Argo Rollouts is a Kubernetes controller and includes a set of CustomResourceDefinition (CRDs). You can integrate Service Mesh (ASM) with Argo Rollouts to provide more powerful capabilities for canary releases. If you want to update an application in a Kubernetes environment and reduce the risk associated with each new application update, you can integrate ASM with Argo Rollouts to implement canary release. In this way, you can gradually push new versions of the application to users in batches and observe the performance of these versions in real time. This helps you effectively control risks, guarantee service stability and user experience, and successfully iterate versions while ensuring business continuity.
Prerequisites
An ASM instance whose version is 1.12.4.50 or later is created. For more information, see Create an ASM instance.
The cluster is added to the ASM instance. For more information, see Add a cluster to an ASM instance.
The ASM instance is connected by using kubectl. For more information, see Use kubectl on the control plane to access Istio resources.
Preparations
Install Argo Rollout
To install Argo Rollouts, perform the following steps. For more information, see Installation.
Run the following commands to install the Argo Rollouts server:
kubectl create namespace argo-rollouts kubectl apply -n argo-rollouts -f https://github.com/argoproj/argo-rollouts/releases/latest/download/install.yamlRun the following command to install the Argo Rollout kubectl plug-in.
The Argo Rollouts kubectl plug-in can provide kubectl-based management.
brew install argoproj/tap/kubectl-argo-rollouts
Enable access to the Istio resources of the ASM instance on the data plane by using the Kubernetes API
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Click Enable to the right of Enable Data-plane KubeAPI access.
In the message that appears, click OK.
Implement a canary release
The following example shows you how to create a stable version and a canary release version and how to progressively switch traffic from the stable version to the canary release version to implement a canary release based on the traffic ratio. For more information about canary release, see Configure a canary release.
Step 1: Create the Rollout and service applications
Create a rollout.
Create a rollout.yaml file that contains the following content:
The
strategyfield defines the canary release policy. The following content describes the setWeight and pause parameters under the strategy field:setWeight: the weight of traffic to be routed to the canary release version.pause: pauses the Rollout. If nodurationis specified for a pause step, the Rollout needs to be manually updated. If thedurationis specified for a pause step, the system automatically updates the Rollout after the specifieddurationends.
Run the following command to deploy the Rollout to the cluster that is added to your ASM instance:
kubectl apply -f rollout.yaml
Create a service.
Create a service.yaml file that contains the following content:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: istio-rollout-canary spec: ports: - port: 80 targetPort: http protocol: TCP name: http selector: app: istio-rollout --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: istio-rollout-stable spec: ports: - port: 80 targetPort: http protocol: TCP name: http selector: app: istio-rolloutRun the following command to deploy the service to the cluster that is added to your ASM instance:
kubectl apply -f service.yaml
Step 2: Create related Istio resources
Create a virtual service named istio-rollout-vsvc.
You have enabled access to the Istio resources of the ASM instance on the data plane by using the Kubernetes API. Therefore, you can use the kubeconfig file on the data plane to access Istio resources such as virtual services, Istio gateways, and destination rules. Alternatively, you can use the ASM console or a kubeconfig file to create Istio resources.
Create an istio-rollout-vsvc.yaml file that contains the following content:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3 kind: VirtualService metadata: name: istio-rollout-vsvc spec: gateways: - istio-rollout-gateway hosts: - '*' http: - match: - uri: prefix: / name: primary route: - destination: host: istio-rollout-stable weight: 100 - destination: host: istio-rollout-canaryRun the following command to deploy istio-rollout-vsvc:
kubectl apply -f istio-rollout-vsvc.yaml
Create an Istio gateway named istio-rollout-gateway.
Create an istio-rollout-gateway.yaml file that contains the following content:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1 kind: Gateway metadata: name: istio-rollout-gateway spec: selector: istio: ingressgateway servers: - hosts: - '*' port: name: http number: 80 protocol: HTTPRun the following command to deploy istio-rollout-gateway:
kubectl apply -f istio-rollout-gateway.yaml
Step 3: Deploy an ingress gateway
Create an ingress gateway for which port 80 is enabled for service access test.
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Ingress Gateway page, click Create. Set the parameters of the ingress gateway and click Create.
The following table describes only some parameters of the ingress gateway. For more information about other parameters of an ingress gateway, see Create an ingress gateway.
Parameter
Description
Name
The name of the ingress gateway. For this example, set the parameter to ingressgateway.
Gateway types
The type of the ingress gateway. For this example, set the parameter to North-South IngressGateway.
Port Mapping
The port mappings of the ingress gateway. Click Add Port. In the row that appears, set the Protocol parameter to HTTP and the Service Port parameter to 80.
Step 4: View the status of the Rollout
Run the following command to view the status of the Rollout:
kubectl argo rollouts get rollout istio-rolloutExpected output:
kubectl argo rollouts get rollout istio-rollout
Name: istio-rollout
Namespace: default
Status: Healthy
Strategy: Canary
Step: 18/18
SetWeight: 100
ActualWeight: 100
Images: argoproj/rollouts-demo:blue (stable)
Replicas:
Desired: 1
Current: 1
Updated: 1
Ready: 1
Available: 1
NAME KIND STATUS AGE INFO
⟳ istio-rollout Rollout Healthy 52s
└──# revision:1
└──⧉ istio-rollout-7f96d86486 ReplicaSet Healthy 52s stable
└──□ istio-rollout-7f96d86486-vpqvb Pod ✔ Running 52s ready:2/2Step 5: Test the initial status of the Rollout
Obtain the IP address of the ingress gateway.
Log on to the ASM console. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Mesh Management page, click the name of the ASM instance. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Obtain the Service address of the ingress gateway.
Use a browser to access http://{IP address of the ingress gateway}/.
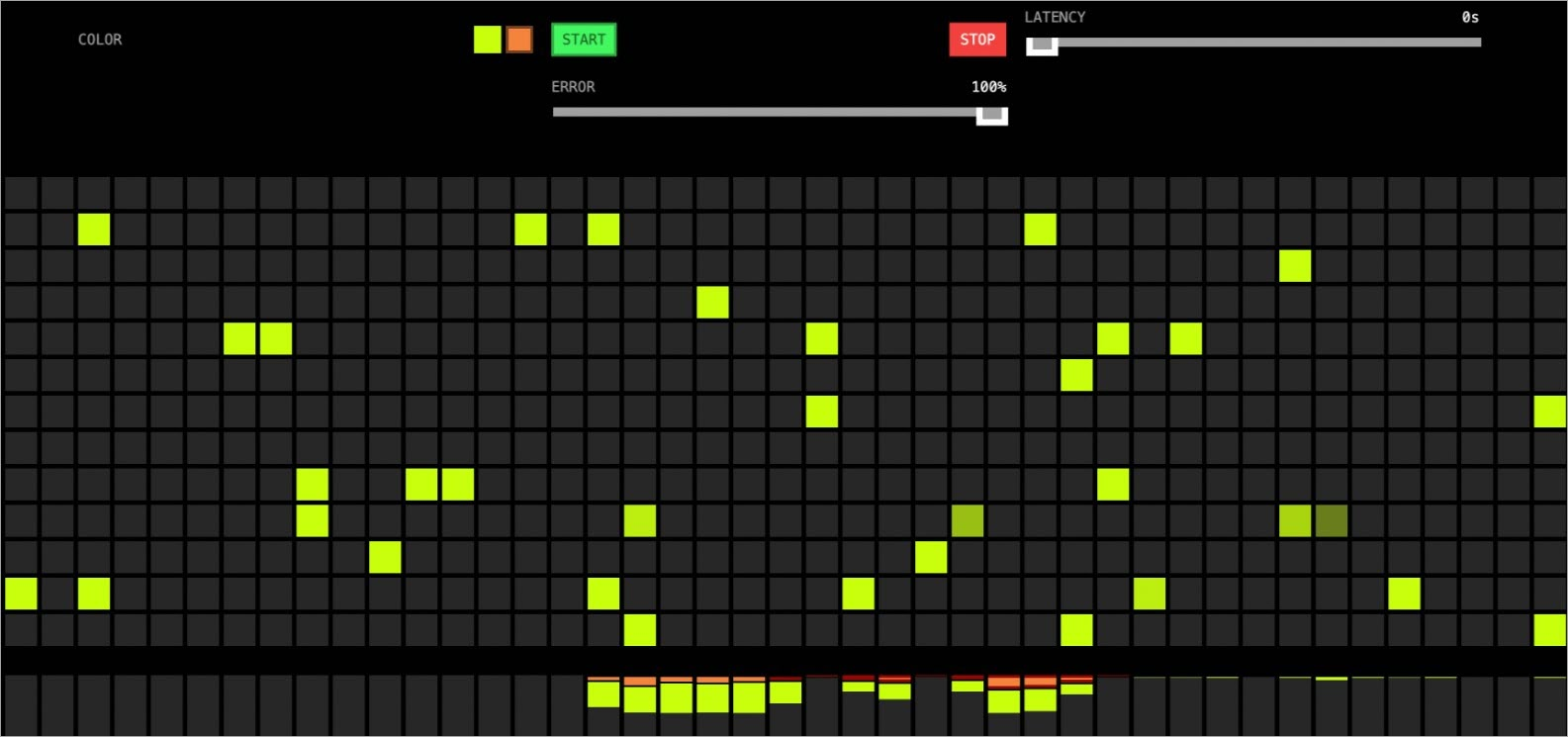
The following figure shows the access result. Concurrent calls to http://{IP address of the ingress gateway}/color are invoked on this page to fill the grids with the obtained color. The color specified in Rollout istio-rollout is
blue, and the canary release is not started. Therefore, the blue color is displayed.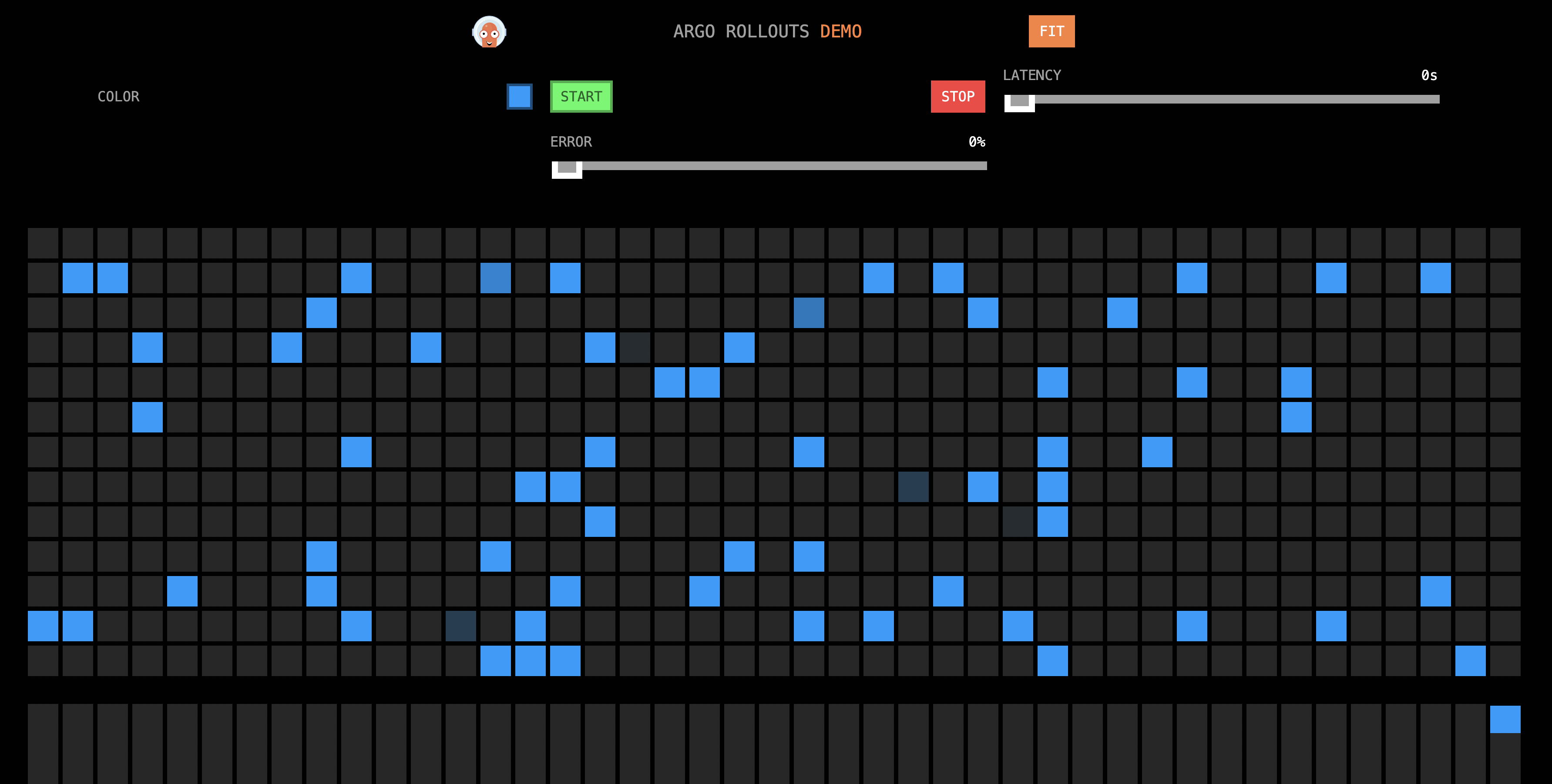
Step 6: Update the Rollout
In this example, yellow is used to indicate a canary release version. When the color of the grids on the http://{IP address of the ingress gateway}/ page changes from blue to yellow, a canary release is implemented.
Update the image version of the container for the Rollout.
Run the following command to update the image version:
kubectl argo rollouts set image istio-rollout "*=argoproj/istio-rollout:yellow"View the image versions of corresponding containers.
Log on to the ACK console and click Clusters in the left-side navigation pane.
On the Clusters page, click the name of the cluster that you want to manage and choose in the left-side navigation pane.
In the Name column, view the image versions of corresponding containers.
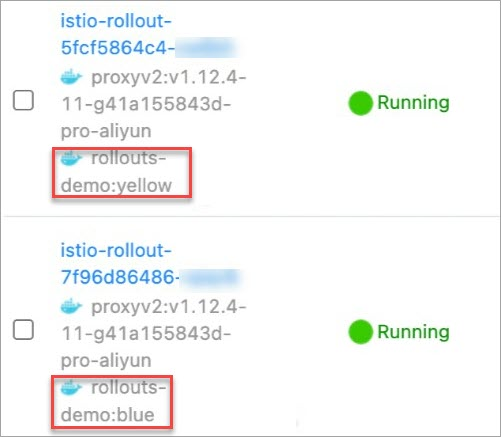
The pod in which the yellow version (canary release version) runs is created, but the pod in which the blue version (stable version) runs also exists, as shown in the following figure.
Use a browser to access http://{IP address of the ingress gateway}/.
The result shows that 10% of the blue grids are changed to yellow, as shown in the following figure.
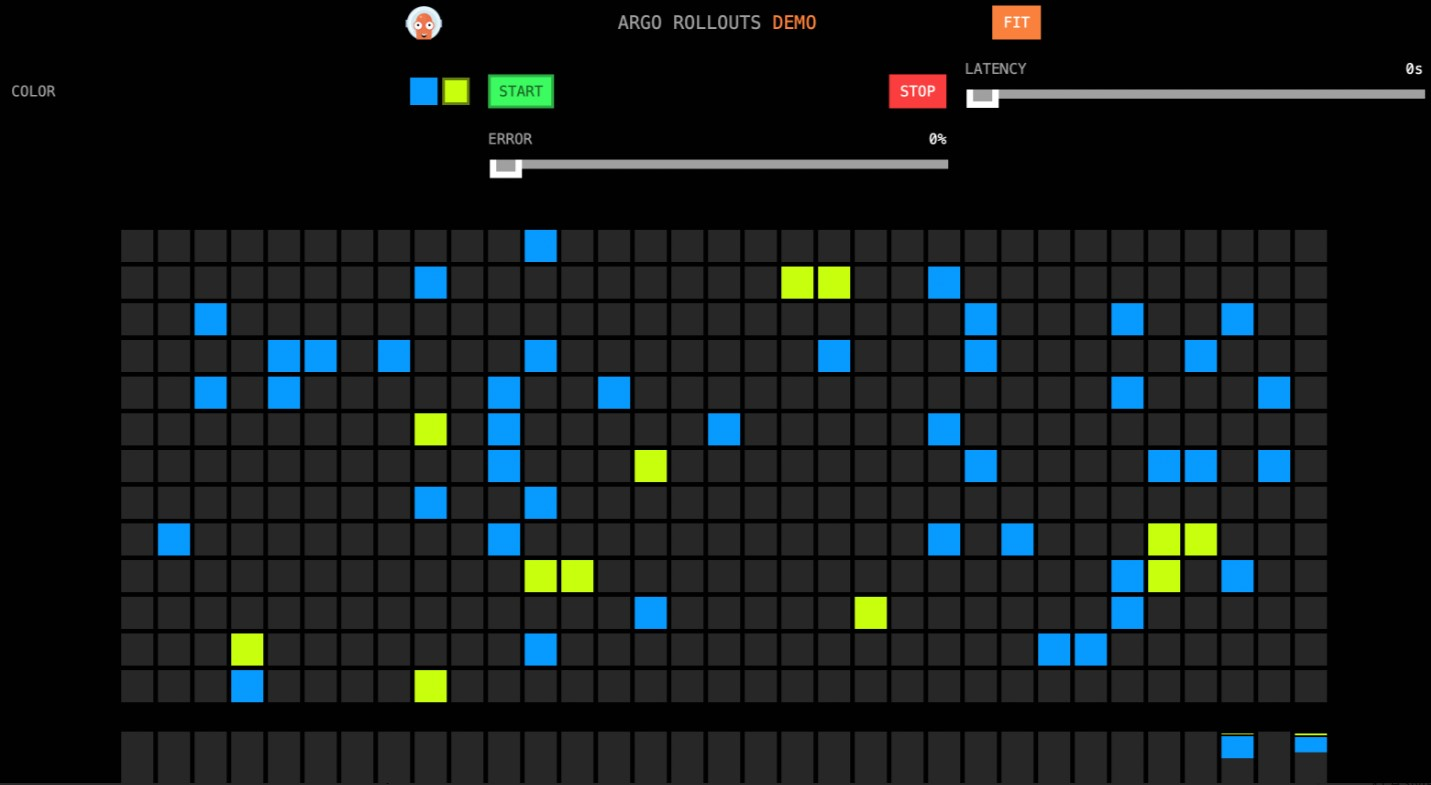 This is because the traffic weight of the configured virtual service changes. Specifically, the traffic weight of the stable version (blue version) changes from 100 to 90, whereas the traffic weight of the canary release version (yellow version) changes from 0 to 10. The Rollout controls the traffic weight of the virtual service. The traffic weight that you specified for the canary release version in the first step is set to
This is because the traffic weight of the configured virtual service changes. Specifically, the traffic weight of the stable version (blue version) changes from 100 to 90, whereas the traffic weight of the canary release version (yellow version) changes from 0 to 10. The Rollout controls the traffic weight of the virtual service. The traffic weight that you specified for the canary release version in the first step is set to 10when the Rollout is created. Therefore, when the Rollout starts, the Argo Rollouts controller changes the traffic weight configured for the virtual service in the Rollout accordingly. In addition, thepauseparameter is left empty. This means that the Rollout needs to be manually confirmed to proceed to the next stage.Continue the canary release.
Run the following command to continue the canary release:
kubectl argo rollouts promote istio-rolloutUse a browser to access http://{IP address of the ingress gateway}/.
The following figure shows the result. The traffic weight of the virtual service continues to be adjusted based on the configuration in the Rollout. In this stage, the
pauseduration is specified. For more information, see Step 1. Therefore, the system automatically adjusts the traffic weight of the virtual service after the specified pause duration ends.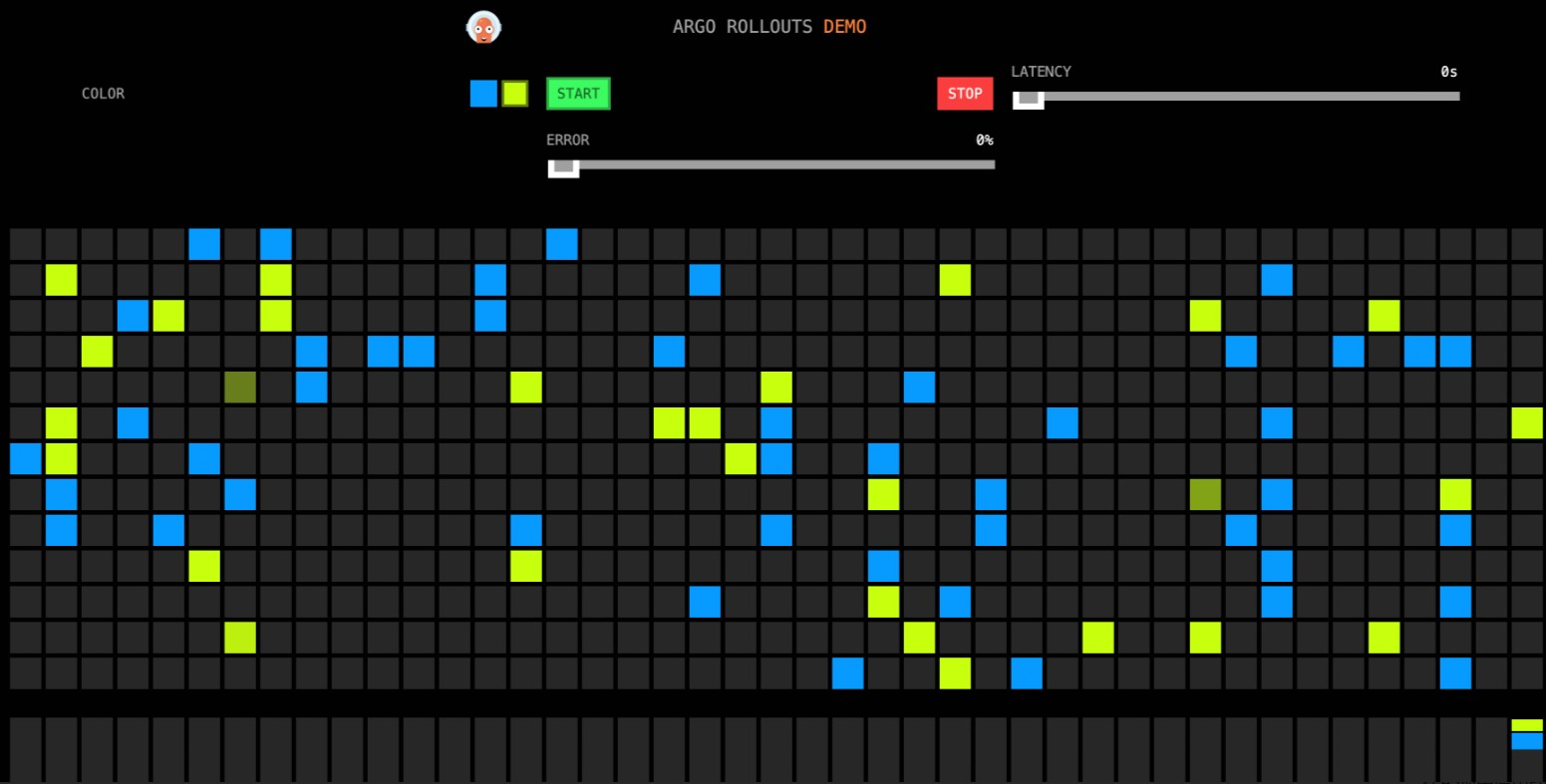
Check whether the canary release is successful.
Wait for a while. Then, use a browser to access http://{IP address of the ingress gateway}/.
All blue grids are changed to yellow, as shown in the following figure.
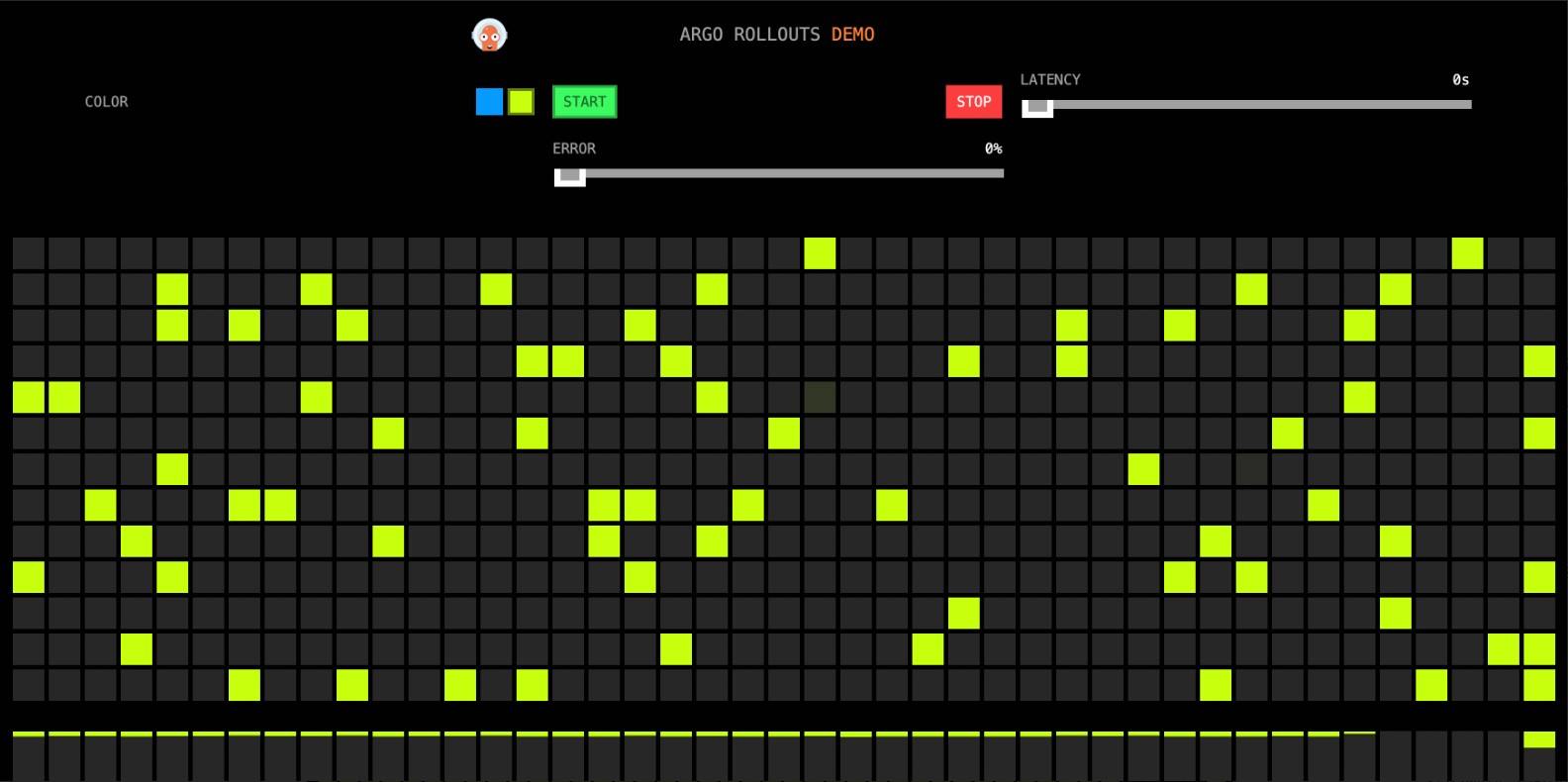
Run the following command to view the status of the Rollout:
kubectl argo rollouts get rollout istio-rollout --watchExpected output:
Name: istio-rollout Namespace: default Status: Healthy Strategy: Canary Step: 18/18 SetWeight: 100 ActualWeight: 100 Images: argoproj/rollouts-demo:yellow (stable) Replicas: Desired: 1 Current: 1 Updated: 1 Ready: 1 Available: 1 NAME KIND STATUS AGE INFO ⟳ istio-rollout Rollout Healthy 48m ├──# revision:4 │ └──⧉ istio-rollout-5fcf5864c4 ReplicaSet Healthy 27m stable │ └──□ istio-rollout-5fcf5864c4-vw6kh Pod Running 26m ready:2/2 ├──# revision:3 │ └──⧉ istio-rollout-897cb5b6d ReplicaSet • ScaledDown 27m └──# revision:1 └──⧉ istio-rollout-7f96d86486 ReplicaSet • ScaledDown 48mThe output shows that the image version of the container for the Rollout is updated to
yellow.
Use Prometheus to implement automatic rollback
During the canary release, you can run the kubectl argo rollouts abort istio-rollout command to roll back to the stable version. You can also use a Prometheus system to monitor the health status of an application involved in the canary release. If a metric anomaly occurs, the canary release version is automatically rolled back to the stable version and is marked as Degraded.
Enable Prometheus in ASM. For more information, see Integrate Managed Service for Prometheus to monitor ASM instances or Monitor ASM instances by using a self-managed Prometheus instance.
Configure an Argo AnalysisTemplate.
Create an istio-success-rate.yaml file that contains the following content.
Set the
addressparameter of the AnalysisTemplate to the endpoint of the Prometheus instance that is connected to ASM.apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1 kind: AnalysisTemplate metadata: name: istio-success-rate spec: args: - name: service - name: namespace metrics: - name: success-rate initialDelay: 60s interval: 20s successCondition: result[0] > 0.90 provider: prometheus: address: http://xxx.aliyuncs.com:9090/api/v1/prometheus/ query: >+ sum(irate(istio_requests_total{ reporter="source", destination_service=~"{{args.service}}.{{args.namespace}}.svc.cluster.local", response_code!~"5.*"}[40s]) ) / sum(irate(istio_requests_total{ reporter="source", destination_service=~"{{args.service}}.{{args.namespace}}.svc.cluster.local"}[40s]) )Run the following command to deploy the Argo AnalysisTemplate:
kubectl apply -f istio-success-rate.yaml
Associate an Analysis with the Rollout.
Create a rollout.yaml file that contains the following content.
Set the
analysisparameter understrategyso that the Analysis can be used for monitoring and automatic rollback from the second step. The initial image version of the container for the Rollout is yellow.Run the following command to update the Rollout:
kubectl apply -f rollout.yaml
Run the following command to update the image version:
kubectl argo rollouts set image istio-rollout "*=argoproj/rollouts-demo:orange"Use a browser to access http://{IP address of the ingress gateway}/. The following figure shows the result.
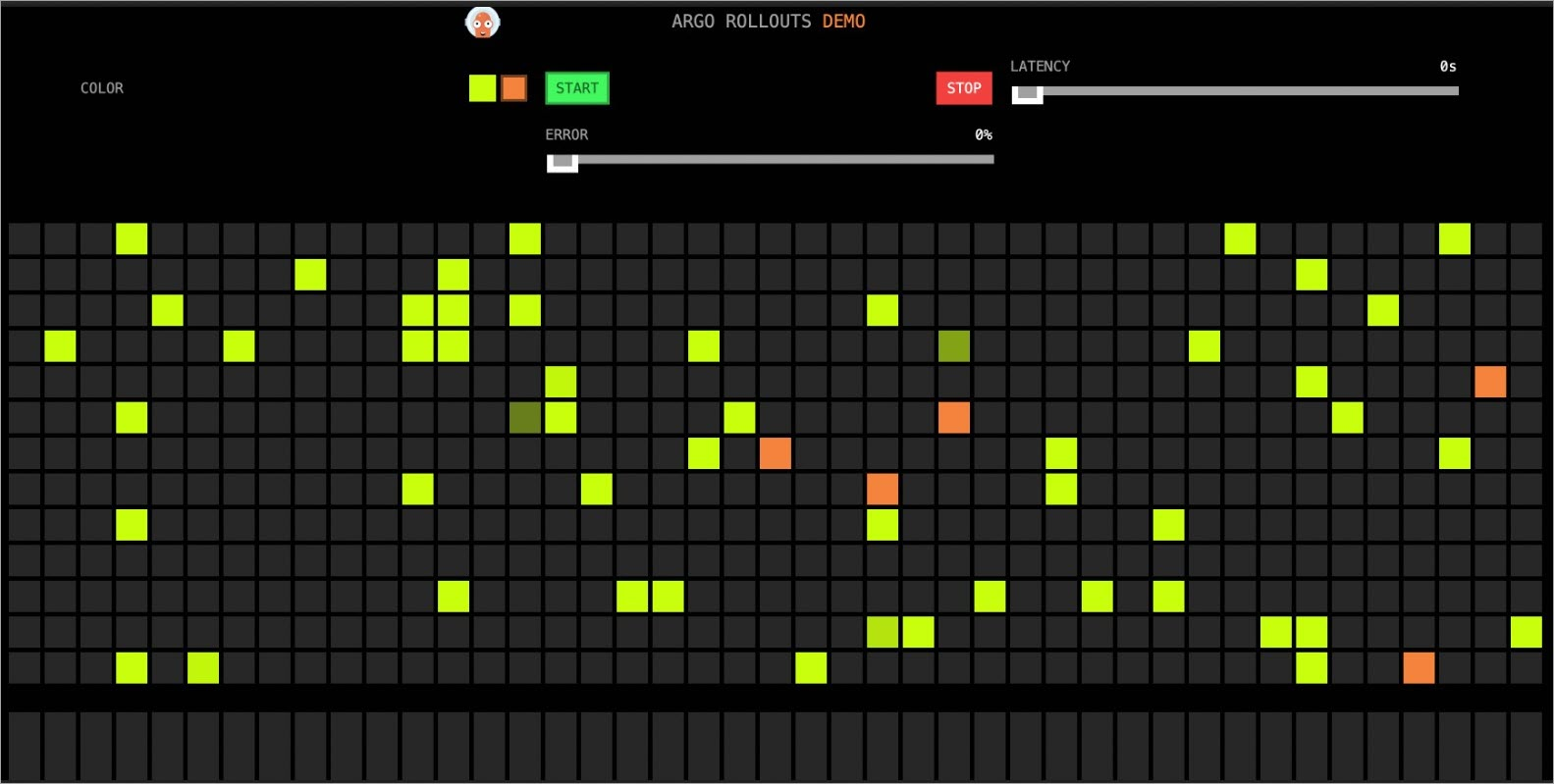
Manually confirm the Rollout update.
Run the following command to continue the canary release.
After you run the command, the automatic canary release starts. In addition, Prometheus monitoring is enabled from the second step. In this case, if the canary release version has an error rate higher than 90%, rollback is triggered.
kubectl argo rollouts promote istio-rolloutRun the following command to view the status of the Rollout:
kubectl argo rollouts get rollout istio-rollout --watchExpected output:
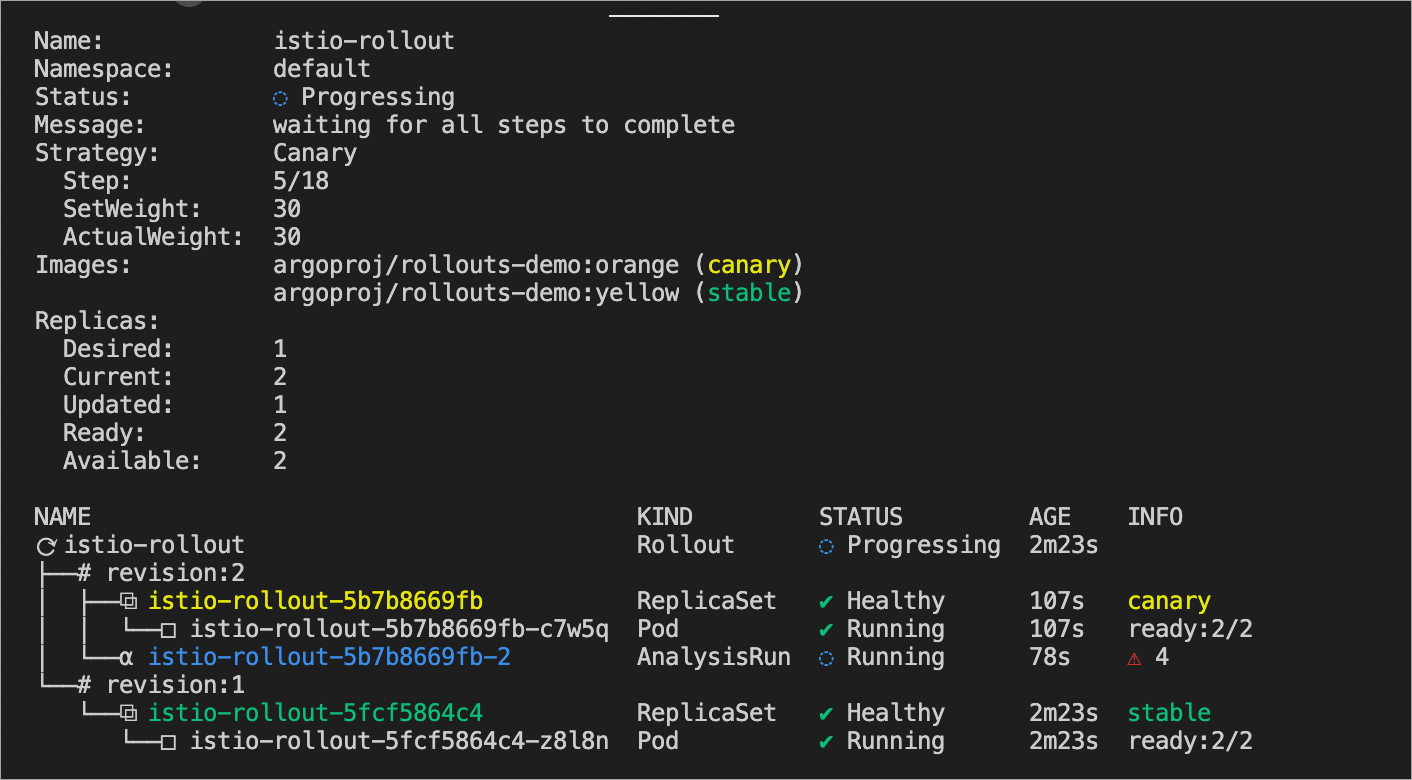
Configure the error rate.
In subsequent progressive releases, you can manually adjust the error rate for canary release versions. If the error progress bar reaches 100%, all orange grids (canary release versions) are framed in red to indicate an error. After a while, all canary release versions are automatically rolled back to their stable versions (yellow grids).
Figure 1. The following figure shows that the canary release is being implemented.
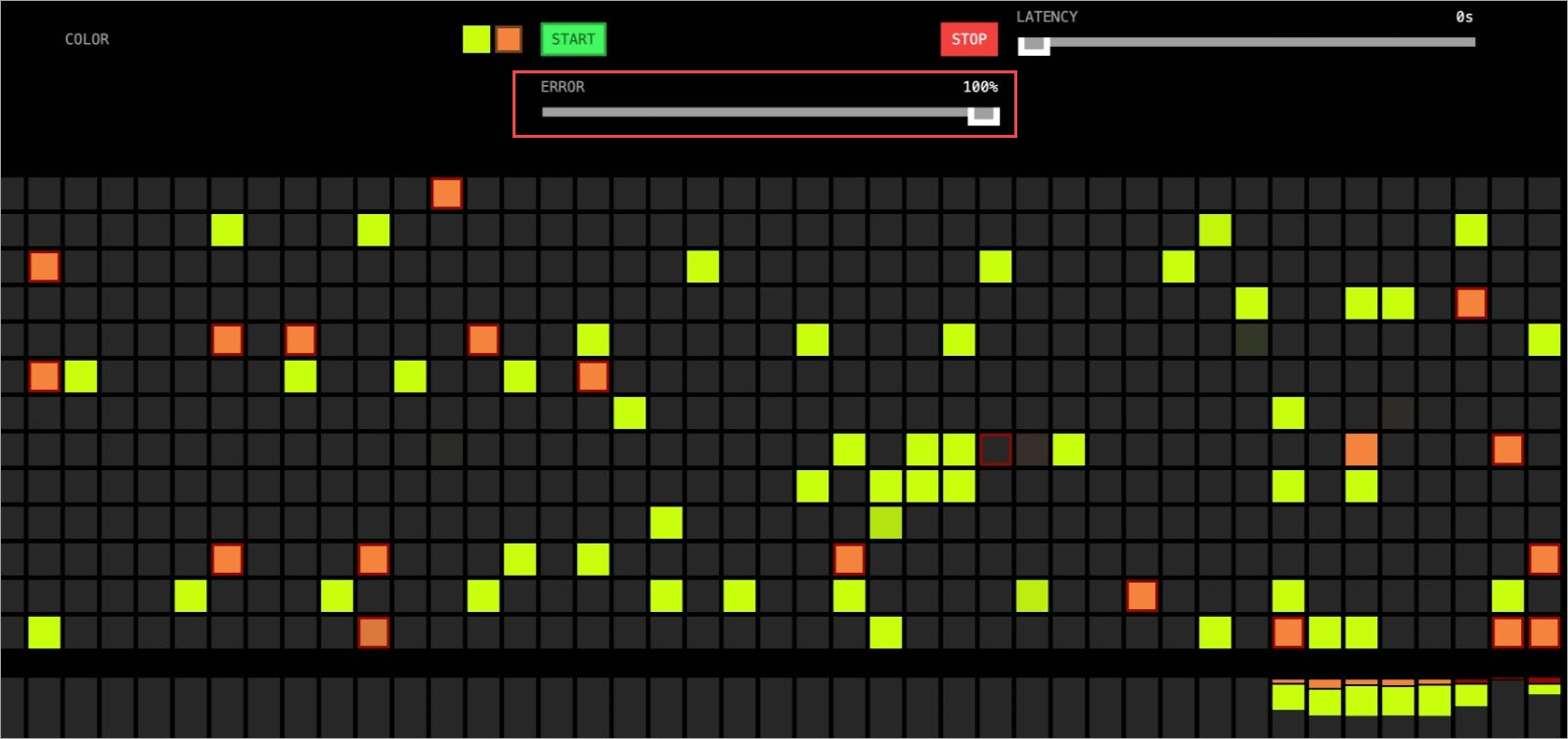
Figure 2. The following figure shows that all canary release versions have been automatically rolled back to their stable versions.