This article provides a step-by-step guide on how to manually deploy a Java web environment on an ECS instance. It is aimed at individual users who are new to website construction on ECS instances.
• An Alibaba Cloud account has been created. To create an Alibaba Cloud account, go to the Sign up to Alibaba Cloud page.
• An ECS instance has been created. For more information, see Create an instance by using the wizard.
In this article, the following instance type and software versions are used. Please note that the operation may vary based on your instance type and software versions.
• Instance type: ecs.c6.large
• Operating system: CentOS 7.4
• Tomcat version: Tomcat 8.5.88
• JDK: 1.8.0_342
• FTP tool: WinSCP
Note: The example in this article uses Apache Tomcat 8.5.88. However, you can manually obtain a version that suits your requirements as the source code is regularly updated..
1. Add an inbound rule to the security group of the ECS instance to allow traffic on the required ports. For information on how to add a security group rule, refer to Add a security group rule. In this example, inbound rules are added to allow traffic on SSH port 22 and HTTP port 8080.
2. Connect to the Linux instance. For more information, see Connect to a Linux instance by using a password or key.
3. Disable the firewall.
a) Run the systemctl status firewalld command to check the status of the firewall.
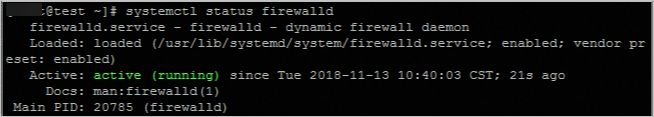
b) Disable the firewall. Skip this step if the firewall is disabled.
systemctl stop firewalldNote: After running this command, the firewall will be temporarily disabled. It will be enabled again when you restart the Linux operating system.
i) Run the following command to stop the firewall:
systemctl stop firewalldii) Run the following command to disable the firewall and prevent the firewall from starting on instance startup:
systemctl disable firewalldNote: After running these commands, the firewall will be permanently disabled. It will remain disabled even after restarting the instance. You can re-enable the firewall if needed. For more information, refer to the Firewalld documentation.
4. Disable Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux).
a) Run the following command to check the status of SELinux.
getenforceThe following figure shows an example command output:
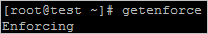
b) Disable SELinux. Skip this step if SELinux is disabled.
setenforce 0Note: After running this command, SELinux will be temporarily disabled. It will be enabled again when you restart the instance.
vi /etc/selinux/configIn the /etc/selinux/config file, move the pointer on the SELINUX=enforcing line and press the I key to enter the edit mode. Set SELINUX=disabled and press the Esc to exit the edit mode. Enter :wq and press the Enter key to save and close the file.
Note: You can re-enable SELinux after it is disabled. For more information, see Enable or disable SELinux.
c) Restart the instance to apply the settings.
1. Run the following command to view the JDK version in the YUM repository:
yum list java*2. Run the following command to install JDK1.8.0:
yum -y install java-1.8.0-openjdk*3. Run the following command to check whether the JDK is installed:
java -versionIf a command output similar to the following one is returned, the JDK is installed.
[root@iZuspq7vnxm**** ~]# java -version
openjdk version "1.8.0_342"
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_342-b07)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.342-b07, mixed mode)4. Configure environment variables.
a) Run the following command to view the JDK installation path.
find /usr/lib/jvm -name 'java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0*'A command output similar to the following one is returned.
[root@test000****~]# find /usr/lib/jvm -name 'java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0*'
/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.342.b07-1.el7_9.x86_64b) Open the configuration file.
vim /etc/profilec) At the end of the configuration file, press the i** key to enter edit mode.
d) Add the following information.
Note: Set JAVA_HOME to the JDK installation path that you obtained.
JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.342.b07-1.el7_9.x86_64
PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin
CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar
export JAVA_HOME CLASSPATH PATHe) Press the Esc key, enter :wq, and then press the Enter key to save and close the configuration file.
f) Run the following command to make the environment variable take effect.
source /etc/profileNote:
After environment variables are modified, the following error message may appear when you run other commands: -bash: chmod: command not found. To resolve the error, run the export PATH=/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin command.
1. Run the following command to download and decompress the Apache Tomcat 8 installation package.
wget --no-check-certificate https://dlcdn.apache.org/tomcat/tomcat-8/v8.5.88/bin/apache-tomcat-8.5.88.tar.gz
tar -zxvf apache-tomcat-8.5.88.tar.gzNote: The download URLs of Apache Tomcat may change. If the preceding download URL is invalid, visit the official Apache Tomcat website to obtain the latest download URL.
2. Run the following command to move the directory where Tomcat is located.
mv apache-tomcat-8.5.88 /usr/local/tomcat/3. For security reasons, perform operations on Apache Tomcat as a regular user.
In this example, a regular user named www is used.
useradd www4. Run the following command to set the owner of the file to www.
chown -R www.www /usr/local/tomcat/The /usr/local/tomcat/ directory contains the following subdirectories:
• bin: stores Apache Tomcat script files, such as scripts used to enable and disable Apache Tomcat.
• conf: stores various global configuration files of the Apache Tomcat server. The most important files are the server.xml and web.xml files.
• webapps: serves as the main web publishing directory of Apache Tomcat. It stores web application files by default.
• logs: stores Apache Tomcat operation log files.
5. Configure the server.xml file.
a) Run the following command to go to the /usr/local/tomcat/conf/ directory:
cd /usr/local/tomcat/conf/b) Run the following command to rename the server.xml file.
mv server.xml server.xml_bkc) Create a new server.xml file.
i) Run the following command to create and open the server.xml file:
vi server.xmlii) Press the i key to add the following content.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<Server port="8006" shutdown="SHUTDOWN">
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.JreMemoryLeakPreventionListener"/>
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.mbeans.GlobalResourcesLifecycleListener"/>
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.ThreadLocalLeakPreventionListener"/>
<Listener className="org.apache.catalina.core.AprLifecycleListener"/>
<GlobalNamingResources>
<Resource name="UserDatabase" auth="Container"
type="org.apache.catalina.UserDatabase"
description="User database that can be updated and saved"
factory="org.apache.catalina.users.MemoryUserDatabaseFactory"
pathname="conf/tomcat-users.xml"/>
</GlobalNamingResources>
<Service name="Catalina">
<Connector port="8080"
protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443"
maxThreads="1000"
minSpareThreads="20"
acceptCount="1000"
maxHttpHeaderSize="65536"
debug="0"
disableUploadTimeout="true"
useBodyEncodingForURI="true"
enableLookups="false"
URIEncoding="UTF-8"/>
<Engine name="Catalina" defaultHost="localhost">
<Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.LockOutRealm">
<Realm className="org.apache.catalina.realm.UserDatabaseRealm"
resourceName="UserDatabase"/>
</Realm>
<Host name="localhost" appBase="/data/wwwroot/default" unpackWARs="true" autoDeploy="true">
<Context path="" docBase="/data/wwwroot/default" debug="0" reloadable="false" crossContext="true"/>
<Valve className="org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve" directory="logs"
prefix="localhost_access_log." suffix=".txt" pattern="%h %l %u %t "%r" %s %b" />
</Host>
</Engine>
</Service>
</Server>iii) Press the Esc key, enter :wq, and press the Enter key to save and close the configuration file.
6. Configure the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) memory parameters.
a) Run the following command to create and open the /usr/local/tomcat/bin/setenv.sh file:
vi /usr/local/tomcat/bin/setenv.shb) Press the i key to add the following content.
Specify the JAVA_OPTS parameter to set JVM memory information and the encoding format.
JAVA_OPTS='-Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom -server -Xms256m -Xmx496m -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8'Press the Esc key to exit the edit mode. Enter :wq and press the Enter key to save and close the configuration file.
7. Configure a script to enable Apache Tomcat to automatically start on system startup.
a) Run the following command to download the script.
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/oneinstack/oneinstack/master/init.d/Tomcat-initNote:
This script is maintained by the community and is provided for reference only. Alibaba Cloud does not make any guarantee, express or implied, with respect to the reliability of the script, as well as potential impacts of operations on the script. If you cannot download the script by running the wget command, access https://raw.githubusercontent.com/oneinstack/oneinstack/master/init.d/Tomcat-init in a browser to obtain the content of the script.
b) Move and rename Tomcat-init.
mv Tomcat-init /etc/init.d/tomcatc) Grant the execute permissions on the /etc/init.d/tomcat file.
chmod +x /etc/init.d/tomcatd) Run the following command to configure the JAVA_HOME script to enable Apache Tomcat to run on system startup.
sed -i 's@^export JAVA_HOME=.*@export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.342.b07-1.el7_9.x86_64@' /etc/init.d/tomcatNote: The JDK version in the script must be the same as the JDK version that you installed. Otherwise, Tomcat cannot start.
8. Run the following commands in sequence to enable Apache Tomcat to automatically start on system startup:
chkconfig --add tomcat
chkconfig tomcat on9. Run the following command to start Apache Tomcat:
service tomcat start10. If a command output similar to the following one is returned, Apache Tomcat is started.
[root@test000**** conf]# service tomcat start
Starting tomcat
Using CATALINA_BASE: /usr/local/tomcat
Using CATALINA_HOME: /usr/local/tomcat
Using CATALINA_TMPDIR: /usr/local/tomcat/temp
Using JRE_HOME: /usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.342.b07-1.el7_9.x86_64
Using CLASSPATH: /usr/local/tomcat/bin/bootstrap.jar:/usr/local/tomcat/bin/tomcat-juli.jar
Using CATALINA_OPTS:
Tomcat started.
Tomcat is running with pid: 11837Upload the WAR package of Java web project files to the website root directory and change the owner of the files in the root directory to www. You can use a remote connection tool that has a file transfer feature or build an FTP site to upload project files. In this example, the website root directory is /data/wwwroot/default. Perform the following operations to create an Apache Tomcat test page in the website root directory and access the page.
1. Run the following command to create a website root directory:
mkdir -p /data/wwwroot/default2. Run the following command to set the owner of the website root directory to www:
chown -R www.www /data/wwwroot3. Run the following command to create the test file:
echo Tomcat test > /data/wwwroot/default/index.jsp4. Enter http:// Public IP address: 8080 in the address bar of your browser to connect to the ECS instance.
If Apache Tomcat is installed, a page similar to the following one appears. If http://<Public IP address of the ECS instance>:8080 is inaccessible, check whether rules are added to the security group of the instance to allow traffic on port 8080. For information about how to add a security group rule, see Add a security group rule.
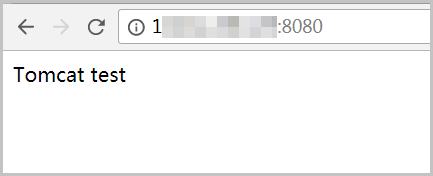
When Apache Tomcat becomes available, we recommend that you configure websites on the instance and map the domain name of the websites to the public IP address of the instance.

1,345 posts | 471 followers
FollowAlibaba Clouder - August 16, 2019
Alibaba Clouder - April 12, 2019
Alibaba Cloud Community - July 5, 2024
Alibaba Clouder - November 14, 2017
liptanbiswas - July 15, 2018
Alibaba Cloud Community - December 12, 2023

1,345 posts | 471 followers
Follow ECS(Elastic Compute Service)
ECS(Elastic Compute Service)
Elastic and secure virtual cloud servers to cater all your cloud hosting needs.
Learn More Elastic High Performance Computing Solution
Elastic High Performance Computing Solution
High Performance Computing (HPC) and AI technology helps scientific research institutions to perform viral gene sequencing, conduct new drug research and development, and shorten the research and development cycle.
Learn More Elastic High Performance Computing
Elastic High Performance Computing
A HPCaaS cloud platform providing an all-in-one high-performance public computing service
Learn More Elastic Desktop Service
Elastic Desktop Service
A convenient and secure cloud-based Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS) solution
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud Community