A scaling activity is triggered when a scaling rule is executed or when an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance or elastic container instance is manually added to or removed from a scaling group. After a scaling activity is triggered, Auto Scaling performs the scale-out or scale-in operation. This topic describes the scaling activity process and status. This topic also describes ECS instance rollback. In this topic, a scaling group of the ECS type is used as an example.
Scaling activity processes
Processes of auto-triggered scaling activities
Process of executing a scale-out rule to automatically create ECS instances in a scaling group
Check the health status and boundary values of the scaling group. The boundary values include the minimum number of instances that must be contained in the scaling group and the maximum number of instances that can be contained in the scaling group.
Assign a scaling activity ID and start the scaling activity.
Create ECS instances.
Change the number of instances in the scaling group.
Assign IP addresses to newly created ECS instances.
(Optional) Add the IP addresses of the newly created ECS instances to the IP address whitelist of the associated ApsaraDB RDS instance.
Start the newly created ECS instances.
(Optional) Attach the newly created ECS instances to the associated Classic Load Balancer (CLB) (formerly known as Server Load Balancer or SLB) instance as backend servers and set the CLB weights of the ECS instances based on the scaling configuration.
Complete the scale-out and enable the cooldown period feature.
Process of executing a scale-in rule to remove ECS instances from a scaling group
Check the health status and boundary values of the scaling group. The boundary values include the minimum number of instances that must be contained in the scaling group and the maximum number of instances that can be contained in the scaling group.
Assign a scaling activity ID and start the scaling activity.
(Optional) Detach ECS instances from the associated CLB instance.
Put the ECS instances into the Stopped state.
(Optional) Remove the IP addresses of the ECS instances from the IP address whitelist of the associated ApsaraDB RDS instance.
Release the ECS instances.
Change the number of instances in the scaling group.
Complete the scale-in and enable the cooldown period feature.
Processes of manually-triggered scaling activities
Process of manually adding independent ECS instances to a scaling group
Execute a health check task to check the health status of the scaling group, and also check the boundary values, ECS instance types, and ECS instance status.
Assign a scaling activity ID and start the scaling activity.
Add ECS instances to the scaling group.
Change the number of instances in the scaling group.
(Optional) Add the IP addresses of the newly created ECS instances to the IP address whitelist of the associated ApsaraDB RDS instance.
(Optional) Attach the ECS instances to the associated CLB instance as backend servers and set the CLB weights of the backend servers based on the scaling configuration.
Complete the scale-out and enable the cooldown period feature.
Process of manually removing ECS instances from a scaling group
Check the health status and boundary values of the scaling group. The boundary values include the minimum number of instances that must be contained in the scaling group and the maximum number of instances that can be contained in the scaling group.
Assign a scaling activity ID and start the scaling activity.
(Optional) Stop forwarding traffic to the ECS instances. The ECS instances are detached from the CLB instance after 60 seconds.
(Optional) Remove the IP addresses of the ECS instances from the IP address whitelist of the associated ApsaraDB RDS instance.
Change the number of instances in the scaling group.
Remove the ECS instances from the scaling group.
Complete the scale-in and enable the cooldown period feature.
Scaling activity status
The following table describes the states that a scaling activity may enter.
Status | Description | Example |
Rejected | The request for executing the scaling activity is rejected. No scale-in or scale-out is performed. Note You can click View Rejection Reason in the Status column to learn the cause. | Scenario:
Result: The scaling condition is unmet and the scale-out request is rejected. No subsequent process is followed, and the scaling group still contains 100 ECS instances. |
Executing | The scaling condition is met and the scaling activity is in progress. Auto Scaling adjusts the number of ECS instances that you want to scale based on the boundary values of the scaling group. | Scenario:
Result: The scaling condition is met and the scaling activity is allowed. However, Auto Scaling creates only five ECS instances. After the scale-out is complete, the scaling group contains 100 ECS instances. |
Successful | The scaling activity is complete, and all ECS instances are added to or removed from the scaling group. | Scenario:
Result: The scaling condition is met and the scale-out is allowed. After the scale-out is complete, the scaling group contains 100 ECS instances. |
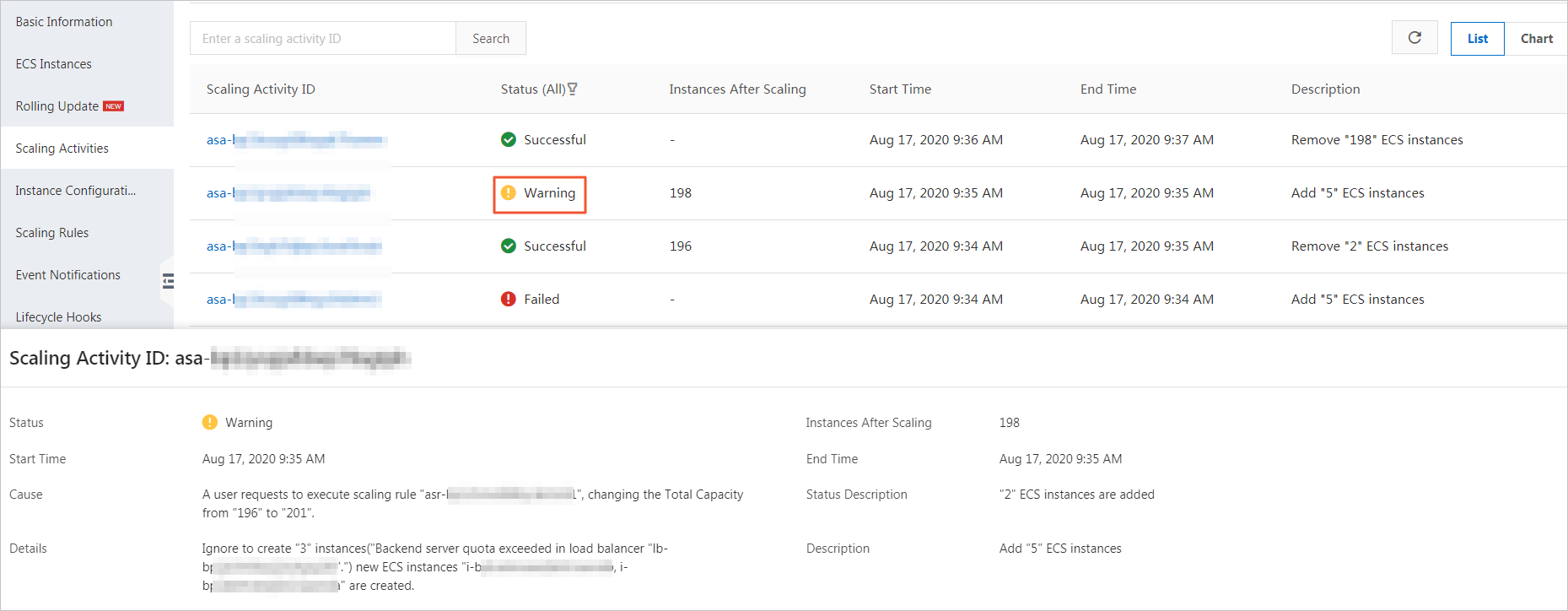
Warning | The scaling activity is complete. However, at least one ECS instance is added to or removed from the scaling group and at least one ECS instance fails to be added to or removed from the scaling group. An ECS instance is considered successfully added to a scaling group only when all the following conditions are met: the ECS instance is created, the ECS instance is attached to the associated CLB instance, and the IP address of the ECS instance is added to the IP address whitelist of the associated ApsaraDB RDS instance. Otherwise, the ECS instance fails to be added to the scaling group. Note If an ECS instance fails to be added to a scaling group, a rollback is triggered. For more information, see ECS instance rollback. | Scenario:
Result: The scaling condition is met and the scale-out is allowed. However, the CLB instance can have a maximum of 200 backend servers. In this case, four ECS instances fail to be attached to the CLB instance and added to the scaling group. After the scale-out is complete, the scaling group contains 200 ECS instances. |
Failed | The scaling activity is complete, but all ECS instances fail to be added to or removed from the scaling group. | Scenario:
Result: The scaling condition is met and the scale-out is allowed. However, instance creation fails due to insufficient instance types. After the scale-out is complete, the scaling group still contains 95 ECS instances. |
ECS instance rollback
If a specific number of ECS instances fail to be added to a scaling group, Auto Scaling continues the scaling operation until the scaling activity is complete. ECS instances that fail to be added to the scaling group are rolled back.
When ECS instances in a scaling group are rolled back, the scaling group does not reach its expected capacity. This means that the scaling group cannot provide the required computing power and maintain monitoring metrics at the required values. In this case, you can use other methods to supplement the number of ECS instances to ensure that the scaling group meets your business requirements. For example, you can manually trigger scaling rules, manually add independent ECS instances to the scaling group, or configure scheduled or event-triggered tasks to trigger scaling activities.
ECS instances that are automatically added
When you call API operations to create ECS instances as a Resource Access Management (RAM) user, you are charged for the rolled-back ECS instances until the ECS instances are released.
For example, you want to add five ECS instances to a scaling group and to the backend server group of the CLB instance that is associated with the scaling group. After you create the five instances, only two instances are added to the scaling group. Three instances fail to be added and are automatically released. Auto Scaling considers the scaling activity complete, even if the status of the scaling activity is Warning.
ECS instances that are manually added
Auto Scaling automatically removes ECS instances that are rolled back from the scaling group. However, the ECS instances that are rolled back are not released.