This topic describes some frequently asked questions about building an FTP site and how to resolve the issues that occur when you build an FTP site, such as issues related to FTP service installation and configuration, security issues, and connection issues, to ensure data security and the stability of the FTP site.
What do I do if I cannot download a file from an FTP server?
Perform the following operations to enable the download permission in Internet Explorer:
Open Internet Explorer on your on-premises host.
Click the
 icon in the upper-right corner of the browser and then click Internet options.
icon in the upper-right corner of the browser and then click Internet options. In the upper part of the Internet Options dialog box, click the Security tab.
In the Select a zone to view or change security settings section, click Internet, and then click Custom level in the Security level for this zone section.
Choose , and then click OK.
Click Apply and then click OK.
What do I do if an error occurs when I connect to an FTP server?
You can troubleshoot the issue based on the error message. If the issue is difficult to troubleshoot, we recommend that you use a third-party FTP client connection tool, such as FileZilla. To download the FileZilla client, visit the FileZilla website. In this example, FileZilla is used to connect to the FTP server in anonymous mode.
Configure vsftpd in anonymous mode.
Run the following command to modify the
/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.confconfiguration file.If you installed vsftpd by running the
apt install vsftpdcommand, the configuration file is located in the following path:/etc/vsftpd.conf.sudo vim /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.confPress the
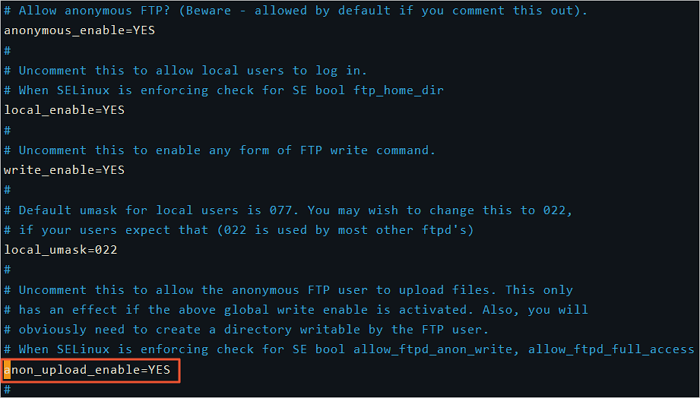
Ikey to enter Insert mode.Comment out the permissions and set the
anon_upload_enableparameter to YES to allow anonymous users to upload files.Press the
Esckey, enter:wq, and then press the Enter key to save and close the file.The following figure shows an example of the modified configuration file.
Run the following command to grant FTP users write permissions on the
/var/ftp/pubdirectory./var/ftp/pubis the default file directory of the FTP service.sudo chmod o+w /var/ftp/pub/Run the following command to reload the configuration file:
sudo systemctl restart vsftpd
Download and install FileZilla.
Use FileZilla to connect to the FTP server in anonymous mode.
Open the FileZilla client.
In the top navigation bar, choose .
In the lower-left corner of the Site Manager dialog box, click New site.
Enter a name for the new site and configure the new site.
NoteIn this example, FileZilla 3.64.0 is used. The actual interface may vary based on the version of FileZilla.
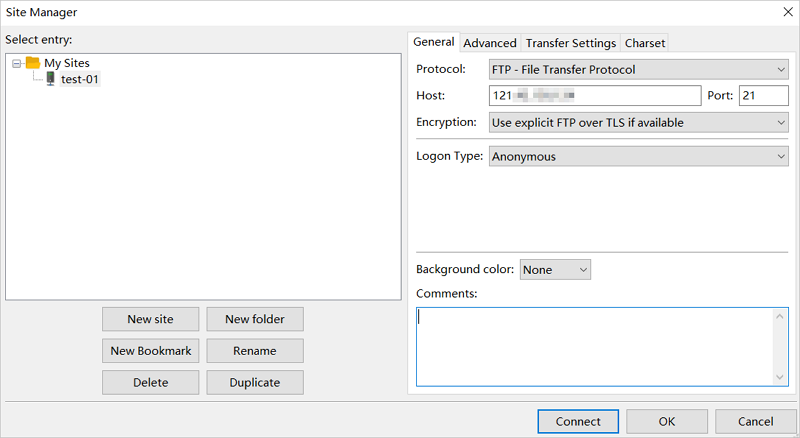 Parameters:
Parameters:Name: a custom site name. Example:
test-01.Protocol: FTP.
Host: the public IP address of the FTP server. In this topic, the public IP address of a Linux instance is used. Example:
121.43.XX.XX.Port: 21.
Logon Type: Anonymous.
In this example, an FTP client is used to connect to the FTP server in anonymous mode. If you want to manage access to the FTP server, set the logon type to normal and configure the username and password.
Click Connect.
After you connect to the FTP server, you can upload, download, and delete files. The following figure shows an example of the FileZilla interface.
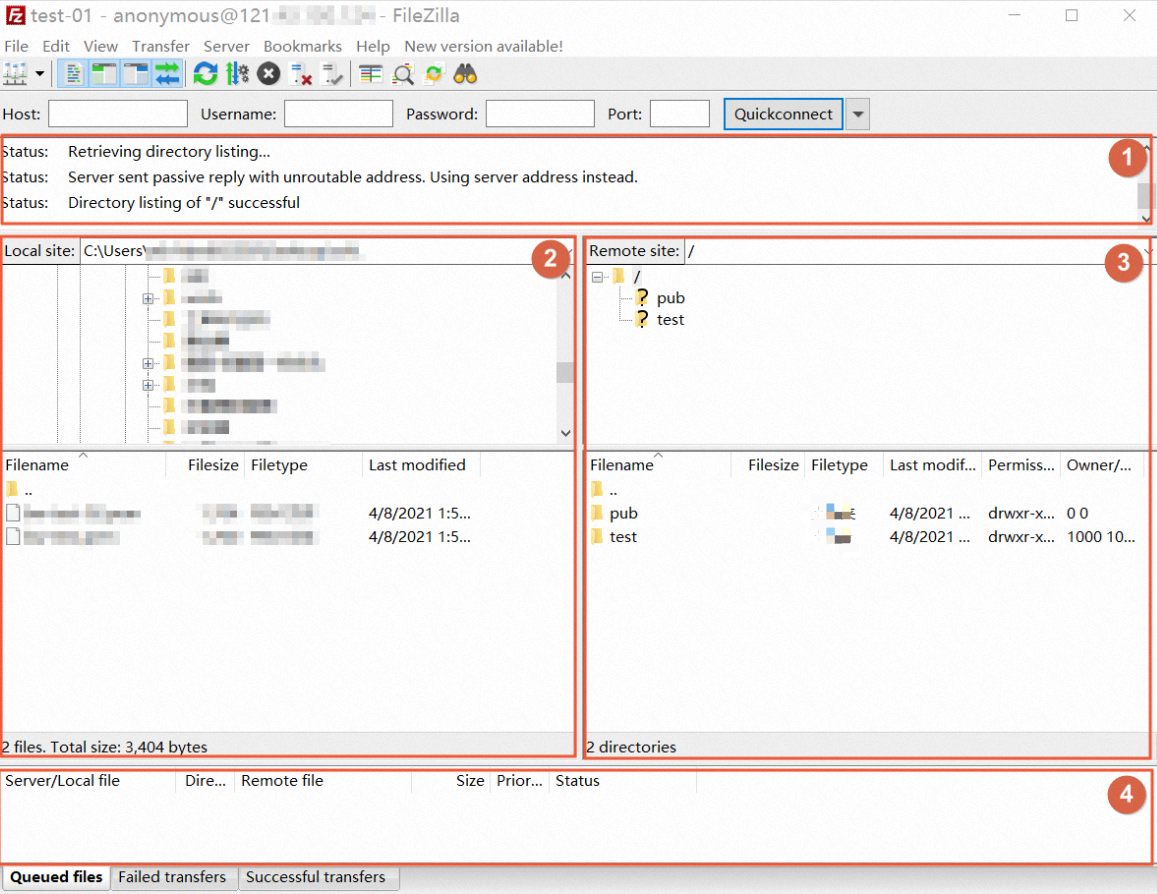 The following table describes the sections in the preceding interface.
The following table describes the sections in the preceding interface. Section
Description
①
Displays commands, the connection status of the FTP server, and task execution results.
②
Displays information about the on-premises host, including the directory information of the host.
③
Displays information about the remote server, including the directory information of the FTP server. In anonymous mode, the default directory is
/pub.④
Displays records, including the FTP task queue and logs.
What do I do if the Everyone option is unavailable when I configure permissions on a folder?
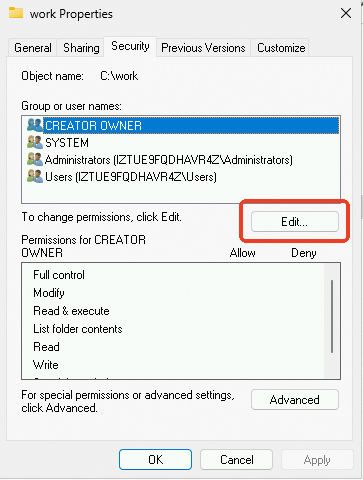
If the Everyone option is unavailable on the Security tab when you configure the properties of a folder, perform the following steps to add the option:
On the Security tab, click Edit.
In the dialog box that appears, click Add.
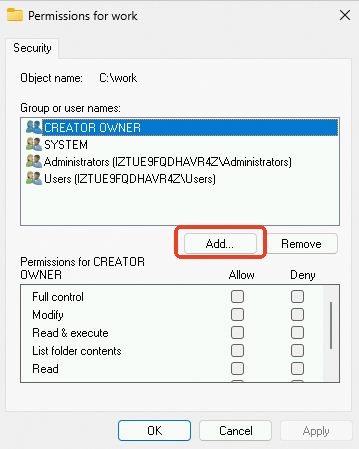
In the dialog box that appears, click Advanced.
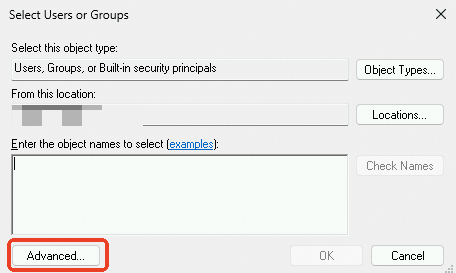
In the dialog box that appears, click Find Now, select Everyone in the search results, and then click OK.
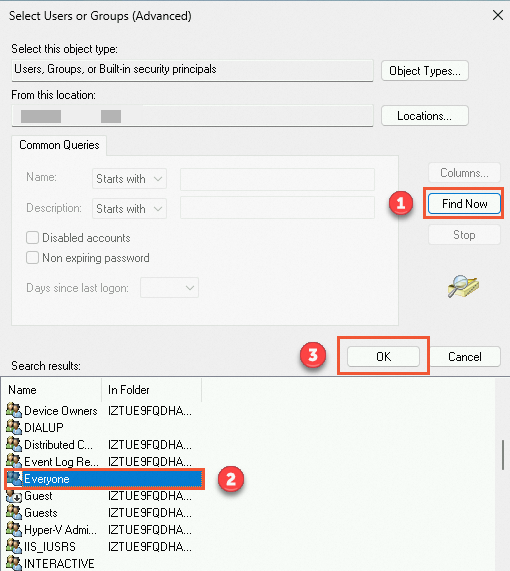
Click OK to return to the dialog box in which you can configure permissions on the folder.
Click OK.
How do I create a server certificate?
If you want to use a secure FTP transfer protocol, such as File Transfer Protocol Secure (FTPS), you must install a server certificate to encrypt the FTP session. This protects the security of data during transmission and prevents data from being stolen or tampered with. Perform the following steps to create a server certificate:
On the Dashboard page of the Server Manager window, choose in the upper-right corner.
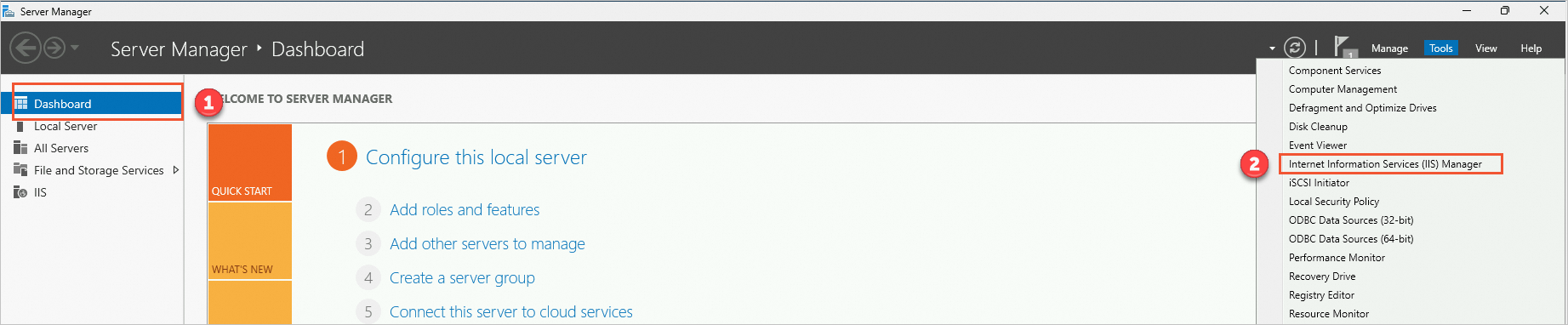
In the left-side navigation pane, click the server ID. In the IIS section of the homepage of the server, double-click Server Certificates. The Server Certificates page appears.
In the Actions pane, click Create Self-Signed Certificate.
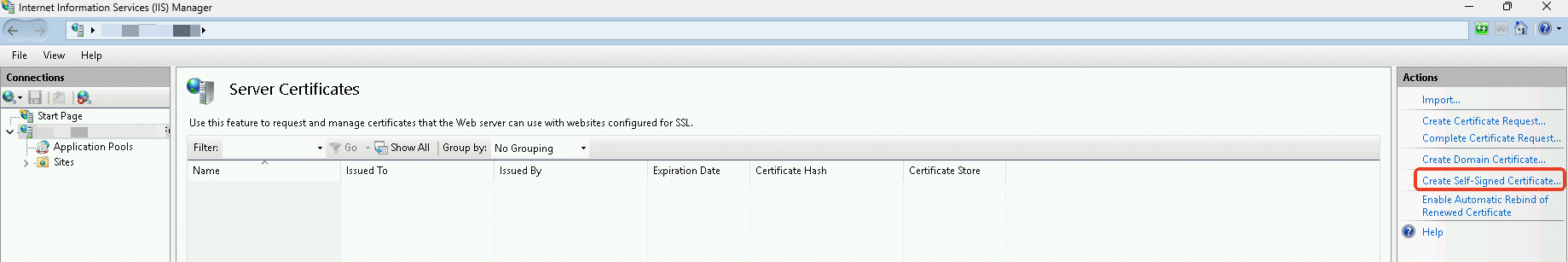
Enter a certificate name, select a certificate storage type, and then click OK.
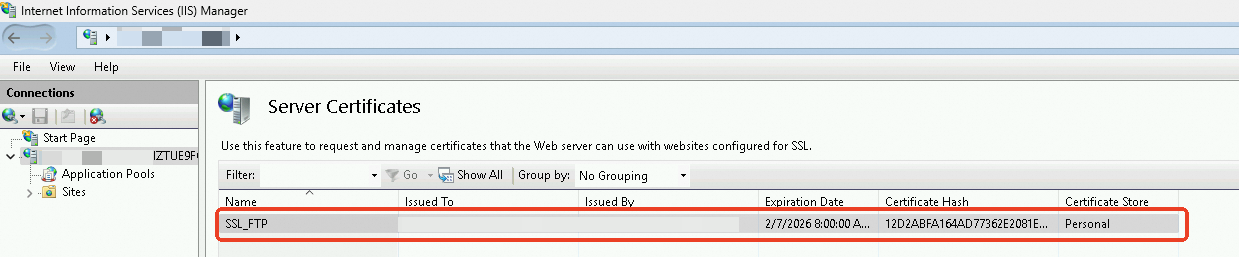
After the server certificate is created, the certificate is displayed on the Server Certificates page.
What suggestions can I obtain when I configure ports in FTP passive mode?
When you configure the FTP passive mode, specify a port range instead of a single port to ensure balance between performance, concurrency, and security. The following section describes the main reasons why you need to open a port range instead of a single port:
Support for concurrent connections
Using a port range allows multiple clients to concurrently transmit data. Each connection occupies one port. Multiple ports can support multiple concurrent connections.
If your FTP server needs to handle a large number of concurrent users, such as users who perform file downloads or uploads, specify a wide port range to reduce latency and prevent connection rejections.
Network flexibility
In a large, high-traffic environment, such as an enterprise or a data center, the dynamic allocation of ports may be required to respond to different types of requests and traffic patterns.
A wide enough port range ensures connection stability in different network scenarios, such as load balancing and cross-subnet communication.
Configuration suggestions
Evaluate concurrency requirements.
Estimate the maximum number of concurrent connections that the FTP server needs to support. If the FTP server has a large number of users or needs to transmit a large amount of data, you must specify a wide port range.
If the network size is small or the FTP server has a small number of users, you can specify a narrow port range.
Specify a suitable port range.
For small and medium-sized enterprises, specify a port range that contains 100 to 200 ports. The port range is narrow but sufficient to cope with common concurrency requirements.
For environments that have a large amount of traffic, specify a wide port range. You can perform load tests to determine the appropriate size of the port range.
Consider security.
Use a firewall rule to restrict access to a specific port range and only accept connections from trusted hosts or networks.
To enhance security, enable the IP address and user blacklist and whitelist features.
Monitor the port usage and change the port range based on the monitoring data.
Monitor the port usage in real time, and use tools and analyze logs to detect anomalous activities and traffic patterns.
Change the size of the port range or the security policy based on the monitoring data to better match your business requirements.
Automate and simplify management.
Automate port range configuration and security policy deployment by using configuration management tools, such as Ansible and Puppet. This prevents errors caused by manual management.
Incorporate port range configuration into a regular review and update process to ensure that the port range can adapt to changing business requirements.
Configure a security protocol.
Configure FTPS or SSH FTP (SFTP) to encrypt transmitted data and enhance data confidentiality, especially for sensitive data.