When you update your application versions, you can implement rolling updates, phased releases, blue-green deployments, and canary releases. This topic describes how to implement canary releases for applications in a Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster by using the NGINX Ingress controller.
Background information
You can implement a canary release or a blue-green deployment to publish applications of an earlier version and a new version to identical production environments. In this case, when users send requests, ACK routes some requests to the new version based on specific rules. If the new version runs as normal for a period of time, you can switch all traffic from the earlier version to the new version.
Blue-green deployment is a way of implementing canary releases. In blue-green deployment, some users use the earlier version, and requests from the other users are forwarded to the new version. If the new version runs as normal for a period of time, you can gradually switch all traffic to the new version.
You can configure how to implement canary releases by using one of the following methods in the ACK console:
Use the canary-* annotations: You can use the canary-* annotations to configure how to implement blue-green deployments and canary releases. The canary-* annotations are used by Kubernetes.
Use the service-* annotations: You can use the service-* annotations to configure how to implement blue-green deployments and canary releases. The service-* annotations are used by early NGINX Ingress controller versions to implement canary releases. The service-match and service-weight annotations are no longer maintained and will be deprecated soon. The service-* annotations can still be used.
Scenarios
Traffic splitting based on requests
For example, you have already created Service A in your production environment to provide Layer 7 access for users. When new features are available, you want to create Service A' for the new application version. If you want to keep Service A for external access, you can forward requests whose values of the foo parameters in the request headers match bar or whose values of the foo parameters in the cookies match bar to Service A'. If the new version stably runs for a period of time, you can switch all traffic from Service A to Service A'. Then, you can delete Service A.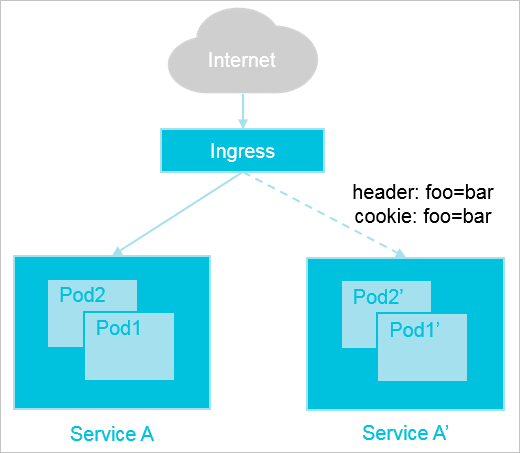
Traffic splitting based on Service weights
For example, you have already created Service B in your production environment to provide Layer 7 access for users. When some issues are fixed, you want to create Service B' for the new application version. If you want to keep Service B for external access, you can switch 20% of traffic to Service B'. If the new version stably runs for a period of time, you can switch all traffic from Service B to Service B'. Then, you can delete Service B.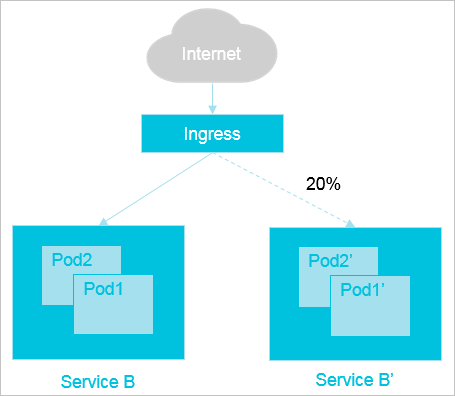
Ingress controllers of ACK provide the following traffic splitting methods to support the preceding requirements of application releases.
Traffic splitting based on request headers. This method applies to scenarios where canary releases or A/B testing is required.
Traffic splitting based on cookies. This method applies to scenarios where canary releases or A/B testing is required.
Traffic splitting based on query parameters. This method applies to scenarios where canary releases or A/B testing is required.
Traffic splitting based on Service weights. This method applies to scenarios where blue-green deployments are required.
Use the canary-* annotations
Annotations
The following table describes the canary-* annotations that are used by the NGINX Ingress controller to implement canary releases:
Annotation | Description | Applicable NGINX Ingress controller version |
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary | | ≥ 0.22.0 |
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header | Implements canary releases based on request headers. The following special values are supported: If you do not specify a header, all requests with headers are forwarded.
| ≥ 0.22.0 |
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header-value | | ≥ 0.30.0 |
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header-pattern | Implements canary releases based on whether request header values match the specified regular expression. You must use this annotation together with the canary-by-header annotation. Set the value to a regular expression that you want to use to match request header values.
| ≥ 0.44.0 |
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-cookie | | ≥ 0.22.0 |
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-weight | Implements canary releases based on weights. Valid values: 0 to the total weight. The default total weight is 100.
| ≥ 0.22.0 |
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-weight-total | | ≥ 1.1.2 |
The preceding annotations take effect in descending order of precedence:
canary-by-header>canary-by-cookie>canary-weight
Note You can specify only one canary Ingress in an Ingress rule. If you specify more than one canary Ingress, only one canary Ingress is used to implement canary releases.
Step 1: Deploy an application
Create an NGINX application and deploy the NGINX Ingress controller to enable Layer 7 access to the application by using domain names.
Create a Deployment and a Service.
Create a file named nginx.yaml.
Click to view details
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: old-nginx
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
run: old-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
run: old-nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs-sample/old-nginx
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: old-nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
protocol: TCP
restartPolicy: Always
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: old-nginx
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
run: old-nginx
sessionAffinity: None
type: NodePort
Run the following command to create the Deployment and Service:
kubectl apply -f nginx.yaml
Create an Ingress.
Create a file named ingress.yaml.
Clusters that run Kubernetes versions earlier than 1.19
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the old application version.
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: old-nginx
servicePort: 80
Clusters that run Kubernetes 1.19 and later
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the old application version.
- path: /
backend:
service:
name: old-nginx
port:
number: 80
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
Run the following command to create the Ingress:
kubectl apply -f ingress.yaml
Test access to the Ingress.
Run the following command to query the public IP address of the Ingress:
Run the following command to access the Ingress:
curl -H "Host: www.example.com" http://<EXTERNAL_IP>
Expected output:
old
Step 2: Implement a canary release of the application
Release a new NGINX application version and configure Ingress rules.
Create a Deployment and a Service for the new application version.
Create a file named nginx1.yaml.
Click to view details
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: new-nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
run: new-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
run: new-nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs-sample/new-nginx
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: new-nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
protocol: TCP
restartPolicy: Always
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: new-nginx
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
run: new-nginx
sessionAffinity: None
type: NodePort
Run the following command to deploy a Deployment and a Service for the new application version:
kubectl apply -f nginx1.yaml
Configure Ingress rules for the new application version.
ACK provides the following types of Ingress rules. Select a type of Ingress rule based on your requirements.
Configure Ingress rules to forward requests that match the rules to the new application version. In the following example, only requests whose values of the foo parameters in the request headers match the regular expression bar are forwarded to the new application version.
Create a new Ingress named gray-release-canary in the ingress1.yaml file.
Clusters that run Kubernetes versions earlier than 1.19
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release-canary
annotations:
# Enable the canary release feature.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary: "true"
# Set the request header to foo.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header: "foo"
# Only requests whose headers are foo and header values are bar are forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header-value: "bar"
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the new application version.
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: new-nginx
servicePort: 80
Clusters that run Kubernetes 1.19 and later
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release-canary
annotations:
# Enable the canary release feature.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary: "true"
# Set the request header to foo.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header: "foo"
# Only requests whose headers are foo and header values are bar are forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header-value: "bar"
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the new application version.
- path: /
backend:
service:
name: new-nginx
port:
number: 80
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
Run the following command to deploy Ingress1:
kubectl apply -f ingress1.yaml
Run the following command to query the IP address of the Ingress for external access:
kubectl get ingress
Test access to the Ingress.
Run the following command to access the NGINX application:
curl -H "Host: www.example.com" http://<EXTERNAL_IP>
Expected output:
old
Run the following command to access the NGINX application by using a request whose value of the foo parameter in the request header matches the regular expression bar:
curl -H "Host: www.example.com" -H "foo: bar" http://<EXTERNAL_IP>
Expected output:
new
You can run the preceding commands again to test access. The result shows that only requests whose values of the foo parameters in the request headers match bar are forwarded to the new application version.
Forward a specific proportion of requests to the new application version when the requests do not match the rules. In the following example, only 50% of the requests in which the value of the foo parameter in the request header does not match bar are forwarded to the new version.
Modify the Ingress that is created in 2 based on the following content:
Clusters that run Kubernetes versions earlier than 1.19
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release-canary
annotations:
# Enable the canary release feature.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary: "true"
# Set the request header to foo.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header: "foo"
# Only requests whose headers are foo and header values are bar are forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header-value: "bar"
# Only 50% of the requests that do not match the preceding rule are forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-weight: "50"
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the new application version.
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: new-nginx
servicePort: 80
Clusters that run Kubernetes 1.19 and later
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release-canary
annotations:
# Enable the canary release feature.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary: "true"
# Set the request header to foo.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header: "foo"
# Only requests whose headers are foo and header values are bar are forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-by-header-value: "bar"
# Only 50% of the requests that do not match the preceding rule are forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-weight: "50"
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the new application version.
- path: /
backend:
service:
name: new-nginx
port:
number: 80
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
Run the following command to create the Ingress:
kubectl apply -f ingress.yaml
Run the following command to query the IP address of the Ingress for external access:
kubectl get ingress
Test access to the Ingress.
Run the following command to access the NGINX application:
curl -H "Host: www.example.com" http://<EXTERNAL_IP>
Expected output:
old
Run the following command to access the NGINX application by using a request whose value of the foo parameter in the request header matches the regular expression bar:
curl -H "Host: www.example.com" -H "foo: bar" http://<EXTERNAL_IP>
Expected output:
new
You can run the preceding commands again to test the access. The result shows that only 50% of the requests whose values of the foo parameters in the request headers match the regular expression bar are forwarded to the new application version.
Configure Ingress rules to forward a specific proportion of requests to the new application version. In the following example, only 50% of requests are forwarded to the new application version.
Modify the Ingress that is created in Step 2 based on the following content:
Clusters that run Kubernetes versions earlier than 1.19
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release-canary
annotations:
# Enable the canary release feature.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary: "true"
# Only 50% of requests are forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
# The default total weight is 100.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-weight: "50"
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the new application version.
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: new-nginx
servicePort: 80
Clusters that run Kubernetes 1.19 and later
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release-canary
annotations:
# Enable the canary release feature.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary: "true"
# Only 50% of requests are forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
# The default total weight is 100.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/canary-weight: "50"
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the new application version.
- path: /
backend:
service:
name: new-nginx
port:
number: 80
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
Run the following command to create the Ingress:
kubectl apply -f ingress.yaml
Run the following command to query the IP address of the Ingress for external access:
kubectl get ingress
Run the following command to access the Ingress:
curl -H "Host: www.example.com" http://<EXTERNAL_IP>
You can run the preceding command again to test access. The result shows that only 50% of the requests are forwarded to the new application version.
Step 3: Delete the old application version and the related Service
If the new application version runs as expected for a period of time, you need to bring the earlier application version offline and provide only the new application version for access. To do this, you must use the Service created for the earlier application version to provide access to the Deployment created for the new application version. You must also delete the Deployment created for the earlier application version and the Service created for the new application version.
Modify the nginx.yaml file of the old application version to select the Deployment created for the new application version.
Click to view details
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: old-nginx
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
# Specify a selector that is used to select the Deployment created for the new application version.
run: new-nginx
sessionAffinity: None
type: NodePort
Run the following command to create the Service for the old application version:
kubectl apply -f nginx.yaml
Run the following command to query the IP address of the Ingress for external access:
kubectl get ingress
Run the following command to access the Ingress:
curl -H "Host: www.example.com" http://<EXTERNAL_IP>
Expected output:
new
You can run the preceding command again to test access. The result shows that all the requests are forwarded to the new application version.
Run the following command to delete the canary Ingress named gray-release-canary:
kubectl delete ingress gray-release-canary
Delete the Deployment that is created for the earlier application version and the Service that is created for the new application version.
Run the following command to delete the Deployment that is created for the earlier application version:
kubectl delete deploy old-nginx
Run the following command to delete the Service that is created for the new application version:
kubectl delete svc new-nginx
service-* annotations
Annotations
The following list describes the service-* annotations that are used by the NGINX Ingress controller to implement canary releases:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/service-match
This annotation is used to configure match rules for requests to the Service that is created for the new application version.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/service-match: |
<service-name>: <match-rule>
# Parameters
# service-name: the name of a Service. Requests that match the rules specified by match-rule are forwarded to the Service.
# match-rule: the match rules for requests.
#
# Match rules:
# 1. The following types of match rules are supported:
# - header: matches requests based on the request header. Regular expressions and exact match rules are supported.
# - cookie: matches requests based on the cookie. Regular expressions and exact match rules are supported.
# - query: based on the query parameters. Regular expressions and exact match rules are supported.
#
# 2. The following match methods are supported:
# - Regular expressions: /{regular expression}/. A regular expression is enclosed within a pair of forward slashes (/).
# - Exact match rules:"{exact expression}". An exact match rule is enclosed within a pair of quotation marks (").
Examples of match rules:
# If the value of the foo parameter in the request header matches the regular expression ^bar$, the request is forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
new-nginx: header("foo", /^bar$/)
# If the value of the foo parameter in the request header exactly matches the value bar, the request is forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
new-nginx: header("foo", "bar")
# If the value of the foo parameter in the cookie matches the regular expression ^sticky-.+$, the request is forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
new-nginx: cookie("foo", /^sticky-.+$/)
# If the value of the foo parameter in the query parameters exactly matches the value bar, the request is forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
new-nginx: query("foo", "bar")
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/service-weight
This annotation is used to set the weights of the Services that are created for the old and new application versions.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/service-weight: |
<new-svc-name>:<new-svc-weight>, <old-svc-name>:<old-svc-weight>
Parameters:
new-svc-name: the name of the Service that is created for the new application version.
new-svc-weight: the traffic weight of the Service that is created for the new application version.
old-svc-name: the name of the Service that is created for the old application version.
old-svc-weight: the traffic weight of the Service that is created for the old application version.
Example of Service weight configurations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/service-weight: |
new-nginx: 20, old-nginx: 60
Step 1: Deploy an application
Create an NGINX application and deploy the NGINX Ingress controller to enable Layer 7 access to the application by using domain names.
Create a Deployment and a Service.
Create a file named nginx.yaml.
Click to view details
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: old-nginx
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
run: old-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
run: old-nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs-sample/old-nginx
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: old-nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
protocol: TCP
restartPolicy: Always
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: old-nginx
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
run: old-nginx
sessionAffinity: None
type: NodePort
Run the following command to create the Deployment and Service:
kubectl apply -f nginx.yaml
Create an Ingress.
Create a file named ingress.yaml.
Clusters that run Kubernetes versions earlier than 1.19
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the old application version.
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: old-nginx
servicePort: 80
Clusters that run Kubernetes 1.19 and later
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the old application version.
- path: /
backend:
service:
name: old-nginx
port:
number: 80
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
Run the following command to create the Ingress:
kubectl apply -f ingress.yaml
Test access to the Ingress.
Run the following command to query the public IP address of the Ingress:
Run the following command to access the Ingress:
curl -H "Host: www.example.com" http://<EXTERNAL_IP>
Expected output:
old
Step 2: Implement a canary release of the application
Release a new NGINX application version and configure Ingress rules.
Create a Deployment and a Service for the new application version.
Create a file named nginx1.yaml.
Click to view details
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: new-nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
run: new-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
run: new-nginx
spec:
containers:
- image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs-sample/new-nginx
imagePullPolicy: Always
name: new-nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
protocol: TCP
restartPolicy: Always
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: new-nginx
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 80
selector:
run: new-nginx
sessionAffinity: None
type: NodePort
Create a Deployment and a Service for the new application version.
kubectl apply -f nginx1.yaml
Configure Ingress rules for the new application version.
ACK provides the following types of Ingress rules. Select a type of Ingress rule based on your requirements.
Configure Ingress rules to forward requests that match the rules to the new application version. In the following example, only requests whose values of the foo parameters in the request headers match the regular expression bar are forwarded to the new application version.
Modify the Ingress that is created in Step 2 based on the following content:
Clusters that run Kubernetes versions earlier than 1.19
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release
annotations:
# Only requests whose values of the foo parameters in the request headers match the regular expression bar are forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/service-match: |
new-nginx: header("foo", /^bar$/)
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the old application version.
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: old-nginx
servicePort: 80
# Information about the Service that is created for the new application version.
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: new-nginx
servicePort: 80
Clusters that run Kubernetes 1.19 and later
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release
annotations:
# Only requests whose values of the foo parameters in the request headers match the regular expression bar are forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/service-match: |
new-nginx: header("foo", /^bar$/)
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the old application version.
- path: /
backend:
service:
name: old-nginx
port:
number: 80
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
# Information about the Service that is created for the new application version.
- path: /
backend:
service:
name: new-nginx
port:
number: 80
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
Run the following command to create the Ingress:
kubectl apply -f ingress.yaml
Run the following command to query the IP address of the Ingress for external access:
kubectl get ingress
Test access to the Ingress.
Run the following command to access the NGINX application:
curl -H "Host: www.example.com" http://<EXTERNAL_IP>
Expected output:
old
Run the following command to access the NGINX application by using a request whose value of the foo parameter in the request header matches the regular expression bar:
curl -H "Host: www.example.com" -H "foo: bar" http://<EXTERNAL_IP>
Expected output:
new
You can run the preceding commands again to test access. The result shows that only requests whose values of the foo parameters in the request headers match the regular expression bar are forwarded to the new application version.
Configure Ingress rules to forward a specific proportion of requests that match the rules to the new application version. In the following example, only 50% of the requests whose values of the foo parameters in the request headers match the regular expression bar are forwarded to the new version.
Modify the Ingress that is created in Step 2 based on the following content:
Clusters that run Kubernetes versions earlier than 1.19
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release
annotations:
# Only requests whose values of the foo parameters in the request headers match the regular expression bar are forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/service-match: |
new-nginx: header("foo", /^bar$/)
# Only 50% of the requests that match the preceding rule are forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/service-weight: |
new-nginx: 50, old-nginx: 50
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the old application version.
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: old-nginx
servicePort: 80
# Information about the Service that is created for the new application version.
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: new-nginx
servicePort: 80
servicePort: 80
Clusters that run Kubernetes 1.19 and later
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release
annotations:
# Only requests whose values of the foo parameters in the request headers match the regular expression bar are forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/service-match: |
new-nginx: header("foo", /^bar$/)
# Only 50% of the requests that match the preceding rule are forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/service-weight: |
new-nginx: 50, old-nginx: 50
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the old application version.
- path: /
backend:
service:
name: old-nginx
port:
number: 80
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
# Information about the Service that is created for the new application version.
- path: /
backend:
service:
name: new-nginx
port:
number: 80
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
Run the following command to create the Ingress:
kubectl apply -f ingress.yaml
Run the following command to query the IP address of the Ingress for external access:
kubectl get ingress
Test access to the Ingress.
Run the following command to access the NGINX application:
curl -H "Host: www.example.com" http://<EXTERNAL_IP>
Expected output:
old
Run the following command to access the NGINX application by using a request whose value of the foo parameter in the request header matches the regular expression bar:
curl -H "Host: www.example.com" -H "foo: bar" http://<EXTERNAL_IP>
Expected output:
new
You can run the preceding commands again to test the access. The result shows that only 50% of the requests whose values of the foo parameters in the request headers match the regular expression bar are forwarded to the new application version.
Configure Ingress rules to forward a specific proportion of requests to the new application version. In the following example, only 50% of requests are forwarded to the new application version.
Modify the Ingress that is created in Step 2 based on the following content:
Clusters that run Kubernetes versions earlier than 1.19
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release
annotations:
# 50% of requests are forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/service-weight: |
new-nginx: 50, old-nginx: 50
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the old application version.
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: old-nginx
servicePort: 80
# Information about the Service that is created for the new application version.
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: new-nginx
servicePort: 80
Clusters that run Kubernetes 1.19 and later
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release
annotations:
# 50% of requests are forwarded to the new-nginx Service.
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/service-weight: |
new-nginx: 50, old-nginx: 50
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the old application version.
- path: /
backend:
service:
name: old-nginx
port:
number: 80
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
# Information about the Service that is created for the new application version.
- path: /
backend:
service:
name: new-nginx
port:
number: 80
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
Run the following command to create the Ingress:
kubectl apply -f ingress.yaml
Run the following command to query the IP address of the Ingress for external access:
kubectl get ingress
Run the following command to access the Ingress:
curl -H "Host: www.example.com" http://<EXTERNAL_IP>
You can run the preceding command again to test access. The result shows that only 50% of the requests are forwarded to the new application version.
Step 3: Delete the old application version and the related Service
If the new application version runs as expected for a period of time, you need to bring the earlier application version offline and provide only the new application version for access.
Modify the Ingress that is created in Step 2 based on the following content:
Clusters that run Kubernetes versions earlier than 1.19
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the new application version.
- path: /
backend:
serviceName: new-nginx
servicePort: 80
Clusters that run Kubernetes 1.19 and later
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: gray-release
spec:
rules:
- host: www.example.com
http:
paths:
# Information about the Service that is created for the new application version.
- path: /
backend:
service:
name: new-nginx
port:
number: 80
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
Run the following command to create the Ingress:
kubectl apply -f ingress.yaml
Run the following command to query the IP address of the Ingress for external access:
kubectl get ingress
Run the following command to access the Ingress:
curl -H "Host: www.example.com" http://<EXTERNAL_IP>
Expected output:
new
You can run the preceding command again to test access. The result shows that all the requests are forwarded to the new application version.
Delete the Deployment and Service that are created for the earlier application version.
Run the following command to delete the Deployment that is created for the earlier application version:
kubectl delete deploy <Deployment name>
Run the following command to delete the Service that is created for the earlier application version:
kubectl delete svc <Service name>

