A streaming domain uses multiple access control policies to prevent unauthorized access and improve the security of your live streaming service. These policies include URL signing, Referer-based hotlink protection, IP address blacklist and whitelist, protocol prohibition, region blocking, and remote authentication. Configure access control policies as needed to protect your live resources.
Overview
To secure your streaming domain and prevent unauthorized use, you can implement several access control policies. Each offers a different layer of protection:
URL signing: Verifies the authenticity of each request using cryptographic signatures, offering the most comprehensive security.
Referer-based hotlink protection: Controls access based on the HTTP Referer header, allowing you to create whitelists of approved domains or blacklists of unauthorized ones.
IP address blacklist and whitelist: Restricts or allows access from specific IP addresses to filter viewers.
Protocol prohibition: Blocks playback from URLs that use a specific streaming protocol.
Region blocking: Allows or restricts viewer access based on their geographical location.
Remote authentication: Enhances flexibility and security by forwarding user requests to your own authentication server for validation.
URL signing
How it works
URL signing prevents hotlinking by coordinating authentication between ApsaraVideo Live and your business server.
Your business server generates a signed URL that contains authentication information.
A user makes a stream ingest or playback request to the ApsaraVideo Live service using this signed URL.
An edge node of ApsaraVideo Live validates the authentication information in the signed URL. The node serves valid requests and denies invalid ones.
After ApsaraVideo Live authenticates your request URL, it escapes special characters in the URL, such as = and +.
To learn more about use cases, the structure of a signed URL, and the signing mechanism, see Signed ingest and streaming URLs.
Configure URL signing
- Log on to the ApsaraVideo Live console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Domain Names. The Domain Management page appears.
Find the streaming domain that you want to configure and click Domain Settings in the Actions column.
Choose .
Click the URL Signing tab and click Modify.
 Note
NoteURL signing is enabled by default when you first add a domain. Modification is supported only when the feature is enabled.
Configure the URL signing parameters and click OK.
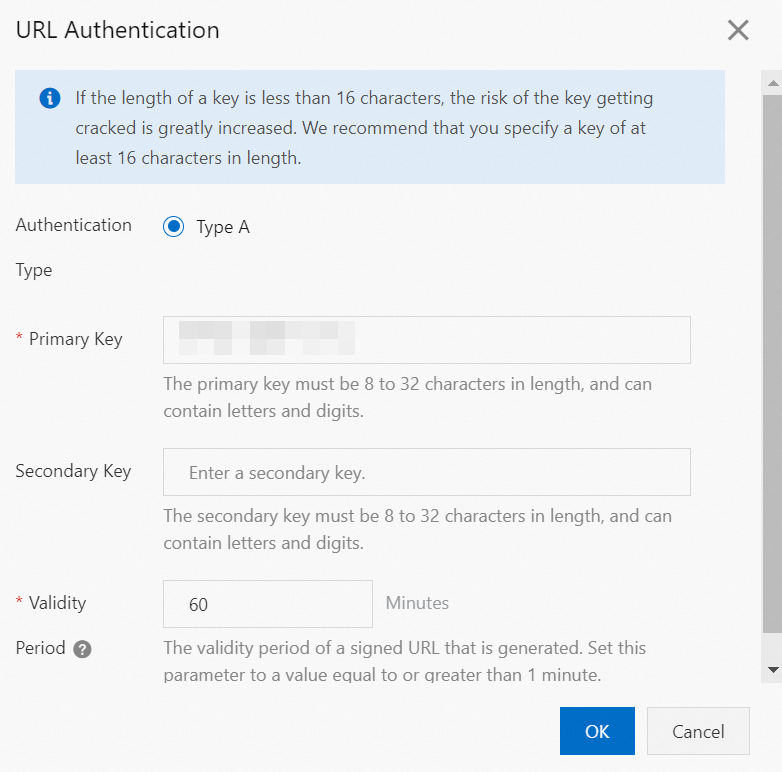
The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Authentication Type
ApsaraVideo Live only supports Authentication Type A to protect your origin resources.
NoteAn invalid URL signing request returns a 403 error. Please recalculate the signature.
Invalid MD5 values
Example:
X-Tengine-Error:denied by req auth: invalid md5hash=de7bfdc915ced05e17380a149bd760beInvalid timestamps
Example:
X-Tengine-Error:denied by req auth: expired timestamp=1439469547
Primary Key
When you add a domain, the console randomly generates a primary key. You can view the primary key on the URL Signing tab of the Access Control page. You can also enter a custom primary key for your chosen authentication method.
Secondary Key
Enter a custom secondary key for your chosen authentication method.
NoteThe primary and secondary keys have the same authentication permissions. The secondary key is mainly used for smooth key rotation.
If you change the primary key, all signed URLs generated with the old key will become invalid. To avoid service interruptions, copy the current primary key to the secondary key field before creating a new primary key. This process ensures that requests signed with the old key remain valid during the transition.
Validity Period
The period during which a signed URL can be used to initiate a playback request. Stream playback is long-lived connection. An active connection will not be terminated when the validity period expires. However, new requests made with the expired URL will fail. The default validity period for a new domain is 1 day (1440 minutes). You can set a custom validity period with a minimum of 1 minute and no upper limit.
Disable URL signing
Before you disable URL signing, understand the risks of unauthorized traffic and sign the disclaimer agreement.
After you disable URL signing, you can generate streaming URLs that never expire.
On the URL Signing tab, turn off the switch.
In the dialog box, select the check box and click Disable URL Signing.
After the feature is disabled, you can no longer encrypt URLs by setting an authentication key.
Referer-based hotlink protection
How it works
Referer-based hotlink protection identifies the source of requests by using the Referer header in the HTTP protocol. It supports a blacklist or a whitelist mechanism. ApsaraVideo Live edge nodes filter viewers based on your configured list. Requests from sources that match the rules are granted access, while others receive a 403 response.
Hotlink protection is an optional feature and is disabled by default.
The blacklist and whitelist are mutually exclusive.
After you configure hotlink protection, ApsaraVideo Live automatically supports wildcard domain names. For example, if you enter
example.com, the rule applies to*.example.com, covering all its subdomains.You can choose whether to allow requests with an empty Referer field, which permits direct access to a resource URL from a browser's address bar.
Because mobile clients often cannot retrieve a Referer, empty Referer requests are allowed by default. If you choose not to allow empty Referer requests, you can use the ApsaraVideo Player SDK to set a Referer on mobile clients.
If you do not allow empty Referer requests, you must configure HTTPS Secure Acceleration and enable forced redirection from HTTP to HTTPS. Some browsers remove the Referer header when handling HTTPS requests for HTTP resources, which would cause access to fail.
Procedure
- Log on to the ApsaraVideo Live console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Domain Names. The Domain Management page appears.
Find the streaming domain that you want to configure and click Domain Settings in the Actions column.
Click .
Click the Referer-based Hotlink Protection tab and turn on the feature.
Configure Type and Referrers, and click OK.
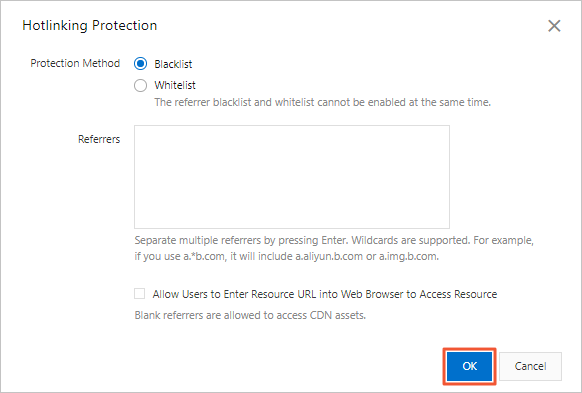
Type
Description
Blacklist
Domains on the blacklist cannot access the resource.
Whitelist
Only domains on the whitelist can access the resource. Other domains are blocked.
IP address blacklist and whitelist
How it works
Add an IP address to a blacklist to block it from accessing the streaming domain.
Add an IP address to a whitelist to allow only that IP address to access the streaming domain.
The IP address blacklist and whitelist both support IPv6 addresses. Only uppercase letters are supported in IPv6 addresses, for example,
2001:DB8:0:23:8:800:200C:417Aor2001:0DB8:0000:0023:0008:0800:200C:417A. IPv6 addresses in abbreviated format, such as2001:0DB8::0008:0800:200C:417A, are not supported.You can add IP address ranges to the blacklist and whitelist. For example,
192.168.0.0/24represents the IP address range from192.168.0.1to192.168.0.254.
Procedure
- Log on to the ApsaraVideo Live console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Domain Names. The Domain Management page appears.
Find the streaming domain that you want to configure and click Domain Settings in the Actions column.
Click the IP Blacklist or Whitelist tab and turn on the feature.
Configure List Type and Rule, and click OK.
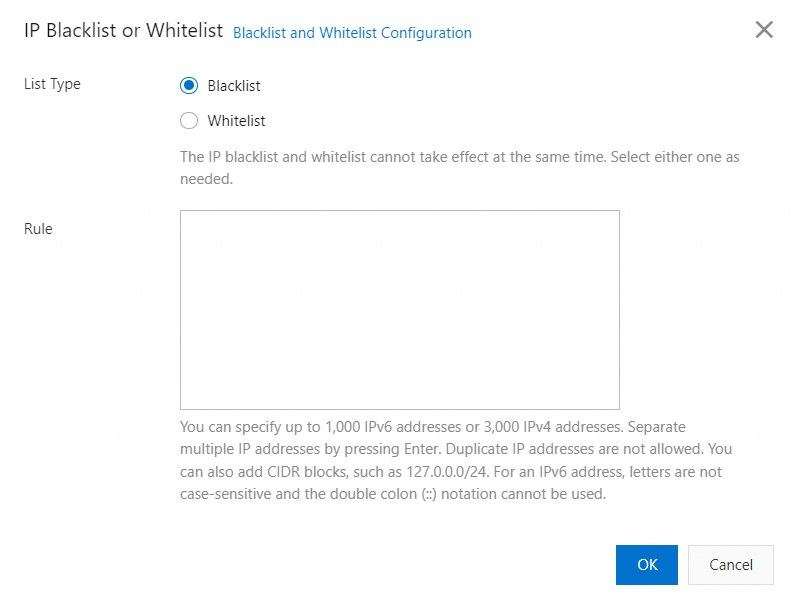
List type
Description
Blacklist
IP addresses on the blacklist cannot access the resource.
Whitelist
Only IP addresses on the whitelist can access the resource. All other IP addresses are blocked.
Choose .
Protocol prohibition
How it works
Protocol prohibition lets you block playback at the protocol level for a streaming domain (including primary and subdomains). When enabled, playback requests that use a prohibited protocol are blocked.
You can also call the BatchSetLiveDomainConfigs API operation and pass the alilive record in the Functions parameter. For more information, see BatchSetLiveDomainConfigs.
Procedure
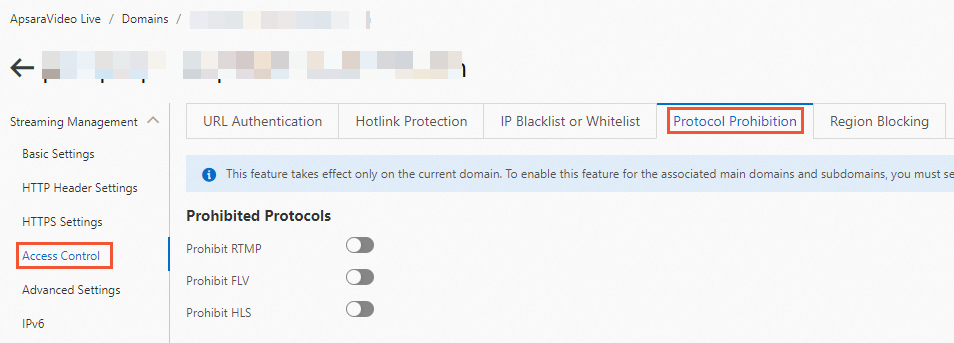
Log on to the ApsaraVideo Live console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Domain Names. The Domain Management page appears.
Find the streaming domain that you want to configure and click Domain Settings in the Actions column.
Click the Protocol Prohibition tab, select the protocol that you want to prohibit.
Choose .
Region blocking
How it works
Region blocking identifies the source region of client access requests. This lets you block or allow only access from specific regions, helping you address issues like malicious requests from certain areas or content distribution rights.
Region blocking is currently supported for HLS, RTMP, FLV, and RTS protocols.
If you configure a domain-level whitelist and a stream-level blacklist for the same region, the stream-level blacklist takes effect. If you configure a domain-level blacklist and a stream-level whitelist for the same region, the domain-level blacklist takes effect.
You can set both domain-level and stream-level region blocking. If the blacklist and whitelist settings conflict, the blacklist configuration takes precedence in determining the blocked regions.I
Configure domain-level region blocking
Log on to the ApsaraVideo Live console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Domain Names. The Domain Management page appears.
Find the streaming domain that you want to configure and click Domain Settings in the Actions column.
On the Region Blocking tab, turn on the Domain-level Region Blocking switch, and select Blocking Type and Blocked Regions.
Parameter
Description
Blocking Type
Blacklist:Regions on the blacklist cannot access any resources under the streaming domain.
Whitelist: Only regions on the whitelist can access resources under the streaming domain. All other regions are blocked.
The blacklist and whitelist are mutually exclusive. Only one can be active at a time.
Blocked Regions
The regions to include on the blacklist or whitelist.
Click OK to complete the configuration.
Choose .
Configure stream-level region blocking
Log on to the ApsaraVideo Live console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Domain Names. The Domain Management page appears.
Find the streaming domain that you want to configure and click Domain Settings in the Actions column.
Click the Region Blocking tab and click Add Rule under Stream-level Region Blocking.
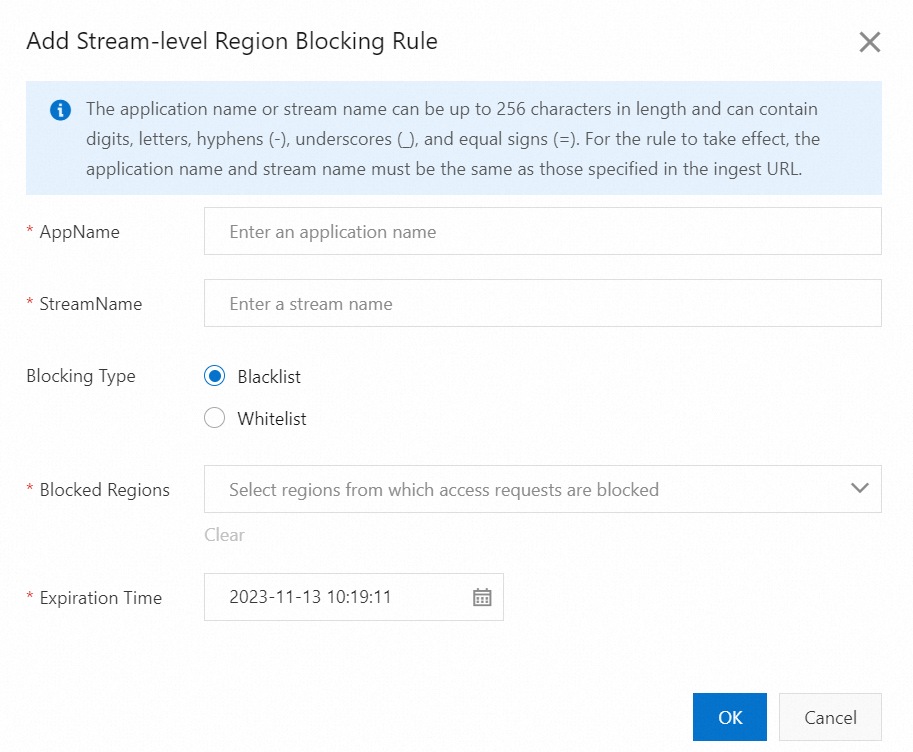
Parameter
Description
AppName
The AppName of the live stream.
NoteThe AppName can be up to 256 characters long and can contain digits, letters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and equal signs (=). It must match the AppName in the live stream URL for the blocking rule to take effect.
StreamName
The name of the live stream.
NoteThe StreamName can be up to 256 characters long and can contain digits, letters, hyphens (-), underscores (_), and equal signs (=). It must match the StreamName in the live stream URL for the blocking rule to take effect.
Blocking Type
Blacklist: Viewers from regions on the blacklist cannot access the specified stream.
Whitelist: Only viewers from regions on the whitelist can access the specified stream.
NoteThe blacklist and whitelist are mutually exclusive. Only one can be active at a time.
Blocked Regions or Allowed Regions
The regions to include on the blacklist or whitelist.
Expiration Time
The time when the blocking rule expires. By default, a blocking rule is valid for seven days, but you can adjust this as needed.
Click OK to complete the configuration.
View the list of stream-level region blocking rules. After configuring a rule, you can refresh the list to see its status. You can filter the list by blacklist/whitelist, AppName, or StreamName.
Choose .
Remote authentication
How it works
Both remote authentication and URL signing protect live stream resources by ensuring that only authorized users can access them. They differ in their technical implementation:
URL signing: You configure authentication rules in the live center, which then handles the entire authentication process.
Remote authentication: You maintain a dedicated authentication server. The live center forwards requests to your server for validation. Remote authentication is not supported for the HLS protocol.
The data flow for remote authentication is as follows:

Step | Description |
1 | A user sends a resource access request that contains authentication parameters to the live center. |
2 | The live center receives the request and forwards it to your authentication server, either directly or after applying specified rules. |
3 | Your authentication server validates the parameters in the request, determines the authentication result, and returns it to the live center. |
4 | The live center takes action based on the result from your server and returns the corresponding data to the user.
|
Procedure
- Log on to the ApsaraVideo Live console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Domain Names. The Domain Management page appears.
Find the streaming domain that you want to configure and click Domain Settings in the Actions column.
Click the Remote Authentication tab, turn on the switch, and configure the parameters as prompted.
NoteWhen remote authentication is enabled, every user request is forwarded to your authentication server. If you expect a high volume of requests, consider the load and performance of your authentication server.
Parameter
Description
Authentication Server Address
The publicly accessible address of your authentication server. The system validates the format and value of the address you enter. You can set a fixed URL or a URL with concatenated variables.
Fixed URL: Supports HTTP(S). The value cannot contain
127.0.0.1orlocalhost, as these are invalid local addresses.Valid formats include:http(s)://example.aliyundoc.com/authhttp(s)://192.0.2.1/auth.
URL with concatenated variables: You can generate the authentication URL by concatenating variables. For details on the rules for concatenating variables, see URL variable concatenation.
Pass Through URL Parameters
Controls which parameters from the user's request URL are included in the authentication request. Valid values: Specified Parameters Passed, Specified Parameters Not Passed, and None.
NoteIf you select Specified Parameters Passed or Specified Parameters Not Passed, enter the parameters in the input box, separated by commas (,). For example:
key1,key2,key3.HTTP Status Code to Return
The HTTP status code that your authentication server returns to the live center upon successful authentication. You can set one of the following:
Successful Authentication: Enter a custom status code for success. The live center allows requests only if your server returns this code. All other status codes block the request.
For example, if you set the success code to 200, a 200 response means authentication is successful.
Failed Authentication: Enter a custom status code for failure. The live center blocks the user request only if the authentication server returns this specific code. All other status codes will result in the request being allowed.
For example, if you set the failure code to 403, a 403 response means authentication has failed.
Authentication Duration (s)
The timeout for the authentication server to respond to a request from the live center.
The duration can be an integer from 0 to 30.Retries on Timeout
The number of times the live center will retry the request to the authentication server after the authentication duration is exceeded. After the specified number of retries, the system will perform the Action After Authentication Timeout.
Action After Timeout
The action the live center takes if the data exchange with the authentication server times out. The available actions are Allow and Deny.
Allow: If authentication times out, the live center directly allows the user request.
Deny: If authentication times out, the live center rejects the user request and returns an authentication failure status code (such as 403) to the user.
Asynchronous Authentication
When enabled, playback starts immediately without waiting for the remote authentication result. If the authentication fails, the connection is then terminated. This avoids increased first-frame latency caused by synchronous remote authentication.
Click OK to complete the parameter configuration.
After successfully configuring remote authentication, you can modify the settings or disable the feature on the Remote Authentication tab.
Choose .
URL variable concatenation
You can generate the authentication URL by concatenating variables. The details are as follows:
Type | Description |
Numeric variables | Numeric variables, such as |
Alphabetic variables | Alphabetic variables, such as |
Custom variables | Custom variables start with the |
NGX variables | All |
Stream name variables | You can add variables in the format |
Suppose the streaming URL is rtmp://domain.aliyundoc.com/app/stream?token=***&name=xrc.
And the remote authentication server address is configured as http://auth.aliyundoc.com/?app=${udv_host}&streamname=${2}&appname=${1}&token=${arg_token}.
Then, the actual authentication URL sent will be http://auth.aliyundoc.com/?app=domain.aliyundoc.com&streamname=stream&appname=app&token=***.