このトピックでは、AnalyticDB for PostgreSQLベクトルデータベースを使用してテキストセマンティック検索システムを構築する方法について説明します。
背景情報
テキスト意味検索は、キーワードを一致させるだけでなく、クエリテキストの意味と意図に基づいてデータを検索することを目的としています。 テキストセマンティック検索は、検索パフォーマンスを大幅に向上させます。
テキストセマンティック検索の概要
次の図は、2つのコンポーネントで構成されるテキストセマンティック検索のアーキテクチャを示しています。
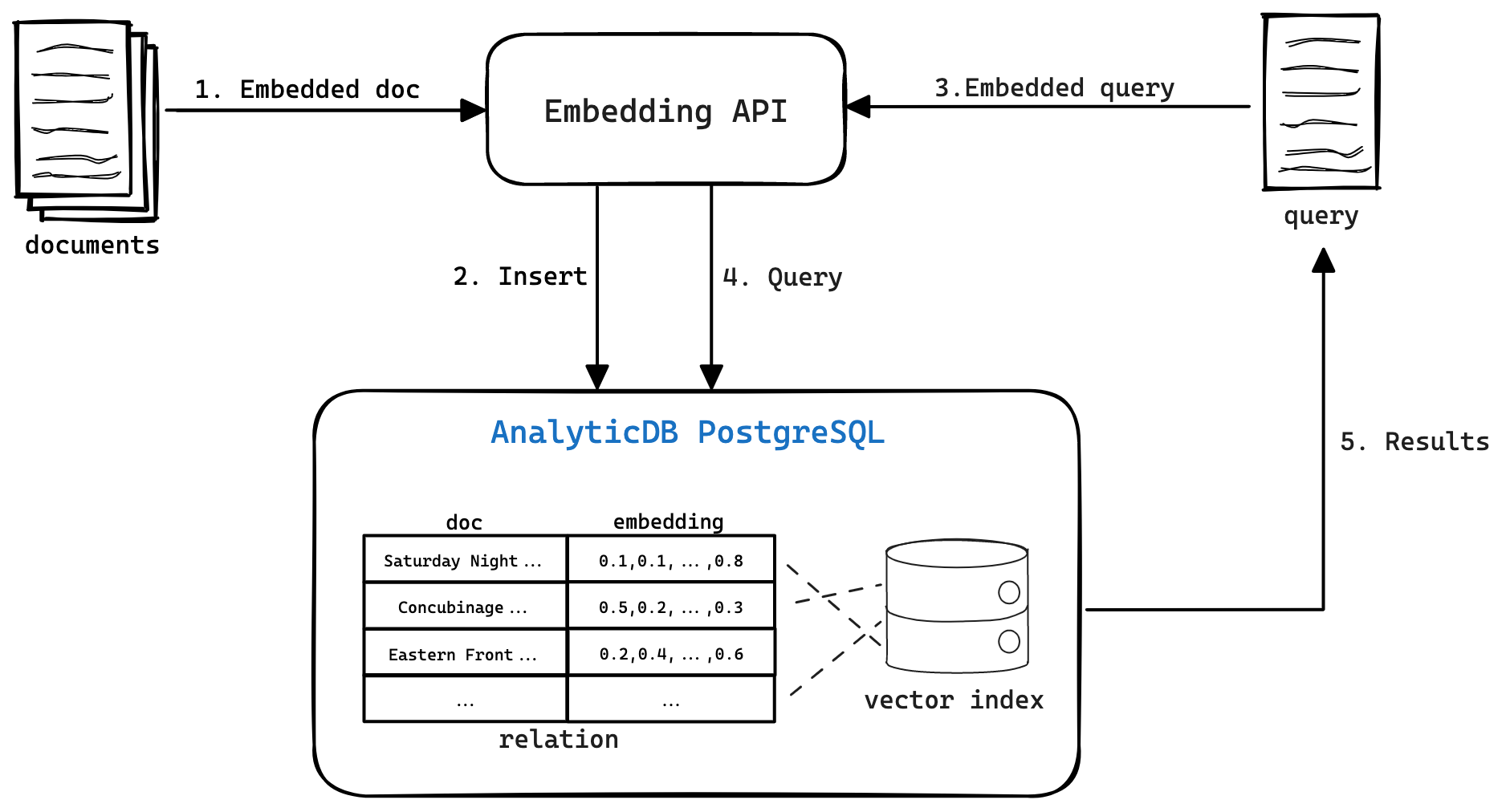
テキストベクトル化とインデックス作成
機械学習モデルを使用して、テキストを特徴ベクトルに変換します。 機械学習モデルは、テキストを符号化して、テキストの意味論的意味を捕捉するベクトル表現を生成する。 同様のテキストは、ベクトル空間において同様のベクトル表現を有する。 Alibaba Cloudの自然言語処理 (NLP) 機能、または埋め込みAPIなどの他のテキストベクトル化サービスを使用して、テキストベクトル化を実装できます。
テキストとその特徴ベクトルをAnalyticDB for PostgreSQLベクトルデータベースに保存し、ベクトルインデックスを作成します。 ベクトルインデックスは、類似の特徴ベクトルのクエリを大幅に高速化できます。
ベクトル検索
クエリテキストを機械学習モデルにインポートして、クエリテキストのベクトル表現を取得します。
クエリベクトルを使用して、AnalyticDB for PostgreSQLベクトルデータベースからテキストをクエリします。
システムは、AnalyticDB for PostgreSQLベクトルデータベースから、特徴ベクトルがクエリベクトルに最も類似しているテキストを取得して返します。
AnalyticDB for PostgreSQLベクトルデータベースを使用してテキストセマンティック検索システムを構築
AnalyticDB for PostgreSQLベクトルデータベースを使用してテキストセマンティック検索システムを構築するには、次の手順を実行します。
ステップ1: Python環境のインストール
ステップ2: データの前処理
ステップ4: データの照会
Python環境のインストール
さまざまなバージョンのPython環境を管理するには、Condaを使用することを推奨します。 この例では、Python仮想環境と必要なすべてのライブラリがインストールされています。 ターミナルで次のコマンドを実行します。
# Create a Python virtual environment and set the Python version to 3.8.
conda create -n adbpg_text_env python=3.8
# Activate the Python virtual environment.
conda activate adbpg_text_env
# Install the required Python packages in the virtual environment.
pip install psycopg2==2.9.3
pip install wget==3.2
pip install pandas==1.2.4
pip install datasets==2.12.0 sentence-transformers==2.2.2
pip install torch==2.0.1 torchvision==0.15.2 torchaudio==2.0.2macOSを使用している場合、psycopg2のインストール時にError: pg_config executable not foundエラーが報告された場合は、次の操作を実行します。
postgresqlをインストールします。
brew install postgresqlpsycopg2 をインストールします。
pip install psycopg2==2.9.3
前処理データ
AnalyticDB for PostgreSQLベクトルデータベースを使用してテキストセマンティック検索システムを構築する前に、テキストライブラリとしてテキストのバッチを選択する必要があります。 この例では、Quoraデータセットが使用されています。
データセットのダウンロード
Huagging Faceが提供するデータセットパッケージからQuoraデータセットをダウンロードします。 Quoraデータセットには約400,000のデータエントリが含まれています。 この例では、10,000のデータエントリが使用される。
from datasets import load_dataset
dataset = load_dataset('quora', split='train[0:10000]')
print(dataset[0])各データエントリは、次のコンテンツで構成されます。
questionsパラメーターには、Quoraからの2つの質問が含まれます。
id: 2つの質問のシリアル番号を指定します。
text: 2つの質問のテキストを指定します。
is_duplicateパラメーターは、2つの質問が同じ意味を持つかどうかを指定します。
本当: はい。
偽: いいえ。
{'questions':
{'id': [1, 2],
'text': ['What is the step by step guide to invest in share market in india?', 'What is the step by step guide to invest in share market?']
},
'is_duplicate': False
}テキストから特徴ベクトルを抽出する
ダウンロードしたデータセットから質問を抽出して、テキストのリストを取得します。 セットを使用して重複テキストをフィルタリングします。
sentences = [] for data in dataset['questions']: sentences.extend(data['text']) # Remove the duplicate texts. sentences = list(set(sentences)) print('\n'.join(sentences[1:5])) print(len(sentences))サンプル結果:
How can I know if my spouse is cheating? Can a snake kill a rabbit? How i get hair on bald head? How can I get my name off the first page on Google search? 19413SentenceTransformerライブラリを使用して、テキストの特徴ベクトルを抽出します。 この例では、all-MiniLM-L6-v2モデルが使用されます。
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer import torch model = SentenceTransformer('all-MiniLM-L6-v2', device='cpu') modelall-MiniLM-L6-v2モデルは、以下の情報を提供する。
max_seq_lengthパラメーターは、モデルで処理できるテキストの最大長 (256) を指定します。 システムは、256を超えるテキストの部分を切り捨てます。word_embeding_dimensionパラメーターは、モデルによって生成される特徴ベクトルの次元を指定します。SentenceTransformer( (0): Transformer({'max_seq_length': 256, 'do_lower_case': False}) with Transformer model: BertModel (1): Pooling({'word_embedding_dimension': 384, 'pooling_mode_cls_token': False, 'pooling_mode_mean_tokens': True, 'pooling_mode_max_tokens': False, 'pooling_mode_mean_sqrt_len_tokens': False}) (2): Normalize() )各テキストの特徴ベクトルを順番に抽出し、テキストとその特徴ベクトルをCSVファイルに保存します。 CSVファイルには3つの列があります。
ID: テキストのシリアル番号。
文: テキストの内容。
Vectors: テキストの特徴ベクトル。
import pandas as pd vectors = [] for sentence in sentences: vector = model.encode(sentence) # Convert the feature vectors into the '{0.04067191854119301, ..., -0.012967484071850777}' format to import them to the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL vector database. vector_str = "{" + ", ".join(str(x) for x in vector.tolist()) + "}" vectors.append(vector_str) # Generate the ID column. ids = [i + 1 for i in range(len(sentences))] # Combine the values of ID, Sentences, and Vectors into a DataFrame. df = pd.DataFrame({'ID': ids, 'Sentences': sentences, 'Vectors': vectors}) df.to_csv('sentences_vectors.csv', index=False)
ドキュメントライブラリとベクターインデックスの作成
一時的な環境変数を設定し、データベースに接続し、簡単なステートメントを実行して接続が成功したかどうかを確認します。
import os import psycopg2 # Run the following code to configure temporary environment variables: # os.environ["PGHOST"] = "xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx" # os.environ["PGPORT"] = "58894" # os.environ["PGDATABASE"] = "postgres" # os.environ["PGUSER"] = "vector_test" # os.environ["PGPASSWORD"] = "password" connection = psycopg2.connect( host=os.environ.get("PGHOST", "localhost"), port=os.environ.get("PGPORT", "5432"), database=os.environ.get("PGDATABASE", "postgres"), user=os.environ.get("PGUSER", "user"), password=os.environ.get("PGPASSWORD", "password") ) cursor = connection.cursor() # Execute a simple statement to check whether the connection is successful. cursor.execute("SELECT 1;") result = cursor.fetchone() if result == (1,): print("Connection successful!") else: print("Connection failed.")が
接続成功!メッセージが返された場合、データベースへの接続は成功です。テキストと特徴ベクトルを格納するテーブルを作成し、ベクトルインデックスを作成します。
説明ベクトルインデックスを作成するときは、
dimパラメーターの値が、all-MiniLM-L6-v2モデルによって生成される特徴ベクトルの次元と同じであることを確認します。 特徴ベクトルの次元は384である。# Specify SQL statements to create a table and change the storage format of the vector column to PLAIN. create_table_sql = ''' CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS public.articles ( id INTEGER NOT NULL, sentence TEXT, vector REAL[], PRIMARY KEY(id) ) DISTRIBUTED BY(id); ALTER TABLE public.articles ALTER COLUMN vector SET STORAGE PLAIN; ''' # Specify an SQL statement to create a vector index. create_indexes_sql = ''' CREATE INDEX ON public.articles USING ann (vector) WITH (dim = '384', hnsw_m = '100', pq_enable='0'); ''' # Execute the preceding SQL statements. cursor.execute(create_table_sql) cursor.execute(create_indexes_sql) connection.commit()sentences_vectors.csvファイルからテーブルにデータをインポートします。
import io # Define a generator function to process the data in the file line by line. def process_file(file_path): with open(file_path, 'r') as file: for line in file: yield line # Specify a COPY statement to import data. copy_command = ''' COPY public.articles (id, sentence, vector) FROM STDIN WITH (FORMAT CSV, HEADER true, DELIMITER ','); ''' # Execute the COPY statement. modified_lines = io.StringIO(''.join(list(process_file('sentences_vectors.csv')))) cursor.copy_expert(copy_command, modified_lines) connection.commit()
クエリデータ
データをインポートした後、AnalyticDB for PostgreSQLベクトルデータベースを使用して、ドキュメントライブラリのクエリテキストと意味的に最も類似したテキストをクエリできます。 テキストをクエリするには、次の手順を実行します。
クエリテキストのベクトル表現を取得します。
ベクトルエンジンを使用して、特徴ベクトルがドキュメントライブラリのクエリベクトルに最も類似しているテキストをクエリします。
例
クエリテキストとしてデータエントリをランダムに選択します。 この例では、「CAコースと一緒に受講する必要があるコース」が使用されています。 システムは、AnalyticDB for PostgreSQLベクトルデータベースから最も類似したテキストを正確に見つけることができます。
def query_analyticdb(collection_name, query, query_embedding, top_k=20):
# Specify a vector index column.
vector_col="vector"
# Specify a query SQL statement.
query_sql = f"""
SELECT id, sentence, dp_distance({vector_col},Array{query_embedding}::real[]) AS similarity
FROM {collection_name}
ORDER BY {vector_col} <-> Array{query_embedding}::real[]
LIMIT {top_k};
"""
# Execute the query to display the query results.
connection = psycopg2.connect(
host=os.environ.get("PGHOST", "localhost"),
port=os.environ.get("PGPORT", "5432"),
database=os.environ.get("PGDATABASE", "postgres"),
user=os.environ.get("PGUSER", "user"),
password=os.environ.get("PGPASSWORD", "password")
)
cursor = connection.cursor()
cursor.execute(query_sql)
results = cursor.fetchall()
connection.close()
return results# Specify a query text.
query = "What courses must be taken along with CA course?"
# Obtain the feature vectors of the query text.
query_vector=model.encode(query)
print('query: {}'.format(query))
query_results = query_analyticdb('articles', query, query_vector.tolist(), 10)
for i, result in enumerate(query_results):
print(f"{i + 1}. {result[1]} (Score: {round(result[2], 2)})")サンプル結果:
query: What courses must be taken along with CA course?
1. What courses must be taken along with CA course? (Score: 1.0)
2. What is the best combination of courses I can take up along with CA to enhance my career? (Score: 0.81)
3. Is it possible to do CA after 12th Science? (Score: 0.66)
4. What are common required and elective courses in philosophy? (Score: 0.56)
5. What are common required and elective courses in agriculture? (Score: 0.56)
6. Which course is better in NICMAR? (Score: 0.53)
7. Suggest me some free online courses that provides certificates? (Score: 0.52)
8. I have only 2 months for my CA CPT exams how do I prepare? (Score: 0.51)
9. I want to crack CA CPT in 2 months. How should I study? (Score: 0.5)
10. How one should know that he/she completely prepare for CA final exam? (Score: 0.48)クエリする他のテキストを引き続き選択できます。 テキストを照会した後、ドキュメントライブラリとインデックスを削除してリソースをリリースできます。
# Specify an SQL statement to delete the document library.
drop_table_sql = '''drop table public.articles;'''
cursor.execute(drop_table_sql)
connection.commit()
connection.close()