You can mount a Network Attached Storage (NAS) file system to a sandboxed container to significantly improve I/O performance. This topic describes how to mount a NAS file system to a sandboxed container.
Prerequisites
Background information
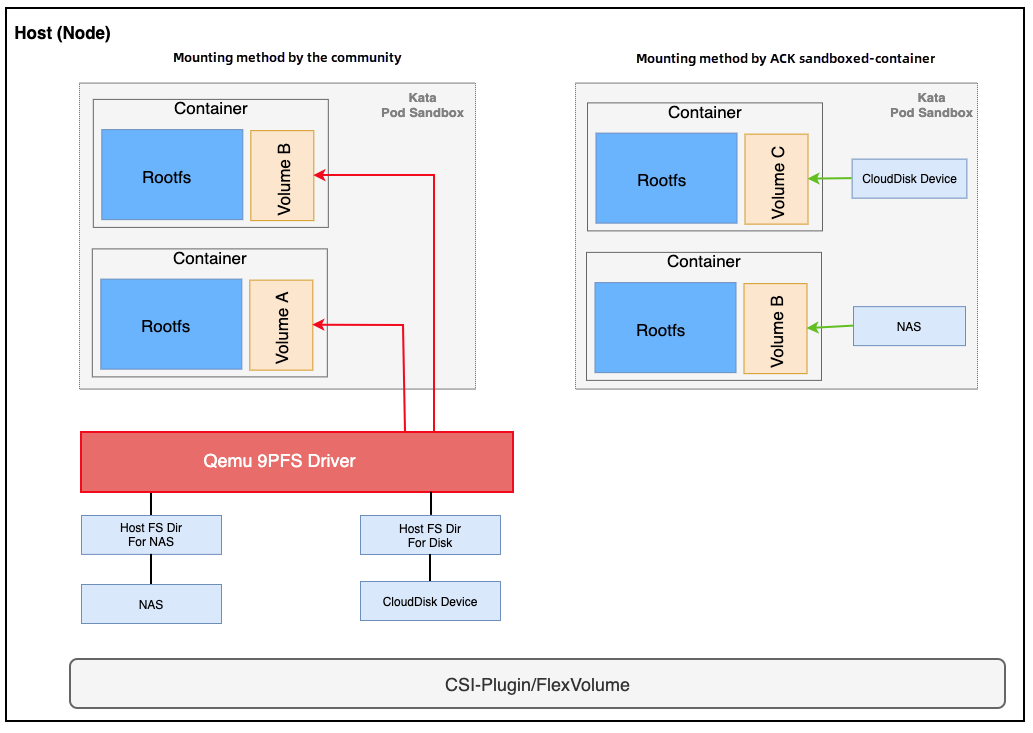
virtio-fs is a shared file system. Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) allows you to use virtio-fs to add volumes, Secrets, and ConfiMaps to the guest operating system of a virtual machine (VM). This directly mounts a NAS file system to a cluster. This method mounts the NAS file system to the host. Applications in the container can write data to and read data from the NAS file system only through virtio-fs. This may cause performance degradation.
Sandboxed containers allow you to directly mount NAS file systems. This method first unmounts NAS mount targets from the host. The NAS file system is mounted to the guest operating system. Then, the system creates a bind mount for the NAS file system. This way, applications in the container can directly write data to and read data from the NAS file system without performance degradation.
How a NAS file system is mounted to a sandboxed container
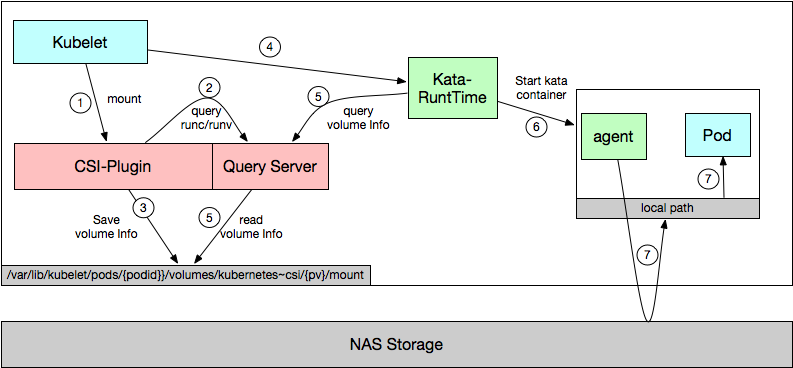
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| ① | The kubelet requests the CSI plug-in to mount a NAS file system. |
| ② | The CSI plug-in mounts the NAS file system to the host. |
| ③ | The Kubelet requests Kangaroo-Runtime to create a pod. |
| ④ | Kangaroo-Runtime parses the unmounting information, passes the information to the guest operating system, and then unmounts the NAS file system from the host. |
| ⑤ | Kangaroo-Runtime requests the agent to create a container. |
| ⑥ | The agent mounts the NAS file system to the guest operating system. |
| ⑦ | The agent creates a bind mount to mount for the NAS file system that is mounted to the guest operating system. |
Examples
The following example describes how to mount a NAS file system to a sandboxed container. In this example, an Apsara File Storage NAS instance is created and a YAML file template is used to create resource objects.
- Create an Apsara File Storage NAS instance. For more information, see Create a General-purpose NAS file system in the NAS console.
Important The NAS file system must be deployed in the same virtual private cloud (VPC) as the cluster.Obtain the mount target of the NAS file system. As shown in the following figure, the URL file-system-id.region.nas.aliyuncs.com in the Mount Command column is the mount target.
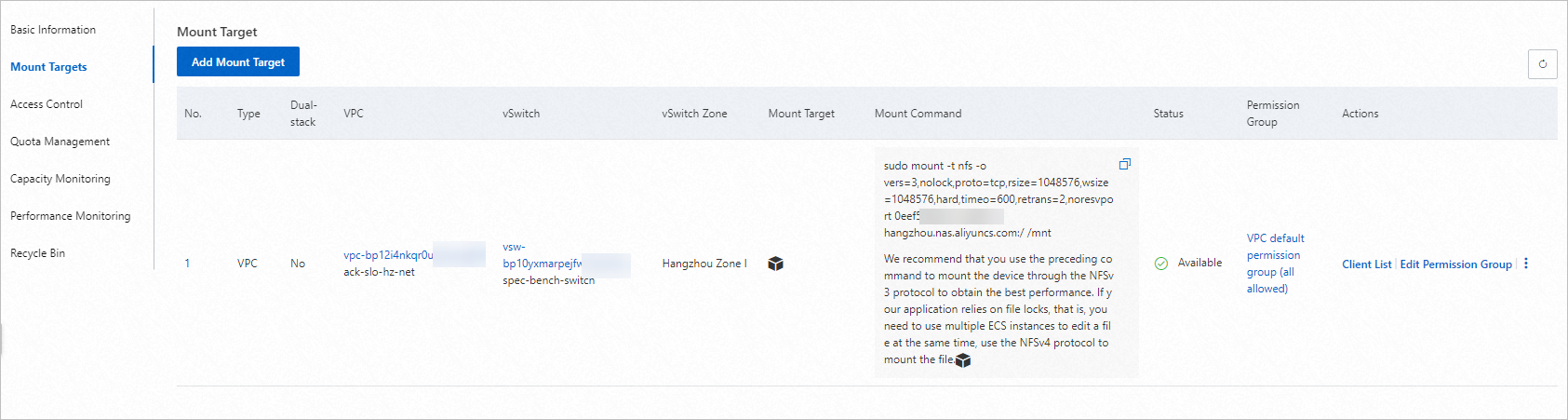 Note file-system-id.region.nas.aliyuncs.com is the address of the mount target. You can obtain the address of the mount target in the NAS console. Log on to the NAS console, click the name of the NAS file system. In the left-side navigation pane, click Mounting Usage. You can find the address of the mount target in the Mount Command column.
Note file-system-id.region.nas.aliyuncs.com is the address of the mount target. You can obtain the address of the mount target in the NAS console. Log on to the NAS console, click the name of the NAS file system. In the left-side navigation pane, click Mounting Usage. You can find the address of the mount target in the Mount Command column. - Use the following template to create resource objects:
cat <<EOF | kubectl create -f - apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: nas-pvc-csi namespace: default spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteMany resources: requests: storage: 5Gi selector: matchLabels: alicloud-pvname: nas-pv-csi --- apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolume metadata: labels: alicloud-pvname: nas-pv-csi name: nas-pv-csi spec: accessModes: - ReadWriteMany capacity: storage: 5Gi csi: driver: nasplugin.csi.alibabacloud.com volumeAttributes: options: noresvport,nolock path: /csi server: ${nas-server-address} vers: "3" volumeHandle: nas-pv-csi persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: deploy-nas-csi spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: busybox template: metadata: labels: app: busybox annotations: storage.alibabacloud.com/enable_nas_passthrough: "true" spec: runtimeClassName: runv containers: - name: busybox image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs/busybox:v1.29.2 command: - tail - -f - /dev/null volumeMounts: - name: nas-pvc mountPath: "/data" restartPolicy: Always volumes: - name: nas-pvc persistentVolumeClaim: claimName: nas-pvc-csi EOFNote- Replace
${nas-server-address}in the template with the address of the mount target.server: ${nas-server-address} - By default, pods cannot communicate with NAS file systems. You must add an annotation in the template to enable the pod to communicate with the NAS file system.
annotations: storage.alibabacloud.com/enable_nas_passthrough: "true"
- Replace
- Run the following commands to query the ID of the pod and query the type of the file system that is mounted to the pod:
kubectl get podskubectl exec -it ${podid} shmount | grep /data | grep nfsIf the output is not empty, it indicates that the NAS file system is mounted to the container.