Sandboxed-Container runtime executes applications in lightweight VMs isolated from the rest of the system. This architecture establishes kernel-level isolation for application pods while maintaining strict environmental segregation from the host infrastructure. This mechanism effectively protects the host or other containers against attacks or vulnerabilities within the sandboxed container. This topic describes the architecture, benefits, and use scenarios of the Sandboxed-Container.
Background information
Sandboxed-Container is suitable in scenarios such as untrusted application isolation, fault isolation, performance isolation, and load isolation among multiple users. Sandboxed-Container provides enhanced security, has minor impacts on application performance, and offers the same user experience as Docker in terms of logging, monitoring, and elastic scaling.
Compared with open-source Kata Containers, Sandboxed-Container is optimized in terms of storage, networking, and stability.

Architecture

Key features
Sandboxed-Container is a container-securing runtime that is developed by Alibaba Cloud. Compared with Sandboxed-Container V1, Sandboxed-Container V2 maintains the same isolation performance and reduces the pod overhead by 90%. It also allows you to start sandboxed containers 3 times faster and increases the maximum number of pods that can be deployed on a host by 10 times. Sandboxed-Container V2 provides the following key features:
Strong isolation based on sandboxed and lightweight VMs.
Compatibility with runC in terms of application management.
High performance that corresponds to 90% the performance of applications based on runC.
File Storage NAS (NAS) file systems, Alibaba Cloud disks, and OSS buckets can be mounted to sandboxed containers through virtio-fs. NAS file systems can also be directly mounted to sandboxed containers.
The same user experience as runC in terms of logging, monitoring, and storage.
Support for RuntimeClass (runC and runV). For more information, see RuntimeClass.
Ease of use with minimum technical skill requirements.
Higher stability compared with the open source Kata Containers runtime. For more information about Kata Containers, see Kata Containers.
Comparison between Sandboxed-Container and Kata Containers
Item | Category | Sandboxed-Container V2 | Kata Containers |
Amount of time consumed to start a sandbox | About 150 ms | About 500 ms | |
Additional overhead of sandboxes | Low | High | |
Root file system | virtio-fs. Performance: ☆☆☆☆ |
| |
Volume | HostPath/EmptyDir | virtio-fs. Performance: ☆☆☆☆ | |
Disks with block storage | virtio-fs. Performance: ☆☆☆☆ | ||
NAS |
| ||
Object Storage Service (OSS) | virtio-fs. Performance: ☆☆☆☆ | ||
Network plug-in |
| Flannel | |
Monitoring and alerting |
| Monitoring of disks and network conditions is unavailable for pods that use Sandboxed-Container. | |
Stability | ☆☆☆☆☆ | ☆☆ | |
Use scenarios of Sandboxed-Container

Scenario 1: Compared to runC, Sandboxed-Container (runV) provides kernel-level isolation foruntrusted applications
Security risks of runC
runC isolates containers by using namespaces and control groups (cgroups). This exposes containers to security risks.
All containers on a node share the host kernel. If the kernel has a vulnerability, malicious code may escape to the host and then infiltrate the backend network. Malicious code execution may cause privilege escalation, compromise sensitive data, and destroy system services and other applications.
Attackers may also exploit application vulnerabilities to infiltrate the internal network.
You can implement the following measures to reduce the security risks of containers in runC.
Seccomp: filters system calls.
SElinux: limits the permissions of container processes, files, and users.
Capability: limits the capability of container processes.
Rootless mode: prohibits users from running container runtimes and containers as the root role.
The preceding measures can enhance the security of containers in runC and reduce attacks on the host kernel by using malicious containers. However, container escapes and host kernel vulnerabilities remain unresolved.
Security risks of runV
runV implements kernel-level isolation through validated lightweight VM sandboxes, where untrusted workloads operate on dedicated guest OS kernels. In the event of guest kernel compromise, the attack surface is strictly confined within the affected sandbox, thereby ensuring complete protection of the host kernel and adjacent containerized environments.
When integrated with the enhanced NetworkPolicy capabilities of Terway, this architecture enables granular configuration of pod network access controls, delivering multi-dimensional isolation including system boundaries, data planes, and network segments.
Scenario 2: Mitigation of failure amplification, resource contention, and performance interference in runC container environments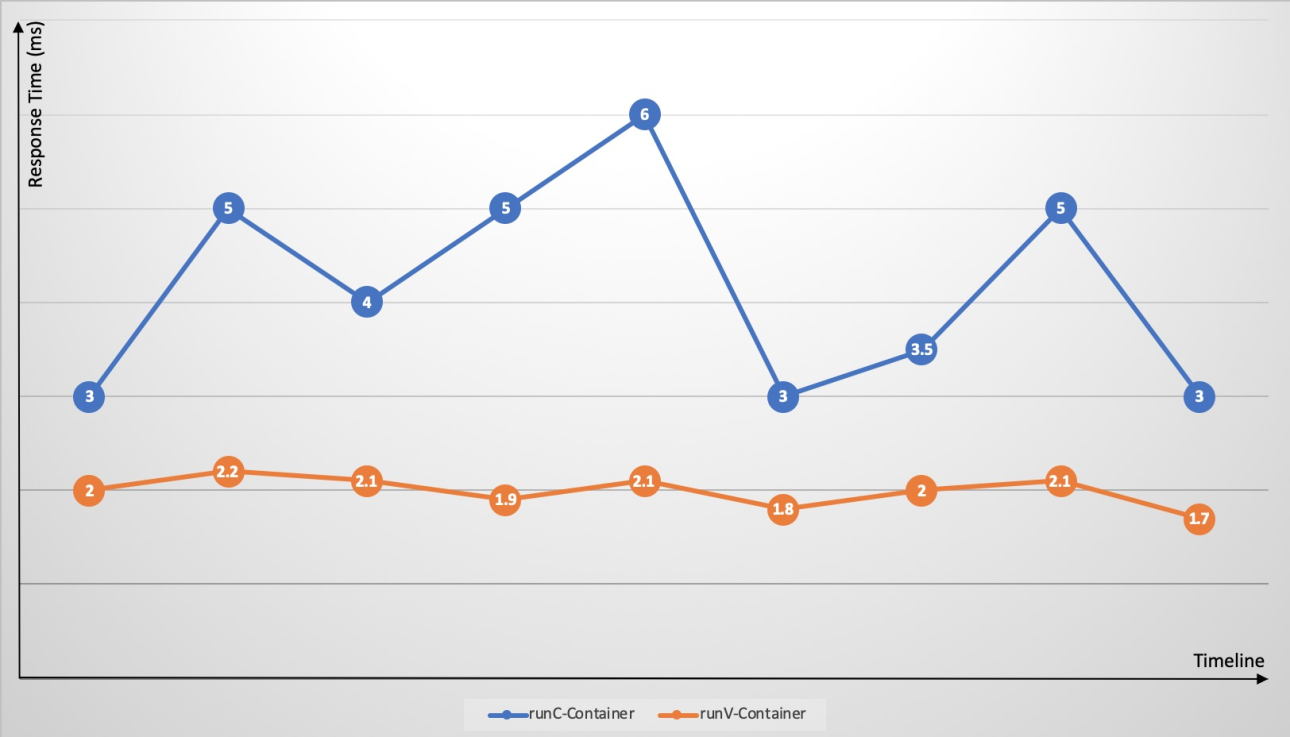
Kubernetes allows you to deploy different containers on a single node with ease. However, cgroups are not optimized to address resource contention. Resource-intensive applications such as CPU-intensive and I/O-intensive applications may compete for the same resources. This causes significant fluctuations in response time and increases the overall response time. Exceptions or faults on an application may spread to the hosting node and disrupt the running of the cluster. For example, memory leaks and frequent core dumps of an application may overload the node, and exceptions on a container may trigger a host kernel bug that results in an entire system failure. Through dedicated guest OS kernels and hypervisors, Sandboxed-Container resolves the issues that are common with runC containers. The issues include failure spreading, resource contention, and performance interference.
Scenario 3: Multi-tenant services
You may need to isolate the applications of an enterprise that consists of multiple business lines or departments. For example, a financial department requires high security applications. However, other non-security-sensitive applications do not have high security requirements. Containers in runC fail to eliminate the potential risks that occur in untrusted applications. In this scenario, you can implement the following counter measures:
Deploy multiple independent single-tenant clusters. For example, deploy financial business and other non-security-sensitive business in different clusters.
Deploy a multi-tenant cluster and separate applications of different business lines by using namespaces. The resource of a node is exclusive to a single business line. This solution provides data isolation for coordination with the resource quotas and network policies to implement multi-tenant isolation. Compared with multiple single-tenant clusters, this solution focuses on fewer management planes and thus reduces management costs. However, this solution cannot prevent resource waste on nodes caused by the low resource utilization of some tenants.
Sandboxed-Container allows you to isolate untrusted applications by using sandboxed virtual machines. This prevents the risks of container escapes. This also allows you to deploy different containerized applications on each node, which brings the following benefits:
Resource scheduling is simplified.
A node is no longer exclusive to a service. This improves node resource usage and reduces resource fragments and cluster resource costs.
Sandboxed containers use lightweight virtual machines to provide almost the same performance as containers in runC.

Usage notes
The Kubernetes versions of ACK managed clusters and ACK dedicated clusters must be 1.16 or later. For more information about how to upgrade clusters, see Manually upgrade ACK clusters.
Custom images are not supported by node pools that run in sandboxed containers.


