When you use images such as CentOS and Busybox images provided by Elastic Container Instance (ECI) to create an ECI instance, you must set the startup command. Otherwise, the instance may remain in the Starting state. This topic describes how to use a CentOS image provided by ECI to create an ECI instance.
Prerequisites
You have activated the Elastic Container Instance service and the Resource Access Management (RAM) service, and completed the required RAM role authorization.
NoteIf you use a RAM user to create an ECI instance, you must grant permissions to the user. For more information, see Grant permissions to a RAM user.
You have created a virtual private cloud (VPC) and a vSwitch in a supported region.
For information about the regions and zones that ECI supports, see Regions and zones.
To learn how to create a VPC and a vSwitch, see Create a VPC and Create a vSwitch.
NoteWe recommend that you create multiple vSwitches. When you create an ECI instance, you can select these vSwitches to deploy the instance across multiple zones. This improves the success rate of instance creation.
You have created a security group. For more information, see Create a security group.
A security group is a virtual firewall that provides stateful inspection and packet filtering. It is used to set up security domains in the cloud. An ECI instance must belong to a security group. For more information, see Configure a security group for an ECI instance.
Procedure
This section describes the key configurations and steps of using a CentOS image to create an ECI instance. For some parameters, only the minimum required or default configurations are used.
Go to the Elastic Container Instance buy page.
Configure basic information for the instance.
Select a billing method and instance type.
Keep the default selections. The billing method is Pay-As-You-Go and the instance type is Regular Instance.
Select a region.
Select a VPC and a corresponding vSwitch.
You can select multiple vSwitches to use the multi-zone feature. The system then creates the instance in a zone that has sufficient resources.
Select a security group. You can add security group rules to allow or deny access to the ECI instance. This includes access from the public network, private networks, or other IP addresses.
NoteTo access the ECI instance from the public network, you must open the required port in the security group. For more information, see Add a security group rule.
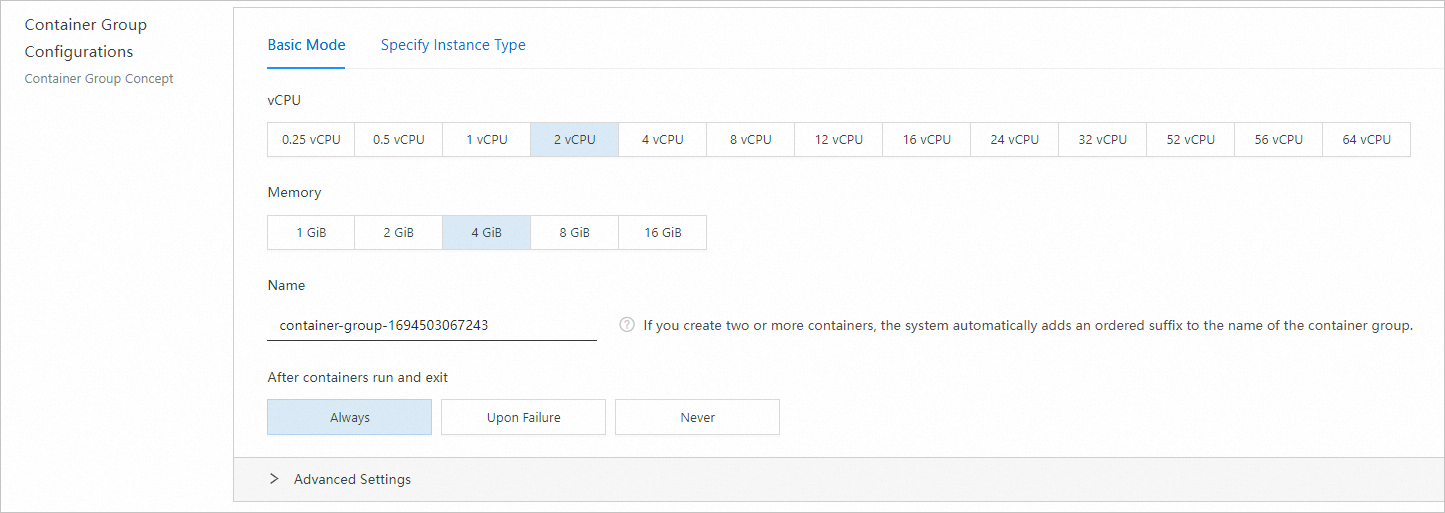
Configure the container group.
Select the specifications for the container group.
This example shows how to select vCPU and memory specifications. This method offers greater flexibility and resource availability. If your business requires special specifications, such as GPUs, you can specify an ECS instance type instead. For more information, see Create an instance by specifying an ECS instance type.
Enter a name for the container group.
Select a restart policy.
The default is Always. This means the container automatically restarts if it exits.
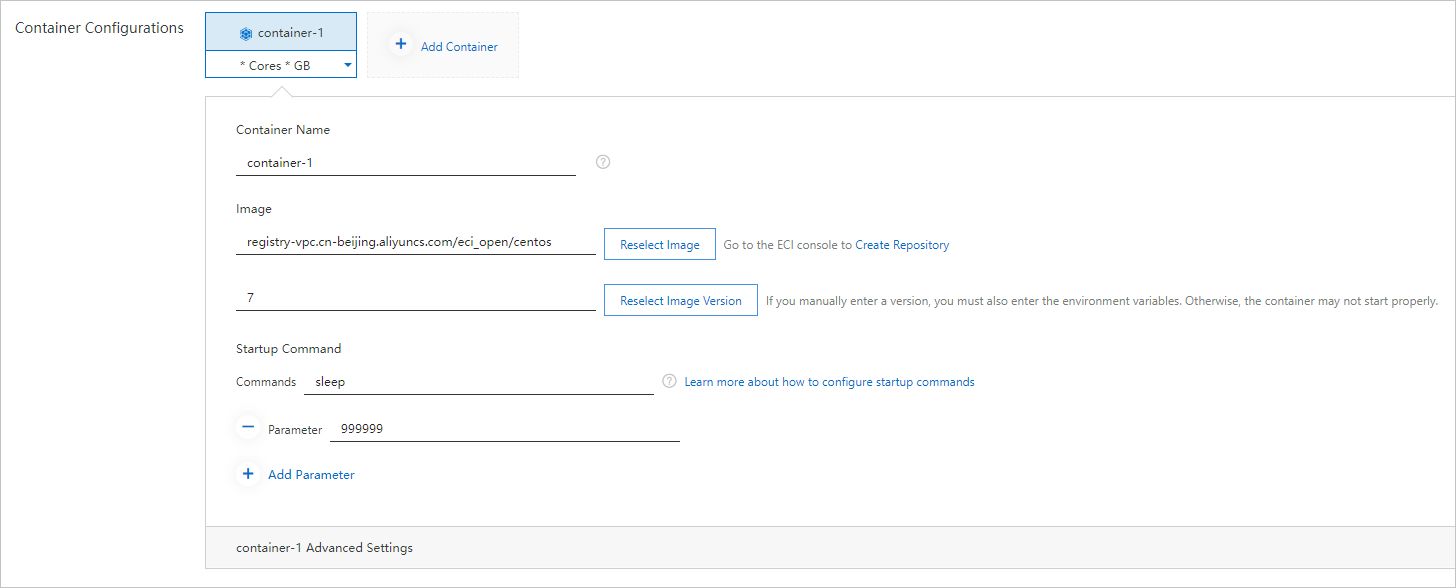
Configure containers.
Enter a name for the container.
Select an image and an image tag.
Click Select Container Image. On the Common Images tab, find eci_open/centos and click Use on the right. Click Select Image Tag and then select 7 in the Image Tag dialog box.
NoteThe image pull policy (imagePullPolicy) is IfNotPresent by default. This means the system first attempts to use a local image. If a local image is not found, the system pulls the image from the repository.
Images with the source ALI_HUB are from the Alibaba Cloud image repository. They are pulled over a VPC (private network) by default.
Configure startup commands for containers.
To ensure that CenOS containers can run as expected, you must configure a startup command. In this topic,
sleep 999999is used as an example.
Click Confirm Configuration.
Confirm the instance configuration, select the Service Agreement, and then click Confirm Order.
After the instance is created, you can view it on the Container Group page. Click the instance ID to view its details.
Troubleshooting
If you did not configure a startup command for the CentOS container, the container exits immediately after it is started because there is no resident process in the container. If Restart Policy is set to Always, the system keeps trying to restart the container. As a result, the container remains in the Starting state.