Before you synchronize data from MySQL to DataHub in real time, you can refer to the operations described in this topic to configure data sources. The configurations of data sources include network environments, whitelists, and permissions. You must configure a source MySQL data source and a destination DataHub data source.
Prerequisites
- Prepare data sources: A MySQL database and a DataHub project are prepared.
- Plan and prepare resources: An exclusive resource group for data integration is purchased and configured. For more information, see Plan and configure resources.
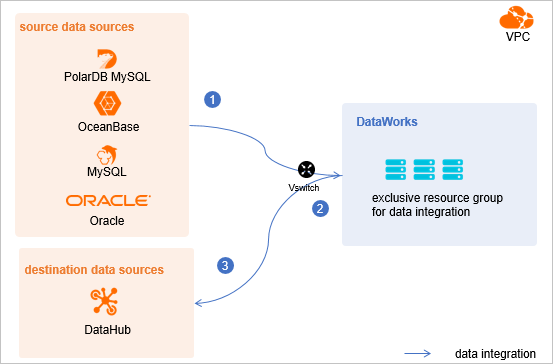
- Evaluate and plan the network environment: Before you perform data integration, connect
data sources to exclusive resource groups for Data Integration based on your business
requirements. After data sources and exclusive resource groups for Data Integration
are connected, you can refer to the operations in this topic to configure access settings
such as vSwitches and whitelists.
- If data sources and exclusive resource groups for Data Integration reside in the same region and virtual private cloud (VPC), they are automatically connected.
- If data sources and exclusive resource groups for Data Integration reside in different network environments, you must connect data sources and resource groups by using methods such as a VPN gateway.
Background information
- Configure whitelists for data sources
If the data sources and exclusive resource group for data integration reside in the same VPC, you must add the CIDR block of the exclusive resource group for data integration to the whitelists of the data sources. This ensures that the exclusive resource group for data integration can be used to access the data sources.
- Create an account and grant permissions the account
You must create an account that can be used to access the data sources, read data from the source, and write data to the destination during the data synchronization process.
- Enable the binary logging feature
If the source data source is a MySQL database, you must enable the binary logging feature. Binary logs record changes to all table schemas and modifications on table data. You can execute statements such as CREATE and ALTER to perform operations on table schemas. You can execute statements such as INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE to perform operations on table data. You can use binary logs to view the change history of the database, back up incremental data and restore data in the database, and replicate data from the primary database to secondary databases.
Formats of binary logs:- Statement: SQL statement-based replication. Binary logs in this format record the SQL statements that are executed to modify data entries.
- Row: row-based replication. Binary logs in this format record only modification details about data entries in rows.
- Mixed: replication in mixed mode. This mode combines the statement and row formats. In most cases, binary logs in the statement format are used to record the SQL statements that are executed to modify data entries, such as functions. If data replication from the primary database to secondary databases cannot be implemented by using binary logs in this format, switch to the row format. MySQL determines which format to use based on each SQL statement that is executed.
Procedure
What to do next
After data sources are configured, the source data source, destination data source, and exclusive resource group for Data Integration are connected. Then, the exclusive resource group for Data Integration can be used to access the data sources. You can add the source data source and destination data source to DataWorks, and associate them with a data synchronization solution when you create the solution.
For more information about how to add a data source, see Add a data source.