Background
Acceleration mechanism
After you add a domain name, the system assigns you a CNAME. This record points to globally distributed DCDN nodes. User requests are routed to these nodes. If a node has the requested content in its cache, the content is returned directly. If the content is not cached, the node requests the content from the origin server and caches it for future access. In this way, DCDN improves content delivery speed and user experience. Make sure that your DNS record points to the CNAME record value provided by DCDN to ensure that traffic is routed through the acceleration service.
Domain name resolution
Domain name resolution is a service that resolves a domain name, such as example.aliyundoc.com, to the IP address that a client connects to. For more information, see What is domain name resolution?
Step 1: Obtain the CNAME for the domain name
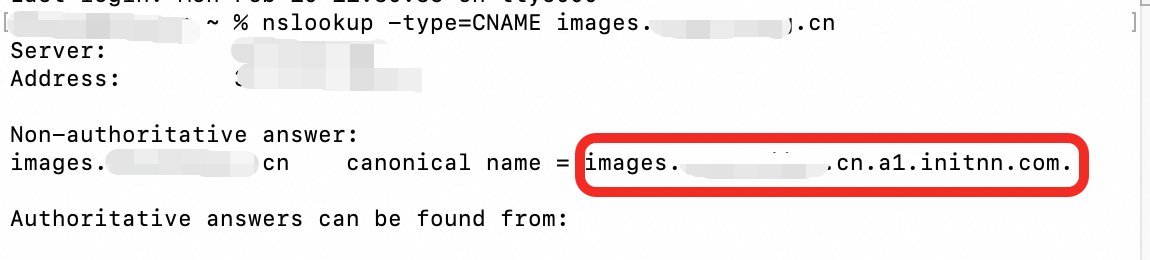
Go to the Domain Names page in the DCDN console. Copy the CNAME record value for the domain name.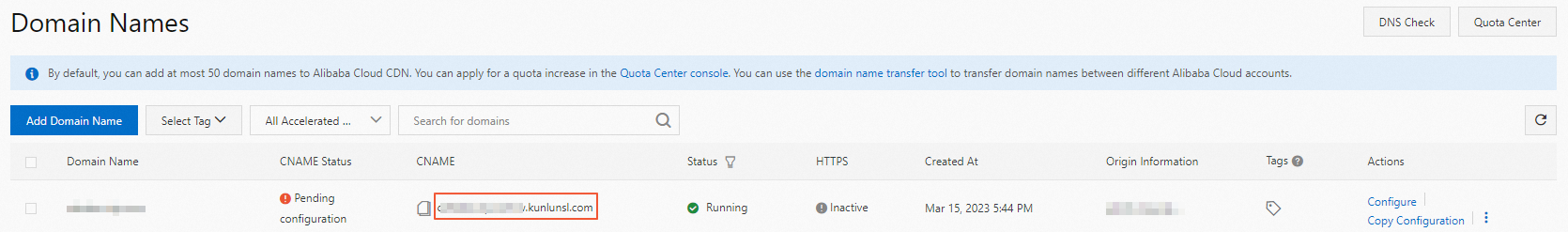
Step 2: Configure CNAME resolution
The method for configuring CNAME resolution varies based on your DNS provider. Follow the procedure that applies to your provider.
Important Domain name resolution rules from the same DNS provider may conflict with each other.
Alibaba Cloud DCDN uses servers in the Chinese mainland to verify DNS records. If you configure different DNS records for different regions, a conflict may occur. For example, you might configure the Alibaba Cloud DCDN CNAME only for regions outside the Chinese mainland, such as Hong Kong (China), Macao (China), and Taiwan (China). In this case, the verification servers cannot resolve the CNAME. The CNAME status of the domain name is then displayed as Pending Configuration in the DCDN console. However, this does not affect the DCDN acceleration service.
The CNAMEs for Alibaba Cloud CDN, DCDN, ApsaraVideo Live, and ApsaraVideo VOD can be used only for scheduling and resolution by Alibaba Cloud CDN. Alibaba Cloud reserves the right to disable the domain names and accounts that maliciously use CNAMEs.
Alibaba Cloud CNAME configuration
If your DNS provider is Alibaba Cloud, you can follow these steps to configure the CNAME.
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console using The Alibaba Cloud Account For The domain name.
Optional: Add the domain name in the Alibaba Cloud DNS console if the domain name is not registered with Alibaba Cloud.
Note If your domain name is not registered with Alibaba Cloud, you must first add the domain name in the Alibaba Cloud DNS console before you can configure domain name resolution. For more information, see Domain Management. If your domain name is registered with Alibaba Cloud, skip this step.
On the Public Zone page, find the root domain of your domain name and click Settings in the Actions column.
Click Add Record to add a CNAME record.
Note The CNAME resolution for an exact domain name has a higher priority than that for a wildcard domain name. If your domain name is a wildcard domain name and the host record is set to an asterisk (*), you must delete the DNS records for any second-level domains that have already taken effect under the wildcard domain name.
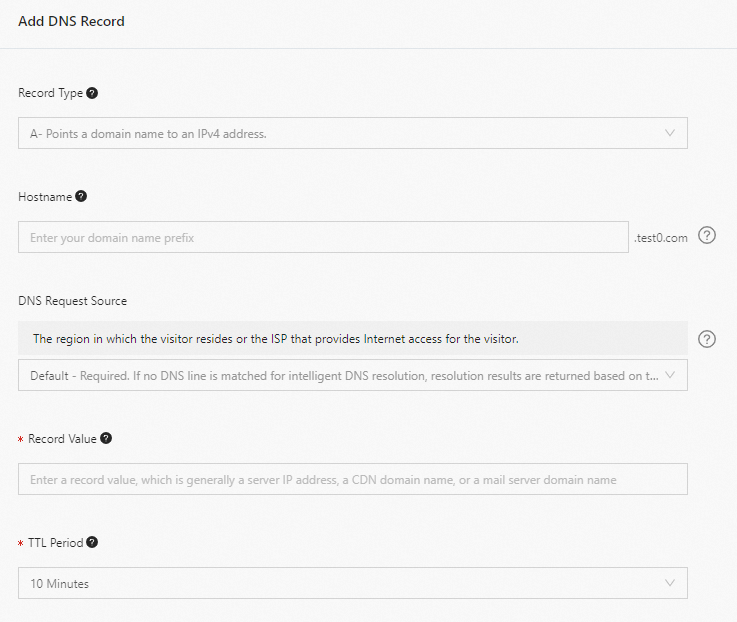
Parameter | Description | Example |
Record Type | Select CNAME. | CNAME |
Hostname | If the domain name is a root domain, set the host record to @. If the domain name is a wildcard domain, set the host record to *. If the domain name is a subdomain, set the host record to the subdomain prefix.
| Root domain example Wildcard domain example domain name: .aliyundoc.com. Host record: *. domain name: .aliyundoc.com.cn. Host record: *. domain name: *.example.aliyundoc.com. Host record: *.example. domain name: *.example.aliyundoc.com.cn. Host record: *.example.
Subdomain example domain name: example.aliyundoc.com. Host record: example. domain name: example.aliyundoc.com.cn. Host record: example. domain name: www.example.aliyundoc.com. Host record: www.example. domain name: www.example.aliyundoc.com.cn. Host record: www.example.
Note The ".com.cn" suffix is an example of a top-level domain that has two parts. |
Query Source | Default. | We recommend that you use the default value. |
Record Value | Enter the CNAME record value of the domain name.
Note Each domain name has a unique CNAME value. A second-level domain cannot use the CNAME of its primary domain name. To accelerate a second-level domain, add it to DCDN and map it to its own CNAME. Alternatively, add a wildcard domain to DCDN. The CNAME of the wildcard domain can be used by its second-level domains. For more information about how to add a wildcard or second-level domain name, see Add a domain name. | www.example.com.w.kunlunsl.com |
TTL | TTL is the cache time. The smaller the value, the faster the modified record takes effect worldwide. The default value is 10 minutes. | We recommend that you use the default value. |
Click Confirm to add the record.
Tencent Cloud CNAME configuration procedure
If your DNS provider is Tencent Cloud, you can follow these steps to configure the CNAME.
Log on to the DNSPod console.
On the domain name's resolution page, click Add Record to add a CNAME record.
Parameter | Description | Example |
Host Record | If the domain name is a root domain, set the host record to @. If the domain name is a wildcard domain, set the host record to *. If the domain name is a subdomain, set the host record to the subdomain prefix.
| Root domain example Wildcard domain example domain name: .aliyundoc.com. Host record: *. domain name: .aliyundoc.com.cn. Host record: *. domain name: *.example.aliyundoc.com. Host record: *.example. domain name: *.example.aliyundoc.com.cn. Host record: *.example.
Subdomain example domain name: example.aliyundoc.com. Host record: example. domain name: example.aliyundoc.com.cn. Host record: example. domain name: www.example.aliyundoc.com. Host record: www.example. domain name: www.example.aliyundoc.com.cn. Host record: www.example.
Note The ".com.cn" suffix is an example of a top-level domain that has two parts. |
Record Type | Select CNAME. | CNAME |
Line Type | Select the Default type. | We recommend that you use the default value. |
Record Value | Enter the CNAME record value of the domain name.
Note Each domain name has a unique CNAME value. A second-level domain cannot use the CNAME of its primary domain name. To accelerate a second-level domain, add it to DCDN and map it to its own CNAME. Alternatively, add a wildcard domain to DCDN. The CNAME of the wildcard domain can be used by its second-level domains. For more information about how to add a wildcard or second-level domain name, see Add a domain name. | www.example.com.w.kunlunsl.com |
Weight | Leave this parameter empty. | Not applicable |
MX | Leave this parameter empty. | Not applicable |
TTL | TTL is the cache time. The smaller the value, the faster the modified record takes effect worldwide. | We recommend that you use the default value. |
Click Save to add the record.
Step 3: Verify the CNAME configuration
References
If the cache hit ratio is low after you enable DCDN, you can use the prefetch feature to prefetch popular resources before peak hours. This can improve the cache hit ratio. For more information, see Purge and prefetch resources.