This topic describes the scenarios of Commit List and Patchset Comparison.
Background information
The Commit Changes tab of the Merge Request page offers two views: Commit List and Patchset Comparison, to assist reviewers in comprehending the code change process.
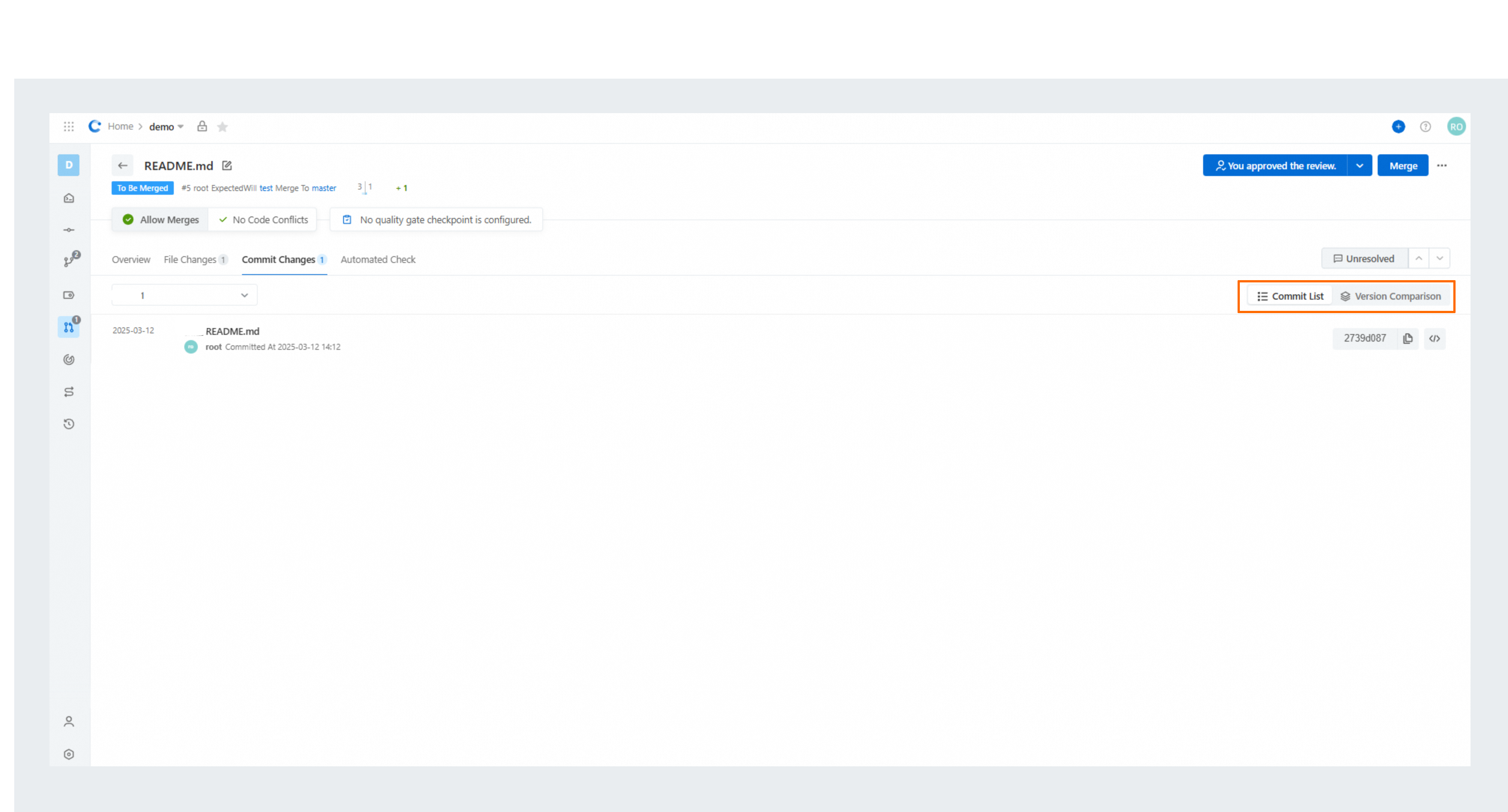
Commit List
You can quickly understand the latest changes and perform a full review through Commit List. The commit history is one of the methods to trace code modifications. Steps for implementing the feature feature-x are as follows:
commit-4: Implementation & Test cases // Implemented the feature and added corresponding test cases.
|
commit-3: Refactor-B // Identified the need for minor refactoring to optimize the implementation logic of function-f.
|
commit-2: Refactor-A // Identified the need for minor refactoring, extracting common methods for reuse.
|
commit-1: Cleanup // Noticed formatting issues in the files being modified and then formatted the files.The preceding implementation path reflects the corresponding design and development of the code. You can use the git log adf3e902..HEAD command in the terminal to view the commit history:
commit 47c53b7ae262fe5a40906884ae9c0c993035c085 (HEAD -> feature-x)
Author: tenglong.tl <tenglong***@email.com>
Date: Tue Sep 26 09:56:47 2023 +0800
feat: implement feature-x and related test cases
Signed-off-by: tenglong.tl <tenglong***@emailc.com>
commit 0b5c42b2bf252069931f724a74f2f0301e7dd8a3
Author: tenglong.tl <tenglong***@email.com>
Date: Mon Sep 25 19:46:09 2023 +0800
refactor: optimize f() to be shorter and simpler
Signed-off-by: tenglong.tl <tenglong***@email.com>
commit 4f80f46afb585497ef3f6e0ecdafde1c4d11c273
Author: tenglong.tl <tenglong***@email.com>
Date: Mon Sep 25 19:40:57 2023 +0800
refactor: extract common func to reuse in future
Signed-off-by: tenglong.tl <tenglong***@email.com>
commit f613e9882a4cb91f87dff215b2d08b94139b40b2
Author: tenglong.tl <tenglong***@email.com>
Date: Mon Sep 25 19:37:43 2023 +0800
cleanup: fixup the format alerts in x.java
Signed-off-by: tenglong.tl <tenglong***@email.com>git log represents the source code organization for developing this feature, known as the commit list. The command git log adf3e902..HEAD can be used to view the commit history from the commit adf3e902 to the latest commit.
An excellent commit list clearly reflects the design thinking of developers. By using atomic commits, it allows reviewers to efficiently understand the implementation path of the feature and review each commit individually. Atomic commits also help developers decouple their work, enabling independent modifications to individual commits.
Reviewers are encouraged to concentrate on the commit list rather than directly reviewing file changes. Reviewing commits is considered a best practice in code reviews. git log, which is one of the most commonly used Git commands, enables viewing the commit history and understanding the programming thought of developers, even outside the context of formal code reviews.
The commit list is particularly useful for scenarios where the reviewer is conducting a full review for the first time. Reviewers typically focus on the latest code changes first. Taking a quick overview of the current commit list for the latest version often makes the review process much more efficient.
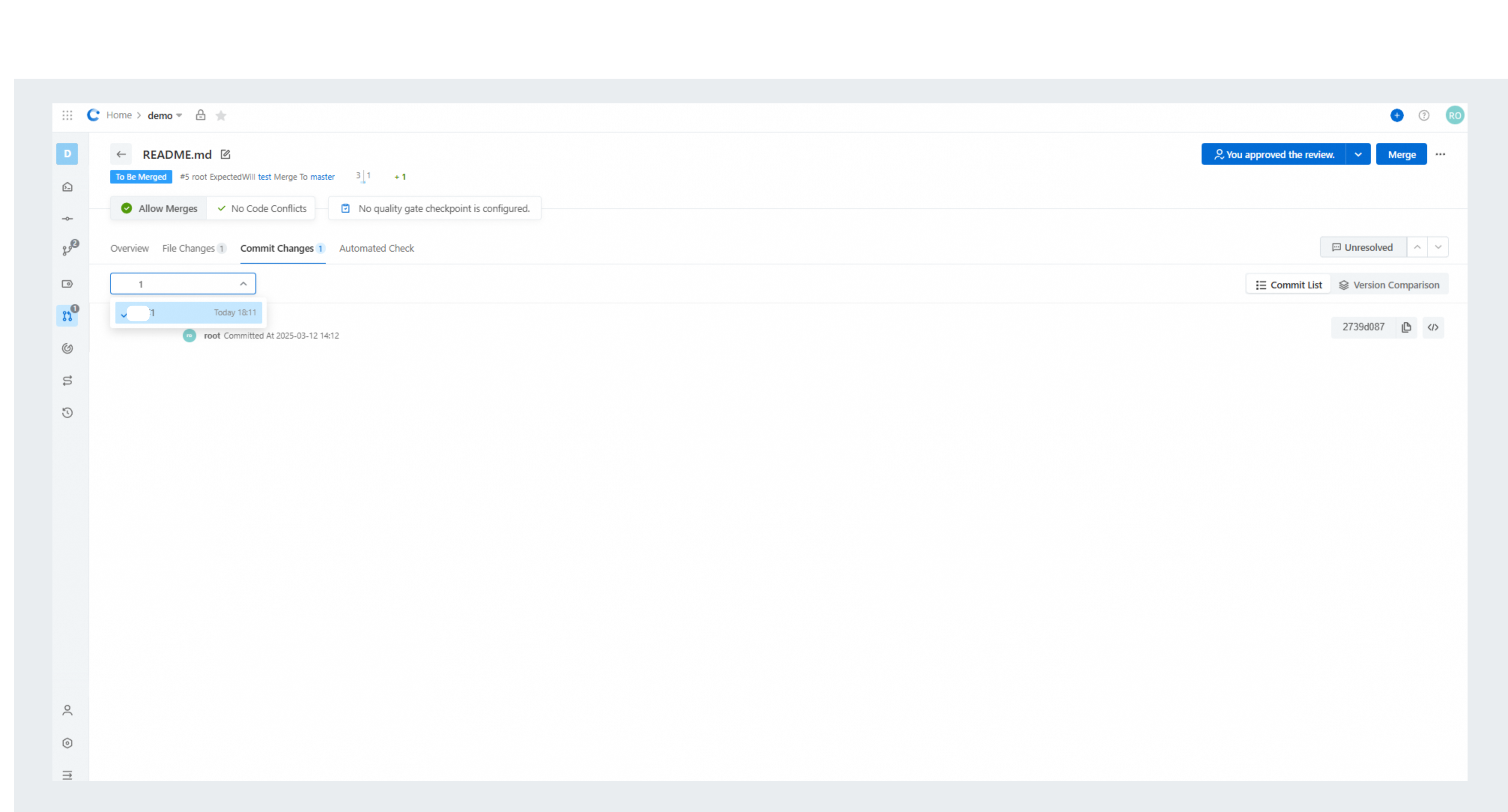
Patchset Comparison
By using Patchset Comparison, you can identify the changes between Patchsets and perform incremental reviews. The commit list is suitable for the initial review to view the latest code changes. As the code evolves iteratively, Patchsets are updated as well. The differences between two Patchsets may be minor or significant.
Focusing on the changes between Patchsets allows reviewers to identify reviewed content and only focus on new changes, enabling incremental reviews and reducing the effort required.
For example, the author creates Patchset-1:
47c53b7 (HEAD -> feature-x) feat: implement feature-x and related test cases
0b5c42b refactor: optimize f() to be shorter and simpler
4f80f46 refactor: extract common func to reuse in future
f613e98 cleanup: fixup the format alerts in x.javaPatchset-1 contains four commits. Reviewer-A suggests splitting the commit feat: implement feature-x and related test cases into smaller commits.
The author then updates the code and submits Patchset-2, keeping the other three commits unchanged while splitting the commit feat: implement feature-x and related test cases into four new commits.
At this point, running the command git log adf3e90..HEAD --oneline displays the latest commit list in the following form:
3add20b controller: REST mapping and ACL implementation
7525c08 service: feat-X implementations and test cases
06a5e4f dao: implements DAO interface
054ea6d api: REST interface declaration
0b5c42b refactor: optimize f() to be shorter and simpler
4f80f46 refactor: extract common func to reuse in future
f613e98 cleanup: fixup the format alerts in x.javaComparing the commit lists of Patchset-2 and Patchset-1 reveals the following details:
Commits
f613e98,4f80f46, and0b5c42bremain unchanged.Commit
47c53b7has been deleted.New commits
054ea6d,06a5e4f,7525c08, and3add20bhave been added.
For Reviewer-A, the three unchanged commits were already reviewed in Patchset-1. Only the deleted commit and the four new commits require a fresh review.
This practice of reviewing significantly improves efficiency. On one hand, the scope of changes that reviewers need to focus on is reduced, eliminating the need to browse through all file changes to identify differences each time. On the other hand, it provides a deeper understanding of the coding thought and design of the author, helping reviewers provide more accurate and constructive feedback.
To identify changes between commits, the range-diff command can be used. For instance, running git range-diff adf3e90..47c53b7 adf3e90..3add20b shows the differences between Patchset ranges, with the results displayed in the terminal as follows.
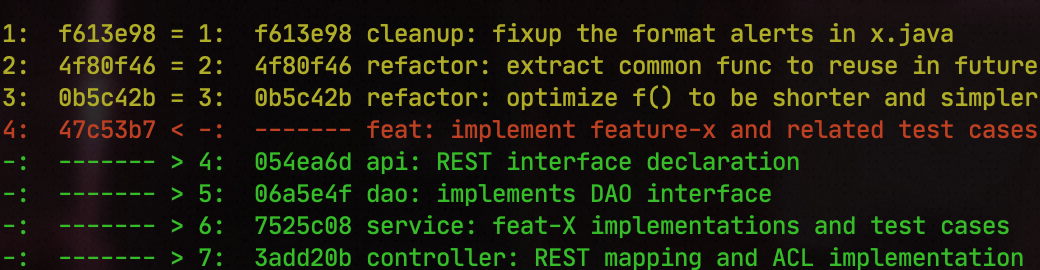
The symbols are interpreted as follows:
=indicates that the commit has not changed.<indicates that the commit has been deleted.>indicates that the commit has been added.!indicates that the commit has changed (for example, metadata such as commit messages or author information, or file changes).
In Alibaba Cloud DevOps code reviews, you can also directly view the range-diff content on the page in the Patchset Comparison view.
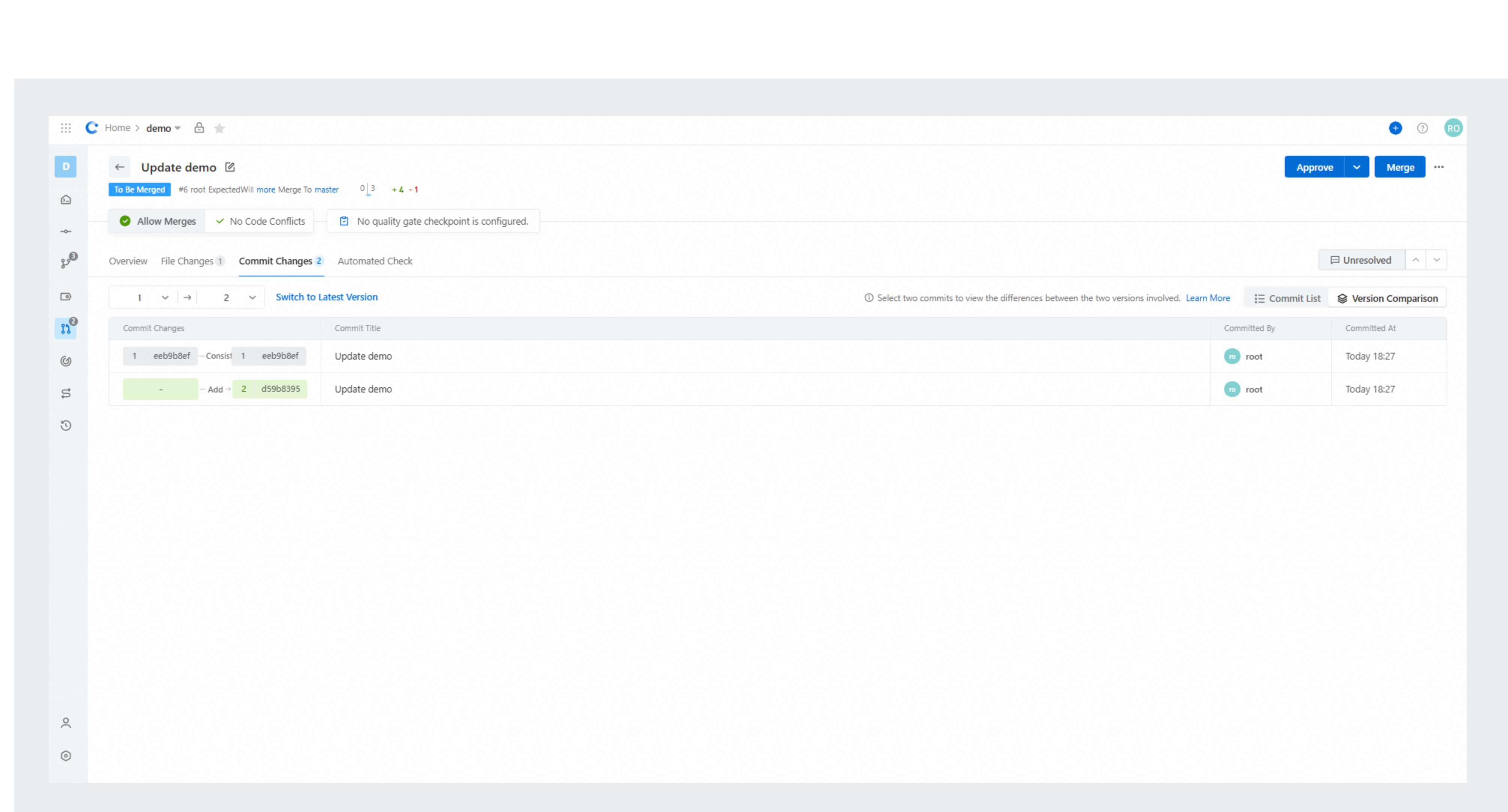
Summary
Commit List is suitable for the initial review scenario, where all commits are reviewed in full. On the other hand, Patchset Comparison is ideal for iterative reviews of multiple patches, focusing on the changes between Patchsets and enabling incremental reviews.
After decoupling the commit content and maintaining atomicity, frequently sending the latest version patches (a patch-based review workflow) becomes an excellent practice. On one hand, it allows developers to promptly inform reviewers of progress; on the other hand, the content reviewed by reviewers in each iteration becomes more manageable and efficient.
For example, if a patch containing four commits (Patch A) is sent out just before leaving work on Friday, but during the review, the reviewer points out issues with the API interface design that require modifying all four commits, this would clearly be less than ideal. The API interface design was completed as early as Monday. Excellent commits allow developers to receive timely feedback from reviewers, address issues earlier, and establish a low-cost, positive review cycle.
Alibaba Cloud DevOps code reviews adhere to the principle of promoting best practices and supports a "small steps, fast iterations" review model, helping developers streamline the code review process and achieve efficient collaboration.