Overview
Solution description
Most application services of enterprises use the IP addresses provided by multiple Internet service providers (ISPs). This may cause issues such as cross-network delay, packet loss, and unavailability. Global Traffic Manager (GTM) can detect the ISP of a user and respond to the Domain Name System (DNS) requests of this user with the IP addresses of application servers nearby to this user. This enables the user to access the nearby application servers and accelerates network access. GTM can also perform failovers, which efficiently reduces fault impact and ensures service access continuity.
Intended audience
This topic is intended for personnel who are responsible for the network or business O&M of an enterprise.
Scenarios
An application service uses the IP addresses provided by multiple ISPs, and latency and packet loss occur in cross-ISP network access.
The IP address of an ISP for a service becomes abnormal and users from this ISP are unable to access the service.
Terms
Term | Description |
GTM | GTM supports intelligent DNS resolution, health checks, fault isolation, and failovers. GTM can help enterprises quickly establish a disaster recovery architecture where two data centers are deployed in the same region or three data centers are deployed across two regions. |
intelligent DNS resolution | GTM allows a user to access a nearby application server by returning the IP address of the server based on the DNS request source of the user, such as an ISP or a specific region. |
health check | GTM performs Layer 3 to Layer 7 health checks on servers to identify exceptions in a timely manner. |
primary and secondary address pools | The addresses of different data centers are added to primary and secondary address pools to achieve fault isolation and failovers among these data centers. |
Solution architecture
Solution architecture diagram

Benefits
High availability: Addresses are monitored in real time and exceptions can be quickly identified. If an address of an ISP is deemed abnormal, the access traffic can be automatically or manually failed over to the IP address of another ISP. The failover takes about only 1 minute, which ensures service access continuity.
Access acceleration: Users can access nearby servers. This improves user experience in cross-ISP network access and cross-region access.
Ease of use: GTM allows enterprises to establish a disaster recovery architecture that receives DNS requests within only 5 minutes. In addition, enterprises can integrate their application services with GTM without the need to adjust their application services. The integration does not impact their application services.
Easy O&M: GTM is the first service in China that allows enterprises to manage the IP addresses and traffic of multiple data centers. The data centers are provided by different ISPs and vendors, and reside in different regions.
Cost effectiveness: You are charged only CNY 1,536 per year for a business domain name that is connected to GTM. No IT resources fees are incurred. However, the cost of building a traffic management system is high. For example, it takes at least tens of thousands of dollars to purchase a set of traditional global server load balancing (GSLB) devices. In addition, it takes a long time to build a disaster recovery system.
Solution implementation
Prerequisites
A GTM instance is created. You can click here to purchase a GTM instance.
NoteTo identify a fault and perform a failover, a GTM instance of Ultimate Edition requires about 1 minute and a GTM instance of Standard Edition requires about 3 minutes. If you require high service availability, we recommend that you purchase a GTM instance of Ultimate Edition.
The following IP addresses are prepared: the IP address of China Unicom
3.3.XX.XX, the IP address of China Telecom2.2.XX.XX, and the IP address of China Mobile1.1.XX.XX.
Procedure
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console and click Global Traffic Manager in the left-side navigation pane. On the Global Traffic Manager page, find the desired GTM instance in the instance list and click Settings in the Actions column. Click Advanced Settings.
Configure address pools: On the Address Pools tab, click Create Address Pool to create three address pools: Mobile, Telecom, and Unicom. For more information, see Address pool configurations. Enable the health check feature for each address pool. For more information, see Health checks.
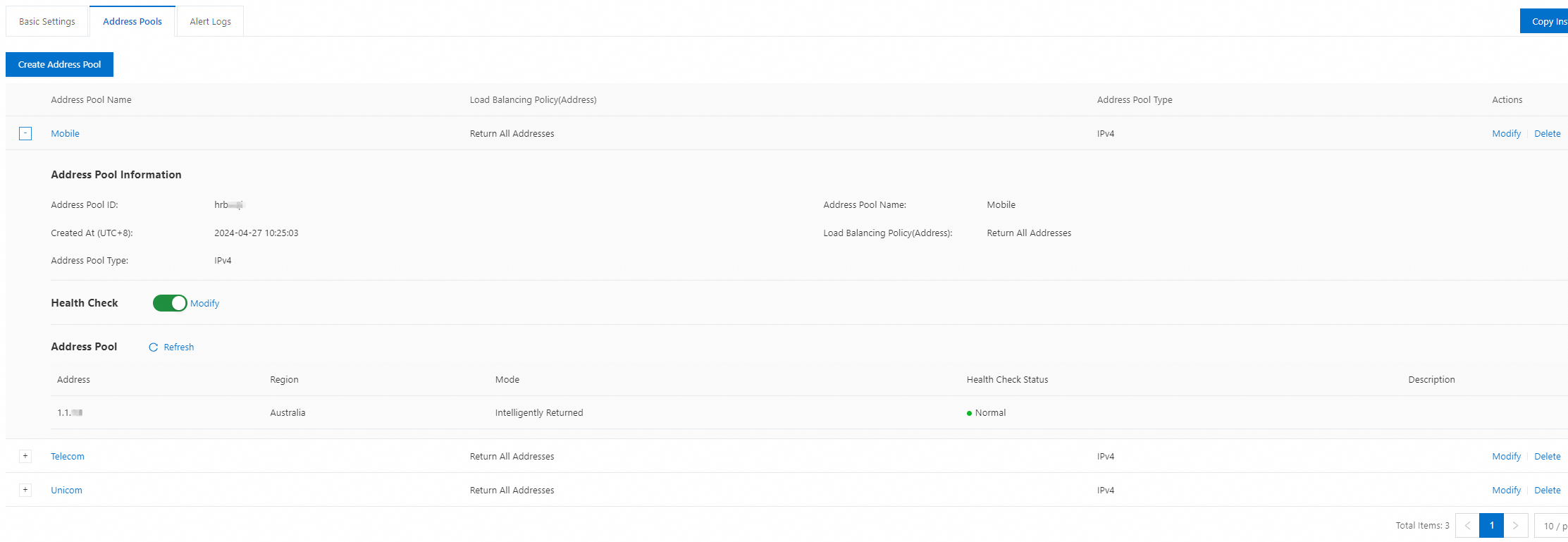
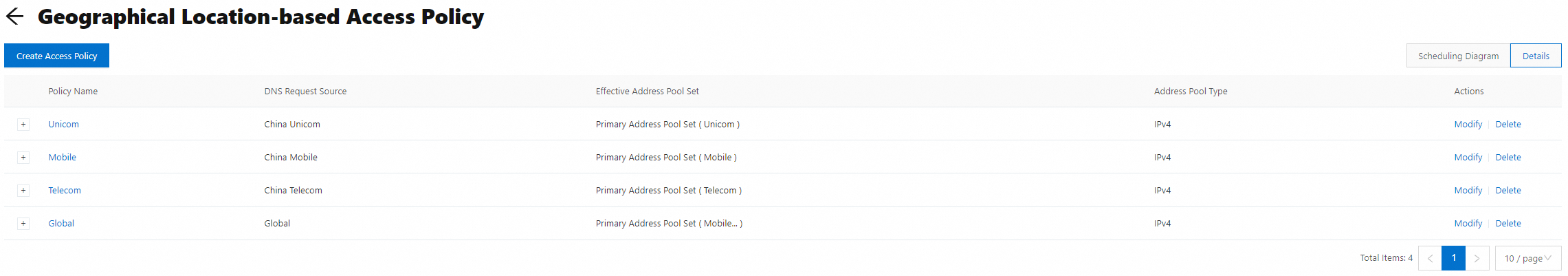
Configure access policies: On the Basic Settings tab, click Settings in the Geographical Location-based Access Policy section and click Create Access Policy. Create four access policies. If the address pool specified in an ISP-based access policy is abnormal, traffic is distributed to the address pools specified in the global access policy. This ensures the normal running of your service.
Global access policy: Select Global for the DNS Request Source parameter, select the Mobile, Telecom, and Unicom address pools for the Primary Address Pool Set parameter, and do not specify the Secondary Address Pool Set parameter.
Access policy for China Telecom users: Select China Telecom for the DNS Request Source parameter, select the Telecom address pool for the Primary Address Pool Set parameter, and do not specify the Secondary Address Pool Set parameter.
Access policy for China Unicom users: Select China Unicom for the DNS Request Source parameter, select the Unicom address pool for the Primary Address Pool Set parameter, and do not specify the Secondary Address Pool Set parameter.
Access policy for China Mobile users: Select China Mobile for the DNS Request Source parameter, select the Mobile address pool for the Primary Address Pool Set parameter, and do not specify the Secondary Address Pool Set parameter.
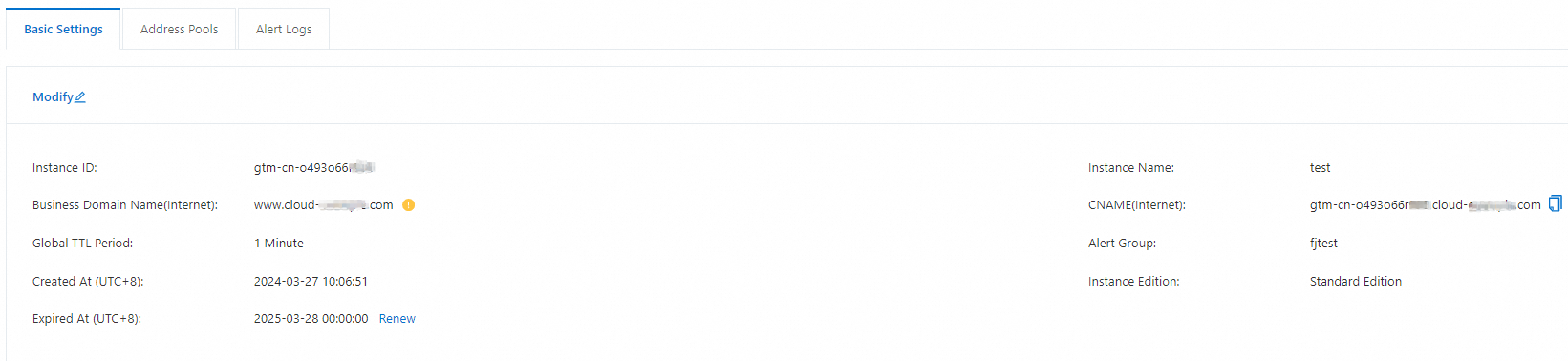
Configure basic settings: On the Basic Settings tab, click Modify. Configure the Global TTL Period parameter based on your business requirements. We recommend that you set the Global TTL Period parameter to 1 Minute. For more information, see Basic settings.
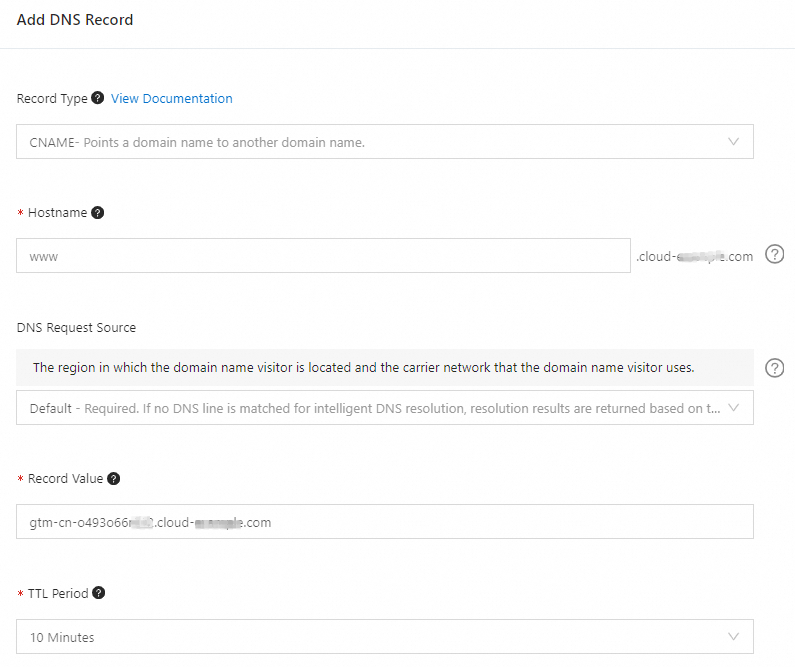
Receive online traffic: Add a canonical name (CNAME) record at the DNS service provider of your business domain name to point the business domain name to an access domain name. This way, the business domain name can connect to GTM. The following figure shows how to configure a CNAME record for a business domain name if the business domain name is hosted by Alibaba Cloud DNS.
FAQ
How long does it take to complete a failover? If you use a GTM instance of Ultimate Edition, you can set the health check interval to 15 seconds, the time to live (TTL) value to 10 seconds, and the number of consecutive failures to 2. In this case, GTM takes about 1 minute to detect a failure after the failure occurs and perform a failover. Theoretically, the new configuration takes effect on the entire network within about 10 seconds.
If you use a GTM instance of Standard Edition, you can set the health check interval to 60 seconds, the TTL value to 60 seconds, and the number of consecutive failures to 2. In this case, GTM takes about 3 minutes to detect a failure after the failure occurs and perform a failover. Theoretically, the new configuration takes effect on the entire network within about 60 seconds.
ImportantThe time required for the new configuration to take effect is affected by the TTL values of DNS records cached in the local DNS servers of ISPs. To reduce the workloads of DNS recursive resolvers, some ISPs may increase the TTL values, which prolongs the time required for the new configuration to take effect on the entire network.
Can I use GTM if I do not use Alibaba Cloud DNS? Yes, GTM can provide an access domain name to allow you to create a CNAME record for your business domain name on the management platform of your DNS service provider.