By Albert Lau, Financial Services Innovation Principal, Alibaba Cloud
The trade war between China and US are in negotiation. There are many different perspectives how this rivalry may be reshaping the global technology landscape. Factors from economics to geo-politics and from science to next-generation workforce all come into play.
Instead of picking sides in this rivalry, we attempt to answer a more fundamental question – how Chinese technologies are actually impacting the world? Very little is actually known about China, except that "Baidu we understand is Google, Alibaba and Tencent are the two giants and Didi is like Uber" [1]. There is probably a reason for the lack of their publicity outside China, as IE Business School Michael C. Wenderoth noted, that there is so much room to grow in China and many innovative Chinese don't need to look for international markets [2].
Apply Pay comes to mind when the world talks about digital wallet. There are around 33 countries accepting Apply Pay at the authoring of this article (Feb 2019). 42 countries accept Alipay, and 38 of them countries and regions accept both Alipay and WeChat Pay.
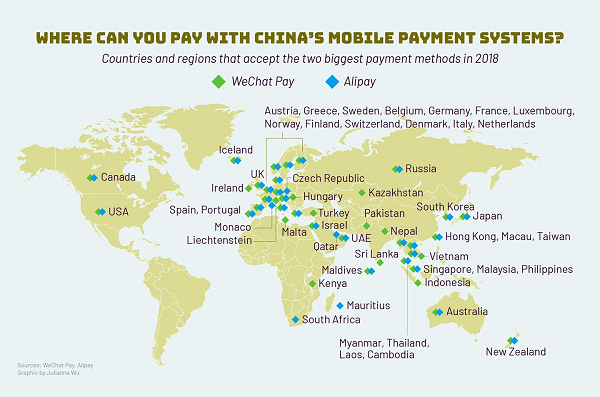
Source: Tech in Asia
It is true that the Chinese tourist has been one major driving force. For example, at Finland, Alipay is so widely accepted among Finnish merchants that Chinese visitors can have their trips completely cashless with Alipay, from making local retail purchases in Helsinki, and dining out, to visiting museums, managing transportation, and even receiving an instant tax refund at the airport [4].
There are, however, much more than Chinese tourists - Kakao Pay of Korea would leverage the experience of Ant Financial in over-counter payments, peer-to-peer transactions, bill payment and more [5]; strategic partnerships with Mynt and its GCash and Fuse at Philipines, bKash of Bangladesh, and so on [6]. Most of such strategic partnerships are founded on the mature experience and technology China already instilled through its extensive applications, and advancements through competition, that few if any other countries may be able to offer. Interested readers may refer to [7] which discusses the innovation boom at China.
In PwC's 2018 China Fintech Survey [8], it is predicting that smart risk management based on big data is going to be the next big technology that would lead in the global arena, agreed by 58% of respondents, followed by 41% on Internet insurance.
Indeed, intelligent risk management accounts for the most investments among the fintechs specializing in AI applications in 2018, accounting for 34.7%, followed by 25.7% in intelligent investment advisory [9]. Unsurpisingly, at Aug 2018, Tongdun Technology became one of the 27 finalists in the "Global Fintech Unicorns" list and was the only intelligent risk management company in the list [10].
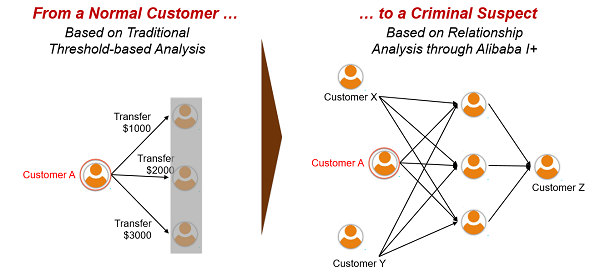
By intelligent risk management, the focus is on ingesting intelligence into the credit risk management processes through mining the customer big data, and the application of them across the entire credit lifecycle from customer acquisition, and loan application and approval, to post-disbursement monitoring and collections strategy.

The advancement of the intelligent risk management technologies follows the popularity of the digital wallet, digital commerce and digital finance activities. Without such technologies, it is imaginably difficult for any payments and loans activities to happen with acceptable business performance for more to boom and happen at scale. In addition to the credit risks, fraud also accompanies as a source of concerns. China has also mastered the anti-fraud approaches and technologies along the journey to enable the continued evolution of China's digital economy.
The digital state of China has given birth to these demand, and the scale of the China market has fueled the development and maturity of such investment.
There are 4 distinguished aspects that this intelligent risk management is founded on that make it different from the traditional approaches.
We have introduced MYbank's 310 model at [7], and highlighted its superior business performance, with non-performing loan ratio (NPL) at around 1% only. This is in fact better than the traditional players who are chasing the more attractive segments of customers.
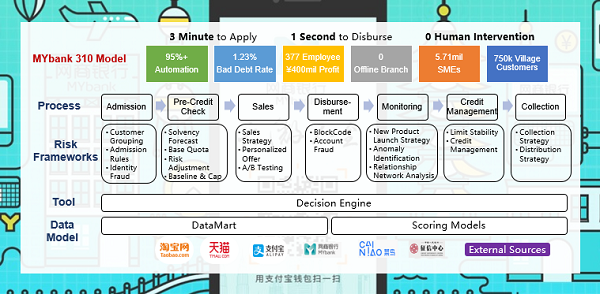
Readers should now better appreciate the complexities in setting up the risk frameworks and models to support the different customer segments, and across the end-to-end lifecycle. This does not only exemplify the business value of big data, but also illustrates how mature technology can drive digital business model innovation.
It is notable though these are results of a multi-year efforts, e.g. experimenting with the risk models, implementing the graphical analytics tool, enhancing the decision engine to orchestrate the touchpoints, etc. Alibaba Group's mission is to make it easy to do business anywhere. In the same vein, Alibaba Cloud is making it easy for businesses to transform and thrive in the digital economy with the proven technologies of Alibaba.
We would soon be able to see whether all these innovations would indeed be the next big technology. Before then, here are a few departing thoughts.
The digital economy at China have continued to amaze me with mature business technologies given its scale and growth prospects which attract all forms of investments. These don't solve all the world's problems though. As technology strategist, I would continue to look for inspirations from around the world.
Creating a Multi-CIDR Block VPN with IKEv1 in a Multi-Network CEN in Alibaba Cloud

2,593 posts | 793 followers
FollowAlibaba Clouder - May 25, 2021
Alibaba Clouder - March 6, 2019
Alibaba Clouder - June 6, 2017
Alibaba Clouder - December 6, 2016
Iain Ferguson - April 28, 2022
Alibaba Cloud Experts Column - September 20, 2022

2,593 posts | 793 followers
Follow CEN
CEN
A global network for rapidly building a distributed business system and hybrid cloud to help users create a network with enterprise level-scalability and the communication capabilities of a cloud network
Learn More WAF(Web Application Firewall)
WAF(Web Application Firewall)
A cloud firewall service utilizing big data capabilities to protect against web-based attacks
Learn More CDN(Alibaba Cloud CDN)
CDN(Alibaba Cloud CDN)
A scalable and high-performance content delivery service for accelerated distribution of content to users across the globe
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Clouder