If you need to provide encrypted access over the secure HTTPS protocol, you can enable HTTPS by using a Service Mesh (ASM) ingress gateway. ASM allows you to enable dynamic certificate loading by using an ingress gateway. This way, you can dynamically configure private keys, server certificates, and root certificates in real time, and you do not need to restart ingress gateways or mount secret volumes. This simplifies operations and eliminates the risk of service interruptions caused by restarts of ingress gateways. An ingress gateway allows you to monitor and manage multiple certificates and their private keys. This provides flexible and secure communication capabilities for different hosts to enhance the security of data transmission.
Prerequisites
Background information
Istio supports dynamic certificate loading. You can configure the private key, server certificate, and root certificate that are required for Transport Layer Security (TLS), without the need to restart the ingress gateway. The ingress gateway listens to the secret that is in the same namespace as the ingress gateway and dynamically loads the secret by using a Gateway resource. You can obtain the following benefits by enabling HTTPS for an ingress gateway:
The ingress gateway can dynamically add, delete, and update the server certificate and private key or the root certificate as required without the need to be restarted.
No secret volume needs to be mounted. After a Kubernetes secret is created, the ingress gateway can obtain the server certificate and private key or the root certificate stored in the secret.
If you create secrets for multiple hosts and update the Istio gateway (Gateway resource), the ingress gateway can listen to multiple server certificates and private key pairs.
Step 1: Prepare server certificates and private keys for multiple servers
A domain name is accessible only after it has obtained an Internet Content Provider (ICP) filing. Create a server certificate and a private key for the aliyun.com domain name and store the server certificate and private key in a secret.
If you have an available server certificate and private key for the aliyun.com domain name, rename the private key to aliyun.com.key and the server certificate to aliyun.com.crt. Alternatively, run the following openssl commands to create a server certificate and a private key for aliyun.com.
Run the following command to create a root certificate and a private key:
openssl req -x509 -sha256 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -subj '/O=myexample Inc./CN=aliyun.com' -keyout aliyun.root.key -out aliyun.root.crtRun the following commands to create a certificate and a private key for the server of aliyun.com:
openssl req -out aliyun.com.csr -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout aliyun.com.key -subj "/CN=aliyun.com/O=myexample organization" openssl x509 -req -days 365 -CA aliyun.root.crt -CAkey aliyun.root.key -set_serial 0 -in aliyun.com.csr -out aliyun.com.crtCreate a secret or certificate based on the version of your ASM instance.
For an ASM instance of a version earlier than 1.17
Use kubectl to connect to the cluster to which the ingress gateway pod belongs, and run the following command to create a secret that contains the certificate and private key in the istio-system namespace:
kubectl create -n istio-system secret tls myexample-credential --key=aliyun.com.key --cert=aliyun.com.crtImportantThe secret name cannot start with istio or prometheus and cannot contain the token field.
For an ASM instance of version 1.17 or later
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Certificate Management page, click Create. In the Certificate Information panel, configure the required parameters and click OK.
Parameter
Description
Name
Enter the name of the certificate. For this example, enter myexample-credential.
Public Key Certificate
Enter the content of the
aliyun.com.crtcertificate that is generated in Substep 2.Private Key
Enter the content of the
aliyun.com.keyprivate key that is generated in Substep 2.
Step 2: Define an internal service for a.aliyun.com
The internal service in this example is implemented based on NGINX. You must create a configuration file for the NGINX server first. In this example, an internal service is created for the a.aliyun.com domain name. Define the requested root path to directly return the sentence Welcome to a.aliyun.com! and status code 200. The myexample-nginx.conf NGINX configuration file contains the following content:
events {
}
http {
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] $status '
'"$request" $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
server {
listen 80;
location /hello {
return 200 'Welcome to a.aliyun.com!';
add_header Content-Type text/plain;
}
}
}In the cluster to which the ingress gateway pod belongs, run the following command to create a ConfigMap for storing the configuration of the NGINX server:
kubectl create configmap myexample-nginx-configmap --from-file=nginx.conf=./myexample-nginx.confEnable automatic sidecar proxy injection for the default namespace. For more information, see Enable automatic sidecar proxy injection.
Create a myexampleapp.yaml file that contains the following content. Then, run the
kubectl apply -f myexampleapp.yamlcommand to create an internal service for the a.aliyun.com domain name.
Step 3: Define an internal service for b.aliyun.com
The internal service in this example is implemented based on HTTPBin.
Create an httpbin.example.yaml file that contains the following content:
In the cluster to which the ingress gateway pod belongs, run the following command to create an internal service for the b.aliyun.com domain name:
kubectl apply -f httpbin.example.yaml
Step 4: Create an Istio gateway
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, click Create from YAML.
On the Create page, select a namespace (the default namespace in this example) and a scenario template, configure the following YAML code, and then click Create:
On the Gateway page, you can view the created Istio gateway.
Step 5: Create virtual services
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, click Create from YAML.
On the Create page, select a namespace and a scenario template, configure the following YAML code, and then click Create to create a virtual service for a.aliyun.com:
Create a virtual service for b.aliyun.com in a similar way.
On the VirtualService page, you can view the created virtual services.
View the result
Use one of the following methods to obtain the IP address of the ingress gateway
Method 1: View the IP address of the ingress gateway in the ASM console. Log on to the ASM console and find the desired Service Mesh instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the Ingress Gateway page, you can view the IP address of the ingress gateway.
Method 2: View the IP address of the ingress gateway in the ACK console. For more information, see the "View the ingress gateway in the ACK console" section of the Create an ingress gateway topic.
Access the ingress gateway
Run the following command to access the a.aliyun.com domain name over HTTPS:
curl -k -H Host:a.aliyun.com --resolve a.aliyun.com:443:{IP address of the ingress gateway} https://a.aliyun.com/helloExpected output:
Welcome to aliyun.com!Run the following command to access the b.aliyun.com domain name over HTTPS:
curl -k -H Host:b.aliyun.com --resolve b.aliyun.com:443:{IP address of the ingress gateway} https://b.aliyun.com/status/418Expected output:
-=[ teapot ]=- _...._ .' _ _ `. | ."` ^ `". _, \_;`"---"`|// | ;/ \_ _/ `"""`
Related operations
Update a gateway certificate
To update the certificate mounted to an ingress gateway, you must create a secret on the data plane and change the value of the credentialName field in the YAML code of the Istio gateway to the name of the secret. Then, the new secret is automatically mounted to the gateway. In the following example, the secret named new-istio-ingressgateway-certs is created for the server of example.com.
Create a certificate whose issuer is myexample.
Run the following openssl command to create a root certificate and a private key:
openssl req -x509 -sha256 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -subj '/O=myexample Inc./CN=example.com' -keyout example.root.key -out example.root.crtRun the following commands to create a certificate and a private key for the server of example.com:
openssl req -out example.com.csr -newkey rsa:2048 -nodes -keyout example.com.key -subj "/CN=example.com/O=myexample organization" openssl x509 -req -days 365 -CA example.root.crt -CAkey example.root.key -set_serial 0 -in example.com.csr -out example.com.crtObtain the kubeconfig file of the cluster and use kubectl to connect to the cluster. For more information, see Obtain the kubeconfig file of a cluster and use kubectl to connect to the cluster.
Run the following command to create a secret named new-istio-ingressgateway-certs:
kubectl create -n istio-system secret tls new-istio-ingressgateway-certs --key example.com.key --cert example.com.crt
Run the following command in the cluster to delete the earlier secret:
kubectl delete secret istio-ingressgateway-certs -n istio-systemUpdate the Istio gateway.
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Gateway page, find the gateway that you want to update and click YAML in the Actions column.
In the Edit dialog box, change the value of credentialName to new-istio-ingressgateway-certs, and click OK.
Verify that the gateway certificate is updated.
Run the following command in the cluster to view the current certificate information:
kubectl exec istio-ingressgateway-xxxx -n istio-system -- curl localhost:15000/config_dump > ingressgateway_dump.yamlRun the following command to search for and display the new-istio-ingressgateway-certs certificate:
cat ingressgateway_dump.yaml | grep new-istio-ingressgateway-certs -A 3Expected output:
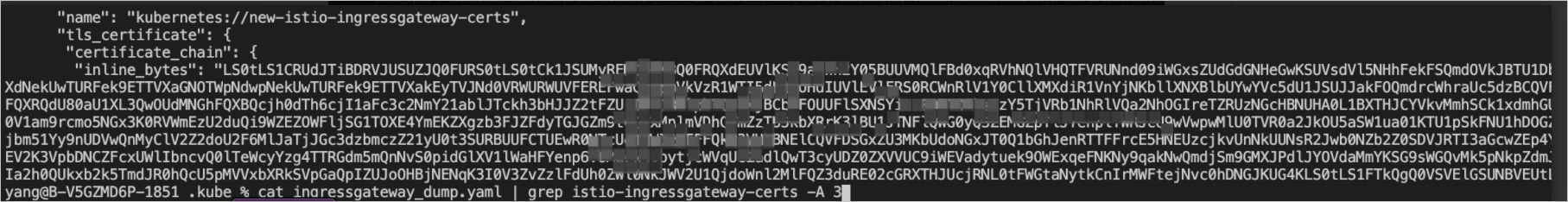
Copy the content of the inline_bytes parameter to obtain the Base64-encoded certificate.
Run the following command in your local command-line tool to decode the Base64-encoded certificate:
echo <Base64-encoded certificate> | base64 --decodeSave the decoded content as the test.com.crt file.
Run the following openssl command to view the organization of the certificate:
openssl x509 -in test.com.crt -text -nooutExpected output:
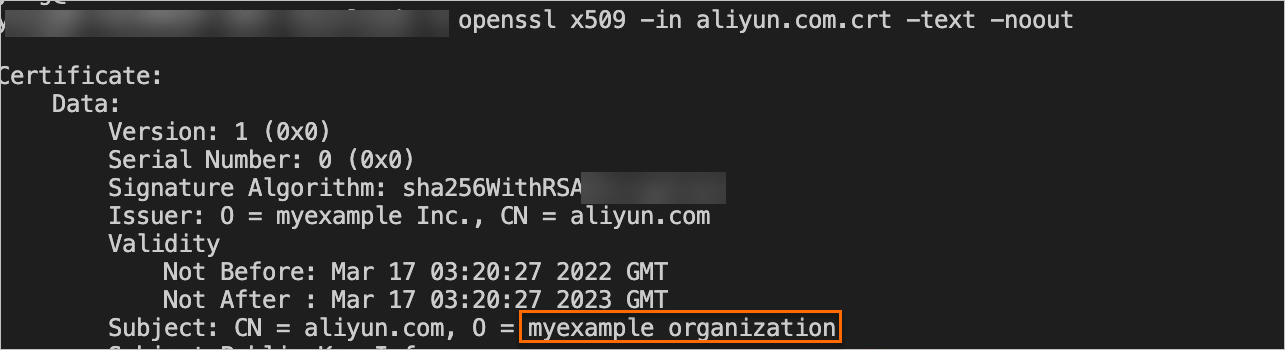
The organization is changed to
myexample. This indicates that the gateway certificate is updated.