TPC-DS is one of the most well-known benchmarks used to measure the performance of big data systems. Alibaba Cloud E-MapReduce (EMR) has repeatedly achieved the best official results in TPC-DS benchmarks. EMR is the first big data system certified to run the TPC-DS 100 TB benchmark. This topic describes how to execute the 99 SQL statements of TPC-DS and achieve optimal performance.
Background
TPC-DS is a standard benchmark formulated by Transaction Processing Performance Council (TPC), the most well-known organization that defines measurement benchmarks for data management systems. TPC also publishes the measurement results of this benchmark. The official tools of TPC-DS include only a query generator and a standalone data generator, which are not suitable for big data scenarios. In this topic, the following tool and cluster information are used:
- Hive TPC-DS benchmark testing tool
This tool is the most commonly used testing tool in the industry. It is developed by Hortonworks and allows you to use Hive and Spark to run benchmarks such as TPC-DS or TPC-H.
EMR V5.19.0
The Hive TPC-DS benchmark testing tool is developed based on Hortonworks HDP 3, which corresponds to Hive 3.1. In this topic, an EMR cluster of V5.19.0 is used.
Limitations
You can perform the operations in this topic to run the TPC-DS benchmark if you use an EMR cluster of V4.8.0 or a later minor version, or an EMR cluster of V5.1.0 or a later minor version.
Usage notes
This topic uses a DataLake cluster. Therefore, the name of the master node is master-1-1. If you use a Hadoop cluster, you need to change the name of the master node to emr-header-1.
Step 1: Create an EMR cluster and download the Hive TPC-DS benchmark testing tool
Create a cluster of EMR V5.19.0. For more information, see Create a cluster.
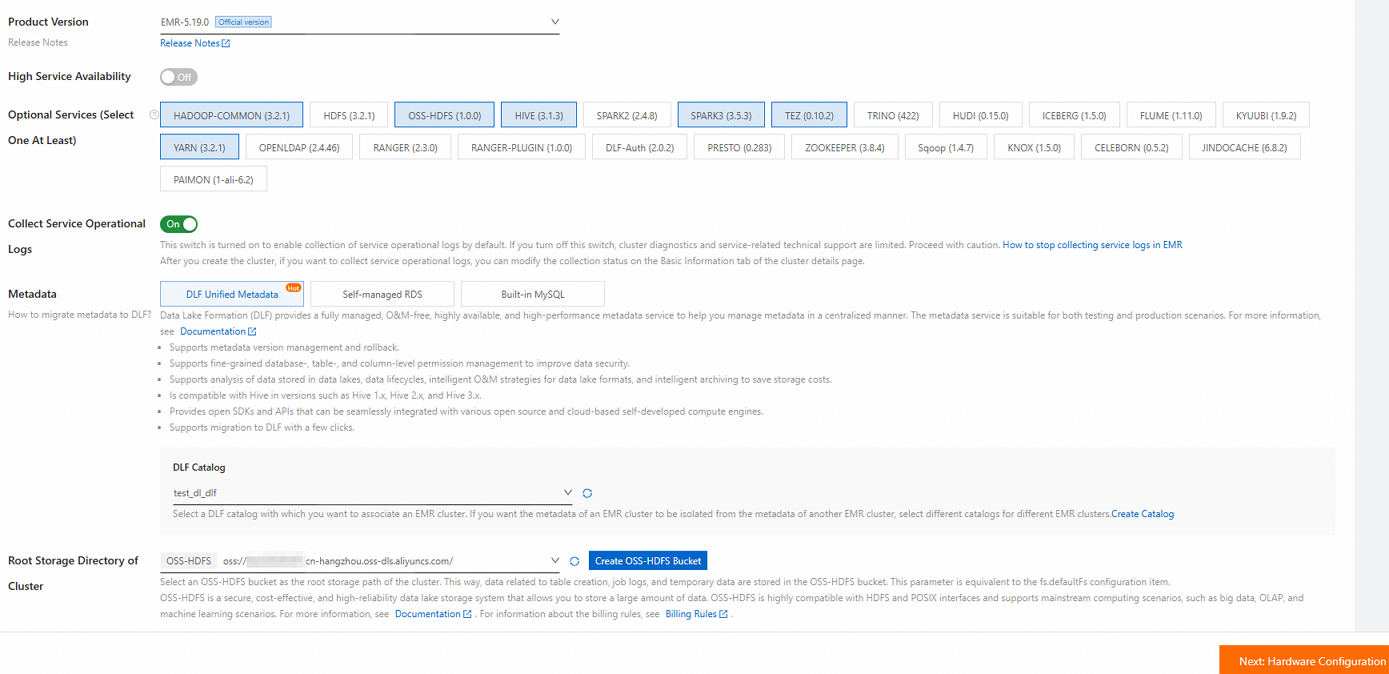
Note the following items when you create the cluster:
Business Scenario: Select Data Lake.
Product Version: Select EMR-5.19.0.
Optional Services (Select One At Least): Use the default settings.
Node Group: If you want to achieve the best performance, we recommend that you select a big data or local SSD instance type for the core nodes. If you want to use a small amount of data to complete all processes in a short period of time, you can also select a general-purpose instance type that has 4 vCPUs and 16 GiB of memory for the core nodes.
ImportantYou can determine the cluster size based on the dataset that you want to use. Make sure that the total capacity of the data disks of the core nodes is more than three times the size of the dataset. For information about datasets, see Step 3: Generate and load data.
Metadata: We recommend that you select DLF Unified Metadata.
Root Storage Directory of Cluster: Select a bucket for which HDFS is enabled.
If OSS-HDFS is not supported in the current region, change the region or select HDFS but not OSS-HDFS for Optional Services (Select One At Least).

Assign Public Network IP: In the master node group, turn on the Assign Public Network IP switch.
Log on to the master node of your cluster in SSH mode. For more information, see Log on to a cluster.
Install Git and Maven.
Run the following command to install Git:
sudo yum install -y gitDownload the Binary tar.gz archive package of the latest version from the Apache Maven Project page.
In this topic, apache-maven-3.9.10-bin.tar.gz is used as an example.
Upload the Binary tar.gz archive package to the master node of your EMR cluster and decompress the package.
tar zxf apache-maven-3.9.10-bin.tar.gz cd apache-maven-3.9.10 # Set Maven environment variables (effective only in the current terminal session) export MAVEN_HOME=`pwd` export PATH=`pwd`/bin:$PATH
Download the Hive TPC-DS benchmark testing tool.
Download the hive-testbench-hdp3.zip package.
Run the following command to upload the ZIP package to the master node of your EMR cluster:
scp hive-testbench-hdp3.zip root@**.**.**.**:/root/Note**.**.**.**indicates the public IP address of the master node. To obtain the public IP address of the master node, perform the following steps: Go to the Nodes tab of your cluster. Find the master node group and click the icon.
icon.Run the following command to decompress the uploaded ZIP package:
unzip hive-testbench-hdp3.zip
Step 2: Compile and package a data generator
Optional. Configure an Alibaba Cloud image.
You can use an image provided by Alibaba Cloud to accelerate Maven compilation in regions in the Chinese mainland. If the image is used, a data generator can be compiled and packaged in 2 to 3 minutes.
Run the following command to create a directory:
mkdir -p ~/.m2/Run the following command to copy the configuration file of Maven to the new directory:
cp $MAVEN_HOME/conf/settings.xml ~/.m2/Add the following image information to the
~/.m2/settings.xmlfile:<mirror> <id>aliyun</id> <mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf> <name>Nexus aliyun</name> <url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public</url> </mirror>
Switch to the
hive-testbenchdirectory.cd hive-testbenchUse the toolset of TPC-DS to compile and package a data generator.
./tpcds-build.sh
Step 3: Generate and load data
Specify a scale factor (SF).
An SF is used to specify the size of a dataset. The size is measured in GB. For example, SF=1 indicates a 1 GB dataset, SF=100 indicates a 100 GB dataset, and SF=1000 indicates a 1 TB dataset. In this example, a small dataset is used, and SF is set to 3. Command:
SF=3ImportantMake sure that the total capacity of data disks of the core nodes is more than three times the size of the dataset. Otherwise, an error will be reported in subsequent operations.
Check and clean up the Hive database that you want to use.
Check whether the Hive database that you want to use exists.
hive -e "desc database tpcds_bin_partitioned_orc_$SF"Optional. If the database exists, clean up the database.
ImportantIf the tpcds_bin_partitioned_orc_$SF database exists, you must run the following command to clean up the database. Otherwise, an error will be reported in subsequent operations. If the database does not exist, skip this step.
hive -e "drop database tpcds_bin_partitioned_orc_$SF cascade"
Configure a Hive service URL.
The default Hive service URL configured in the
tpcds-setup.shscript file is inconsistent with the Hive service URL configured in the EMR cluster. You must run the following command to replace the default Hive service URL with the Hive service URL configured in the EMR cluster:sed -i 's/localhost:2181\/;serviceDiscoveryMode=zooKeeper;zooKeeperNamespace=hiveserver2?tez.queue.name=default/master-1-1:10000\//' tpcds-setup.shThe default Hive service URL in the script file is
jdbc:hive2://localhost:2181/;serviceDiscoveryMode=zooKeeper;zooKeeperNamespace=hiveserver2?tez.queue.name=default. After you run the preceding command, the Hive service URL is changed tojdbc:hive2://master-1-1:10000/.Fix configuration issues for the Hive TPC-DS benchmark testing tool.
Some parameters are not supported in open source Hive of specific versions such as Hive 2 and Hive 3. If you continue to use TPC-DS in Hive 2 or Hive 3, an error may be reported for jobs. You must run the following command to replace the unsupported parameters:
sed -i 's/hive.optimize.sort.dynamic.partition.threshold=0/hive.optimize.sort.dynamic.partition=true/' settings/*.sqlGenerate and load data.
If SF is set to 3, data can be generated and loaded in approximately 40 to 50 minutes. If this step is successful, the generated TPC-DS data table is loaded to the tpcds_bin_partitioned_orc_$SF database. The compute-storage separation architecture of EMR simplifies the operations of storing data in OSS-HDFS.
Run the following command to generate and load data:
./tpcds-setup.sh $SFThe following output is returned.
Obtain Hive table statistics.
We recommend that you use the Hive SQL ANALYZE command to obtain Hive table statistics. This helps speed up subsequent SQL queries. If SF is set to 3, the Hive table statistics can be obtained in approximately 20 to 30 minutes.
hive -f ./ddl-tpcds/bin_partitioned/analyze.sql \ --hiveconf hive.execution.engine=tez \ --database tpcds_bin_partitioned_orc_$SF
Data Lake Formation (DLF) is used to store the metadata of Hive tables. Therefore, you can release the EMR cluster based on your business requirements after data is generated. After the cluster is released, you can query the generated TPC-DS data in other EMR clusters that are in the same region as the released cluster.
Step 4: Execute TPC-DS SQL statements
You can use Hive or Spark to execute TPC-DS SQL statements.
Use Hive to execute TPC-DS SQL statements
Execute a single SQL statement.
TPC-DS has a total of 99 SQL files, such as
query10.sqlandquery11.sql. All the files are placed in thesample-queries-tpcdsdirectory. If SF is set to 3, every TPC-DS SQL statement can return output within 5 minutes.ImportantTPC-DS queries and TPC-DS data are randomly generated. Therefore, some SQL statements may return no records.
cd sample-queries-tpcds hive --database tpcds_bin_partitioned_orc_$SF set hive.execution.engine=tez; source query10.sql;After you execute the command, you can exit Hive
Execute all 99 SQL statements in sequence by using the script file that is provided in the toolset of TPC-DS. Example:
cd ~/hive-testbench # Generate a Hive configuration file and set the Hive execution engine to Tez. echo 'set hive.execution.engine=tez;' > sample-queries-tpcds/testbench.settings ./runSuite.pl tpcds $SFThe following output is returned.
Use Spark to execute TPC-DS SQL statements
The toolset of TPC-DS provides some sample Spark SQL statements in the spark-queries-tpcds directory. You can use a command-line tool, such as spark-sql or spark-beeline, to execute the sample statements. In this step, Spark Beeline, which is connected to Spark Thrift Server, is used in the example. This example shows how to execute TPC-DS SQL statements to query the TPC-DS dataset that is generated in Step 3: Generate and load data.
EMR Spark allows you to store tables in multiple storage media, such as HDFS and OSS, and allows you to store metadata in DLF.
Run the Spark Beeline ANALYZE command to obtain Hive table statistics. This helps speed up subsequent SQL queries.
cd ~/hive-testbench spark-beeline -u jdbc:hive2://master-1-1:10001/tpcds_bin_partitioned_orc_$SF \ -f ./ddl-tpcds/bin_partitioned/analyze.sqlSwitch to the directory in which the sample Spark SQL statements are placed.
cd spark-queries-tpcds/Execute a single SQL statement.
spark-beeline -u jdbc:hive2://master-1-1:10001/tpcds_bin_partitioned_orc_$SF -f q1.sqlExecute all 99 SQL statements in sequence.
The toolset of TPC-DS does not contain a script file that can be used to execute all the Spark SQL statements at once. You can use the following simple script for reference:
for q in `ls *.sql`; do spark-beeline -u jdbc:hive2://master-1-1:10001/tpcds_bin_partitioned_orc_$SF -f $q > $q.out doneImportantIn the
q30.sqlfile, the column namec_last_review_date_skis written asc_last_review_dateby mistake. Therefore, the thirtieth SQL statement fails.If an error is reported when you use the script to execute all 99 SQL statements in sequence, you may find a solution in FAQ.