Throttling is one of the most commonly used methods for traffic control. You can use throttling to prevent backend services from being overwhelmed by excessive external requests. Throttling prevents cascaded avalanches. The throttling feature helps you block some requests if the number of concurrent requests is large. This ensures the availability of backend services. Cloud-native API Gateway allows you to configure route-level throttling policies. These fine-grained policies ensure that the number of requests on a route does not exceed a specified threshold during a specified period of time. This topic describes how to configure a throttling policy for a cloud-native gateway.
Configure a throttling policy
The throttling threshold that you configure is a gateway-level throttling threshold. You can calculate the throttling threshold for a gateway node by using the following formula: Gateway-level throttling threshold/Number of nodes. If the calculated throttling threshold is a decimal value, the decimal value is rounded up to the nearest integer. For example, the queries per second (QPS) of a demo route is 1001. If your gateway has two nodes, the QPS limit for the demo route on each gateway node is 501.
Log on to the Cloud-native API Gateway console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click API. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
Click the target API. On the API details page, click the name of the target route. Click the Configure Policy tab and then click Throttling on the left.
Configure a throttling rule
Throttling rules are used to monitor the QPS of a route. If the QPS reaches the specified threshold, traffic is blocked immediately. This prevents a breakdown of backend services due to traffic surges and ensures the high availability of the backend services.
Click the Throttling Rule tab on the right.
Configure the parameters on the Throttling Rule tab.

Parameter
Description
Enable or Not
If you turn on this switch, the configured throttling policy takes effect.
Overall QPS Threshold
Enter a value for the overall QPS threshold.
Web Fallback Behavior
Select Return Specific Content or Redirect to Specified Page.
If you set Web Fallback Behavior to Return Specific Content:
HTTP Status Code
Specify the HTTP status code that you want to return. The default value is 429.
Type of Returned Content
Select Regular Text or JSON.
HTTP Text
Specify the text that you want to return.
If you set Web Fallback Behavior to Redirect to Specified Page:
Redirect URL
Specify the URL to which you want to redirect.
Click Save. In the message that appears, click OK.
Configure a concurrency rule
Concurrency rules are used to calculate the total number of requests that are being processed by a gateway. If the total number reaches the specified threshold, traffic is blocked immediately. When you configure concurrency rules, you can specify the maximum number of concurrent requests that can be processed by backend services. This ensures the availability of backend services in scenarios in which a large number of concurrent requests are initiated.
Click the Concurrency Rule tab.
Configure the parameters.
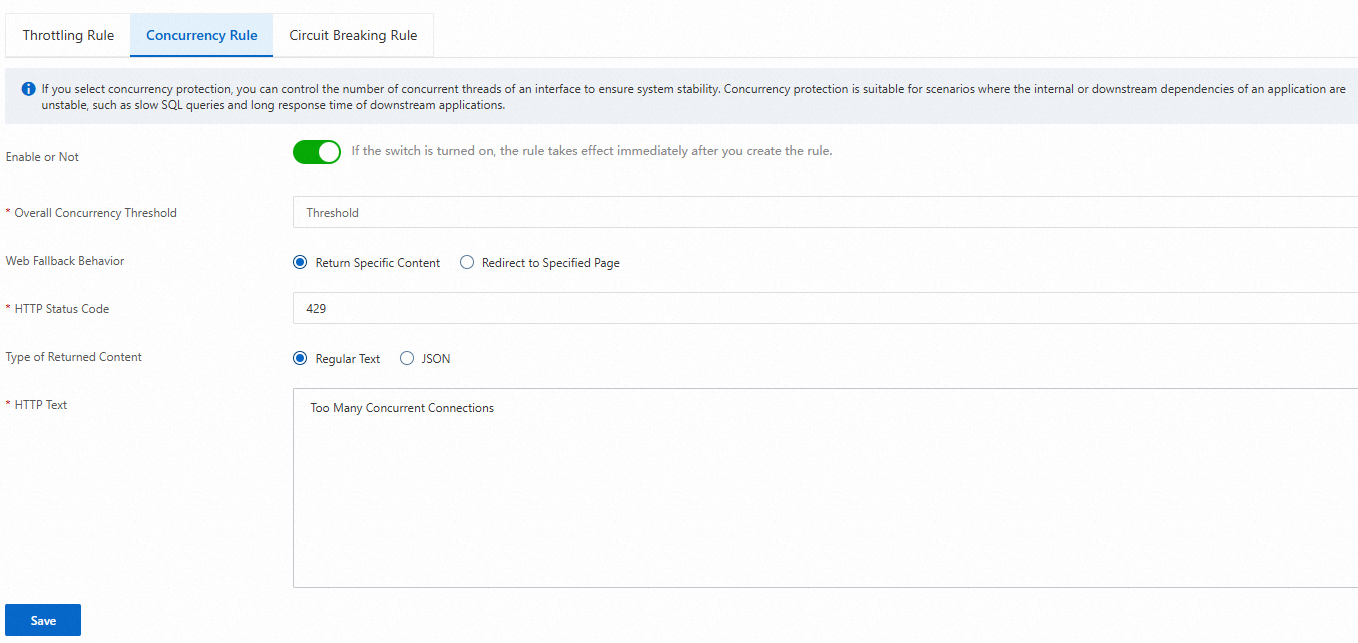
Parameter
Description
Enable or Not
If you turn on this switch, the configured concurrency rule takes effect.
Overall Concurrency Threshold
Enter a value as the overall concurrency threshold.
Web Fallback Behavior
Select Return Specific Content or Redirect to Specified Page.
If you set Web Fallback Behavior to Return Specific Content:
HTTP Status Code
Specify the HTTP status code that you want to return. The default value is 429.
Type of Returned Content
Select Regular Text or JSON.
HTTP Text
Specify the text that you want to return.
If you set Web Fallback Behavior to Redirect to Specified Page:
Redirect URL
Specify the URL to which you want to redirect.
Click Save. In the message that appears, click OK.
Configure a circuit breaking rule
Circuit breaking rules are used to lower the dependency priority of a route immediately if the system detects that the RT of requests or the percentage of abnormal requests on the route reaches a specified threshold. If circuit breaking is triggered, the system does not call the requests on the route in the specified period of time. This ensures high availability of backend services. After the specified period of time elapses, the system resumes the calls to the requests for the route.
Click the Circuit Breaking Rule tab.
Configure the parameters on the tab.
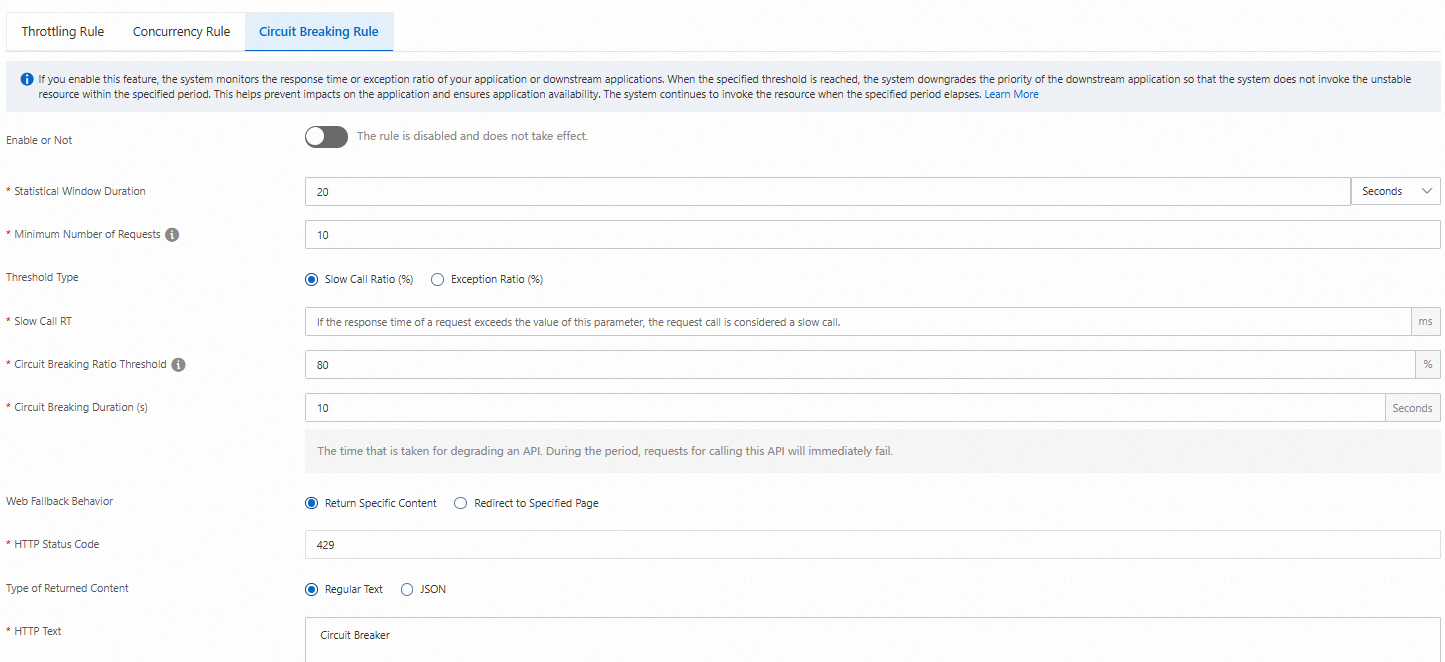
Parameter
Description
Enable or Not
If you turn on this switch, the configured throttling rule takes effect.
Statistical Window Duration
The length of the time window. The valid range is 1 second to 120 minutes.
Minimum Number of Requests
The minimum number of requests to trigger circuit breaking. If the number of requests in the current time window is less than the value of this parameter, circuit breaking is not triggered even if the circuit breaking rule is met.
Threshold type
The threshold type. Valid values: Slow Call Ratio (%) and Exception Ratio (%).
If you set this parameter to Slow Call Ratio (%), you must configure the Slow Call RT parameter. The Slow Call RT parameter specifies a threshold for the response time of requests. If the response time of a request exceeds the value of the Slow Call RT parameter, the request is counted as a slow call. Set the downgrade threshold to a threshold for the percentage of slow calls. After the circuit breaking rule is enabled, if the number of requests that are initiated in a specified period of time is greater than the specified minimum number of requests and the percentage of slow calls is greater than the specified threshold, circuit breaking is automatically implemented on requests that are processed in the next circuit breaking period. After the circuit breaking period elapses, the circuit breaker starts to detect the RT of the next request. If the RT of the next request is less than the value of the Slow Call RT parameter, circuit breaking ends. If the RT of the next request is greater than the value of the Slow Call RT parameter, circuit breaking is triggered again.
If you set this parameter to Exception Ratio (%), you must set the downgrade threshold to a threshold for the percentage of exceptional requests. After the rule is enabled, if the number of exceptional requests in a specified period of time is greater than the specified minimum number of requests and the percentage of exceptional requests is greater than the specified threshold, circuit breaking is automatically implemented on requests that are processed in the next circuit breaking period.
Slow Call RT
The threshold for the response time of requests.
Circuit Breaking Ratio Threshold
The percentage threshold for slow calls. If the specified threshold is reached or exceeded, circuit breaking is triggered. Valid values: 0-100. These values represent 0% to 100%.
Circuit Breaking Duration (s)
The period in which circuit breaking is implemented. If circuit breaking is implemented on the requests for the route, the calls to all the requests for the route fail in the configured circuit breaking period.
Web Fallback Behavior
Select Return Specific Content or Redirect to Specified Page.
If you set Web Fallback Behavior to Redirect to Specified Page:
Redirect URL
Specify the URL to which you want to redirect.
If you set Web Fallback Behavior to Return Specific Content:
HTTP Status Code
Specify the HTTP status code that you want to return. The default value is 429.
Type of Returned Content
Select Regular Text or JSON.
HTTP Text
Specify the text that you want to return.
Click Save. In the message that appears, click OK.
Verify the result
Run the following command to check the result:
curl -I http://121.196.XX.XX/demo/item/list //The ingress IP address of the gateway.A response that is similar to the following one is returned if the throttling policy is not enabled:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK x-content-type-options: nosniff x-xss-protection: 1; mode=block cache-control: no-cache, no-store, max-age=0, must-revalidate pragma: no-cache expires: 0 x-frame-options: DENY content-type: application/json content-length: 86 date: Mon, 29 Nov 2021 08:28:00 GMT x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 4 server: istio-envoyA response that is similar to the following one is returned if the throttling policy is enabled. The HTTP status code 429 is returned.
HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requests x-local-rate-limit: true content-length: 18 content-type: text/plain date: Mon, 29 Nov 2021 08:28:01 GMT server: istio-envoy