ApsaraDB RDS for SQL Server has several usage constraints to ensure the stability and security of instances.
Feature | Cluster Edition | High-availability Series | Basic Series | |
2025 Enterprise Cluster Edition 2022 Enterprise Cluster Edition 2019 Enterprise Cluster Edition 2017 Enterprise Cluster Edition | 2025 Standard Edition 2022 Standard Edition 2019 Standard Edition 2017 Standard Edition 2016 Standard Edition, Enterprise Edition 2014 Standard Edition, Enterprise Edition 2012 Standard Edition, Enterprise Edition | 2008 R2 | 2025 Standard Edition, Enterprise Cluster Edition 2022 Web Edition, Standard Edition, Enterprise Cluster Edition 2019 Web Edition, Standard Edition, Enterprise Cluster Edition 2017 Web Edition, Standard Edition, Enterprise Cluster Edition 2016 Web Edition, Standard Edition, Enterprise Edition 2014 Standard Edition 2012 Web Edition, Enterprise Edition (single-node) | |
Maximum number of databases (related to the instance type) | 300 | 300 | 50 | 400 |
Maximum number of database accounts | Unlimited | Unlimited | 500 | Unlimited |
Maximum number of client connections to an instance | Unlimited | Unlimited | Unlimited | |
Create users, logins, or databases | Support | Support | Support | Support |
Database-level DDL triggers | Support | Support | Not supported | Support |
Permissions granted within a database | Support | Support | Not supported | Support |
Permission to kill threads | Support | Support | Support | Support |
Linked Server | Supported (not supported for shared instance types) | Supported (not supported for shared instance types) | Not supported | Not supported |
Distributed transactions | Support | Support | Not supported | Not supported |
SQL Profiler | Supported | Supported | Support | Support |
Tuning Advisor | Support | Supported | Not supported | Support |
Change Data Capture (CDC) | Support | Supported (not supported for 2012 Standard Edition) | Disk support Not supported on high-performance local disks | Not supported |
Change Tracking | Support | Support | Not supported | Support |
Logon with a Windows domain account | Supported (not supported for shared instance types) | Supported (not supported for shared instance types) | Not supported | Not supported |
Data integration feature (SSIS) | Supported (not supported for shared instance types) | Supported (not supported for shared instance types) | Not supported | Supported (not supported for shared instance types) |
Data analytics feature (SSAS) | ||||
Data reporting feature (SSRS) | ||||
Asynchronous messaging | Support | Support | Support | Supported |
Mail feature | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported | Not supported |
R Services | ||||
Common Language Runtime (CLR) integration | ||||
Publish/subscribe feature | ||||
Policy-Based Management | ||||
Number of databases
The maximum number of databases for an SQL Server 2008 R2 instance is 50. For other SQL Server instances, the maximum number of databases depends on the instance type. Use the following formulas to calculate the limit:
Cluster Edition/High-availability Series
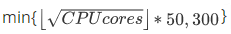
This value is calculated by taking the square root of the number of CPU cores, rounding the result down to the nearest integer, and then multiplying the result by 50. The maximum number of databases is the minimum value of the calculated result and 300. For example, a 2016 standard high-availability series (4-core 8 GB) instance supports a maximum of 100 databases.
Basic Edition
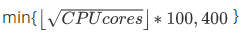
The value is calculated by taking the square root of the number of CPU cores, rounding the result down to the nearest integer, and then multiplying the result by 100. The maximum number of databases is the minimum value of the calculated result and 400. For example, a 2019 Standard RDS Basic Edition (4-core 8 GB) instance supports a maximum of 200 databases.
In the formulas, min indicates the minimum value in a range. For example, min{100, 300} is 100.