This topic describes how to quickly troubleshoot issues with accessing websites that run on Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances.
Problem description
When you access a website that runs on an ECS instance, you may encounter the following issues:
You receive a prompt that says "No ICP filing or not connected" or "Website content does not match the ICP filing information".
The browser returns a numeric error code, such as 403, 404, 502, or 503.
You cannot access a website that you built for the first time.
A website that was previously running becomes inaccessible.
You cannot use a Server Load Balancer (SLB) instance to access the website on the ECS instance.
You cannot access the website after it is accelerated by Alibaba Cloud CDN.
You cannot access a website that is protected by Web Application Firewall (WAF).
Causes
A website that runs on an ECS instance can be inaccessible for many reasons. This section lists common causes. The actual cause depends on the results of your troubleshooting.
TCP port 80 is unavailable.
The web service is unavailable.
The website does not have an ICP filing.
An exception occurs in the website resources or backend services.
The website was not built by following the standard procedure.
An issue occurs on the origin server.
Many factors and symptoms can cause website access exceptions. For more information about the causes of website access failures on ECS instances, see Troubleshooting and guidelines for ECS instance access exceptions.
Troubleshooting
Website access failures on ECS instances have various symptoms and causes. Select one of the following methods to quickly troubleshoot the issue.
Troubleshoot using the flowchart
Follow the steps in the flowchart to troubleshoot the issue.
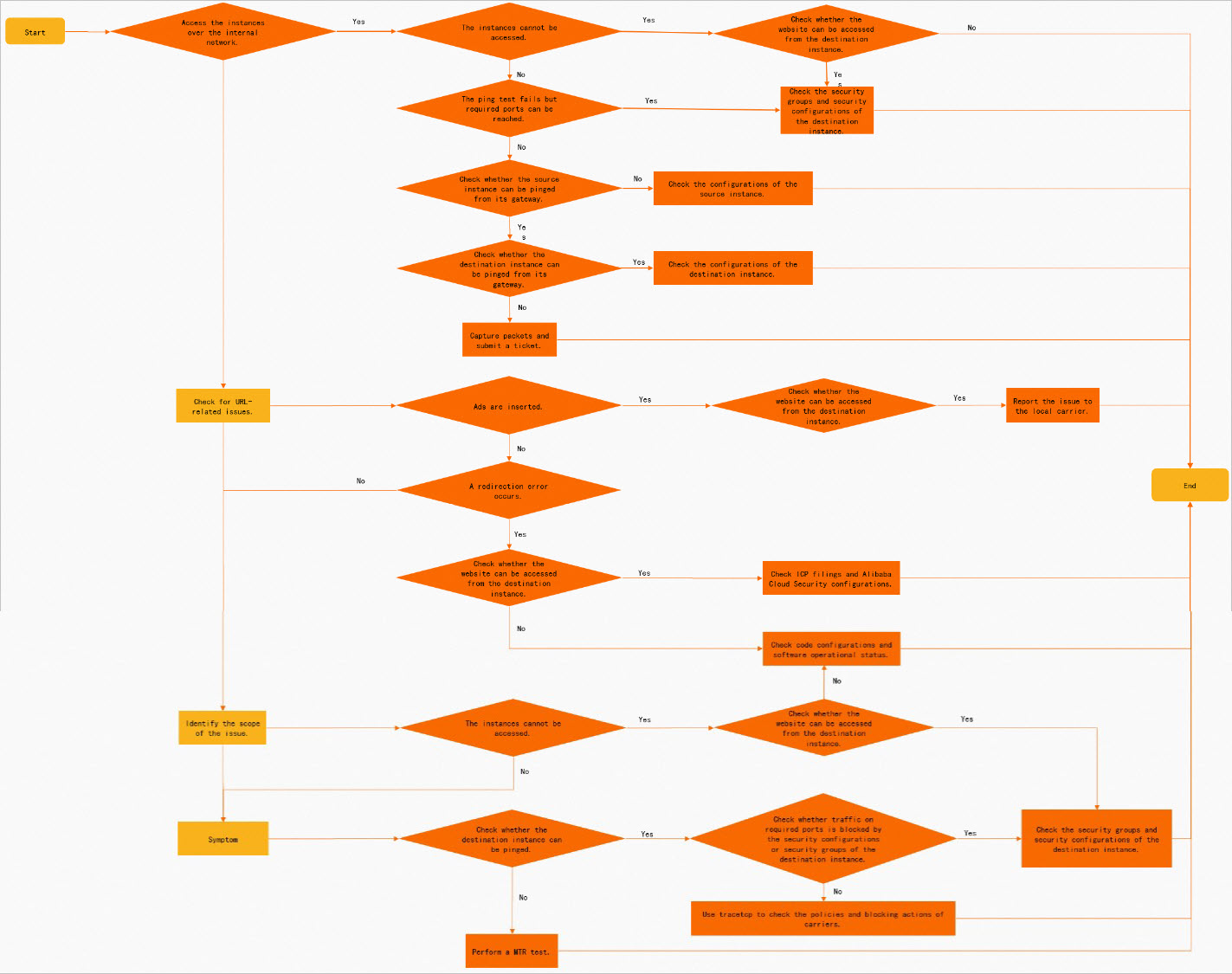
Select a solution based on the symptom
For the common symptoms listed below, you can quickly select the corresponding solution.
You receive a prompt that says "No ICP filing or not connected" or "Website content does not match the ICP filing information".
Before you obtain an ICP filing for your website, you cannot enable website access, regardless of whether the website is accessed using an IP address or a domain name. You must apply for an ICP filing for the IP address or domain name of your website. For more information, see General ICP filing.
The browser returns a numeric error code, such as 403, 404, 502, or 503.
When the browser returns a numeric error, it usually indicates that the network between the client and the server is normal, but an exception exists in the website resources or backend services.
You cannot access a website that you built for the first time.
Make sure that you follow the standard website building procedure. For more information about the procedure, see Quick start.
A website that was previously running becomes inaccessible.
Check to ensure the web service and backend database are running. If a service is not running, check its logs for error messages and use them to fix the issue.
NoteThe web service log file is typically named access.log or error.log. For more information, see the official website for your web service.
Problems with backend services, such as PHP, Java, Tomcat, or the database, can also make the website inaccessible. In this case, you can contact your website administrator for help.
You cannot use an SLB instance to access the website on the ECS instance.
If an SLB instance is used at the frontend of the ECS instance, the issue may be caused by an exception in the listener policy of the SLB instance. For more information, see Cannot access a website on an ECS instance through an SLB instance.
You cannot access the website after it is accelerated by CDN.
You must first determine whether the issue is with the origin server. For more information, see Troubleshooting steps for inaccessible websites after CDN acceleration.
You cannot access a website that is protected by WAF.
You must first determine whether the issue is with the origin server, and then determine whether it is a false positive from WAF. For more information, see Cannot access a website protected by Web Application Firewall (WAF).
Solutions
This section describes solutions for issues caused by an unavailable TCP port 80 or web service. Follow these steps:
A website that runs on a Linux instance is inaccessible because TCP port 80 or the web service is unavailable
The following steps use an instance that runs CentOS 7 as an example. The actual operations may vary based on your operating system.
TCP port 80 is unavailable
Remotely connect to the Linux instance.
For more information, see ECS remote connection methods overview.
Check whether TCP port 80 is being listened on.
netstat -an | grep 80The following sample command output indicates that the web service is started on TCP port 80 and the check is passed. If an exception occurs, see The web service is unavailable to resolve the issue.
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN # Listening on all network interfacestcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN # Listening on the local machineNoteListening on 127.0.0.1 prevents external access to the web service. Only the local machine can access it. You must change the configuration to listen on all network interfaces.
Check whether TCP port 80 is allowed and whether the connection is normal.
Check whether the instance's security group allows traffic on TCP port 80. If not, you must add a security group rule. For more information, see Add a security group rule.
Check whether the firewall of the instance's operating system is enabled. If it is enabled, we recommend that you disable it and use security groups instead. For more information, see Manage the system firewall on a Linux instance.
Use the telnet and traceroute commands to trace the connectivity of TCP port 80. For more information, see How to troubleshoot port connectivity issues when the server can be pinged.
Check whether the ECS instance has sufficient bandwidth.
For more information, see Query and analyze the system load of a Linux instance.
If the bandwidth is insufficient, you can upgrade the instance bandwidth. For more information, see Modify bandwidth configurations.
The web service is unavailable
Remotely connect to the Linux instance.
For more information, see ECS remote connection methods overview.
Check the web service logs.
View the Apache error logs.
You can analyze and troubleshoot the issue based on the error logs.
CentOS or Alinux:
less /var/log/httpd/error_logUbuntu:
less /var/log/apache2/error.log
View the Nginx error logs.
You can analyze and troubleshoot the issue based on the error logs.
less /var/log/nginx/error_log
Run the
topcommand to view the running status of the instance.Check for abnormal processes. The following figure shows a sample command output.
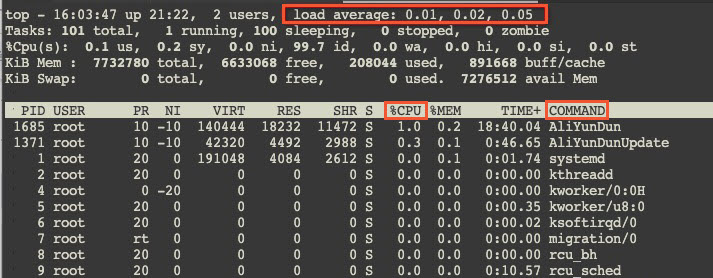
The
load averageparameters0.01,0.02, and0.03represent the average system load over the last 1, 5, and 15 minutes, respectively. Generally, if this value divided by the number of logical CPUs is greater than 5, the system is overloaded. The specific value depends on the server's CPU processing power and system usage. In this case, you can find the process ID (PID) with a high%CPUvalue in the process list, locate the abnormal process (theCOMMANDparameter value), and then handle the exception based on your system's actual situation.View instance monitoring information in the console.
For more information, see View instance monitoring information.
Check whether the instance has sufficient CPU and memory. If not, see Troubleshooting high CPU utilization on Linux ECS instances.
Check whether the instance has sufficient bandwidth. If not, you can upgrade the instance bandwidth. For more information, see Modify bandwidth configurations.
Check whether there are too many TCP connections on port 80 of the instance.
netstat -anp | grep ':80 ' | grep tcpThe following is a sample response.
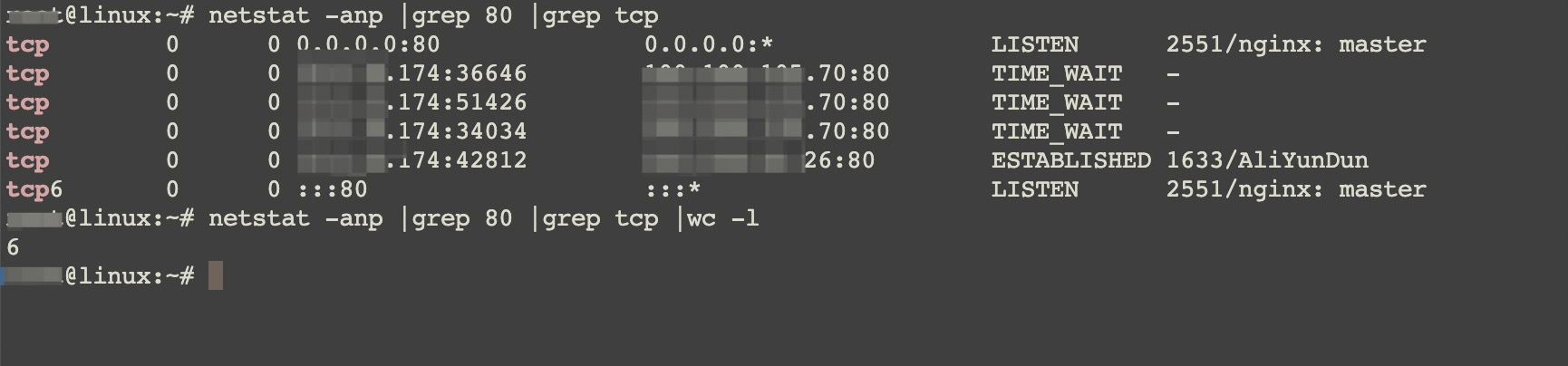
Count all TCP connections.
netstat -anp |grep tcp |wc -lCompare the total number of TCP connections with the maximum value of the
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_bucketsparameter in the/etc/sysctl.confconfiguration file. If the total number of TCP connections exceeds this maximum value, perform the following operations:Run the
vi /etc/sysctl.confcommand to edit the/etc/sysctl.confconfiguration file and query thenet.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_bucketsparameter.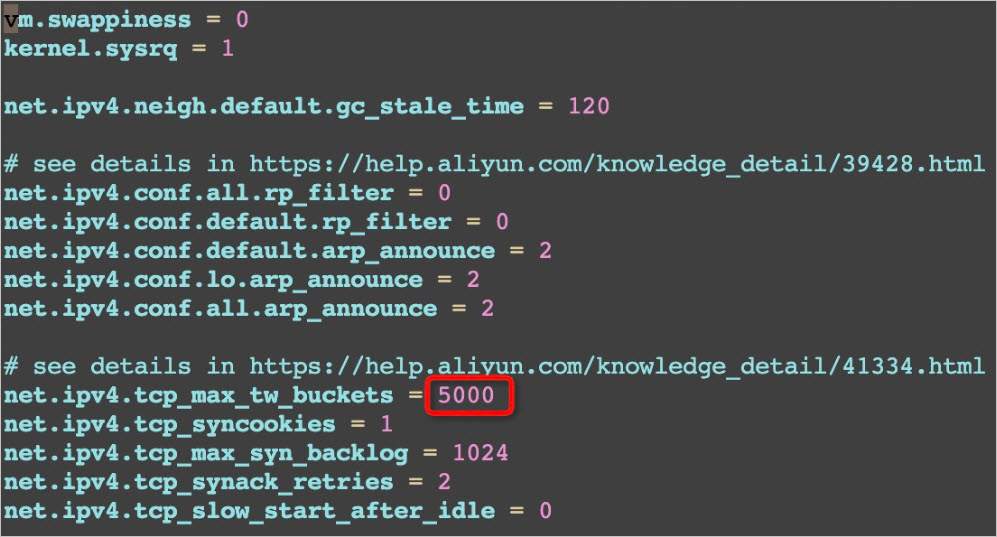
If you confirm that the number of TCP connections is high and likely to exceed the limit, you can increase the value of the
net.ipv4.tcp_max_tw_bucketsparameter as needed.Run the
sysctl -pcommand to apply the configuration.
A website that runs on a Windows instance is inaccessible because TCP port 80 or the web service is unavailable
The following steps use an instance that runs Windows Server 2012 R2 as an example. The actual operations may vary based on your operating system.
TCP port 80 is unavailable
Remotely connect to the Windows instance.
For more information, see ECS remote connection methods overview.
Open the command prompt.
Click the
 icon in the lower-left corner of the desktop, and then click the
icon in the lower-left corner of the desktop, and then click the  icon.
icon.In the search box, enter
cmd.
Click Command Prompt.
The command prompt opens.
Check whether TCP port 80 is being listened on.
netstat -ano | findstr :80The following sample command output indicates that the web service is started on TCP port 80 and the check is passed. If an exception occurs, see The web service is unavailable to resolve the issue.
TCP 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 1172 # Indicates listening on all network interfaces TCP 127.0.0.1:80 0.0.0.0:0 LISTENING 1172 # Indicates local listeningNoteListening on 127.0.0.1 prevents external access to the web service. Only the local machine can access it. You can run the
netsh http delete iplisten ipaddress= 127.0.0.1:80command to change the configuration to listen on all network interfaces.Check whether TCP port 80 is allowed and whether the connection is normal.
Check whether the instance's security group allows traffic on port 80. If not, you must add a security group rule. For more information, see Add a security group rule.
Check whether the firewall of the instance's operating system is enabled. If it is enabled, we recommend that you disable it and use security groups instead. For more information, see Configuration guide for Windows system firewall policies.
Use the telnet and tracert commands to trace the connectivity of port 80. For more information, see How to troubleshoot port connectivity issues when the server can be pinged.
Check whether the ECS instance has sufficient bandwidth.
For more information, see Troubleshoot high or full bandwidth and CPU usage on Windows instances.
If the bandwidth is insufficient, you can upgrade the instance bandwidth. For more information, see Modify bandwidth configurations.
The web service is unavailable
Remotely connect to the Windows instance.
For more information, see ECS remote connection methods overview.
Check the web service logs.
Method 1: Browse the log folder.
The log path for Windows Server 2008 R2 and later is:
C:\inetpub\logs\LogFiles.Method 2: Check the IIS Manager.
Select
 > Windows Administrative Tools > Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.
> Windows Administrative Tools > Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager.In the IIS section of the web service's homepage, click Logging, and then click Browse in the Actions column.
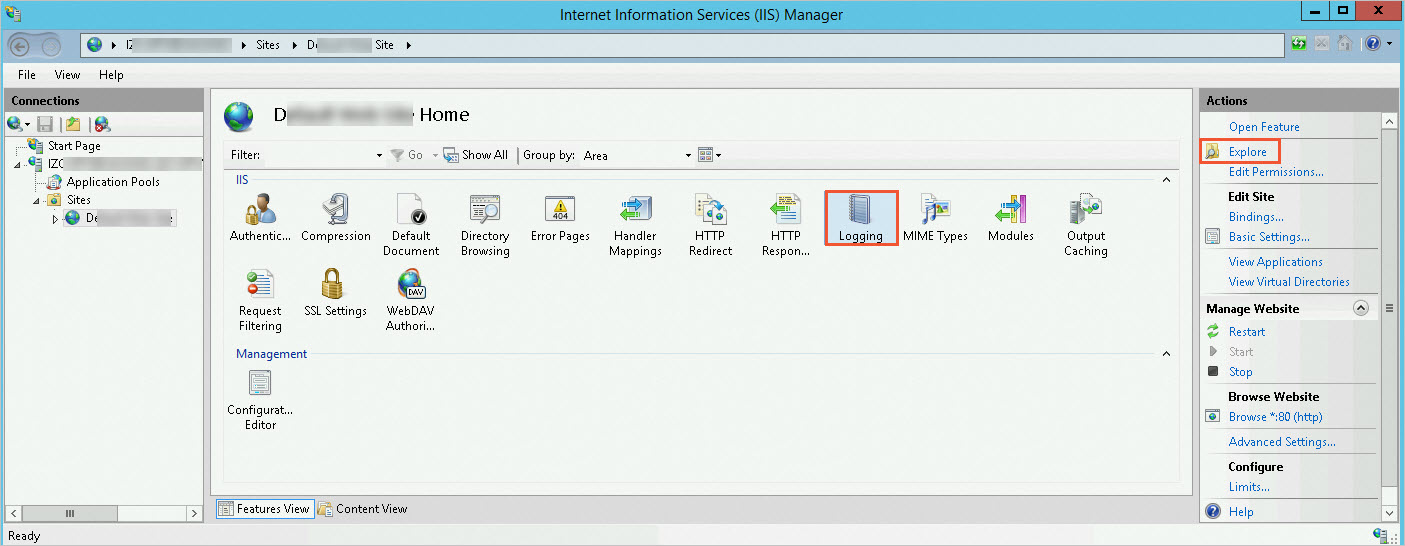
On the Logging page, you can modify the log storage path as needed, copy the corresponding address, paste it into File Explorer, and then press
Enter.You can view the corresponding log folder in File Explorer.
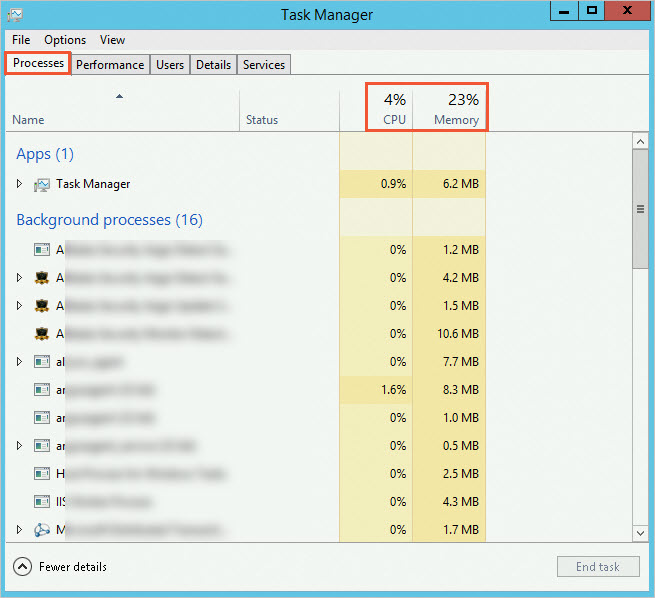
Use Task Manager to view the running status of the instance and check for abnormal processes.
Right-click the desktop and select Task Manager.
Click the Processes tab.
You can view the CPU and memory information of processes in Task Manager to locate abnormal processes.
View instance monitoring information in the console.
For more information, see View instance monitoring information.
Check whether the instance has sufficient CPU and memory. If not, see Troubleshoot high or full bandwidth and CPU usage on Windows instances.
Check whether the instance has sufficient bandwidth. If not, you can upgrade the instance bandwidth. For more information, see Modify bandwidth configurations.
Check whether there are too many TCP connections on port 80 of the instance.
Open the command prompt.
Click the
 icon in the lower-left corner of the desktop, and then click the
icon in the lower-left corner of the desktop, and then click the  icon.
icon.In the search box, enter
cmd.
Click Command Prompt.
The command prompt opens.

Run the following commands in sequence to count the TCP connections.
netstat -n |find /i "time_wait" /c netstat -n |find /i "close_wait" /c netstat -n |find /i "established" /cBy default, the number of dynamic ports is 16,384 (from 49152 to 65535). If the number of connections in the
CLOSE_WAITstate is close to the number of dynamic ports, it indicates that manyCLOSE_WAITconnections have not been released. You must proceed to the next step to modify the registry to reduce the Time Wait duration.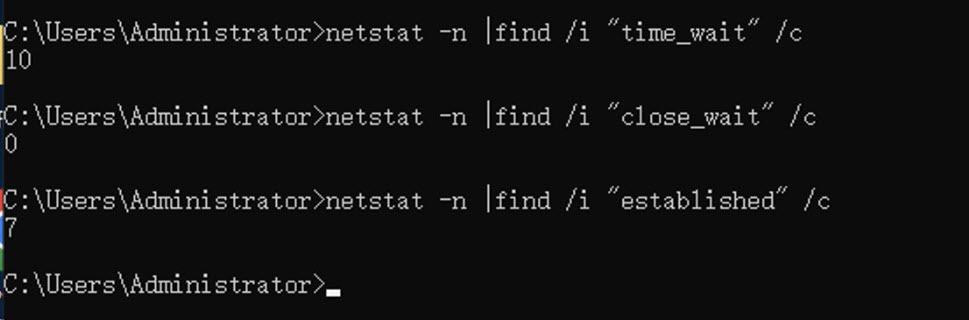
Open the Registry Editor.
Click the
 icon in the lower-left corner of the desktop, and then click the
icon in the lower-left corner of the desktop, and then click the  icon.
icon.In the search box, enter
regedit.
Click regedit.
The Registry Editor opens.
In the Registry Editor, navigate to the
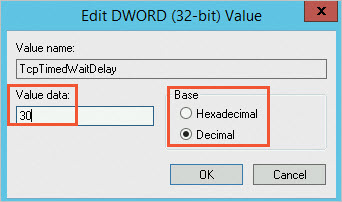
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services>Tcpip>Parameterspath, and set the value data of theTcpTimedWaitDelayregistry key to the decimal value30.If the
TcpTimedWaitDelaykey does not exist, you must create the registry key and then modify its value data. The following steps show how to do this:In the
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services>Tcpip>Parameterspath in the Registry Editor, right-click a blank area and select New > DWORD (32-bit) Value.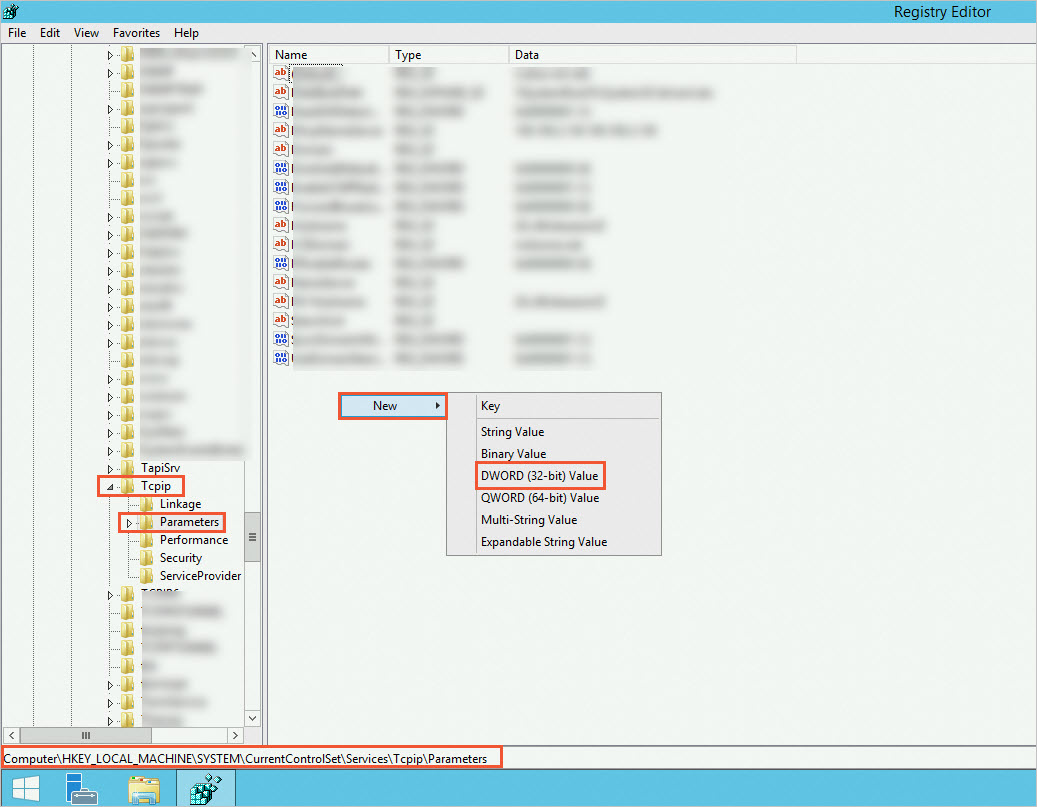
Enter
TcpTimedWaitDelayand pressEnter.Right-click the
TcpTimedWaitDelayregistry key and click Modify.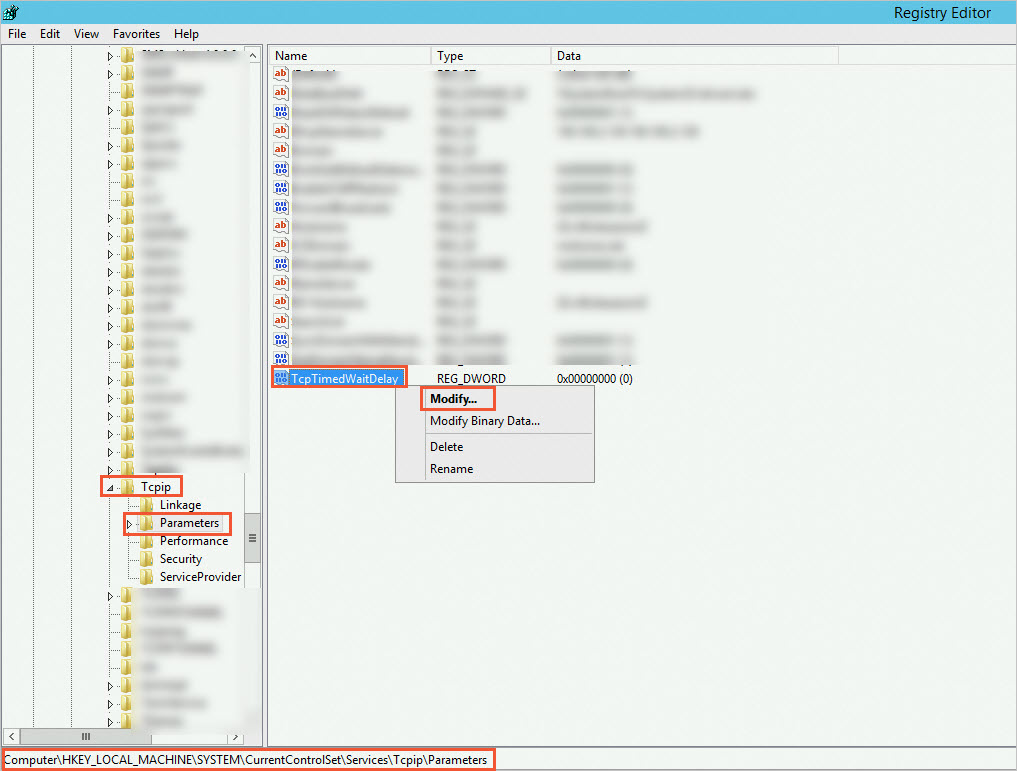
In the dialog box, select Decimal and set Value Data to
30.
Click OK.