Issue index
Resolve the "500 - Internal Server Error"
Causes
Hidden detailed errors: By default, IIS displays a generic "500 Internal Server Error" page to remote clients to avoid exposing sensitive server information, such as code paths or database connection strings.
Configuration or code defects: The root cause is typically a syntax error in the
web.configfile or an exception in the application code.
Solution
Enable Detailed Errors in IIS to display the specific error cause and line number in the browser. This helps you pinpoint the problem.
Log on to the ECS instance.
Go to ECS console - Instances. In the top navigation bar, select the target region and resource group.
Go to the details page of the target instance, click Connect, and select Workbench. Set the connection method to Terminal, enter the username and password, and then log on to the graphical terminal page.
Open IIS Manager.
Click Start and select Server Manager.
In Server Manager, select .
Enable detailed errors.
In the navigation pane on the left of the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager page, click the target website.
In the IIS section, double-click Error Pages.

In the Actions pane, click Edit Feature Settings..., select Detailed errors, then click OK.
Access the website to view the detailed error message.
Press
Ctrl+F5to force a refresh. The browser now displays a detailed error message that points to the exact configuration file (such asweb.config) and line number causing the issue. Use this information to correct the corresponding configuration file or application code.
How to block direct website access by IP address in IIS
Blocking direct access to your website by its IP address helps mitigate security risks, such as having unassociated or malicious domains pointed to your server's public IP.
Log on to the ECS instance.
Go to ECS console - Instances. In the top navigation bar, select the target region and resource group.
Go to the details page of the target instance, click Connect, and select Workbench. Set the connection method to Terminal, enter the username and password, and then log on to the graphical terminal page.
Open IIS Manager.
Click Start and select Server Manager.
In Server Manager, select .
Configure the site binding.
In the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager navigation pane, select the target website and click Bindings... in the Actions pane. In the Site Bindings window, find the record with an empty Host name and double-click it. In the Edit Site Binding window, enter your domain name and click OK.
Verify that the website is accessible by domain name but not by public IP address.
Resolve website access issues caused by a port conflict
Log on to the ECS instance.
Go to ECS console - Instances. In the top navigation bar, select the target region and resource group.
Go to the details page of the target instance, click Connect, and select Workbench. Set the connection method to Terminal, enter the username and password, and then log on to the graphical terminal page.
Open Command Prompt as an administrator.
Click Start, type
cmd, right-click Command Prompt, and select Run as administrator.Check if the service port is in use.
Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort <Port>The output includes the port status
Stateand the owning processOwningProcess.LocalAddress LocalPort RemoteAddress RemotePort State AppliedSetting OwningProcess ------------ --------- ------------- ---------- ----- -------------- ------------- :: 80 :: 0 Listen 4In this example, process ID
4is using port80.Find the application by its PID.
Replace
<PID>with the process ID shown in theOwningProcesscolumn from the previous step.Get-Process -Id <PID>Resolve the port conflict.
Stop the process that is using the port.
If you confirm that the program using the port can be closed, use the
taskkillcommand to terminate the process:taskkill <PID>Change the application's port.
To minimize port conflicts, use a port in the registered range (8000–49151).
Click Start, select Server Manager. In Server Manager, select .
In the navigation pane on the left of the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager page, click the target website, then click Bindings... in the Actions pane.
In the Site Bindings window, select an existing binding record, click Edit..., modify the port, and then click OK.
Restart IIS.
iisreset /noforceVerify that the website is accessible.
Resolve the "403.14 - Forbidden" error
Causes
Missing default document: The website's root directory or the accessed subdirectory does not have a default entry file (such as
index.htmlordefault.aspx) configured.Directory browsing disabled: For security, IIS prohibits listing directory contents by default. This setting triggers a 403.14 error when a default document cannot be found.
Solutions
Solution 1: Configure a default document (Recommended)
Log on to the ECS instance.
Go to ECS console - Instances. In the top navigation bar, select the target region and resource group.
Go to the details page of the target instance, click Connect, and select Workbench. Set the connection method to Terminal, enter the username and password, and then log on to the graphical terminal page.
Open IIS Manager.
Click Start and select Server Manager.
In Server Manager, select .
Configure the default document.
In Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager, click the target website. In the IIS section, double-click Default Document, then click Enable in the Actions pane.
In the default document list, add the website's entry file name, such as
index.htmlordefault.htm. Ensure this file exists in the website's root directory.
Verify that the website is accessible.
Solution 2: Enable directory browsing
Enabling directory browsing exposes your site's file and directory structure, which poses a security risk.
Log on to the ECS instance.
Go to ECS console - Instances. In the top navigation bar, select the target region and resource group.
Go to the details page of the target instance, click Connect, and select Workbench. Set the connection method to Terminal, enter the username and password, and then log on to the graphical terminal page.
Open IIS Manager.
Click Start and select Server Manager.
In Server Manager, select .
Enable directory browsing.
In the navigation pane on the left of the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager page, click the target website.
In the IIS section, double-click Directory Browsing. In the Actions pane, click Enable.
Verify that the website is accessible.
Resolve the "0x80070002 The system cannot find the file specified" error
Cause
IIS relies on Handler Mappings to determine how to process requests for specific file types, such as .aspx files. This error occurs when the .NET Framework is installed in the wrong order or its registration in IIS is corrupted or missing, preventing IIS from finding the correct component to handle ASP.NET requests.
Solution
Use the aspnet_regiis.exe tool to re-register the correct .NET Framework version in IIS. This action repairs the corrupted handler mappings.
Click Start, type
cmd, right-click Command Prompt, and select Run as administrator.Navigate to the
Frameworkdirectory.The
aspnet_regiis.exetool resides in the .NET Framework installation directory.It is typically located in the
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework64directory. For example, for .NET Framework 4.x:cd /d C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework64\v4.0.30319Uninstall ASP.NET.
aspnet_regiis.exe -uInstall and register ASP.NET with IIS.
aspnet_regiis.exe -iRestart IIS.
iisreset /noforceVerify that the website is accessible.
Resolve the "534 Policy requires SSL" error
Cause
This error occurs when the FTP client is configured to use FTPS (FTP over SSL/TLS) for a secure connection, but the FTP site in IIS is not configured to allow SSL connections. The server then rejects the SSL/TLS handshake request from the client.
Solution
Check and enable the SSL connection policy for the FTP site in IIS to match the client's security requirements.
Log on to the ECS instance.
Go to ECS console - Instances. In the top navigation bar, select the target region and resource group.
Go to the details page of the target instance, click Connect, and select Workbench. Set the connection method to Terminal, enter the username and password, and then log on to the graphical terminal page.
Open IIS Manager.
Click Start and select Server Manager.
In Server Manager, select .
Configure the FTP site's SSL policy.
Click the target FTP site. In the FTP section of the home page, double-click FTP SSL Settings.
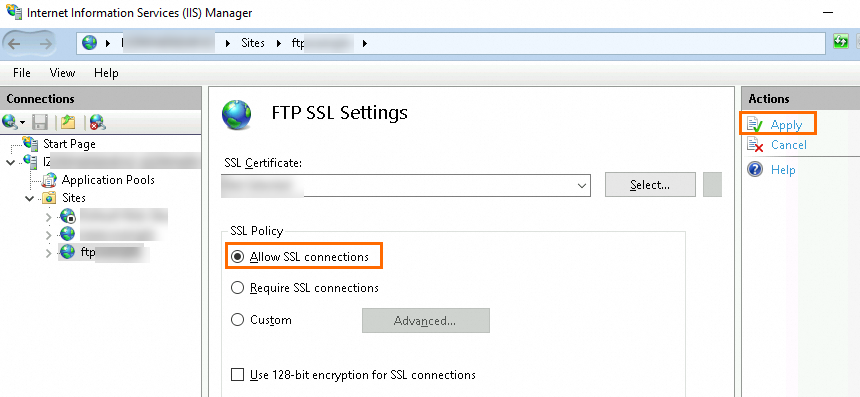
In the FTP SSL Settings section, set the SSL Policy to Allow SSL connections, then click Apply in the Actions pane.
Verify that the FTP site is accessible.
Resolve the "Bad Request - Invalid Hostname" error
Causes
The IIS server received an HTTP request but could not find a configured site that matched the hostname in the request header. This error has the following common causes:
Hostname not bound: The target website does not have a binding for the requested domain name.
Incorrect binding information: The website has a hostname binding, but it contains a spelling error or is bound to the wrong IP address or port.
Binding conflict: The domain name is already bound to another site in IIS, causing a request routing conflict.
Solution
Check and correctly configure the target site's bindings to ensure the domain name used for access matches the site's configuration.
Log on to the ECS instance.
Go to ECS console - Instances. In the top navigation bar, select the target region and resource group.
Go to the details page of the target instance, click Connect, and select Workbench. Set the connection method to Terminal, enter the username and password, and then log on to the graphical terminal page.
Open IIS Manager.
Click Start and select Server Manager.
In Server Manager, select .
Check and configure site bindings.
In the navigation pane on the left of the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager page, click the target website, then click Bindings... in the Actions pane.
On the Site Bindings page, either add a new domain name binding or check if the existing binding information is correct.
Add a new binding.
On the Site Bindings page, click Add....
On the Add Site Binding page, enter the website's domain name in the Host name field, then click OK.
View or modify an existing binding.
On the Site Bindings page, double-click the existing binding record.
On the Edit Site Binding page, review the binding information.
If you need to modify the domain name, edit the Host name and click OK.
Verify that the website is accessible.
Resolve the "500.19 - Absolute physical path...is not allowed" error
Cause
A malformed or unrecognized XML element in the ApplicationHost.config or Web.config file causes this error.
ApplicationHost.config serves as the server's root configuration file, defining global defaults and server-level settings.The Web.config file provides application-level configuration, used to override or extend settings inherited from a higher level.Solution
Log on to the ECS instance.
Go to ECS console - Instances. In the top navigation bar, select the target region and resource group.
Go to the details page of the target instance, click Connect, and select Workbench. Set the connection method to Terminal, enter the username and password, and then log on to the graphical terminal page.
Open IIS Manager.
Click Start and select Server Manager.
In Server Manager, select .
Check the
web.configfile.In the navigation pane on the left of the Internet Information Services (IIS) Manager page, click the target website, then click Explore in the Actions pane to open the site's directory.
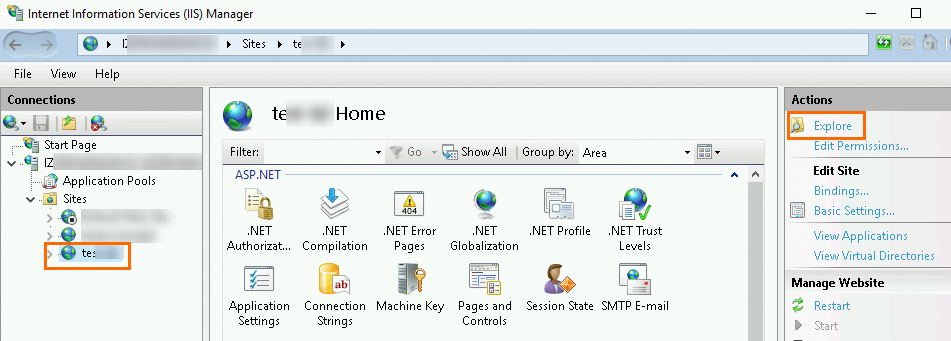
Open the
web.configfile in the site directory. Review the file and correct any errors, referring to the IIS Configuration Reference.
Check the
ApplicationHost.configfile.Go to the
C:\Windows\System32\inetsrv\config\folder and open theApplicationHost.configfile. Review the file and correct any errors, referring to the Introduction to ApplicationHost.config.Open Command Prompt and restart IIS.
iisreset /noforceVerify that the website is accessible.