Hologres支持三种表存储格式,分别为:行存、列存和行列共存,不同的存储格式适用于不同的查询场景,您需要根据表的使用场景设置表的存储格式,合适的存储格式可以显著提高数据处理和查询速度,同时也可以节省存储空间。
设置存储格式语法
在Hologres中支持行存、列存和行列共存三种存储格式,在建表时通过设置orientation属性指定表的存储格式,语法如下:
-- 2.1版本起支持
CREATE TABLE <table_name> (...) WITH (orientation = '[column | row | row,column]');
-- 所有版本支持
BEGIN;
CREATE TABLE <table_name> (...);
CALL set_table_property('<table_name>', 'orientation', '[column | row | row,column]');
COMMIT;table_name:表名称。
orientation:指定了数据库表在Hologres中的存储模式是列存还是行存,Hologres从 V1.1版本开始支持行列共存的模式。
建表时默认为列存(column storage)形式。行存或行列共存需要在建表时显式指定。修改表的存储格式需要重新建表,不能直接转换。
使用建议
表的存储格式使用建议如下。
存储格式 | 适用场景 | 列限制 | 使用说明 |
列存 | 适用于OLAP场景,适合各种复杂查询、数据关联、扫描、过滤和统计。 | 建议不超过300列。 | 列存会默认创建更多的索引,包括对字符串类型创建bitmap索引,这些索引可以显著加速查询过滤和统计。 |
行存 | 适合基于Primary Key点查的场景,即查询语句如下所示。 | 建议不超过3000列。 | 行存默认仅对主键创建索引,仅支持主键的快速查询,使用场景也受到限制。 |
行列共存 | 支持行存和列存的所有场景,以及非主键点查的场景。 | 建议不超过300列。 | 行列共存适用的场景更广,但会带来更多的存储开销,以及内部数据状态同步的开销。 |
技术原理
列存
如果表是列存,那么数据将会按照列的形式存储。列存默认使用ORC格式,采用各种类型的Encoding算法(如RLE、字典编码等)对数据进行编码,并且对编码后的数据应用主流压缩算法(如Snappy、 Zlib、 Zstd、 Lz4等)对数据进一步进行压缩,并结合Bitmap index、延迟物化等机制,提升数据的存储和查询效率。
系统会为每张表在底层存储一个主键索引文件,详情请参见主键Primary Key。列存表如果设置了主键PK,系统会自动生成一个Row Identifier(RID),用于快速定位整行数据,同时如果为查询的列设置合适的索引(如Distribution Key、Clustering Key等),那么就可以通过索引快速定位到数据所在的分片和文件,从而提升查询性能,因此列存的适用范围更广,通常用于OLAP查询的场景。示例如下。
V2.1版本起支持的建表语法:
CREATE TABLE public.tbl_col ( id TEXT NOT NULL, name TEXT NOT NULL, class TEXT NOT NULL, in_time TIMESTAMPTZ NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id) ) WITH ( orientation = 'column', clustering_key = 'class', bitmap_columns = 'name', event_time_column = 'in_time' ); SELECT * FROM public.tbl_col WHERE id ='3333'; SELECT id, class,name FROM public.tbl_col WHERE id < '3333' ORDER BY id;所有版本支持的建表语法:
BEGIN; CREATE TABLE public.tbl_col ( id TEXT NOT NULL, name TEXT NOT NULL, class TEXT NOT NULL, in_time TIMESTAMPTZ NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id) ); CALL set_table_property('public.tbl_col', 'orientation', 'column'); CALL set_table_property('public.tbl_col', 'clustering_key', 'class'); CALL set_table_property('public.tbl_col', 'bitmap_columns', 'name'); CALL set_table_property('public.tbl_col', 'event_time_column', 'in_time'); COMMIT; SELECT * FROM public.tbl_col WHERE id ='3333'; SELECT id, class,name FROM public.tbl_col WHERE id < '3333' ORDER BY id;
示意图如下。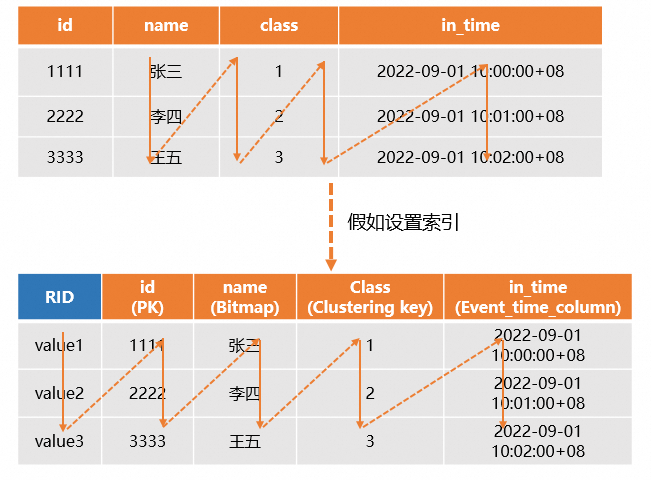
行存
如果Hologres的表设置的是行存,那么数据将会按照行存储。行存默认使用SST格式,数据按照Key有序分块压缩存储,并且通过Block Index、Bloom Filter等索引,以及后台Compaction机制对文件进行整理,优化点查查询效率。
(推荐)设置主键Primary Key
系统会为每张表在底层存储一个主键索引文件,详情请参见主键Primary Key。行存表设置了Primary Key(PK)的场景,系统会自动生成一个Row Identifier(RID),RID用于定位整行数据,同时系统也会将PK设置为Distribution Key和Clustering Key,这样就能快速定位到数据所在的Shard和文件,在基于主键查询的场景上,只需要扫描一个主键就能快速拿到所有列的全行数据,提升查询效率,SQL示例如下。
V2.1版本起支持的建表语法:
CREATE TABLE public.tbl_row ( id TEXT NOT NULL, name TEXT NOT NULL, class TEXT, PRIMARY KEY (id) ) WITH ( orientation = 'row', clustering_key = 'id', distribution_key = 'id' ); --基于PK的点查示例 SELECT * FROM public.tbl_row WHERE id ='1111'; --查询多个key SELECT * FROM public.tbl_row WHERE id IN ('1111','2222','3333');所有版本支持的建表语法:
BEGIN; CREATE TABLE public.tbl_row ( id TEXT NOT NULL, name TEXT NOT NULL, class TEXT , PRIMARY KEY (id) ); CALL set_table_property('public.tbl_row', 'orientation', 'row'); CALL set_table_property('public.tbl_row', 'clustering_key', 'id'); CALL set_table_property('public.tbl_row', 'distribution_key', 'id'); COMMIT; --基于PK的点查示例 SELECT * FROM public.tbl_row WHERE id ='1111'; --查询多个key SELECT * FROM public.tbl_row WHERE id IN ('1111','2222','3333');
示意图如下。

(不建议使用)设置的PK和Clustering Key不一致
但如果在建表时,设置表为行存表,且将PK和Clustering Key设置为不同的字段,查询时,系统会根据PK定位到Clustering Key和RID,再通过Clustering Key和RID快速定位到全行数据,相当于扫描了两次,有一定的性能牺牲,SQL示例如下。
V2.1版本起支持的建表语法,设置行存表,PK和Clustering Key不一致:
CREATE TABLE public.tbl_row ( id TEXT NOT NULL, name TEXT NOT NULL, class TEXT, PRIMARY KEY (id) ) WITH ( orientation = 'row', clustering_key = 'name', distribution_key = 'id' );所有版本支持的建表语法,设置行存表,PK和Clustering Key不一致:
BEGIN; CREATE TABLE public.tbl_row ( id TEXT NOT NULL, name TEXT NOT NULL, class TEXT , PRIMARY KEY (id) ); CALL set_table_property('public.tbl_row', 'orientation', 'row'); CALL set_table_property('public.tbl_row', 'clustering_key', 'name'); CALL set_table_property('public.tbl_row', 'distribution_key', 'id'); COMMIT;
示意图如下所示。
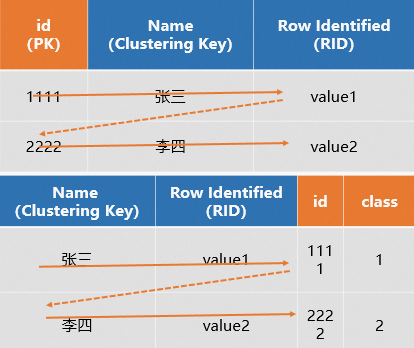
综上:行存表非常适用于基于PK的点查场景,能够实现高QPS的点查。同时建表时建议只设置PK,系统会自动将PK设置为Distribution Key和Clustering Key,以提升查询性能。不建议将PK和Clustering Key设置为不同的字段,设置为不同的字段会有一定的性能牺牲。
行列共存
在实际应用场景中,一张表可能用于主键点查,又用于OLAP查询,因此Hologres在V1.1版本支持了行列共存的存储格式。行列共存同时拥有行存和列存的能力,既支持高性能的基于PK点查,又支持OLAP分析。数据在底层存储时会存储两份,一份按照行存格式存储,一份按照列存格式存储,因此会带来更多的存储开销。
数据写入时,会同时写一份行存格式和写一份列存格式,只有两份数据都写完了才会返回成功,保证数据的原子性。
数据查询时,优化器会根据SQL,解析出对应的执行计划,执行引擎会根据执行计划判断走行存还是列存的查询效率更高,要求行列共存的表必须设置主键:
对于主键点查场景(如
select * from tbl where pk=xxx语句)以及Fixed Plan加速SQL执行场景,优化器会默认走行存主键点查的路径。对于非主键点查场景(如
select * from tbl where col1=xx and col2=yyy语句),尤其是表的列很多,且查询结果需要展示很多列,行列共存针对该场景,优化器在生成执行计划时,会先读取列存表的数据,读取完成后根据列存键值Key查询行存表的数据,避免全表扫描,提升非主键查询性能。该场景能充分发挥行列共存的优势,提高数据的快速检索性能。对于其他的普通查询,则会默认走列存。
因此行列共存表在通常查询场景,尤其是非主键点查场景,查询效率更好,示例如下。
V2.1版本起支持的建表语法:
CREATE TABLE public.tbl_row_col ( id TEXT NOT NULL, name TEXT NOT NULL, class TEXT NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id) ) WITH ( orientation = 'row,column', distribution_key = 'id', clustering_key = 'class', bitmap_columns = 'name' ); SELECT * FROM public.tbl_row_col WHERE id =‘2222’; --基于主键的点查 SELECT * FROM public.tbl_row_col WHERE class=‘二班’;--非主键点查 SELECT * FROM public.tbl_row_col WHERE id =‘2222’ AND class=‘二班’; --普通OLAP查所有版本支持的建表语法:
BEGIN; CREATE TABLE public.tbl_row_col ( id TEXT NOT NULL, name TEXT NOT NULL, class TEXT , PRIMARY KEY (id) ); CALL set_table_property('public.tbl_row_col', 'orientation','row,column'); CALL set_table_property('public.tbl_row_col', 'distribution_key','id'); CALL set_table_property('public.tbl_row_col', 'clustering_key','class'); CALL set_table_property('public.tbl_row_col', 'bitmap_columns','name'); COMMIT; SELECT * FROM public.tbl_row_col WHERE id =‘2222’; --基于主键的点查 SELECT * FROM public.tbl_row_col WHERE class=‘二班’;--非主键点查 SELECT * FROM public.tbl_row_col WHERE id =‘2222’ AND class=‘二班’; --普通OLAP查
示意图如下。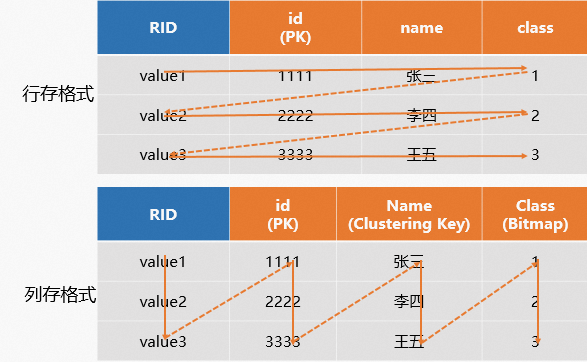
使用示例
创建不同存储模式的表使用示例如下。
V2.1版本起支持的建表语法:
--建行存表 CREATE TABLE public.tbl_row ( a INTEGER NOT NULL, b TEXT NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (a) ) WITH ( orientation = 'row' ); --建列存表 CREATE TABLE tbl_col ( a INT NOT NULL, b TEXT NOT NULL ) WITH ( orientation = 'column' ); --建行列共存 CREATE TABLE tbl_col_row ( pk TEXT NOT NULL, col1 TEXT, col2 TEXT, col3 TEXT, PRIMARY KEY (pk) ) WITH ( orientation = 'row,column' );所有版本支持的建表语法:
--建行存表 BEGIN; CREATE TABLE public.tbl_row ( a INTEGER NOT NULL, b TEXT NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (a) ); CALL set_table_property('public.tbl_row', 'orientation', 'row'); COMMIT; --建列存表 BEGIN; CREATE TABLE tbl_col ( a INT NOT NULL, b TEXT NOT NULL); CALL set_table_property('tbl_col', 'orientation', 'column'); COMMIT; --建行列共存 BEGIN; CREATE TABLE tbl_col_row ( pk TEXT NOT NULL, col1 TEXT, col2 TEXT, col3 TEXT, PRIMARY KEY (pk)); CALL set_table_property('tbl_col_row', 'orientation', 'row,column'); COMMIT;
相关文档
根据业务查询场景设置合适的表属性指南请参见场景化建表调优指南。