He Jun, Product Expert, ApsaraDB Team
As one of the most important yet complex technologies, the database plays an indispensable role in the age of digitalized economy. Yet, the development of these technologies are still lagging in China. For China's tech giants like Alibaba Cloud, understanding the transformation of the IT industry in the cloud computing era is the key for it to remain competitive in the international market. When developing innovative cloud database services, Alibaba Cloud also needs to consider the prospects for the future development of co-opetition (cooperation and competition) with other global tech giants.
In this article, I will share my experience and opinions on the innovation, evolution, co-competition, and open thinking - development of POLARDB, a cloud-native relational database, developed by Alibaba Cloud.
In the modern Internet era, our life is full of fresh, interesting, and exciting commodities, services, and diverse business models, benefiting us in many ways. The goal of emerging Internet companies is no longer only for meeting basic needs but also to create needs.
The quote of Charles Dickens "it was the best of times, it was the worst of times" also applies to describing the Internet today. It is an era that closely integrates technologies with economy. It is also an era to drive and accelerate the innovation and progress with the dreams of achieving commercial successes.
As we know, various applications that make the Internet prosperous are all based on IT technologies such as CPU, operating system, database, algorithm, open-source software, project management, and network. As a new technology, cloud computing undertakes the mission to provide more innovative services to customers. New concepts such as the wave of big data, the emergence of artificial intelligence, and the grand dream of smart planet are all built on cloud computing.
However, when new applications appear to replace previous ones, the Internet still remains. As one of the key technologies for the Internet, database has become an inseparable element in the era of the digitalized economy. In the modern society, databases are everywhere; databases play an important role in banking, securities, insurances, Internet, e-businesses, e-government, mobile payments, sales and circulation of commodities, shared economy, education, and media services. Databases are the backup for social activities and ensure continuity and efficiency of these activities, such as metropolitan operations, company operations, trades of commodities, and commercialized services.
Owing to this, cloud service providers increase their investment in the development of databases in the Internet era. A new orientation appears in front of them, which is the development of cloud-native databases. Cloud-native databases are integrated with advantages, such as the service capability and elastic architecture of cloud computing, the simplicity and open eco-system of open-source databases, and the SQL management and processing performance, over traditional databases. Based on these integrations and innovations, cloud-native databases provide better database services than ever for customers in the cloud environment.
To cope with the growing demand of enterprises, Alibaba Cloud released POLARDB, a cloud-native database, in Sep 2017. After a beta testing phase of more than half a year, Alibaba Cloud shared the technical topic of cloud-native databases at Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE) and commercialized POLARDB in Apr 2018.
POLARDB has gained the attention within the IT industry and obtained a collection of supporters since its release. Cloud-native databases gives us faith in the business and a bright future ahead. When looking back to the past, analyzing the present, and looking to the future, we should first take a look at the industry framework of the era of cloud computing. This move allows us to get a better understanding why we chose to develop a cloud-native database.
In 2007, the new word "Cloud Computing" first appeared. No one would think that after more than 10 years, cloud computing would bring such profound industrial changes to the entire IT industry. From the IT industry's hesitation and wait-and-see attitude for cloud computing 10 years ago, cloud computing has served all walks of life and gradually won the trust of customers. The Internet and big data played a vital role in the transformation of cloud computing.
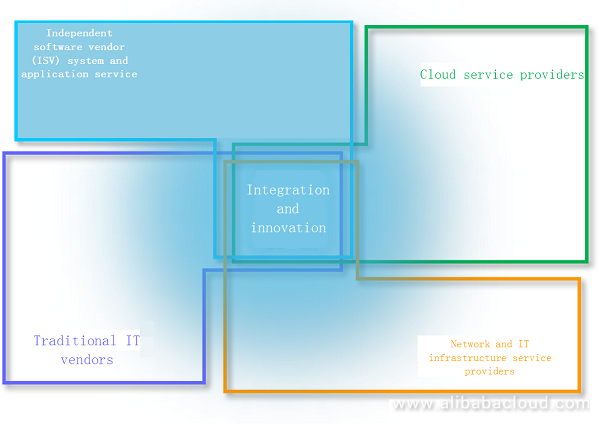
Before the emergence of cloud computing services, the IT industry was separated into two groups. One group is IT technology companies and the other is ISV system and application service providers. After the Internet and cloud computing became the mainstream, the IT industry was separated into four groups as shown in the preceding figure. As for the extension of cloud computing technologies, boundaries among four groups of IT companies were being broken. These companies were looking for cooperation and innovation in other domains. Traditional IT companies tried to provide cloud services. Cloud service providers tried to develop technical services based on the cloud environment. Network and IT infrastructure service providers tried to build a globalized network that can accelerate the connection speed and expand the distance between cloud services and end-users. ISV system and application service providers tried to develop applications that were closer to end-users, or provide a set of solutions for enterprises. Thus, traditional competition has been replaced with co-opetition.
The previous framework of the IT industry has undergone tremendous industry changes, and this change will affect the direction of the next 20 or 30 years. Cloud computing service providers have been expanding the boundaries of business services. Amazon and Alibaba Cloud and other domestic and foreign cloud vendors have been expanding the boundaries of cloud-based business services. It can be seen that almost all industries are carrying out their own business services on cloud computing.
After looking back at the development and history of leading IT companies, you will find that the main theme along with the evolution of times is undoubtedly the cross-domain integration. We are continuously expanding the boundaries of businesses and industries. As for the IT industry framework of the cloud computing era, traditional IT service providers are dedicated on expanding the boundaries of computing, storage, and network performance.
Integration and division of four forms of technologies in the cloud environment brought not only the impact on the way we think but also the mutual integration among four forms. Any one of the four groups of IT companies have a promising future in the era of cloud computing. What they need to do is to avoid restrictions and bias on cognition of the era and form a better competitive relationship. By this move, they can make their resources, technologies, services, and applications complementary and interdependent to build a mutually benefic eco-system, which breaks the Nash equilibrium dilemma and creates more values.
As a cloud service provider, Alibaba Cloud provides database services that are based on three types of databases. They are open-source databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, Redis, MongoDB, and HBase, commercial databases such as SQL Server and PPAS, and databases of its own such as POLARDB and HybridDB.
POLARDB, a cloud-native database that was developed by Alibaba Cloud, includes all the services provided by relational databases and is compatible with mainstream databases such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, and Oracle. Currently, the commercially available version is MySQL-compatible. Other SQL-compatible versions are being developed.
Cloud-native databases appear to serve applications better in the cloud environment. A cloud-native database is provided as a cross-domain service integrated with multiple innovative technologies. The database integrates the capability of cloud and SQL. Cloud-native databases have the following advantages in the SQL management and data processing over traditional databases:
In the IT era, traditional computes serve in the scenarios that isolate the system and hardware from multiple users. For example, you can process structured data by using relational databases. In the cloud computing era, load computing scenarios are more complicated in a multi-tenant self-service environment. In this environment, to accommodate the technical products of the IT era and the application environment of the cloud computing era, is the inherent driving force behind the integration of cloud-native databases.
For example, in a public cloud environment, with the increasing number of users, transactions and data growth, issues such as backup, performance, migration, upgrade, read-only instance, disk capacity, and Binlog latency gradually emerge. These issues are mostly caused by the architecture of storing data on local disks. What we need to do is to replace the previous architecture with technical innovations.
In addition, a cloud-native database can better integrate with extract, transform, and load (ETL) of cloud data and migration tools to form a closed loop of the management of data life cycle.
The core of the cloud is flexibility. Serverless computing and storage make the cloud a single image operating system. Single points of failure of the hardware, performance bottlenecks, and availability are not a concern. The core value of SQL in the cloud is to provide a cloud environment that is totally transparent to end users and to run SQL processes with high performance. Most cloud database services are "SQL on Cloud"
Another remarkable feature of a cloud-native database is to provide a solution to meet the requirements of processing data at the enterprise level and turn the solution to a service. For a traditional on-premises database that run in an IDC, the following capabilities must be provisioned by working out a solution. These capabilities include providing 7*24 services of high availability, providing the self-adaptive server load balance of read/write splitting, providing automatic failovers to ensure business continuity, providing the online scalability of computing resources instantly, and providing the cross-zone and cross-region disaster recovery. However, for a cloud-native database, it was born with these capabilities to process data at the enterprise level.
Cloud service providers, provide full hosting services including the construction of IDC rooms, the resource supply chain and deployment, the monitoring operation and maintenance, and the after-sales service support. Compared with the process of purchasing traditional databases, the full hosting service greatly reduces the cost of purchasing a database and maintenance in the future. This allows users to focus on the definition, collection, processing and, representation of data by offloading the workloads such as resource management, performance monitoring, and database maintenance to cloud service providers.
In addition to computing resources provided by physical servers, cloud-native databases brought users more benefits including ultra-high-speed network connections, IDC rooms with advanced green computing environment, and reliable security defense system and infrastructure. After the cost of using hi-tech products was aggressively reduced, the cost of risks and failures was also undertaken in a shared way. Cloud service providers provided service level agreements (SLA) to ensure the quality of service and compensated for failures that were out of the committed service scope.
As a cloud-native database, POLARDB integrates a collection of innovative technologies and takes advantage of the latest technologies of IT hardware including high-speed network and storage devices. With a design of distributed storage architecture, POLARDB separates compute and storage. The MySQL-compatible version of POLARDB features full compatibility, high performance, flexibility, read-only nodes, self-adaptive data scalability, three replicas, backup in seconds, and high availability.
In later sections, we will focus on the service architecture and technical innovations of POLARDB. For more information about POLARDB, see Official documentation.
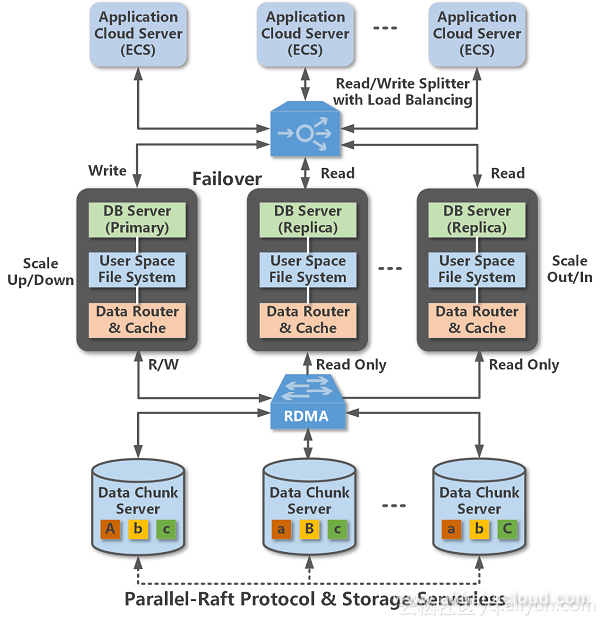
POLARDB clusters that provide the capability of high throughput processing
As shown in the preceding figure, POLARDB is designed as the architecture of distributed clusters. By integrating a number of advanced technologies, POLARDB makes a qualitative leap in the performance of database online transaction processing (OLTP). POLARDB adopts the design concept of separation between storage and compute. With high-speed network connections between compute and storage nodes and data transmission through the remote direct memory access (RDMA) protocol, this design removes the bottleneck for I/O performance.
Database nodes are designed to be fully compatible with MySQL. POLARDB uses an Active-Active failover model between the primary node and the read-only node to ensure high-availability of services. POLARDB transfers data files and redo logs through the user-space file system, through the block device data management routing, relying on high-speed network and RDMA protocol to transfer to the remote chunk server. At the same time, only the metadata information related to the redo log needs to be synchronized between the database servers. Chunk Server's data uses multiple copies to ensure data reliability and data consistency through the Parallel-Raft protocol.
Multiple ECS instances forward requests to each node of POLARDB with the capability of self-adaptive load balancing by read/writing splitting.
After describing the product architecture of POLARDB, let's take a look at the following technical innovations integrated by POLARDB, such as distributed architecture, high availability, network protocol, block device, file system, and virtualization.
As the requirement for separation of computing and storage, POLARDB uses a distributed storage system developed by Alibaba Cloud. Logically, database data is placed on data chunk storage servers that all database servers can share access to. Internally on the storage server, the actual data is cut into chunks to achieve the I/O goal of handling concurrent requests from multiple servers.
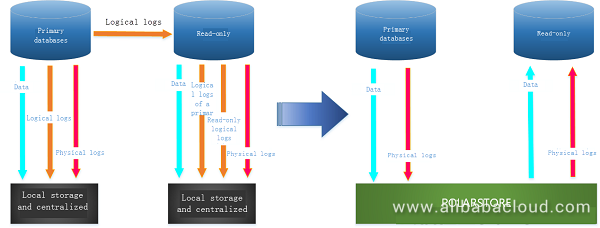
As shown in the preceding figure, POLARDB stores database files and redo logs on shared storage devices. With shared storage, read-only nodes are added by sharing a single copy of data and redo logs across all nodes without the full replication of data. Database servers only need to synchronize metadata between each other. Master and read-only nodes use Active-Active Failover methods to provide a high availability database service. When failures occur on the master node, the time to failover to a replica can be less than 30 seconds to ensure high availability. In addition, the latency between master and read-only nodes can be reduced to milliseconds.
RDMA communicates with network interface controller (NIC) drivers of network devices such as NICs and switches that support high-speed connections by using certain APIs. RDMA supports zero-copy networking by enabling the network adapter to transfer data directly to or from application memory to ensure high efficiency but low latency. Without interrupting CPUs, RDMA allows data to be copied from memory to applications to ensure the processing performance of the entire system, while significantly mitigating the impact on performance.
Snapshot is a popular backup solution that is based on block devices. When POLARDB finds that modifications occur on a block device, it creates a new copy of the block device with these modifications. The new copy is called a snapshot. You can restore a database to a certain point in time based on the data at the time of snapshot creation. The snapshot uses a post-processing scheme based on time and copy-on-write. When you create a snapshot, POLARDB balances the workload of backing up data to a time window after the snapshot creation to ensure a quick response to backup and restore. With the support of snapshots and redo logs, POLARDB is more efficient on performing the point-in-time data restore than traditional databases that use full data backup and incremental Binlog data to restore.
Parallel-Raft is an optimized and consistent algorithm that is based on the Raft algorithm, dedicated to the I/O model of POLARDB chunk servers. The Raft algorithm assume that logs are submitted in a continuous manner. If log#n has not been submitted, the following logs are not allowed to be submitted. However, the Parallel-Raft algorithm used by POLARDB allows non-associated data on chunk servers to concurrently submit. This design improves concurrent performance based on the consistency of multiple replicas.
The implementation of Docker container virtualization is more lightweight than virtualization technologies such as KVM. If you allow the functionality of the entire operating system to be transparent to you, then Docker container virtualization should theoretically achieve a better computational energy efficiency ratio. POLARDB uses a Docker container to run database compute nodes, which solves resource isolation and performance isolation and saves system resources with a more lightweight virtualization approach.
POLARDB uses the User-Space file system to design the API interface dedicated to the database server. Since it is not required to be fully compatible with the POSIX standard, it does not need to perform 1:1mapping docking of the system call in the operating system kernel. You can directly manage metadata and read or write data in user space. This design is much less difficult to implement the system and ensures high-speed data transmission between a database server and a distributed storage system.
Technical innovations require continuous investment in research and development. Cloud-native databases still need to meet the requirements of cloud users for high-speed data processing. For cloud service providers, they need to dive into the research of technical advantages of traditional database vendors, such as SQL compile, optimizer, and parallel execution plans. It is a process full of challenges.
Independent research and development and innovation are based on a long-term accumulation and continuous investments on development. In addition, a key to succeed in independent development and innovation is to find a way to make products marketable and a business model of self-sufficiency to continuously invest on development. Fortunately, the business model of cloud computing, and Alibaba Cloud's current database services have the ability to support this aggressive research and development cost. POLARDB has also begun to win the favor of more and more users. The self-sufficient capacity of the cloud service business will support more investment in independent research and development, and achieve closed-loop feedback. This is the primary problem that needs to be solved in the independently developed database.
The independently developed cloud-native database, using the business model of cloud computing, backs up the long-term investment of resources, and exploits the advantages of latecomers to continuously win the trust of users in the data age. The feedback from user business service requirements built on POLARDB also provide direction for POLARDB's own evolution. We are very pleased to see that in the Internet plus (+) industry applications such as new finance, new education, new media, and pan-entertainment, more and more customers use POLARDB to deploy their applications in the digital era. This is the reason that independently developed databases exist.
Looking back at the history of database development, in this ever-changing TMT era, it sounds ancient. This IT technology, which originated half a century ago, has in fact been at the foundation of modern commercial technology, supporting the vast majority of business in today's world. The CPU, operating system, and database are basically the epitome of the IT era, and also the cornerstone of all information processing, computing power, and intelligence. In 1970 E.F.Codd published a milestone paper "A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks". In the early 1980s, the relational databases such as DB2 and Oracle that were compatible with SQL, were released. In the early 1990s, the first version of SQL Server was released.
How can independently developed databases cope with a database project at the data level of over 10 million rows? How can independently developed databases deal with the investment and development of thousands of human resources? In the situation that the accumulation in the core layer of SQL is still not sufficient enough to compete with commercial databases, the answer is to innovate. Especially, to integrate with and innovate based the user experience of the cloud computing environments is the key to survive with traditional commercial databases at the same time. In the long run, the substance is to accumulate.
Independently developed databases can indeed evolve and grow under the guidance of the needs of cloud users. However, scenarios of enterprise customers are different from those of personal customers. When enterprise customers make choices and judgements, decisions are usually made on the process of collective participation and decision-making of multiple related roles within the company. Based on the size of different companies, the longer the decision-making chain is. There are more roles. For different companies, the specific user Persona is different. DBA, architect, R&D engineer, even technical director and CTO will participate in the selection of major products and technologies. That is to say, while the self-developed database itself provides the ability to solve problems based on certain scenarios, there is still a big appeal behind the product's general capabilities. These general capabilities include security, reliability, easy to manage, multifunctional, and fine-grained. Aspects must reflect the maturity of an independently developed database once it is released. The database is required to achieve a high standard of maturity as its competitors. Based on the maturity, the database can gain the recognition and superiority of customers by resolving particular issues in some scenarios.
To learn more about Alibaba Cloud PolarDB, visit https://www.alibabacloud.com/blog/a-brief-history-of-development-of-alibaba-cloud-polardb_594254
ApsaraDB - December 5, 2018
Alex - July 9, 2020
Alibaba Clouder - December 24, 2018
Alibaba Clouder - July 16, 2020
Alibaba Clouder - April 10, 2018
Alibaba Clouder - July 23, 2018
 PolarDB for MySQL
PolarDB for MySQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for MySQL is a cloud-native relational database service 100% compatible with MySQL.
Learn More ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL
ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL
An on-demand database hosting service for MySQL with automated monitoring, backup and disaster recovery capabilities
Learn More PolarDB for PostgreSQL
PolarDB for PostgreSQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for PostgreSQL is an in-house relational database service 100% compatible with PostgreSQL and highly compatible with the Oracle syntax.
Learn More PolarDB for Xscale
PolarDB for Xscale
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for Xscale (PolarDB-X) is a cloud-native high-performance distributed database service independently developed by Alibaba Cloud.
Learn MoreMore Posts by ApsaraDB
Raja_KT March 13, 2019 at 5:17 am
bypassing CPUs , means a lot.