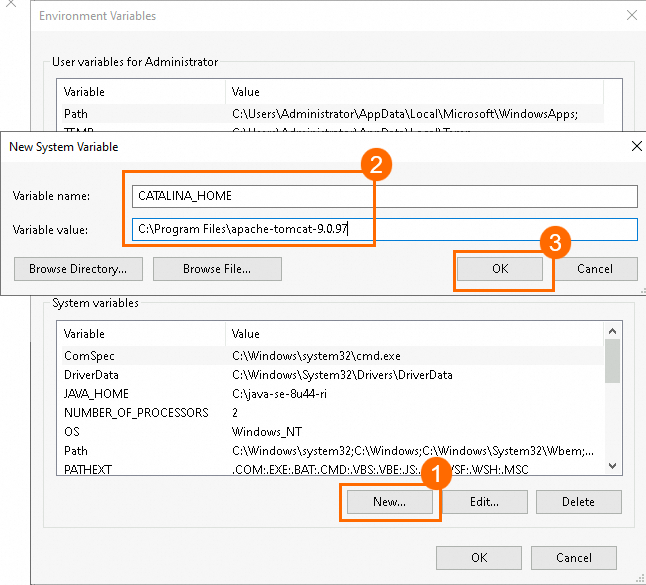
In System variables, find the
Pathvariable, select it, and click Edit....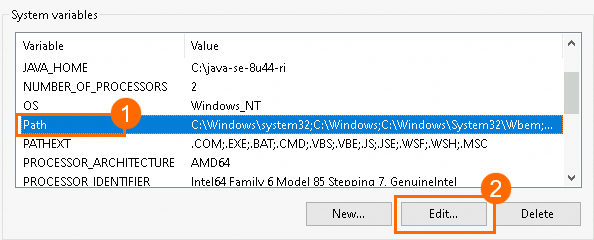
In Edit environment variable window, click New, add
%CATALINA_HOME%\bin, and then click OK to save the configuration.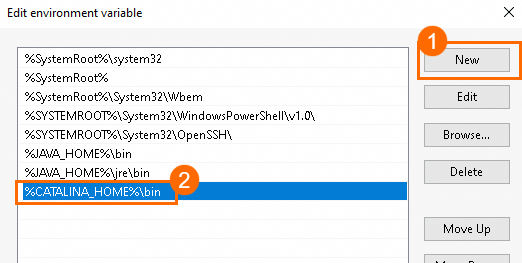
Step 2: Install Tomcat as a Windows service and start it
To allow Tomcat to run stably in the background and start automatically at system startup, install it as a Windows service instead of running it temporarily with startup.bat.
Install the service.
Open Command Prompt as an administrator, change to Tomcat's
bindirectory, and run the installation command.service.bat install Tomcat9If the message
The service 'Tomcat9' has been installed.appears, the installation was successful.Tomcat9is a custom service name. You will use this name to manage the service.Start the service and set it to start automatically.
Right-click
 , click Run, enter
, click Run, enter services.msc, and press Enter to open the Services Manager.Locate the
Apache Tomcat 9.0 Tomcat9service, right-click the service, select Properties, set the Startup type to Automatic, and then click Start.
If you see garbled characters in the logs, see Tomcat logs display garbled characters.
Step 3: Verify the deployment
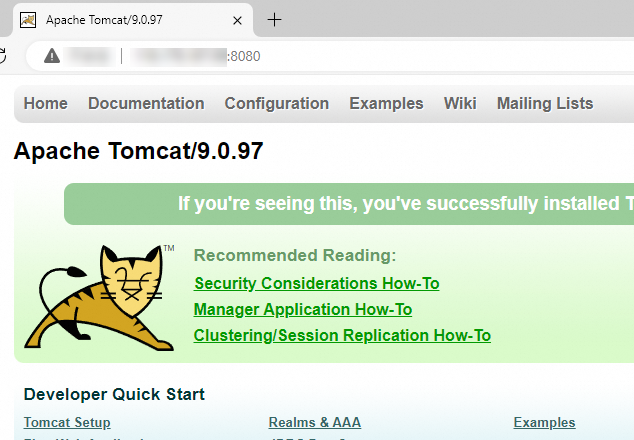
In your local browser's address bar, enter http://<ECS_instance_public_IP_address>:8080. If the Tomcat welcome page appears, the Java web environment is deployed successfully.
What to do next
Upload a web project
Use Workbench to upload or download files to upload a web application (.war file) to Tomcat's website root directory (default is webapps). Tomcat automatically detects and deploys WAR files.
After deployment, access the application at http://<ECS_instance_public_IP_address>:8080/<project_name>.
Configure Tomcat
Modify the configuration file
Go to the
conffolder in the Tomcat installation directory and open theserver.xmlfile.Modify the Tomcat configuration as needed.
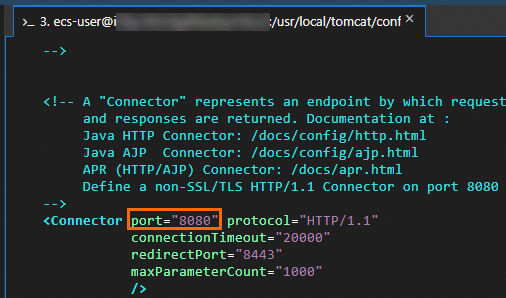
Tomcat uses port
8080by default. To change the port number, modify the value of theportattribute.To allow traffic on the new port, you must add a security group rule to the instance's security group.
Tomcat's default website root directory is
webapps. To change it, modify the value of theappBaseattribute.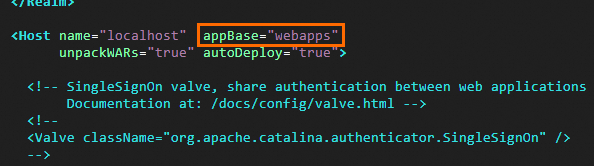
Set JVM memory parameters for Tomcat
Linux
To centrally manage JVM parameters, create a
setenv.shfile.Adjust the initial and maximum JVM heap sizes based on your ECS instance type and application load.
sudo tee /usr/local/tomcat/bin/setenv.sh > /dev/null <<'EOF' #!/bin/bash # Example: For an ECS instance with 2 GB of memory, allocate 512 MB JAVA_OPTS="-server -Xms512m -Xmx512m" export JAVA_OPTS EOFMake the file executable.
sudo chmod +x /usr/local/tomcat/bin/setenv.shRestart Tomcat for the configuration to take effect.
Windows
Go to the
binfolder in the Tomcat installation directory and open thecatalina.batfile.Add or modify the JVM parameters.
Add or modify
JAVA_OPTSnear the beginning of the file (usually aftersetlocaland beforecall "%CATALINA_HOME%\bin\setenv.bat"). Adjust the initial and maximum JVM heap sizes based on your ECS instance type and application load.# Example: For an ECS instance with 2 GB of memory, allocate 512 MB set "JAVA_OPTS=%JAVA_OPTS% -Xms512m -Xmx512m"If
JAVA_OPTSalready exists, append the new parameters to it, separated by spaces.Restart Tomcat for the configuration to take effect.
Apply in production
To reduce security risks in a production environment, we recommend taking the following steps after deployment.
Delete default applications
To reduce the potential attack surface, delete all default example applications (
docs,examples,manager,host-manager) from thewebappsdirectory.Linux:
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/tomcat/webapps/*Windows: Manually delete all subdirectories in the
CATALINA_HOME\webappsdirectory by using File Explorer.
Configure HTTPS
Production environments should use HTTPS. You need to install an SSL Certificate on a Tomcat server (Linux) and use Nginx or Server Load Balancer (SLB) as a reverse proxy to handle HTTPS requests.
FAQ
Browser times out or shows "This site can't be reached"
Check the security group: Verify that the inbound rules of your ECS instance's security group allow traffic on port
8080.Check the operating system firewall: Ensure the OS-level firewall (like
firewalldorWindows Defender Firewall) is disabled or has a rule to allow traffic on port8080.Check the port listener: Confirm that Tomcat is listening on port
8080.Linux:
ss -lntp | grep 8080Windows:
netstat -ano | findstr ":8080"
Tomcat fails to start
Check the logs: Tomcat's main logs are in the
logsfolder of its installation directory. Check thecatalina.out(Linux) orcatalina.<date>.log(Windows) andlocalhost.<date>.logfiles. If you find anAddress already in useerror, the port is occupied by another program. For details, see Troubleshoot port connectivity issues on an ECS instance that can be pinged.Incorrect JDK path: Check if the
JAVA_HOMEenvironment variable is configured correctly.
Tomcat logs display garbled characters
This issue is usually caused by a mismatch between the Windows Command Prompt's default encoding (typically GBK) and Tomcat's log output encoding (usually UTF-8).
Open the
conffolder in the Tomcat installation directory and edit thelogging.propertiesfile.Change all instances of the default encoding
UTF-8in the file toGBK.Save the file and restart Tomcat. Verify that the characters in the logs are now displayed correctly.