Message Push Service (MPS) is a mobile push solution provided by Mobile PaaS (mPaaS). MPS offers various push types for different scenarios to meet your custom push requirements. To improve the delivery rate, mPaaS integrates third-party push features from vendors such as Huawei and Xiaomi into MPS. It provides a console for quick pushes and a server-side integration solution. This lets you quickly integrate mobile push features and interact with your app users. As a result, you can improve user retention and the user experience.
Features
You can use MPS to send various types of messages through self-hosted channels and third-party vendor channels. You can send pushes from the console or using an API. You can choose the push type, channel, and method that best fits your business scenario.
MPS provides the following core features:
Multiple push methods: You can send targeted messages to custom user groups, single users, or all users. Messages can be sent from the Mobile Push Service console or using API calls.
Custom message validity period: If a device is offline when a message is first sent, the message can be resent when the device reconnects or a user binding is initiated within the validity period. This ensures that the message reaches the target user.
Different push target types: You can establish a relationship between devices and logged-in users. This lets you push messages based on device IDs or user IDs.
Custom message templates: You can use the template management page to configure custom templates. This helps meet the personalized push requirements of your business.
Usage analysis: Based on data reported from client-side instrumentation, MPS analyzes push data across dimensions such as platform, version, push channel, push type, and time. It generates analysis reports that can display statistical results with minute-level granularity.
Push configuration: On the push configuration page, you can configure certificates to select the Apple Push Notification service (APNs) gateway for pushes to iOS devices.
Push channel configuration: You can connect to third-party vendor push channels and integrate push features from vendors such as Huawei and Xiaomi to improve the push delivery rate.
Key management: All external MPS API requests must be signed to ensure business security. A key configuration page is provided for you to configure your own keys. MPS also provides a message receipt feature to track message delivery results.
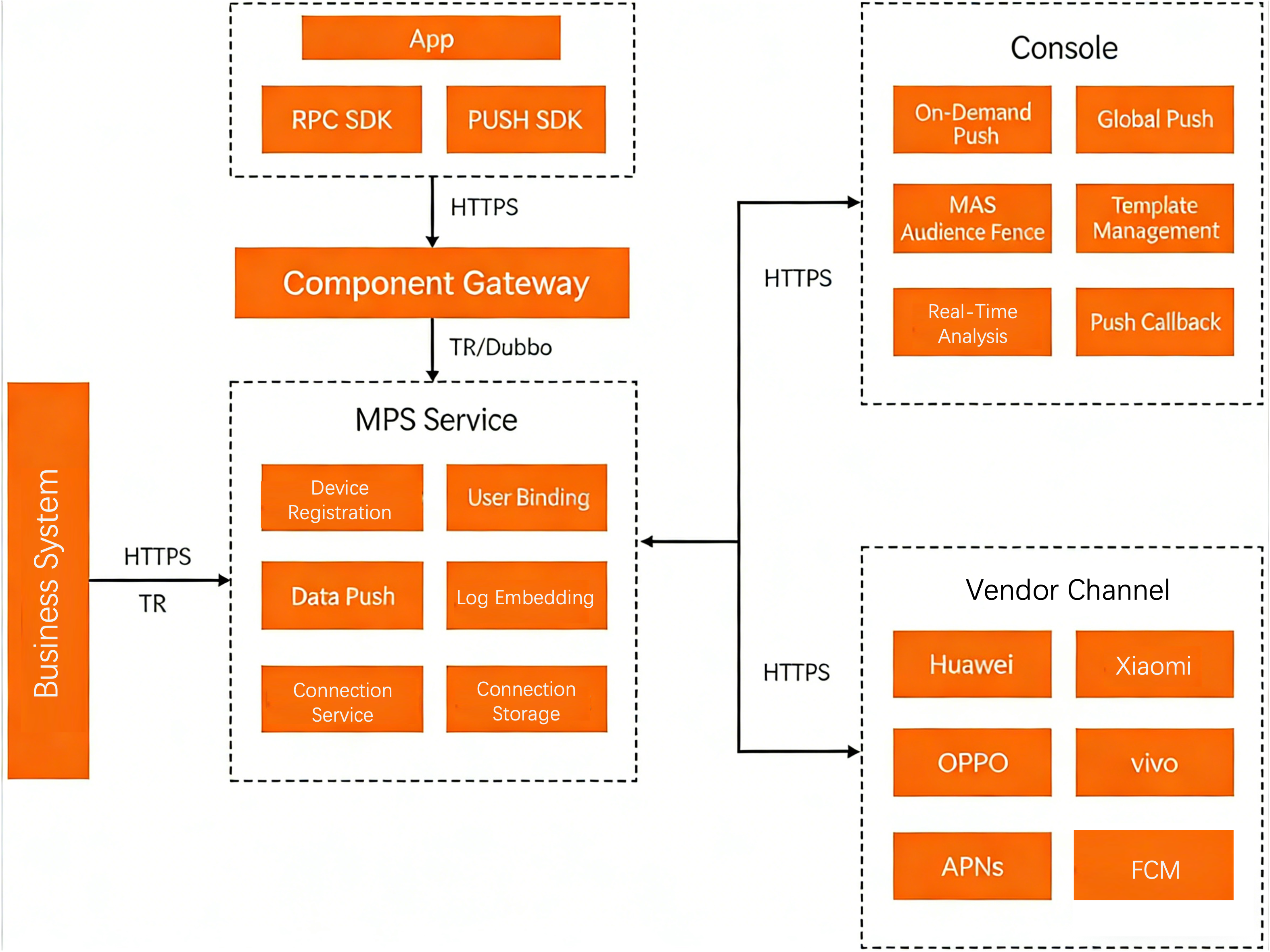
Principle framework
MPS is a core component in the mPaaS framework that communicates directly with clients. It works by transmitting notification data through long-lived TCP connections or third-party vendor channels.
Clients use the mPaaS Mobile Gateway Service (MGS) to make remote procedure calls (RPCs) to the gateway. This process registers devices, binds users, and establishes relationships with vendor channels, which enables message pushes based on device and user dimensions. The backend collects and uploads client behavior logs based on predefined specifications. It then analyzes the push data in real time to generate statistical reports. MPS supports both API pushes and console pushes. You can use API calls on your server to send custom messages based on your business logic, or you can send messages directly from the console. To improve the delivery rate, MPS supports channels such as Huawei, Xiaomi, Firebase Cloud Messaging (FCM), and APNs. This integration is transparent to your backend systems, which allows your business systems to focus on their functions without needing to handle different device models.
Benefits
MPS provides the following benefits:
Fast and stable: Messages are delivered quickly and reliably.
Simple integration: Reduces integration costs and improves efficiency.
Quantifiable results: Integrated data statistics provide intelligent analysis of delivery rates and open rates. This helps clarify the effectiveness of your pushes.
Targeted and personalized pushes:
You can send personalized information to single users, custom user groups, and targets based on various other dimensions.
You can use the console for simple push needs. A server-side integration solution is also available for more complex requirements.
You can use message receipts to track message delivery results. This helps improve user retention and popularity.
You can establish a relationship between device IDs and your app's user system. You can then send messages directly to app usernames as recipients. The messages are delivered accurately, regardless of which device the user logs in to.
Scenarios
Common scenarios for MPS include the following:
Marketing campaigns
You can send targeted messages to users, such as marketing promotions or business reminders, to increase customer stickiness. Your app can call the push API to send targeted messages to users. This proactive approach helps you reach more users, encourage spending, and improve the conversion rate of your marketing campaigns.
System notifications
You can specify the target audience based on your app's server-side business logic and push messages directly to the target devices.
For different application scenarios, MPS provides the following push types:
Simple Push: You can quickly push a message to a single user or device with a simple configuration.
Template Push: You can push a message to a single user or device. You can specify a message template, and the message content is generated by replacing placeholders in the template.
Multiple Push: You can push messages to many devices or users. You can specify a message template and set different placeholder variable values for different devices or users in a configuration file.
Broadcast Push: You can push a message to all devices on the network. You can specify a message template, and the message content is generated by replacing placeholders in the template.