Search indexes support multi-dimensional data queries and statistical analysis in big data scenarios based on inverted indexes and column stores. You can create one or more search indexes for a data table to accelerate data queries. When you create a search index, you must add the fields that you want to query to the search index. You can configure advanced settings, such as the routing key, time to live (TTL), and pre-sorting of the search index based on your business requirements.
Usage notes
We recommend that you create a search index that contains all fields that you want to query. We recommend that you do not create a separate search index for each field.
After you create a search index, you must wait several seconds before you can use the search index. During this period, data can be written to the data table. However, you cannot query the index metadata or use the search index to query data.
For information about the limits on the number of rows, total size, and number of fields in a search index, see Search index limits.
Procedure
Go to the Indexes tab.
Log on to the Tablestore console.
In the top navigation bar, select a resource group and a region.
On the Overview page, click the instance name or click Manage Instance in the Actions column of the instance.
In the Tables section of the Instance Details tab, click the data table name or click Indexes in the Actions column of the data table.
On the Indexes tab, click Create Search Index.
In the Create Index dialog box, create a search index.
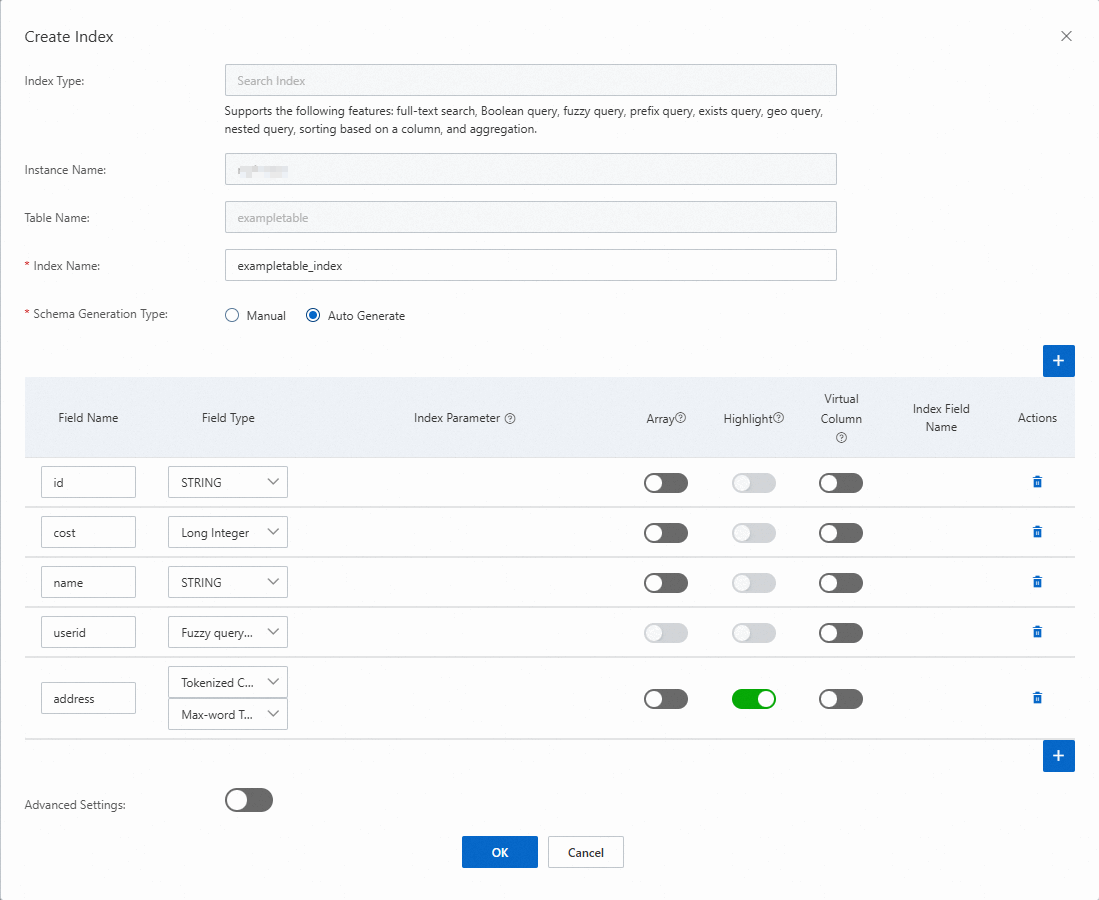
Retain the default index name that is generated by the system, or enter an index name based on your business requirements.
Configure the schema of the search index.
ImportantThe values of the Field Name and Field Type parameters must match the field names and field types in the data table. For information about the field type mappings between data tables and search indexes, see Data types.
If you want to highlight the content that meets the specified conditions in a Text field, you can enable the highlight feature for the Text field. For more information, see Highlight.
If you set Schema Generation Type to Manual, manually enter the field name, select the field type, and specify whether to enable Array.
If you set Schema Generation Type to Auto Generate, the system automatically uses the primary key columns and attribute columns of the data table as index fields. You can select the field type and specify whether to enable Array based on your business requirements.
NoteIn some cases, you can use virtual columns to optimize performance.
If you want to configure the Time to Live, Routing Key, and Pre-sorting parameters, turn on the Advanced Settings switch and configure the parameters. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Routing Key
The custom routing fields. You can specify specific primary key columns as the routing fields. In most cases, you need to specify only one routing field. If you specify multiple routing fields, the system concatenates the values of the routing fields into one value as the routing key.
Tablestore distributes data that is written to a search index across different partitions based on the specified routing fields. Data with the same routing field values is distributed to the same partition.
Time to Live
The retention period of data in the search index. Unit: seconds. The default value is -1, which specifies that the data never expires.
The TTL must be at least 86,400 seconds (one day) or -1. A value of -1 specifies that the data never expires. The TTL value of a search index must be smaller than or equal to the TTL value of the data table for which the search index is created.
If you want the system to automatically delete the historical data in the search index, specify a value that is greater than or equal to 86400 as the value of the Time to Live parameter. If the retention period of data exceeds the TTL value, Tablestore automatically deletes the expired data.
Pre-sorting
The default order in which the data that meets the query conditions is returned.
Valid values: Default and Custom. A value of Default specifies that the data is sorted based on the primary key. A value of Custom specifies that the data is sorted based on the field that you specify. Configure the Pre-sorting parameter based on your business requirements.
ImportantSearch indexes that contain Nested fields do not support index presorting.
Click OK.
After the search index is created, click Index Details in the Actions column of the index on the Indexes tab to view the basic information, index metrics, routing key, index fields, and pre-sorting information of the search index.
Development integration
You can use Tablestore SDKs or the Tablestore CLI to create a search index.
References
Data query types
Basic queries: match all query, term query, terms query, fuzzy query (wildcard query, prefix query, suffix query, tokenization-based wildcard query), range query, exists query, geo query (applicable to Geo-point fields), nested query (applicable to Nested fields), and collapse (distinct)
Composite query: Boolean query
Full-text search (applicable to Text fields): match query, match phrase query, tokenization, and highlight
Vector search (applicable to Vector fields): KNN vector query, Use KNN vector query, and Generate vectors
Data analysis: Aggregation, SQL query, and Computing and analysis
Data export: Parallel scan