If your MaxCompute data exceeds 200 GB and you have complex queries that require response times in seconds, import the data directly into Hologres internal tables. This method is more efficient than querying data through foreign tables because you can create indexes on the internal tables. This topic describes how to import data in different scenarios and provides answers to frequently asked questions.
Notes
When you import MaxCompute data to Hologres using SQL, note the following:
-
MaxCompute partitions do not have a strong mapping relationship with Hologres partitions. A MaxCompute partition field is mapped to a regular field in Hologres. Therefore, you can import data from a partitioned MaxCompute table into either a non-partitioned or a partitioned table in Hologres.
-
Hologres supports only single-level partitioning. When you import data from a multi-level partitioned MaxCompute table into a partitioned Hologres table, map only one partition field. The other partition fields are mapped to regular fields in Hologres.
-
To update or overwrite existing data during the import, use the INSERT ON CONFLICT (UPSERT) syntax.
-
For information about the data type mapping between MaxCompute and Hologres, see Data type summary.
-
After data in a MaxCompute table is updated, there is a cache latency in Hologres, which is usually within 10 minutes. Before you import data, run the IMPORT FOREIGN SCHEMA command to update the foreign table and retrieve the latest data.
-
When you import MaxCompute data to Hologres, use SQL instead of data integration. SQL import provides better performance.
Import data from a non-partitioned MaxCompute table to Hologres and query the data
-
Prepare data in a non-partitioned MaxCompute table.
Create a non-partitioned source data table in MaxCompute, or use an existing one.
This example uses the customer table from the public_data public dataset in MaxCompute. For more information about how to log on and query the dataset, see Use public datasets. The DDL statement for the table and its data are as follows.
-- DDL of the table in the MaxCompute public dataset CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS public_data.customer( c_customer_sk BIGINT, c_customer_id STRING, c_current_cdemo_sk BIGINT, c_current_hdemo_sk BIGINT, c_current_addr_sk BIGINT, c_first_shipto_date_sk BIGINT, c_first_sales_date_sk BIGINT, c_salutation STRING, c_first_name STRING, c_last_name STRING, c_preferred_cust_flag STRING, c_birth_day BIGINT, c_birth_month BIGINT, c_birth_year BIGINT, c_birth_country STRING, c_login STRING, c_email_address STRING, c_last_review_date STRING, useless STRING); -- Query the table in MaxCompute to check for data SELECT * FROM public_data.customer;The following figure shows some of the data.
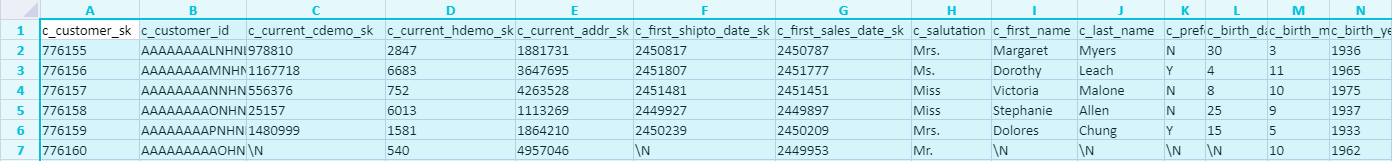
-
Create a foreign table in Hologres.
Create a foreign table in Hologres to map the source data table in MaxCompute. The following sample SQL statement is used.
CREATE FOREIGN TABLE foreign_customer ( "c_customer_sk" int8, "c_customer_id" text, "c_current_cdemo_sk" int8, "c_current_hdemo_sk" int8, "c_current_addr_sk" int8, "c_first_shipto_date_sk" int8, "c_first_sales_date_sk" int8, "c_salutation" text, "c_first_name" text, "c_last_name" text, "c_preferred_cust_flag" text, "c_birth_day" int8, "c_birth_month" int8, "c_birth_year" int8, "c_birth_country" text, "c_login" text, "c_email_address" text, "c_last_review_date" text, "useless" text ) SERVER odps_server OPTIONS (project_name 'public_data', table_name 'customer');Parameter
Description
Server
You can directly call the foreign table server named odps_server that is already created in the underlying layer of Hologres. For more information about the principles, see Postgres FDW.
Project_Name
The name of the project where the MaxCompute table resides.
Table_Name
The name of the MaxCompute table to query.
The data types of the fields in the foreign table must be consistent with the data types of the fields in the MaxCompute table. For more information about data type mapping, see Data type mapping between MaxCompute and Hologres.
-
Create a storage table in Hologres.
Create a storage table in Hologres to receive data from the MaxCompute source table.
This is a basic DDL example. When you import data, create a table with a schema and appropriate indexes as needed to achieve better query performance. For more information about table properties, see CREATE TABLE.
-- Create a sample column-oriented table BEGIN; CREATE TABLE public.holo_customer ( "c_customer_sk" int8, "c_customer_id" text, "c_current_cdemo_sk" int8, "c_current_hdemo_sk" int8, "c_current_addr_sk" int8, "c_first_shipto_date_sk" int8, "c_first_sales_date_sk" int8, "c_salutation" text, "c_first_name" text, "c_last_name" text, "c_preferred_cust_flag" text, "c_birth_day" int8, "c_birth_month" int8, "c_birth_year" int8, "c_birth_country" text, "c_login" text, "c_email_address" text, "c_last_review_date" text, "useless" text ); CALL SET_TABLE_PROPERTY('public.holo_customer', 'orientation', 'column'); CALL SET_TABLE_PROPERTY('public.holo_customer', 'bitmap_columns', 'c_customer_id,c_salutation,c_first_name,c_last_name,c_preferred_cust_flag,c_birth_country,c_login,c_email_address,c_last_review_date,useless'); CALL SET_TABLE_PROPERTY('public.holo_customer', 'dictionary_encoding_columns', 'c_customer_id:auto,c_salutation:auto,c_first_name:auto,c_last_name:auto,c_preferred_cust_flag:auto,c_birth_country:auto,c_login:auto,c_email_address:auto,c_last_review_date:auto,useless:auto'); CALL SET_TABLE_PROPERTY('public.holo_customer', 'time_to_live_in_seconds', '3153600000'); CALL SET_TABLE_PROPERTY('public.holo_customer', 'storage_format', 'segment'); COMMIT; -
Import data to Hologres.
NoteHologres V2.1.17 and later support Serverless Computing. For scenarios such as large-scale offline data import, large extract, transform, and load (ETL) jobs, and large-volume queries on foreign tables, you can use Serverless Computing to execute these tasks. This feature uses additional serverless resources instead of your instance's own resources. You do not need to reserve extra compute resources for your instance. This significantly improves instance stability, reduces the probability of out-of-memory (OOM) errors, and you are charged only for the individual tasks. For more information about Serverless Computing, see Serverless Computing. For information about how to use Serverless Computing, see Guide to using Serverless Computing.
Use the
INSERTstatement to import data from the MaxCompute source table to Hologres. You can import data from some or all fields. If you import data from some fields, the fields must be in the correct order. The following sample DDL statements are used.-- (Optional) Use Serverless Computing to execute offline import of large amounts of data and ETL jobs. SET hg_computing_resource = 'serverless'; -- Import data from some fields INSERT INTO holo_customer (c_customer_sk,c_customer_id,c_email_address,c_last_review_date,useless) SELECT c_customer_sk, c_customer_id, c_email_address, c_last_review_date, useless FROM foreign_customer; -- Import data from all fields INSERT INTO holo_customer SELECT * FROM foreign_customer; -- Reset the configuration to ensure that unnecessary SQL statements do not use serverless resources. RESET hg_computing_resource; -
Query the MaxCompute table data in Hologres.
Query the imported MaxCompute table data in Hologres. The following sample SQL statement is used.
SELECT * FROM holo_customer;
Import data from a partitioned MaxCompute table to Hologres and query the data
For more information, see Import data from a partitioned MaxCompute table.
Best practices for INSERT OVERWRITE
For more information, see INSERT OVERWRITE.
Synchronize data using a visualization tool or by periodically scheduling synchronization
To synchronize a large amount of data at a time, you can use a visualization tool or a scheduling task.
-
To perform one-click synchronization of MaxCompute data using the HoloWeb visualization tool, follow these steps.
-
Go to the HoloWeb page. For more information, see Connect to HoloWeb and execute a query.
-
In the top menu bar of the HoloWeb developer page, choose , and then click Import MaxCompute Data.
-
Configure the parameters on the Create MaxCompute Data Import Task page.
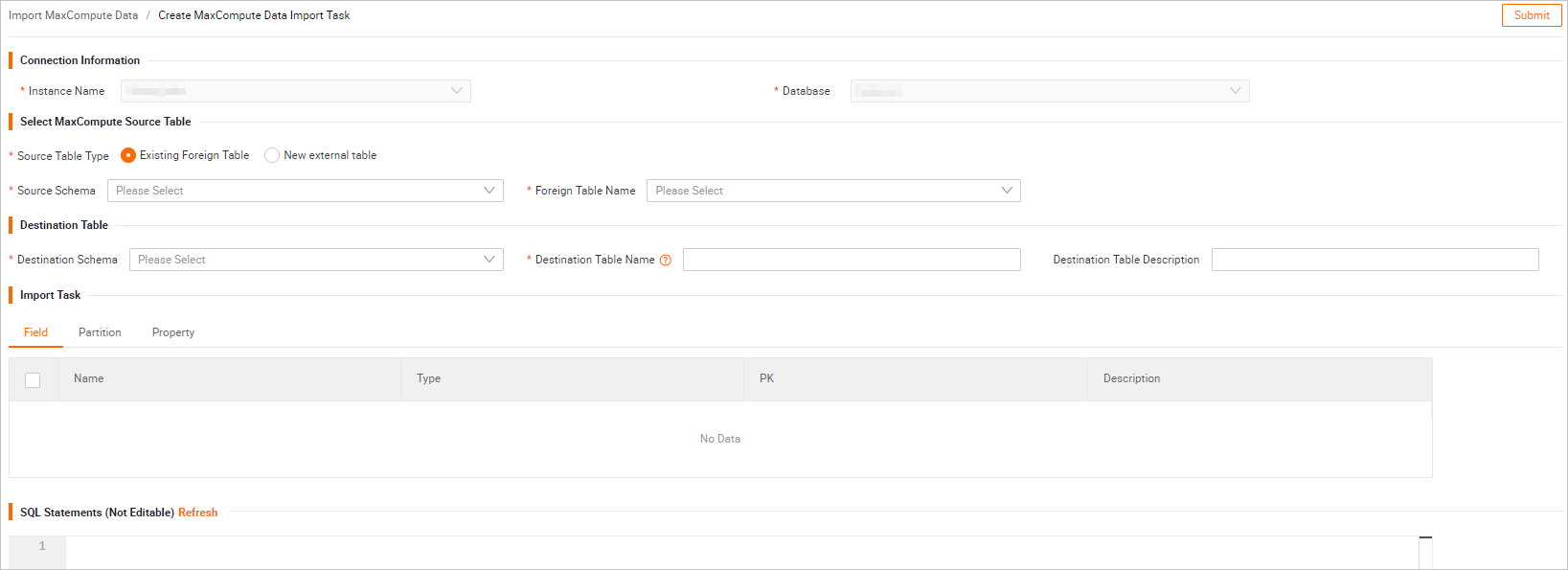 The following table describes the parameters.Note
The following table describes the parameters.NoteSQL Script automatically parses the SQL statement that corresponds to the current visualization operation. You cannot modify the SQL statement in SQL Script. To modify the statement, copy it, make changes manually, and then use SQL to synchronize the data.
Section
Parameter
Description
Instance
Instance Name
The name of the instance that you have logged on to.
Source MaxCompute Table
Project Name
The name of the MaxCompute project.
Schema Name
The schema name in MaxCompute. This parameter is hidden for MaxCompute projects that use a two-layer model. For projects that use a three-layer model, you can select a schema for which you have permissions from the drop-down list.
Table Name
The name of the MaxCompute table. Fuzzy search by prefix is supported.
Destination Hologres Table
Database Name
Select the name of the Hologres database where the internal table is located.
Schema Name
The schema name in Hologres.
The default value is public. You can also select another schema for which you have permissions.
Table Name
The name of the new Hologres internal table.
After you select a MaxCompute table, the name of the MaxCompute table is automatically used. You can also rename the table.
Destination Table Description
The description of the new Hologres internal table. You can customize the description.
Parameter Settings
GUC Parameters
Enter the Grand Unified Configuration (GUC) parameters that you want to set. For more information about GUC parameters, see GUC parameters.
Import Task
Fields
The fields to import from the MaxCompute table.
You can import some or all of the fields.
Partition Configurations
Partition Field
Select a partition field. Hologres then creates a partitioned table by default.
Hologres supports only single-level partitioning. To import multi-level partitions from MaxCompute, set only the first-level partition in Hologres. The other partition fields are automatically mapped to regular fields in Hologres.
Data Timestamp
If the MaxCompute table is partitioned by date, you can select a specific partition date. The system then imports data of the specified date to the Hologres table.
Property
Storage mode
Column-oriented Storage: Suitable for various complex queries.
Row-oriented Storage: Suitable for point queries and scans based on primary keys.
Row-column Storage: Supports all scenarios of row store and column store, and also supports point queries that are not based on primary keys.
If you do not specify a storage mode, Column-oriented Storage is used by default.
Data Lifecycle
The lifecycle of table data. By default, data is stored permanently.
If you specify a lifecycle, the DPI engine deletes the data at some point after the specified period expires if the data is not modified within the period.
Binlog
Specifies whether to enable binary logging. For more information, see Subscribe to Hologres Binlog.
Lifecycle of Binary Logs
The time to live (TTL) for binary logs. The default value is 30 days, which is 2,592,000 seconds.
Distribution Column
Hologres shuffles data to shards based on the distribution column. Rows with the same value in the distribution column are stored in the same shard. Using the distribution column as a filter condition improves query performance.
You can specify columns as the segment key. When a query condition includes a segment column, Hologres uses the segment key to quickly find the data's storage location.
Clustering Key
You can specify columns as the clustering key. The index type is closely related to the column order. A clustering index accelerates range and filter queries on the index columns.
Dictionary Encoding Columns
Hologres supports creating a dictionary mapping for values in a specified column. Dictionary encoding transforms string comparisons into numeric comparisons to accelerate Group By and Filter queries.
Hologres builds a dictionary mapping for the values in specified columns. Dictionary encoding converts string comparisons into numeric comparisons. This accelerates GROUP BY and filter queries. By default, all text columns are set as dictionary encoding columns.
Bitmap Column
Hologres supports bit encoding on bitmap columns. This lets you quickly filter data within a field based on specified conditions.
Hologres builds a bitmap index on specified columns. The bitmap index quickly filters data based on specified conditions. By default, all text columns are set as bitmap columns.
-
Click Submit. After the data is imported, you can query the internal table data in Hologres.
-
-
One-click synchronization in HoloWeb does not support periodic scheduling. To synchronize a large amount of historical data or periodically schedule data import, use DataStudio of DataWorks. For more information, see Best practices for periodically importing MaxCompute data using DataWorks.
FAQ
An out-of-memory (OOM) error occurs when you import data from MaxCompute to Hologres, and an exception that indicates the memory limit is exceeded is reported. The Query executor exceeded total memory limitation xxxxx: yyyy bytes used error is usually reported. The following content describes four possible causes of the error and their solutions.
-
Troubleshooting Step 1
-
Possible cause:
The import query contains a subquery, but the
analyzecommand has not been run on some tables. Alternatively, theanalyzecommand was run, but the data was updated, resulting in inaccurate statistics. This causes the query optimizer to make an incorrect decision on the join order, leading to high memory overhead. -
Solution:
Run the
analyzecommand on all involved internal and foreign tables to update their statistical metadata. This helps the query optimizer generate a better execution plan and resolves the OOM error.
-
-
Step 2
-
Possible cause:
The table has many columns, and the data volume of a single row is large. This increases the amount of data read at a time and leads to high memory overhead.
-
Solution:
Add the following parameter before the SQL statement to control the number of data rows read at a time. This can effectively reduce the occurrence of OOM errors.
SET hg_experimental_query_batch_size = 1024;-- The default value is 8192. INSERT INTO holo_table SELECT * FROM mc_table;
-
-
Step 3: Troubleshooting
-
Possible cause:
During data import, the concurrency is high and CPU consumption is large, which affects internal table queries.
-
Solution:
In Hologres versions earlier than V1.1, you can control the concurrency using the hg_experimental_foreign_table_executor_max_dop parameter. The default value is the number of cores of the instance. During import, you can set hg_experimental_foreign_table_executor_max_dop to a smaller value to reduce memory usage for the import and resolve the OOM error. This parameter is valid for all jobs that are run on foreign tables. The following sample code is used.
SET hg_experimental_foreign_table_executor_max_dop = 8; INSERT INTO holo_table SELECT * FROM mc_table;
-
-
Step 4: Troubleshooting
-
Possible cause:
During data import, the concurrency is high and CPU consumption is large, which affects internal table queries.
-
Solution:
In Hologres V1.1 and later, you can control the concurrency using the hg_foreign_table_executor_dml_max_dop parameter. The default value is 32. During import, set hg_foreign_table_executor_dml_max_dop to a smaller value to reduce the concurrency for running DML statements, especially in data import and export scenarios. This prevents DML statements from consuming excessive resources. The following sample code is used.
SET hg_foreign_table_executor_dml_max_dop = 8; INSERT INTO holo_table SELECT * FROM mc_table;
-