This topic describes the pre-checks to perform before you change an instance type and provides solutions for common issues.
Pre-change check process
1. Check if the current instance type can be changed and if it can be changed to the target instance type
You must first confirm that the instance type of your current instance can be changed and that the target instance type is a valid option.
Confirm that the current instance type is not in the list of instance types that do not support changes.
In the list of supported instance type changes, find the instance family of the current instance and confirm that the target instance family is supported.
You can also call the DescribeResourcesModification API operation to query the list of instance types to which the current instance can be changed.
2. Check operating system compatibility
Some instance types, especially those based on different CPU architectures such as AMD, Intel, and Yitian, have specific operating system requirements. If the operating system of the current instance is not compatible with the target instance type, the change fails.
Use the following official compatibility lists to ensure that the operating system of the current instance is supported by the target instance type.
If they are not compatible but you still need to change the instance type, you can request that the restriction be lifted.
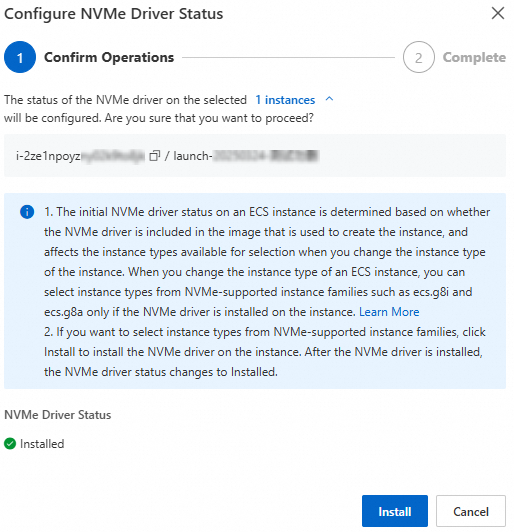
3. Check NVMe driver compatibility with the target instance type
ECS instances of the 8th generation and later, such as g8i, c8i, r8i, u2i, g8a, c8a, r8a, and u2a, use the NVMe protocol to communicate with disks. These instances require the NVMe driver to be installed. You must check the NVMe driver of the source instance in the following scenarios:
Scenario 1: Changing from a 7th-generation or earlier instance type to an 8th-generation or later instance type
The source ECS instance must have the NVMe driver installed, or the image of the instance must support NVMe driver installation.
Scenario 2: The source instance is an 8th-generation or later instance type
The source ECS instance must have the NVMe driver installed.
You can determine the generation of an instance type from its family name. For more information, see Instance type naming convention
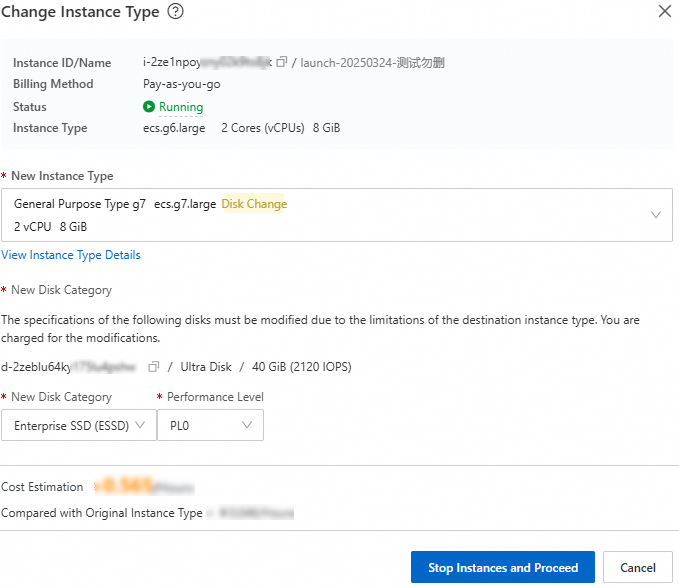
4. Check disk type compatibility
Different instance types support different disk types. For example, the g7 instance family supports only ESSD-series disks. If the current instance has an attached disk that is not supported by the target instance type, you cannot change the instance type.
On the instance type change page, if a disk compatibility issue exists, the system automatically detects it and prompts you to also change the disk type. Review the prompts and note any cost changes, as shown in the following figure.
Supported instance type changes
When you change an instance type, you can change from the following source instance types to the target instance types:
You can call the DescribeResourcesModification API operation to query the supported instance type changes for an existing instance.
Table 1. Entry-level x86 compute-optimized instance families
Source instance family | Supported target instance families |
e |
|
t6 |
|
t5 |
|
n4, mn4, xn4, e4 |
|
t1, s1, s2, s3, m1, m2, c1, c2 |
|
n1, n2, e3 |
|
Table 2. Enterprise-level compute-optimized instance families
Source instance type (family) | Supported target instance families |
g9a, c9a, r9a, g9ae, c9ae, r9ae, u2a | g9a, c9a, r9a, g9ae, c9ae, r9ae, u2a |
g9i, c9i, r9i, hfg9i, hfc9i, hfr9i | g9i, c9i, r9i, hfg9i, hfc9i, hfr9i, u2i |
|
|
|
|
g8y, c8y, r8y | g8y, c8y, r8y |
g7se, c7se, r7se |
|
g7a, c7a, r7a |
|
ebmg7a, ebmc7a, ebmr7a | ebmg7a, ebmc7a, ebmr7a |
ebmhfc7, ebmhfg7, ebmhfr7 | ebmhfc7, ebmhfg7, ebmhfr7 |
g7, c7, r7 |
|
ebmg7, ebmc7, ebmr7 | ebmg7, ebmc7, ebmr7 |
|
|
g7nex, c7nex |
Important ecs.g7nex.32xlarge can only be changed to ecs.c7nex.32xlarge. |
g6r, c6r |
|
|
|
g6a, c6a, r6a |
|
g6t | g6t |
c6t | c6t |
ebmg6a, ebmc6a, ebmr6a | ebmg6a, ebmc6a, ebmr6a |
g5, g5ne, r5, c5, ic5 |
|
hfc5, hfg5 |
|
u2i | u2i |
u1 |
|
sn1ne, sn2ne, se1ne |
|
se1 |
|
re6 |
|
re4e |
|
re4 |
|
gn8v | gn8v |
gn8v-tee | gn8v-tee |
sgn8ia | sgn8ia |
gn8is | gn8is |
sgn7i-vws | sgn7i-vws |
vgn7i-vws | vgn7i-vws |
gn7e | gn7e |
gn7s | gn7s |
gn7i | gn7i |
gn7 | gn7 |
gn6i | gn6i |
vgn6i | vgn6i, vgn6i-vws, sgn7i-vws |
vgn6i-vws | vgn6i-vws |
gn6e | gn6e |
gn6v | gn6v |
gn5i | gn5i |
sn1, sn2, se1 |
|
c4, ce4, cm4 |
|
Instance types that do not support changes
On the instance type change page in the ECS console, if the instance type of the current instance cannot be changed, the operation button is typically disabled and a prompt appears.
Instance types in the following instance families cannot be changed:
Instance family type | Instance family |
Enterprise-level x86 compute-optimized instance families |
|
Enterprise-level heterogeneous computing instance family |
|
ECS Bare Metal Instance family |
|
High-performance computing (HPC) & Super Computing Cluster (SCC) instance families |
|
FAQ
If you encounter the following issues when changing an instance type, refer to the corresponding solutions.
Issue | Description | Solution |
Specification not found | The target instance type does not exist. | Select another target instance type. For more information, see Instance families. |
Instance type is retired | The target instance type is retired. | Select another target instance type. For more information, see Instance families. |
No inventory in the region | The target instance type is out of stock in the current region. | Select another instance type that is in stock, or change the instance type across zones (only changes within the same instance family are supported). View purchasable regions for an instance type Call an API operation to query the inventory of an instance type in a specific zone. |
Only changes within the same instance family are supported | For some instance types, you can only change to another instance type within the same family. | Select a target instance type that is in the same family as the source instance. For example, when you change a gn7e instance, you can only select an instance type from the gn7e family. |
The target instance family does not match the source instance family | The selected target instance type is not in a family that is compatible with the source instance family. | Refer to Supported instance type changes and select a target instance type that is compatible with the source instance family. |
The architecture of the target instance type does not match the source instance | The architecture (ARM or x86) of the selected target instance does not match that of the source instance. | Select a target instance type that has the same architecture as the source instance. |
The number of CPU cores or the memory size of the target instance type is not supported | The number of CPU cores or the memory size of the selected target instance is not supported by the operating system of the source instance. For information about the limits on the number of CPU cores and memory size for Windows operating systems, see Memory Limits for Windows and Windows Server Releases. | Select a target instance type with a compatible number of CPU cores or memory size. |
The boot mode of the target instance type does not match the current instance | For example, if the selected target instance is a security-enhanced instance type that supports only the UEFI boot mode, the source instance must also support the UEFI boot mode. | Select a target instance type that has a boot mode compatible with the source instance. |
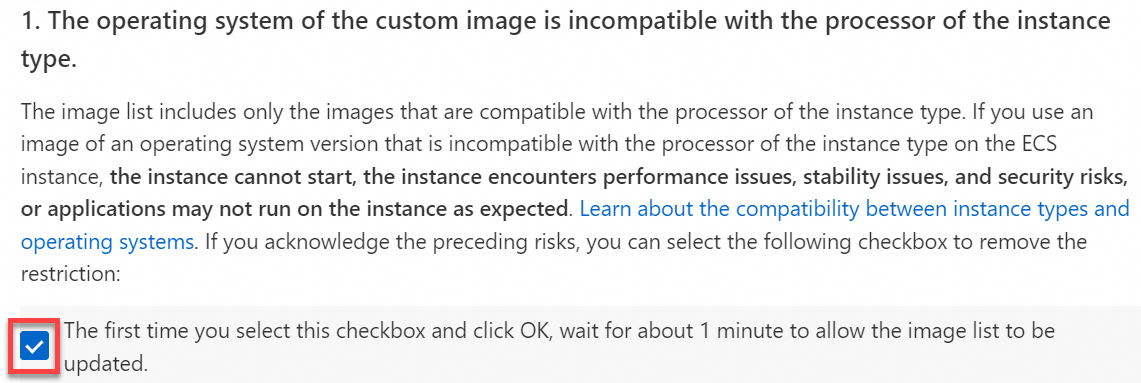
 > Configure NVMe Driver Status.
> Configure NVMe Driver Status.