Link IoT Edge allows you to use Function Compute to create edge applications.
Prerequisites
A function is created. For more information, see What is Function Compute?
Procedure
Log on to the Link IoT Edge console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Applications.
On the Applications page, click Create Application.
On the page that appears, set the parameters and click Confirm.
Application Information
Parameter
Description
Application Name
The name of the edge application. The application name must be 1 to 128 characters in length, and can contain letters, digits, and underscores (_).
Application Type
The method that is used to create the edge application. Valid values:
Function Compute: Function Compute is used to create the edge application.
Container Image: Container Registry is used to create the edge application.
Local Upload: A function developed on premises is used to create the edge application.
In this example, set this parameter to Function Compute.
Region
The region where your Function Compute service resides.
Service
The service where the function resides.
Function
The function that you created.
ImportantYou can use functions that are created by using the Python programming language only in Link IoT Edge Professional Edition.
Authorization
The RAM role that Link IoT Edge assumes to connect to Function Compute. For more information, see Access resources of other Alibaba Cloud services.
Application Version
The unique version number of the edge application. You cannot specify two identical version numbers for an edge application.
Version Description
Optional. The description of the edge application version. For example, you can specify the version features.
Function Configurations
Parameter
Description
Running Mode
The execution mode of the function. Valid values:
On-demand: This execution mode is native to Function Compute. After functions are deployed to the edge, the functions are triggered by events. If no events trigger the functions within a specified period of time, the functions that are being run stop execution. If your program is triggered by events every less than 20 minutes, we recommend that you select this execution mode. This reduces the consumed resources of edge gateways, such as CPU and memory. If your program is frequently triggered by events, functions can be run on demand to reduce the event response time.
Continuous: This execution mode is available only at the edge. Functions are loaded and run immediately after the functions are deployed to the edge. This helps you meet the needs of server programs that are required to run on a permanent basis. If you use server programs and the listening ports must respond to requests, we recommend that you select this execution mode. One of the examples is HTTP servers. Link IoT Edge ensures that functions run on a permanent basis. Functions are automatically resumed if they stop execution due to unexpected errors.
Memory Limit
The upper limit of the memory for the function. If the consumed memory of a function reaches the upper limit, the function is restarted. This allows you to prevent system instability that is caused by memory leaks. If the upper limit is set to an excessively small value, the function may fail to run. The default upper limit is 512 MB. You can keep the default setting.
Timeout
The timeout period. If a specified event occurs, the edge application to be created invokes the handler function in the code to process the event. After the event is processed, the handler function sends response messages and returns the processing result. If the handler function does not return the processing result before the specified timeout period expires, the handler function fails to run as expected. In this case, the handler function is restarted.
Scheduled Execution
Specifies whether to enable scheduled execution for the function. If you turn on Scheduled Execution, you can configure when and how often the function is triggered by using a CRON expression. For example,
* * * * *indicates that the function is triggered every minute, and20 * * * *indicates that the function is triggered at the twentieth minute of each hour. For more information, visit CRONTAB.Environmental Variables
The custom environment variables. The edge application to be created can read the specified environment variables when you run the function code. To add an environment variable, click Add Environment Variable. Then, specify the variable name and variable value. You can add a maximum of 10 environment variables.
Environment variables allow you to enhance code portability by separating configurations from code. For example, to run the function code, you may need to send requests to call services from other servers on the network. In most cases, the server IP address and port number vary based on the network environment. In this scenario, you can specify the IP address and port number as input parameters by using environment variables. This ensures that the function code is portable across gateways in various network environments.
Container Configurations
Parameter
Description
Host Mode
Specifies whether to isolate the container network from the host network. Valid values:
Yes: The container network is the same as the host network.
No: The container network is isolated from the host network. If you select this option, you must set the Network Port Mapping parameter.
Network Port Mapping
The mappings between host network ports and container network ports. This parameter is available only when you set the Host Mode parameter to No. The network where the function runs is isolated from the host network. You can map the listening port of the function in the container to a host network port. This allows client programs on various hosts to access the services that are provided by the function. You can specify a maximum of 10 entries.
For example, the
fc-http-serverfunction runs in a host container, and provides services by using Port 80. The client programs on other hosts cannot access thefc-http-serverfunction by accessing Port 80 on the current host. To enable the client programs on other hosts to access thefc-http-serverfunction, you must map Port 80 in the container where the function runs to a host network port, such as Port 8080. Then, the client programs on other hosts can accessIP address:port 8080on the host network, and use the services provided by thefc-http-serverfunction.Privilege Mode
Specifies whether to enable the privilege mode. Root users of containers can access host services only as regular users. If you need to change the system time or run the mount command in containers, you must be granted the required root permissions. In this scenario, you must enable the privilege mode for the containers.
NoteIf you enable the privilege mode, applications and programs in the containers are granted the host root permissions, and all the host devices are mapped to the containers. Therefore, you do not need to set the Device Mapping parameter.
Device Mapping
The device mappings. This parameter is available only when you set the Privilege Mode parameter to No. The network where the device management system resides is isolated from the host network. To enable a function to access a host device such as a serial port, you must map the device to the container where the function runs. You can specify a maximum of 10 entries.
Volume Mapping
The volume mappings. The network where the file system resides is isolated from the host network. To enable a function to access a host file, you must map the file to the container where the function runs. You can specify a maximum of 10 entries.
View the edge application that you created on the Applications page. You can also click buttons in the Actions column to manage the edge application.
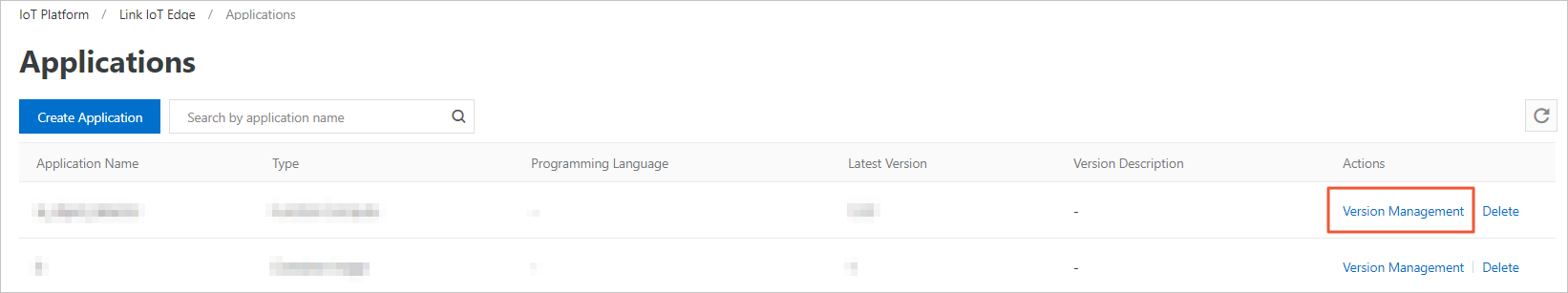
Manage versions
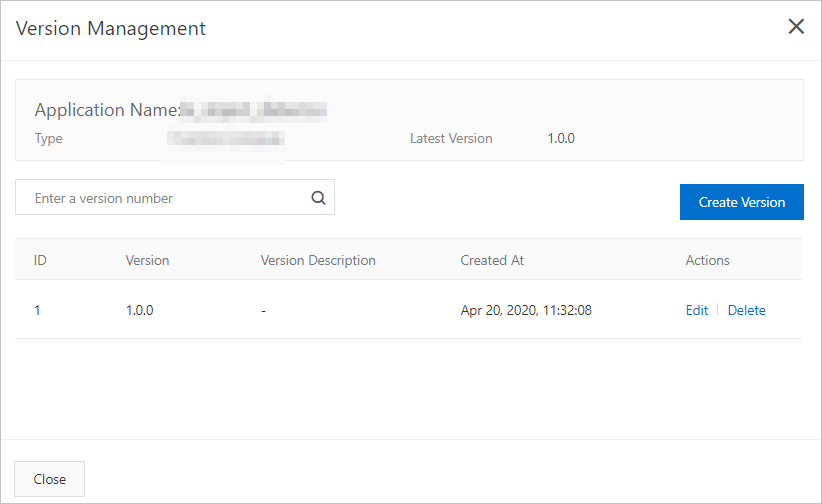
To manage versions, click Version Management. In the Version Management panel, you can create, modify, or delete versions based on your business requirements.
Delete the edge application
To delete the edge application, click Delete.
NoteBefore you delete the edge application, you must delete all versions of the edge application. Otherwise, the edge application cannot be deleted.
What to do next
Assign the created edge application to the edge instance. For more information, see Assign edge applications to edge instances.