The Wide Column model is similar to the data model of Bigtable or HBase and is suitable for various scenarios such as the storage of metadata and big data. The Wide Column model stores data in data tables. A single data table can store petabyte-level data and supports tens of millions of queries per second (QPS). The data tables are schema-free and support wide columns, max versions, and time to live (TTL) management. The data tables also support features, such as auto-increment primary key column, local transaction, atomic counter, filter, and conditional update.
Overview
The Wide Column model of Tablestore is similar to the data model of Bigtable or HBase. The Wide Column model stores data in data tables in a three-dimensional structure, which is defined by rows, columns, and time. Each row of a data table can have different columns. The attribute columns of a data table can be dynamically added or removed. When you create a data table, you do not need to define a strict schema for the attribute columns of the data table.
Components
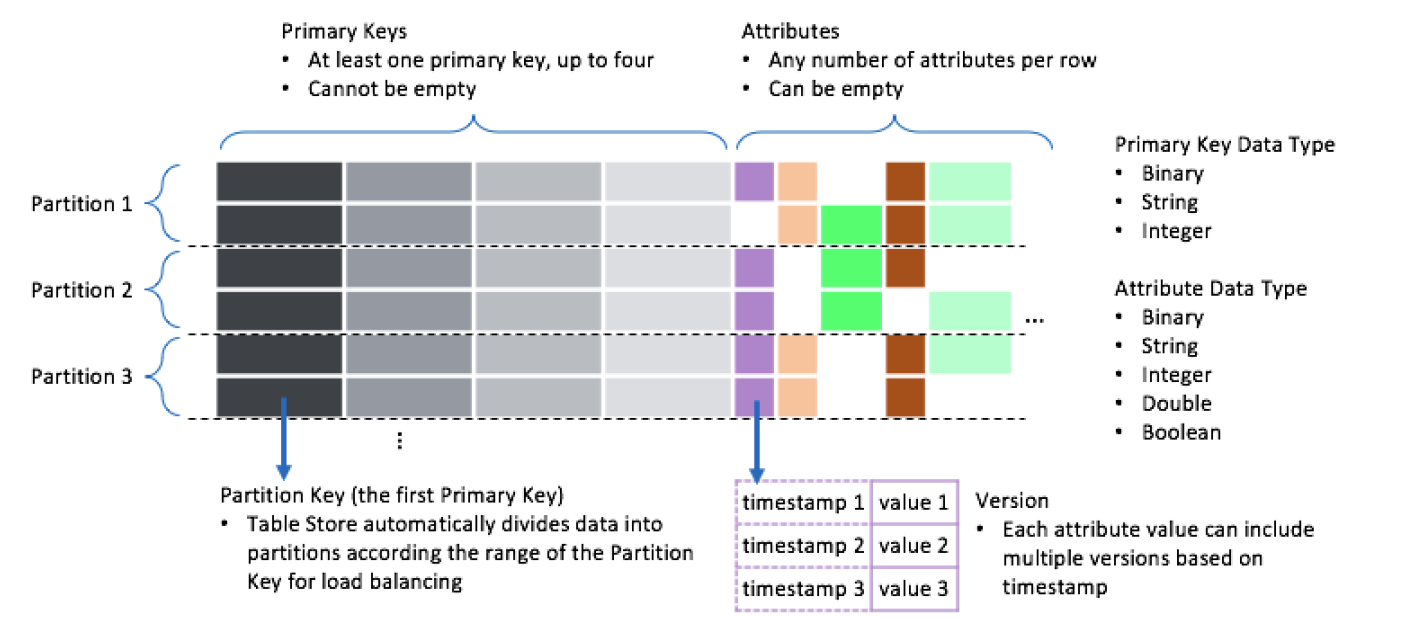
The preceding figure shows the components of the Wide Column model. The following table describes the components.
Component | Description |
Primary key | A primary key uniquely identifies a row in a data table. A primary key consists of one to four primary key columns. |
Partition key | The first primary key column is called the partition key. Tablestore partitions data in a data table based on the partition key values. Rows that share the same partition key value are allocated to the same partition to ensure balanced distribution of data access requests. |
Attribute column | All columns except for the primary key columns in a row are called attributed columns. Each attribute column can contain values of different versions. Tablestore does not impose limits on the number of attribute columns that can be contained in each row. |
Version | Each value in an attribute column has a unique version number. The version number is a timestamp based on which you can manage the TTL of attribute column values. For more information, see Version number. |
Data type | Tablestore supports the following data types: String, Binary, Double, Integer, and Boolean. For more information, see Data types. |
TTL | You can specify the TTL for each data table. For example, if you set the TTL to one month for a data table, Tablestore automatically deletes data that is written to the data table one month ago. For more information, see TTL. |
Max versions | You can specify the maximum number of versions for the value in each attribute column of a data table. Max versions can be used to control the number of versions for the value in each attribute column. When the actual number of versions in an attribute column exceeds the max versions value, Tablestore asynchronously deletes earlier versions. For more information, see Max versions. |
Core component
Data tables, rows, primary keys, and attributes are the core components of the Wide Column model of Tablestore. A data table consists of rows. Each row consists of a primary key and one or more attributes. The first primary key column is called the partition key.
The following table describes the primary key, attribute, and partition key.
For more information about data types supported by primary key columns and attribute columns, see Naming conventions and data types.
Component | Description |
Primary key | A primary key uniquely identifies a row in a data table. A primary key consists of one to four primary key columns. When you create a data table, you must specify primary key columns, including the name, data type, and sequence of the primary key columns. Tablestore indexes data in a data table based on the primary key values of the rows in the data table. By default, rows in a data table are sorted in ascending order based on the primary key values. |
Partition key | The first primary key column is called the partition key. To ensure load balancing, Tablestore automatically distributes a row of data to the corresponding partition and machine based on the range to which the partition key value of the row belongs. Rows that share the same partition key value belong to the same partition. A partition may store rows that have different partition key values. Tablestore splits and merges partitions based on specific rules. Note Partition key values are the basic unit to partition data. Data that shares the same partition key value cannot be further split. To prevent partitions from being too large to split, we recommend that you keep the total size of all rows that share the same partition key value to up to 10 GB. For more information about how to select a partition key, see Table operations. |
Attribute | A row can have multiple attribute columns. The number of attribute columns in a row is unlimited, and the attribute columns in each row can be different. The value of an attribute column in a row can be empty. The values in the same attribute column of multiple rows can be of different data types. An attribute column can store multiple versions of values. You can specify the number of versions of values that can be retained for an attribute column. You can also specify a TTL value for attribute column values. For more information, see Data versions and TTL. |
Differences between the Wide Column model and the relational model
The following table describes the differences between the Wide Column model and the relational model.
Model | Characteristics |
Wide Column model | Three-dimensional structure (row, column, and time), schema-free, wide columns, max versions, and TTL management |
Relational model | Two-dimensional structure (row and column) and fixed schema |
Limits
For information about the general limits on the Wide Column model, see Limits.
If you use secondary indexes or search indexes to accelerate data queries, take note of the limits on the indexes. For more information, see Secondary index limits and Search index limits.
If you use SQL statements to query and analyze data, take note of the limits on SQL queries. For more information, see SQL limits.
Features
Feature | Description | References |
Operations on tables | You can list all data tables in an instance, create a data table, query and update the configurations of a data table, and delete a data table. | |
Basic data operations | You can call the PutRow, GetRow, UpdateRow, and DeleteRow operations to perform operations on a single row or call the BatchWriteRow, BatchGetRow, and GetRange operations to perform operations on multiple rows. You can read and write data in a table by calling an operation to perform operations on a single row or multiple rows in the table. | |
Max versions and TTL | You can use the max versions and TTL features to manage the lifecycle of your data to optimize storage efficiency and reduce costs. | |
Auto-increment primary key column | You can specify a primary key column that is not the partition key as the auto-increment primary key column. If you write data to a table that contains an auto-increment primary key column, you do not need to specify values for the auto-increment primary key column. Tablestore automatically generates values for the auto-increment primary key column. The values generated for the auto-increment primary key column are unique and increase monotonically within a partition. | |
Conditional update | If you use conditional update, data in the table can be updated only when the conditions are met. If the conditions are not met, the update fails. | |
Local transaction | You can create a local transaction for data that shares the same partition key value. You can read and write data in the local transaction and then commit or discard the local transaction based on your business requirements. | |
Atomic counter | Atomic counter allows you to implement an atomic counter on a column, and provides real-time statistic data for online applications such as the number of page views (PVs) on various topics. | |
Filter | Filters sort results on the server side. Only results that meet the filter conditions are returned. This feature effectively reduces the volume of transferred data and shortens the response time. | |
Secondary index | You can create one or more index tables for a data table and perform queries by using the primary key columns of the index tables. Secondary indexes are classified into global secondary indexes and local secondary indexes.
| |
Search index | Search indexes are used for multi-dimensional data queries and statistical analysis in big data scenarios based on inverted indexes and column stores. Search indexes support various query methods, including query based on non-primary key columns, full-text search, prefix query, fuzzy query, Boolean query, nested query, and geo query. Search indexes also support parallel scan and multiple aggregation operations. You can perform aggregation operations to obtain the maximum and minimum values, count and distinct count of rows, sums, and averages, and group results by specific conditions. | |
SQL query | The SQL query feature provides a unified access interface for multiple data engines. You can use the SQL query feature to perform complex queries and analytics on data in Tablestore in an efficient manner. You can also use indexes in combination with the SQL query feature to optimize queries. | |
Tunnel Service | Tunnel Service provides tunnels that are used to export and consume data in full, incremental, and differential modes. After you create a tunnel, you can use it to consume historical and incremental data of a table. |
Billing rules
The billable items include read throughput, write throughput, storage usage, and outbound traffic over the Internet. For more information, see Billing overview.
FAQ
References
To implement data center-level disaster recovery for instance data, you can create an instance of the zone-redundant storage (ZRS) redundancy type. For more information, see ZRS.
To ensure data storage security and network access security, you can encrypt data tables or bind a virtual private cloud (VPC) to your Tablestore instance to allow access only over the VPC. For more information, see Data encryption and Network security management.
To prevent important data from being accidentally deleted, you can use the data backup feature to back up important data on a regular basis. For more information, see Back up data in Tablestore.
To consume historical and incremental data in a data table, you can use Tunnel Service. For more information, see Tunnel service.
To configure alert notifications for monitoring metrics, you can use CloudMonitor. For more information, see Monitoring and alerting.
To visualize data, you can use DataV or Grafana. For example, you can use DataV or Grafana to display data in charts. For more information, see Data visualization.