This document shows you how to use the DataWorks Open API (2024-05-18) to programmatically query the lineage of data tables and fields. It provides specific API call examples and SDK code to help you get started quickly and perform automated and batch lineage analysis.
What is data lineage?
Imagine that you are looking at an important business report that shows a large increase in sales for this quarter. As a careful data analyst or manager, several questions will come to your mind:
How is this "sales" metric calculated?
What is the source business data? Is it from an order table or a payment transaction table?
What processing steps did the data go through from the source to the final report, such as cleaning, transformation, and aggregation?
If there is an error in this metric's data, what downstream reports or applications will it affect?
Clear data lineage is essential. It provides the following core benefits:
Data traceability and troubleshooting
When you find data anomalies or errors, you can trace the lineage upstream to quickly locate the processing step or source data that caused the problem. This greatly reduces troubleshooting time.Impact analysis
When you need to change a table schema, field, or calculation logic, you can analyze the lineage downstream. This lets you accurately assess which downstream data and business reports will be affected. This helps you avoid the unknown risks of a single change causing widespread issues.Data governance and credibility
Clear lineage is the foundation for data asset management, data standard implementation, and Data Quality monitoring. It makes the entire data lifecycle transparent and increases business users' trust in the data.Cost optimization and asset inventory
By analyzing lineage, you can identify data tables or computing tasks that have no downstream consumers. This provides a basis for data warehouse cost optimization and for unpublishing old assets.
DataWorks automatically parses and records the data lineage generated by various computing tasks, such as MaxCompute SQL and EMR Spark. The DataWorks Open API lets you programmatically access this lineage information. You can then integrate lineage analysis into your own data management platform or automated O&M processes.
Preparations: Get the entity ID
Before you can query any lineage, you must first obtain the unique identifier for the target data (table or field). This identifier is the entity ID. The entity ID is the core credential for calling metadata and lineage-related APIs.
You can obtain an entity ID in one of two ways:
1. Get the ID from the DataWorks interface
For a small number of known tables or fields, copying the ID from the interface is the fastest method.
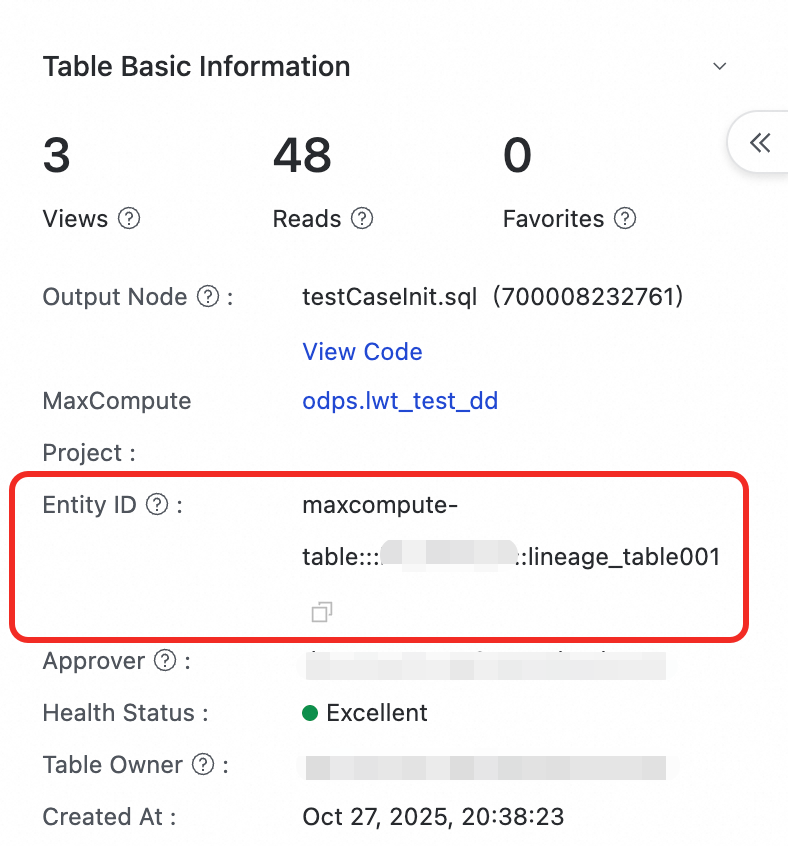
Get a table's entity ID
Go to the Data Map module in DataWorks.
Search for and open the details page of the table you want to query.
In the Table Basic Information panel on the left, find the Entity ID and copy it.
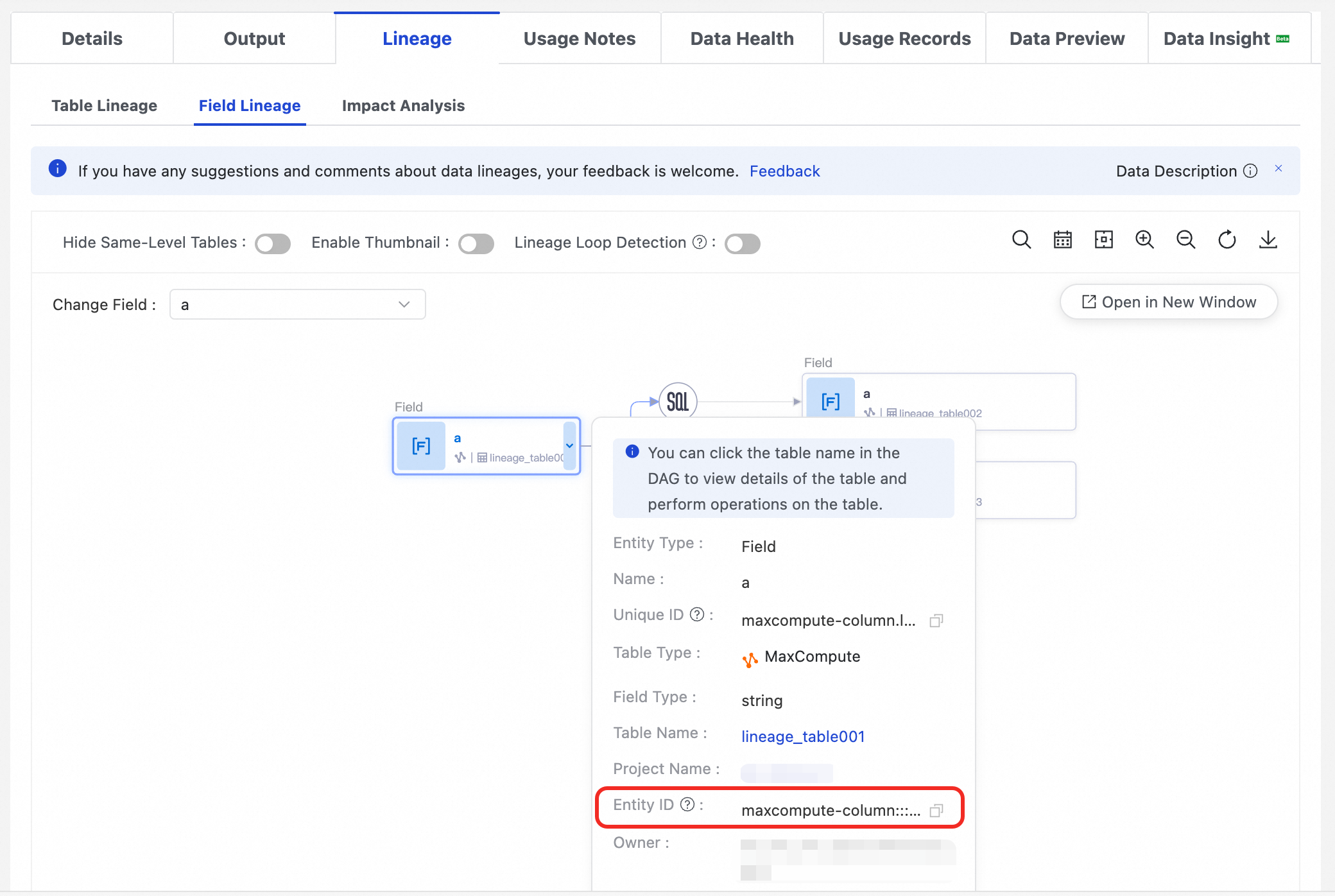
Get a field's entity ID
On the table's details page, switch to the Lineage tab and select Field Lineage.
In the field lineage graph, click the field node you are interested in.
The field's details panel appears on the right. In the panel, find the Entity ID and copy it.
2. Get IDs in batches using the API
When you need to obtain many entity IDs, manual operations are inefficient. In this case, you can use the Open API to perform a batch query:
Obtain table IDs in batches: Call the
ListTablesAPI. For more information, see ListTables - Query a list of tables in Data Map.Obtain field IDs in batches: Call the
ListColumnsAPI. For more information, see ListColumns - Query a list of fields in a Data Map table.
Use the ListLineages API to query lineage
After you obtain the entity ID, you can use the core ListLineages API to query its upstream and downstream lineage.
1. Core API parameters
The following table describes the key request parameters for the ListLineages API. You can test the API online in the Open API Portal.
Parameter | Type | Description |
| String | Used to query downstream lineage. Pass the source (upstream) entity ID. The API returns all downstream lineage for that entity. |
| String | Used to query upstream lineage. Pass the destination (downstream) entity ID. The API returns all upstream lineage for that entity. |
| String | Used with |
| String | Used with |
| Boolean | Specifies whether to include detailed lineage relationship information in the response. Set this to |
If you provide both
SrcEntityIdandDstEntityId, the API returns the lineage relationship between the specified upstream and downstream entities.If
SrcEntityIdandDstEntityIdare the same, the API returns a self-referencing lineage relationship for that entity.
2. Call examples
Assume that you have a MaxCompute table with the entity ID maxcompute-table:::test_project::test_table.
Example 1: Query the table's downstream lineage
To query all downstream tables of this table, you need to set it as the source:
SrcEntityId:maxcompute-table:::test_project::test_tableNeedAttachRelationship:true
To find only downstream tables with names that contain "report", you can add the DstEntityName parameter:
DstEntityName:report
Example 2: Query the table's upstream lineage
To find out which tables or tasks generated this table, you need to set it as the destination:
DstEntityId:maxcompute-table:::test_project::test_tableNeedAttachRelationship:true
You can also use the SrcEntityName parameter to filter upstream sources.
3. Understand the API response
After a successful call to ListLineages, you will receive a list of lineage relationships. Each relationship includes the source entity, the destination entity, and their association information.
Example of a single lineage relationship response (JSON):
{
"SrcEntity": {
"Id": "maxcompute-table:::test_project::table_from",
"Name": "table_from",
"Attributes": {
"rawEntityId": "maxcompute-table:::test_project::table_from"
}
},
"DstEntity": {
"Id": "maxcompute-table:::test_project::table_to",
"Name": "table_to",
"Attributes": {
"project": "test_project",
"region": "cn-shanghai",
"table": "table_to"
}
},
"Relationships": [
{
"Id": "123456789:maxcompute-table.test_project.table_from:maxcompute-table.test_project.table_to:maxcompute.SQL.76543xxx",
"CreateTime": 1761089163548,
"Task": {
"Id": "76543xxx",
"Type": "dataworks-sql",
"Attributes": {
"engine": "maxcompute",
"channel": "1st",
"taskInstanceId": "12345xxx",
"projectId": "123456",
"taskId": "76543xxx"
}
}
}
]
}How to read the response:
SrcEntityandDstEntity: These represent the upstream and downstream entities of the lineage. You can obtain theirIdand then call the GetTable or GetColumn API to retrieve more detailed metadata.Relationships: This describes howSrcEntityandDstEntityare related.Task: This describes the task that generated this lineage relationship. If the task is a DataWorks scheduling task,Task.Attributeswill contain thetaskIdandtaskInstanceId. You can use these IDs to call the GetTask API to obtain the task's detailed definition and running status.
Java SDK hands-on tutorial
The following example uses the Java SDK to show the complete process of a lineage query.
1. Prepare the environment
JDK version: Make sure you have JDK 8 or a later version installed.
Maven dependency: Add the following dependency to your project's
pom.xmlfile. Replace${latest.version}with the latest SDK version number.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun</groupId>
<artifactId>dataworks_public20240518</artifactId>
<version>${latest.version}</version>
</dependency>2. Complete code example
The following code shows how to initialize the client, query the upstream and downstream lineage of a specified table, and print key information.
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import com.aliyun.dataworks_public20240518.Client;
import com.aliyun.dataworks_public20240518.models.GetTableRequest;
import com.aliyun.dataworks_public20240518.models.GetTableResponse;
import com.aliyun.dataworks_public20240518.models.LineageEntity;
import com.aliyun.dataworks_public20240518.models.LineageRelationship;
import com.aliyun.dataworks_public20240518.models.LineageTask;
import com.aliyun.dataworks_public20240518.models.ListLineagesRequest;
import com.aliyun.dataworks_public20240518.models.ListLineagesResponse;
import com.aliyun.dataworks_public20240518.models.ListLineagesResponseBody.ListLineagesResponseBodyPagingInfo;
import com.aliyun.dataworks_public20240518.models.ListLineagesResponseBody.ListLineagesResponseBodyPagingInfoLineages;
import com.aliyun.dataworks_public20240518.models.Table;
import com.aliyun.tea.TeaException;
public class LineageQuerySample {
/**
* description