Data Security Center (DSC) supports the static data masking and dynamic data masking methods. If you use the static data masking method, you must create a data masking task that specifies the data assets to be masked, masking rules for matching sensitive fields, and masking algorithms, such as redaction, encryption, or substitution, to process the specific fields. You must also specify a storage destination for the masked data. If you use the dynamic data masking method, you can call the ExecDatamask operation to mask specific fields in the JSON format based on specific masking rules.
Data masking methods
Data masking method | Data source | Scenario | Operation |
Static data masking |
| You want to share specific data sources with other users but you do not want to disclose sensitive fields. If you use the static data masking method to mask a specific data table or file, you can store the masked data in another data table or file for data sharing. This way, the raw data is not affected. | In the DSC console, create a masking task and configure the data to be masked, masking rules, destination in which the masked data is stored, and task execution cycle. |
Dynamic data masking | You can construct data sources in the following JSON format. dataHeaderList specifies the column names of the data to be masked. dataList specifies the data to be masked. The values specified in dataList must correspond to the column names specified in dataHeaderList. ruleList specifies the data masking rules. For more information, see ExecDatamask. | The dynamic data masking method is more flexible and allows you to construct the data sources to be masked. | You can use API online debugging, Alibaba Cloud SDKs, or custom encapsulated APIs to call the ExecDatamask operation to dynamically mask data. For more information, see ExecDatamask |
Examples of data masking results
DSC supports the following masking algorithms: hashing, redaction, substitution, rounding, encryption, and shuffling. The following tables provide examples of data masking results based on different masking algorithms.
Hashing
Applicable sensitive data and scenario | Algorithm description | Algorithm configuration | Raw data | Masked data |
The data masking process is irreversible. You can use common hash algorithms and specify a salt value. This type of algorithm is applicable to password protection or scenarios in which you must check whether data is sensitive by comparison.
| MD5 | Set the salt value to | 123456 | d6f82c64df3dc34921d79e5f22e5d43a |
SHA-1 | 59056c7c6faa5eeb7151d30a01c17b25f35b021c | |||
SHA-256 | 84ca63076a5966e9b726490c8b6a5c9c6d6bdc018bb0a05df754c0c2770aca72 | |||
HMAC | ed029027322fedb0ac40b7759ac1521f0121cb018cf0f6f078e61764d810e00f |
Redaction
Applicable sensitive data and scenario | Algorithm description | Algorithm configuration | Raw data | Masked data |
The data masking process is irreversible. This type of algorithm redacts specified text in sensitive data with asterisks (*) or number signs (#). This type of algorithm is applicable to scenarios in which sensitive data is to be shown on a user interface or shared with others.
| Keeps the first n characters and the last m characters. | Use asterisks ( | 123456 | 1****6 |
Keeps characters from the Xth position to the Yth position. | Use asterisks ( | **34** | ||
Redacts the first n characters and the last m characters. | Use asterisks ( | **34** | ||
Redacts characters from the Xth position to the Yth position. | Use asterisks ( | 1****6 | ||
Redacts characters that precede a special character, such as an at ( | & | 1@34&6 | ****&6 | |
Redacts characters that follow a special character such as an at ( | @ | 1@**** |
Substitution
Data is masked based on an algorithm that depends on the configuration of a mapping table. Each masking result is different. For example, if the mobile phone number "13900001234" is replaced with a random value, the masked result may be "13271561461", "18355370496", or "18856540773".
Applicable sensitive data and scenario | Algorithm description | Algorithm configuration |
The data masking process is reversible when a specific algorithm is used. This type of algorithm substitutes the entire value or part of the value of a field with a mapped value by using a mapping table. In this case, raw data can be retrieved after it is masked. This type of algorithm also substitutes the entire value or part of the value of a field randomly based on a random interval. In this case, raw data cannot be retrieved after it is masked. DSC provides multiple built-in mapping tables and allows you to create custom substitution algorithms. This type of algorithm can be used to mask fields in fixed formats, such as ID card numbers.
| Substitutes specific content in ID card numbers with mapped values. | Mapping table for substituting the IDs of administrative regions |
Randomly substitutes specific content in ID card numbers. | Mapping table for substituting the IDs of administrative regions | |
Randomly substitutes specific content in the IDs of military officer cards. | Mapping table for substituting the IDs of administrative regions | |
Randomly substitutes specific content in passport numbers. | Code table for randomly substituting purpose fields | |
Randomly substitutes specific content in permit numbers of Exit-Entry Permits for Travelling to and from Hong Kong and Macao. | Code table for randomly substituting purpose fields | |
Randomly substitutes specific content in bank card numbers. | Code table for randomly substituting Bank Identification Numbers (BINs) | |
Randomly substitutes specific content in landline telephone numbers. | Mapping table for substituting the IDs of administrative regions | |
Randomly substitutes specific content in mobile numbers. | Code table for randomly substituting mobile network codes | |
Randomly substitutes specific content in unified social credit codes. | Code table for randomly substituting the IDs of registration authorities, code table for randomly substituting type codes, and code table for randomly substituting the IDs of administrative regions | |
Substitutes specific content in the universal reserved format based on a mapping table. | Mapping table for substituting uppercase letters, mapping table for substituting lowercase letters, mapping table for substituting digits, and mapping table for substituting special characters | |
Randomly substitutes specific content in the universal reserved format. | Code table for randomly substituting uppercase letters, code table for randomly substituting lowercase letters, code table for randomly substituting digits, and code table for randomly substituting special characters |
Rounding
Applicable sensitive data and scenario | Algorithm description | Algorithm configuration | Raw data | Masked data |
The data masking process is reversible when a specific algorithm is used. DSC provides two types of rounding algorithms. One algorithm rounds numbers and dates, and raw data cannot be retrieved after it is masked. The other algorithm bit-shifts text, and raw data can be retrieved after it is masked. This type of algorithm can be used to analyze and collect statistics on sensitive datasets.
| Number rounding: Numbers are rounded to the Nth digit before the decimal point. Valid values of N: 1 to 19. | N=4 | 12345.6789 | 12000 |
Date rounding: Dates are rounded to the year, month, day, hour, or minute. | Hours | 2023-04-15 14:30:45 | 2023-04-15 14:00:00 | |
Character offset: number of places by which specific bits are moved to the left or right. | Three bits to the left | test | ttes |
Encryption
Applicable sensitive data and scenario | Algorithm description | Algorithm configuration | Raw data | Masked data |
The data masking process is reversible. Common symmetrical encryption algorithms are supported. This type of algorithm can be used to encrypt sensitive fields that need to be retrieved after encryption.
| Data Encryption Standard (DES) algorithm | Encryption key: | 123456 | c2TwheTI+rw= |
Triple Data Encryption Standard (3DES) algorithm | Encryption keys: | XUwzslGadsk= | ||
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm | Encryption key: | YueDcm92UuqvKpVbeS+0Ng== |
Shuffling
Applicable sensitive data and scenario | Algorithm description | Algorithm configuration |
The data masking process is irreversible. This type of algorithm extracts values of a field in a specified range from the source table and rearranges the values in a specific column. Alternatively, this type of algorithm randomly selects values from a specific column within the value range and rearranges the selected values. This way, the values are mixed up and masked. This type of algorithm can be used to mask structured data columns.
| Randomly shuffles data. |
|
For example, the city information about a group of devices is randomly rearranged.
Raw data | Masked data | ||
Device ID | City | Device ID | City |
D001 | China (Shanghai) | D001 | China (Xi'an) |
D002 | China (Hangzhou) | D002 | China (Shanghai) |
D003 | China (Xi'an) | D003 | China (Chengdu) |
D004 | China (Chengdu) | D004 | China (Hangzhou) |
Billing overview
Only DSC Enterprise Edition supports the data masking feature. After you purchase DSC Enterprise Edition, you can use the data masking feature. DSC uses the subscription billing method. For more information, see Billing overview. If you use the static data masking method, you may be charged additional fees.
Data masking method | Data source | DSC-side billing | Additional fee |
Static data masking |
| The data assets to be masked must grant access permissions to DSC. The number of purchased database protection instances and the storage protection capacity are deducted based on the authorized data assets. | If the cloud service whose data to be masked uses the pay-as-you-go billing method, you are charged based on the amount of the data that you read or write on the cloud service side. |
Structured TXT, CSV, XLSX, and XLS files saved on your local computer. | Instance resources are not deducted. | You are not charged additional fees. | |
Dynamic data masking | Self-constructed data | Instance resources are not deducted. | You are not charged additional fees. |
Activate DSC
If you do not activate DSC or only activate the free edition of DSC, you can purchase DSC Enterprise Edition. For more information, see Purchase DSC.
If you activate the free edition of DSC and want to use the data masking feature, you must upgrade DSC to Enterprise Edition. For more information, see Instance upgrades.
If you use the static data masking method, you must authorize DSC to access your data assets. Make sure that you have purchased sufficient database protection instances and OSS protection capacity.
Static data masking
Feature description
When you create a static data masking task, you can select a configured masking template. You can also configure masking algorithms for sensitive fields to be masked. For more information about how to configure a data masking template, see Configure data masking templates and algorithms.

Prerequisites
If you use the static data masking method to mask a database or an OSS object, you must grant DSC access permissions on the data assets to be masked. For more information, see the following topics:
Authorize DSC to access a self-managed database hosted on an ECS instance
Authorize DSC to access unstructured data in OSS and Simple Log Service
DSC is authorized to access the required data asset and connected to the data asset by using an account that has read and write permissions on the data asset. This prerequisite applies when you want to store masked data in the tables of ApsaraDB RDS, PolarDB for Xscale (PolarDB-X), MaxCompute, PolarDB, ApsaraDB for OceanBase, AnalyticDB for MySQL, or self-managed databases or want to store masked data in Object Storage Service (OSS) buckets. If you want to store masked data in a database of ApsaraDB RDS, PolarDB for Xscale (PolarDB-X), PolarDB, ApsaraDB for OceanBase, or AnalyticDB for MySQL, you must use the account-based connection mode.
Create a data masking task
If you enable data masking in the production environment, your database performance may be compromised.
You can create a data masking task to specify the scope and rules for data masking.
Log on to the DSC console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Static Desensitization tab, click the Task Configurations tab. Then, click the Add Desensitization Task tab.
Follow the on-screen instructions to configure the parameters for a data masking task.
Configure the parameters in the Basic Task Information step of the Add Desensitization Task wizard and click Next.
NoteYou can specify a custom task name.
Configure the parameters in the Desensitization Source Configuration step of the Add Desensitization Task wizard and click Next.
ApsaraDB RDS tables, PolarDB-X tables, MaxCompute tables, PolarDB tables, ApsaraDB for OceanBase tables, AnalyticDB for MySQL tables, and self-managed database tables
Parameter
Required
Description
Types of data storage
Yes
The storage type of the source file for data masking. Set the parameter to ApsaraDB RDS Tables/PolarDB-X Tables/MaxCompute Tables/PolarDB Tables/ApsaraDB for OceanBase Tables/AnalyticDB for MySQL Tables/Self-managed Database Tables.
Source Service
Yes
The service that provides the source table for data masking. Valid values: RDS, PolarDB-X, OceanBase, MaxCompute, ADB-MYSQL, PolarDB, and ECS self-built database.
Source Database/Project
Yes
The database or project that stores the source table.
SOURCE table name
Yes
The name of the source table.
Source Partition
No
If you set the Source Service parameter to MaxCompute, you can configure the Source Partition parameter.
The name of the partition that stores the data to mask in the source table. If you leave this parameter empty, DSC masks the sensitive data in all partitions of the source table.
You can specify partitions when you create a MaxCompute table. Partitions define different logical divisions of a table. When you query data, you can specify partitions to improve query efficiency. For more information, see Partition.
Sample SQL
No
If you set the Source Service parameter to RDS, PolarDB-X, OceanBase, or ECS self-built database, you can configure the Sample SQL parameter.
The SQL statement that specifies the scope of the sensitive data to mask. If you leave this parameter empty, DSC masks all data in the source table.
OSS objects
ImportantOnly TXT, CSV, XLSX, and XLS objects can be masked.
Parameter
Required
Description
Types of data storage
Yes
The storage type of the source file for data masking. Set the parameter to OSS files.
File source
Yes
The source of the OSS object for data masking. Valid values: Uploaded Local File and OSS Bucket.
Upload files
Yes
If you set the File source parameter to Uploaded Local File, click Select a local file to upload the OSS object.
OSS Bucket where the source file is located
Yes
If you set the File source parameter to OSS Bucket, select the OSS bucket to which the OSS object belongs from the drop-down list. You can enter a keyword to search for and select the OSS bucket from the drop-down list.
Source file names
Yes
If you set the File source parameter to OSS Bucket, specify the name of the source OSS object. The name must contain a file extension.
If you want to mask data in an OSS object, specify the name of the OSS object. Example: test.csv.
If you want to mask data in multiple OSS objects, turn on Open the pass. The system uses the same masking rule to mask multiple OSS objects. The objects must have the same format and identical column structure.
After you turn on Open the pass, you can use asterisks (*) as wildcards to specify multiple OSS objects and mask data in the objects at a time. You can use asterisks (*) only in the prefix of an object name. Example: test*.xls, which matches XLS files whose name starts with test.
Source file description
No
If you set the File source parameter to Uploaded Local File, enter a description for the source OSS object.
Separator selection
No
The column delimiter. Select a delimiter based on the delimiter of the source OSS object. This parameter is required for CSV and TXT objects. Valid values:
Semicolon ";" (macOS/Linux default)
Comma "," (Windows default)
Operator '|'.
Table contains header rows
No
Specifies whether the source OSS object contains header rows.
Configure the parameters in the Desensitization algorithm step and click Next.
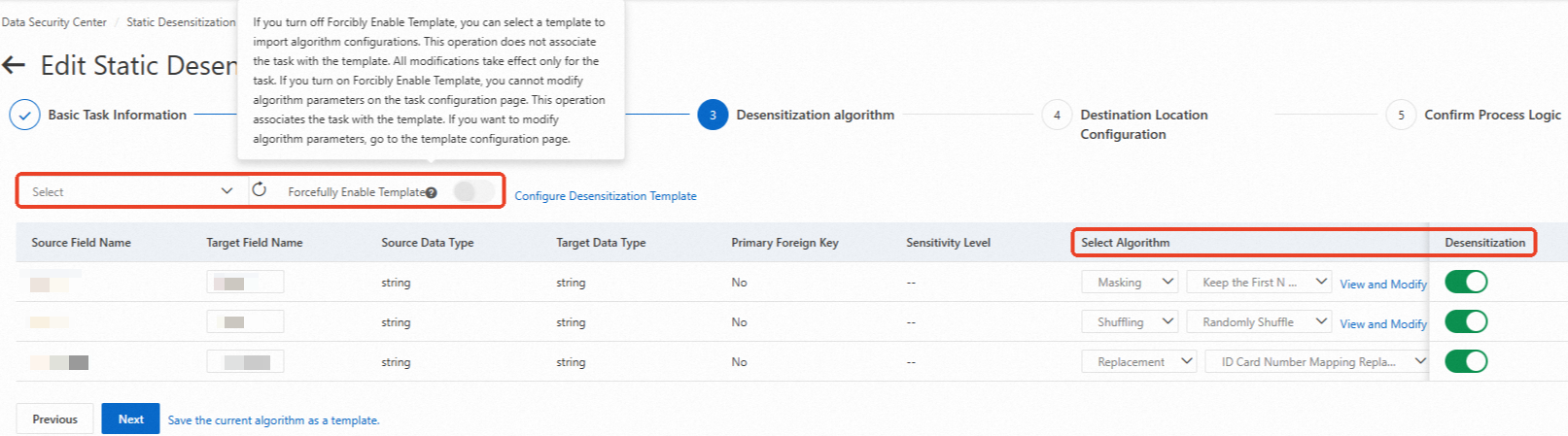
Select a data masking template from the drop-down list. In the source field list, the switch in the Desensitization column is automatically turned on and masking algorithms are automatically configured for fields based on the data masking template.
The settings in the rule list of the data masking template must match the source fields that you want to mask. Otherwise, the data masking template does not take effect. For more information about how to configure a data masking template, see Configure data masking templates and algorithms.
Find the source field whose data you want to mask in the list, turn on the switch in the Desensitization column, and then select a masking algorithm based on your business requirements.
You can click View and Modify Parameters in the Select Algorithm column to view and modify the rule of the selected algorithm. For more information about partition formats in algorithm rules, see Partition formats.
NoteIf you turn on Forcefully Enable Template, you cannot change the algorithm on the page. To change the algorithm, you must modify the relevant template rule.
Configure the destination where you want to store masked data and click Test below Write Permission Test. After the test is passed, click Next.
ImportantThe account that is used to connect to the data asset must have the write permissions on the data asset.

Configure the processing logic.
Parameter
Required
Description
How the task is triggered
Yes
The method that is used to run the data masking task. Valid values:
Manual Only: If you select this option, you must manually run the data masking task.
Scheduled Only: If you select this option, you must configure automatic running of the data masking task. After the configuration is complete, the data masking task is automatically run at a specific point in time on an hourly, daily, weekly, or monthly basis.
Manual + Scheduled: If you select this option, you can click Start in the Actions column on the Task Configurations tab to manually run the data masking task. You can also configure automatic running of the data masking task. After the configuration is complete, the data masking task is automatically run at a specific point in time on an hourly, daily, weekly, or monthly basis.
Turn on incremental desensitization
No
Specifies whether to enable incremental masking. If you turn on this switch, DSC masks only the data that is added after the previous data masking task is complete. You must specify a field whose value is increased over time as the incremental identifier. For example, you can specify the creation time field or the auto-increment ID field as the incremental identifier.
ImportantDSC supports incremental data masking only for ApsaraDB RDS databases.
Shard field
No
The shard field based on which DSC divides the source data into multiple shards. DSC concurrently masks the source data in the shards to improve the efficiency of data masking. You can specify one or more shard fields based on your business requirements.
DSC supports incremental data masking only for ApsaraDB RDS databases. We recommend that you use a primary key or a field on which a unique index is created as the shard field.
If you leave this parameter empty, a primary key is used as the shard field. DSC divides the source data based on the primary key and masks the source data.
ImportantIf the source data does not have a primary key, you must specify a shard field. Otherwise, the data masking task fails.
If you specify excessive shard fields, query performance and data accuracy may deteriorate. Proceed with caution.
Table name conflict resolution
Yes
The method that is used to handle a table name conflict. Valid value:
Delete the target table and create a new table with the same name.
Attach data to the target table. We recommend that you select this option.
Row Conflict Resolution
Yes
The method that is used to handle row conflicts. Valid value:
Keep conflicting rows in the target table and discard the new data. We recommend that you select this option.
Delete conflicting rows in the target table and insert the new data.
Click Submit.
Run and view a data masking task
If you set the How the task is triggered parameter to Manual Only, you must manually run the data masking task. If you set the How the task is triggered parameter to Scheduled Only, you must configure automatic running of the data masking task. After the configuration is complete, the data masking task is automatically run at a specific point in time. If you set the How the task is triggered parameter to Manual + Scheduled, you can manually run the data masking task or configure settings to automatically run the data masking task.
On the Static Desensitization tab, click the Task Configurations tab. Then, find the created data masking task and click Start in the Actions column to run the data masking task.

On the Static Desensitization tab, click the Status tab to view the progress and status of the data masking task.

Troubleshoot the errors that occur in a data masking task
If a data masking task fails, you can refer to the following table to troubleshoot the errors.
Error | Cause |
The data masking task does not exist. The task may be deleted or closed. | The switch in the Actions column of the data masking task is turned off. |
The scheduling settings of the scheduled data masking task are invalid. | The value of Triggered Daily is invalid. |
The source instance does not exist. | The instance to which the source table belongs does not exist. |
The destination instance does not exist. | The destination instance may be deleted or the destination instance-related permissions may be revoked. |
The source table cannot be found. | The source table may be deleted or the source instance-related permissions may be revoked. |
The parameters that are configured for the masking algorithm are invalid. | The parameters that are configured for the masking algorithm are invalid. |
The partition key column in the source table is empty. | The partition key column in the source table is empty. |
The operation that writes data to the destination table failed. | DSC failed to write data to the destination table due to invalid destination settings. |
The operation that queries data from the source table failed. | DSC failed to query data from the source table. |
The operation that creates the destination table failed. | The destination table does not exist in the destination. |
No primary key can be found. | No primary key exists in the ApsaraDB RDS source table. |
The MaxCompute table-related partition that is configured for the data masking task is invalid. | Source Partition that is configured in the Desensitization Source Configuration step or the Target Partition that is configured in the Destination Location Configuration step of the Add Desensitization Task wizard is invalid. |
Modify or delete a data masking task
You cannot modify or delete a data masking task that is pending execution or is running.
Modify a data masking task
If you want to modify the settings of a data masking task, find the task and click Modify in the Actions column.
Delete a data masking task
ImportantAfter a data masking task is deleted, it cannot be restored. Proceed with caution.
If you no longer use a data masking task, you can delete the task. Find the task and click Delete in the Actions column. In the message that appears, click OK.
Dynamic data masking
Feature description
Dynamic data masking tasks rely on configured masking templates to mask the specified data. You can call the ExecDatamask operation to specify the data (Data) that you want to mask and the ID of the masking template (TemplateId ). Then, the data specified in the dataList field of the Data parameter is masked based on the matching mode (field and sensitive type) defined in the masking template.
You can obtain the template ID on the Masking Configurations tab of the page in the DSC console. You can also create a custom data masking template. For more information, see Configure data masking templates and algorithms.
The following table describes the masking methods in the masking template that is used when you call the ExecDatamask operation to mask data.
Matching mode | Description |
Field | Match the field names specified in the dataHeaderList field with the data field names and masking algorithms configured in the Rule list section in the masking template to mask the data in the dataList field. |
Sensitive type | Match the rule IDs specified in the ruleList field with the rule IDs in the Rule list section in the masking template to mask the data in the dataList field based on the data field names and masking algorithms in the rules. If you set the Matching mode parameter to Sensitive type, you can select the fields in the Data Feature column on the Identification Features tab in the Rule list section. You can select built-in or custom fields. Feature names are used as rule names in the Rule list section. You can call the DescribeRules operation and configure the CustomType and Name parameters to query the ID (Id) of a data feature. CustomType specifies the data feature source: built-in or custom. Name specifies the data feature name. |
Example

Limits
Before you can call the ExecDatamask operation to dynamically mask sensitive data, make sure that the size of the sensitive data that you want to mask is less than 2 MB.
View the call records of the ExecDatamask operation
Log on to the DSC console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Data Desensitization page, click the Dynamic desensitization tab.
On the Dynamic desensitization tab, view the call records of the ExecDatamask operation.
NoteIf you use the same account and IP address to call the ExecDatamask operation multiple times, only one record is retained. The cumulative number of calls is recorded.
Example on how to share masked data based on the static data masking method
DSC provides a static data masking method that can be used to mask sensitive data in structured CSV files in an OSS bucket. You can store the masked data in a specific OSS bucket within the same account for secure data sharing. For more information, see Mask sensitive data in OSS table files.