OSS objects are private by default, and only the file owner can access them. However, file owners can generate shared links (presigned URLs) to authorize others to download or preview specific files online within a validity period.

How it works
The generation of presigned URLs relies on secret key encryption and parameter concatenation. The process is as follows:
Permission verification: When you generate a presigned URL, you need to have the
oss:GetObjectpermission for third parties to successfully download/preview files through the presigned URL.Local encryption: Based on AK/SK, encrypt and calculate the file path, expiration time, and other information to obtain a signature (
x-oss-signature).Append signature: Add signature parameters (
x-oss-date,x-oss-expires,x-oss-credential, etc.) as query strings to the file URL.Form the link: Compose the complete presigned URL.
Presigned URL format
https://BucketName.Endpoint/Object?signature parametersComplete example
https://examplebucket.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/exampleobject.txt?x-oss-process=image%2Fresize%2Cp_10&x-oss-date=20241115T095058Z&x-oss-expires=3600&x-oss-signature-version=OSS4-HMAC-SHA256&x-oss-credential=LTAI****************%2F20241115%2Fcn-hangzhou%2Foss%2Faliyun_v4_request&x-oss-signature=6e7a*********************************
For detailed generation process, see Signature Version 4 (Recommended).
Get file download links
Use the OSS default endpoint to generate a file download link with an expiration date (presigned URL).
Using the OSS console
You can log on to the OSS Management Console, go to the Files list of the target bucket, click the target file, and then click Copy File URL in the details panel on the right to obtain a temporary download link with a default validity period of 32400 seconds (9 hours).
Using Alibaba Cloud SDK
The following are code examples for generating file download links (presigned URLs) in common languages.
Java
For more information, see Download files using presigned URLs in Java.
import com.aliyun.oss.*;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.*;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.Date;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
// In this example, the endpoint of the China (Hangzhou) region is used. Specify your actual endpoint.
String endpoint = "https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
// Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = CredentialsProviderFactory.newEnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider();
// Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket.
String bucketName = "examplebucket";
// Specify the full path of the object. Example: exampleobject.txt. Do not include the bucket name in the full path of the object.
String objectName = "exampleobject.txt";
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou.
String region = "cn-hangzhou";
// Create an OSSClient instance.
// Call the shutdown method to release resources when the OSSClient is no longer in use.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4);
OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create()
.endpoint(endpoint)
.credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
.region(region)
.build();
try {
// Specify the validity period of the presigned URL. Unit: milliseconds. In this example, the validity period is 1 hour.
Date expiration = new Date(new Date().getTime() + 3600 * 1000L);
// Generate a presigned URL that allows HTTP GET requests. In this example, no additional request headers are specified. Other users can access the relevant content directly by using the browser.
URL url = ossClient.generatePresignedUrl(bucketName, objectName, expiration);
System.out.println(url);
} catch (OSSException oe) {
System.out.println("Caught an OSSException, which means your request made it to OSS, "
+ "but was rejected with an error response for some reason.");
System.out.println("Error Message:" + oe.getErrorMessage());
System.out.println("Error Code:" + oe.getErrorCode());
System.out.println("Request ID:" + oe.getRequestId());
System.out.println("Host ID:" + oe.getHostId());
} catch (ClientException ce) {
System.out.println("Caught an ClientException, which means the client encountered "
+ "a serious internal problem while trying to communicate with OSS, "
+ "such as not being able to access the network.");
System.out.println("Error Message:" + ce.getMessage());
} finally {
if (ossClient != null) {
ossClient.shutdown();
}
}
}
}Python
For more information, see Download files using presigned URLs in Python.
import argparse
import alibabacloud_oss_v2 as oss
# Create a command-line parameter parser and describe the purpose of the script.
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="presign get object sample")
# Specify the --region parameter to indicate the region in which the bucket is located. This parameter is required.
parser.add_argument('--region', help='The region in which the bucket is located.', required=True)
# Specify the --bucket parameter to indicate the name of the bucket in which the object is stored. This parameter is required.
parser.add_argument('--bucket', help='The name of the bucket.', required=True)
# Specify the --endpoint parameter to indicate the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. This parameter is optional.
parser.add_argument('--endpoint', help='The domain names that other services can use to access OSS')
# Specify the --key parameter to indicate the name of the object. This parameter is required.
parser.add_argument('--key', help='The name of the object.', required=True)
def main():
# Parse the command-line parameters to obtain the specified values.
args = parser.parse_args()
# From the environment variables, load the authentication information required to access OSS.
credentials_provider = oss.credentials.EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider()
# Use the default configuration to create a cfg object and specify the credential provider.
cfg = oss.config.load_default()
cfg.credentials_provider = credentials_provider
# Set the region attribute of the cfg object to the region provided in the command line.
cfg.region = args.region
# If a custom endpoint is provided, update the endpoint attribute of the cfg object with the provided endpoint.
if args.endpoint is not None:
cfg.endpoint = args.endpoint
# Use the preceding settings to initialize the OSSClient instance.
client = oss.Client(cfg)
# Initiate a request to generate a presigned URL.
pre_result = client.presign(
oss.GetObjectRequest(
bucket=args.bucket, # Specify the bucket name.
key=args.key, # Specify the object key.
)
)
# Display the HTTP method, expiration time, and presigned URL.
print(f'method: {pre_result.method},'
f' expiration: {pre_result.expiration.strftime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.000Z")},'
f' url: {pre_result.url}'
)
# Display the signed headers.
for key, value in pre_result.signed_headers.items():
print(f'signed headers key: {key}, signed headers value: {value}')
# Call the main function to start the processing logic when the script is directly run.
if __name__ == "__main__":
main() # Specify the entry point of the script. The control flow starts here.Go
For more information, see Download files using presigned URLs in Go.
package main
import (
"context"
"flag"
"log"
"time"
"github.com/aliyun/alibabacloud-oss-go-sdk-v2/oss"
"github.com/aliyun/alibabacloud-oss-go-sdk-v2/oss/credentials"
)
// Specify the global variables.
var (
region: string; // The region in which the bucket is located.
bucketName string // The name of the bucket.
objectName string // The name of the object.
)
// Specify the init function used to initialize command line parameters.
func init() {
flag.StringVar(®ion, "region", "", "The region in which the bucket is located.")
flag.StringVar(&bucketName, "bucket", "", "The name of the bucket.")
flag.StringVar(&objectName, "object", "", "The name of the object.")
}
func main() {
// Parse command line parameters.
flag.Parse()
// Check whether the bucket name is empty.
if len(bucketName) == 0 {
flag.PrintDefaults()
log.Fatalf("invalid parameters, bucket name required")
}
// Check whether the region is empty.
if len(region) == 0 {
flag.PrintDefaults()
log.Fatalf("invalid parameters, region required")
}
// Check whether the object name is empty.
if len(objectName) == 0 {
flag.PrintDefaults()
log.Fatalf("invalid parameters, object name required")
}
// Load the default configurations and specify the credential provider and region.
cfg := oss.LoadDefaultConfig().
WithCredentialsProvider(credentials.NewEnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider()).
WithRegion(region)
// Create an OSS client.
client := oss.NewClient(cfg)
// Generate a presigned URL for the GetObject request.
result, err := client.Presign(context.TODO(), &oss.GetObjectRequest{
Bucket: oss.Ptr(bucketName),
Key: oss.Ptr(objectName),
},
oss.PresignExpires(10*time.Minute),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to get object presign %v", err)
}
log.Printf("request method:%v\n", result.Method)
log.Printf("request expiration:%v\n", result.Expiration)
log.Printf("request url:%v\n", result.URL)
if len(result.SignedHeaders) > 0 {
// If you specify request headers when you generate a presigned URL that allows HTTP GET requests, make sure that the request headers are included in the GET request initiated by using the presigned URL. This prevents request failures and signature errors.
log.Printf("signed headers:\n")
for k, v := range result.SignedHeaders {
log.Printf("%v: %v\n", k, v)
}
}
}
Node.js
For more information, see Download files using presigned URLs in Node.js.
const OSS = require("ali-oss");
// Specify a function used to generate a presigned URL.
async function generateSignatureUrl(fileName) {
// Obtain the presigned URL.
const client = await new OSS({
// Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
accessKeyId: process.env.OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID,
accessKeySecret: process.env.OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET,
bucket: 'examplebucket',
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if your bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to oss-cn-hangzhou.
region: 'oss-cn-hangzhou',
// Set secure to true and use HTTPS to prevent the generated download link from being blocked by the browser.
secure: true,
authorizationV4: true
});
return await client.signatureUrlV4('GET', 3600, {
headers: {} // Specify the request headers based on the actual request headers.
}, fileName);
}
// Call the function and pass in the name of the object.
generateSignatureUrl('yourFileName').then(url => {
console.log('Generated Signature URL:', url);
}).catch(err => {
console.error('Error generating signature URL:', err);
});PHP
For more information, see Download files using presigned URLs in PHP.
<?php
// Include the autoload file to ensure that dependency libraries are correctly loaded.
require_once __DIR__ . '/../vendor/autoload.php';
use AlibabaCloud\Oss\V2 as Oss;
// Define the descriptions of command-line parameters.
$optsdesc = [
"region" => ['help' => 'The region in which the bucket is located.', 'required' => True], // (Required) The region in which the bucket is located.
"endpoint" => ['help' => 'The domain names that other services can use to access OSS.', 'required' => False], // (Optional) The endpoint.
"bucket" => ['help' => 'The name of the bucket', 'required' => True], // (Required) The name of the bucket.
"key" => ['help' => 'The name of the object', 'required' => True], // (Required) The name of the object.
];
// Convert the parameter descriptions to the long options format required by getopt.
// Add a colon (:) after each parameter to indicate that a value is required.
$longopts = \array_map(function ($key) {
return "$key:";
}, array_keys($optsdesc));
// Parse the command-line arguments.
$options = getopt("", $longopts);
// Verify that all required parameters are provided.
foreach ($optsdesc as $key => $value) {
if ($value['required'] === True && empty($options[$key])) {
$help = $value['help']; // Obtain the help information for the parameter.
echo "Error: the following arguments are required: --$key, $help" . PHP_EOL;
exit(1); // If a required parameter is not provided, exit the program.
}
}
// Extract values from the parsed parameters.
$region = $options["region"]; // The region in which the bucket is located.
$bucket = $options["bucket"]; // The name of the bucket.
$key = $options["key"]; // The name of the object.
// Load the access credential from the environment variable.
// Use EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider to read the Access Key ID and Access Key Secret from environment variables.
$credentialsProvider = new Oss\Credentials\EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider();
// Use the default configurations of the SDK.
$cfg = Oss\Config::loadDefault();
$cfg->setCredentialsProvider($credentialsProvider); // Set the credential provider.
$cfg->setRegion($region); // Set the region in which the bucket is located.
if (isset($options["endpoint"])) {
$cfg->setEndpoint($options["endpoint"]); // If an endpoint is provided, set the endpoint.
}
// Create an OSS client instance.
$client = new Oss\Client($cfg);
// Create a GetObjectRequest object to download an object.
$request = new Oss\Models\GetObjectRequest(bucket:$bucket, key:$key);
// Call the presign method to generate a signed URL.
$result = $client->presign($request);
// Print the presign result.
// Output the signed URL. Users can use this URL to perform download operations.
print(
'get object presign result:' . var_export($result, true) . PHP_EOL . // The details of the presign result.
'get object url:' . $result->url . PHP_EOL // The signed URL, which is used to directly download the object.
);
.NET
For more information, see Download files using presigned URLs in .NET.
using Aliyun.OSS;
using Aliyun.OSS.Common;
// Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com.
var endpoint = "https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
// Obtain a credential from the environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
var accessKeyId = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID");
var accessKeySecret = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET");
// Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket.
var bucketName = "examplebucket";
// Specify the full path of the object. The full path cannot contain the bucket name. Example: exampledir/exampleobject.txt.
var objectName = "exampledir/exampleobject.txt";
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou.
const string region = "cn-hangzhou";
// Create a ClientConfiguration instance and modify the default parameters based on your requirements.
var conf = new ClientConfiguration();
// Specify the V4 signature.
conf.SignatureVersion = SignatureVersion.V4;
// Create an OSSClient instance.
var client = new OssClient(endpoint, accessKeyId, accessKeySecret, conf);
client.SetRegion(region);
try
{
var metadata = client.GetObjectMetadata(bucketName, objectName);
var etag = metadata.ETag;
// Generate a presigned URL.
var req = new GeneratePresignedUriRequest(bucketName, objectName, SignHttpMethod.Get)
{
// Set the validity period of the presigned URL. Default value: 3600. Unit: seconds.
Expiration = DateTime.UtcNow.AddHours(1),
};
var uri = client.GeneratePresignedUri(req);
// Print the generated presigned URL
Console.WriteLine("Generated Signed URL: " + uri);
}
catch (OssException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed with error code: {0}; Error info: {1}. \nRequestID:{2}\tHostID:{3}",
ex.ErrorCode, ex.Message, ex.RequestId, ex.HostId);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed with error info: {0}", ex.Message);
}Android
For more SDK information, see Download files using presigned URLs in Android.
// Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket.
String bucketName = "examplebucket";
// Specify the full path of the source object. Do not include the bucket name in the full path. Example: exampleobject.txt.
String objectKey = "exampleobject.txt";
String url = null;
try {
// Generate a presigned URL to download the object.
GeneratePresignedUrlRequest request = new GeneratePresignedUrlRequest(bucketName, objectKey);
// Set the validity period of the presigned URL to 30 minutes.
request.setExpiration(30*60);
request.setMethod(HttpMethod.GET);
url = oss.presignConstrainedObjectURL(request);
Log.d("url", url);
} catch (ClientException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}iOS
For more SDK information, see Download files using presigned URLs in iOS.
// Specify the name of the bucket.
NSString *bucketName = @"examplebucket";
// Specify the name of the object.
NSString *objectKey = @"exampleobject.txt";
__block NSString *urlString;
// Generate a presigned URL with a validity period for downloading the object. In this example, the validity period of the URL is 30 minutes.
OSSTask *task = [client presignConstrainURLWithBucketName:bucketName
withObjectKey:objectKey
httpMethod:@"GET"
withExpirationInterval:30 * 60
withParameters:@{}];
[task continueWithBlock:^id _Nullable(OSSTask * _Nonnull task) {
if (task.error) {
NSLog(@"presign error: %@", task.error);
} else {
urlString = task.result;
NSLog(@"url: %@", urlString);
}
return nil;
}];C++
For more SDK information, see Download files using presigned URLs in C++.
#include <alibabacloud/oss/OssClient.h>
using namespace AlibabaCloud::OSS;
int main(void)
{
/* Initialize information about the account that is used to access OSS. */
/* Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com. */
std::string Endpoint = "yourEndpoint";
/* Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou. * /
std::string Region = "yourRegion";
/* Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket. */
std::string BucketName = "examplebucket";
/* Specify the full path of the object. Do not include the bucket name in the full path. Example: exampledir/exampleobject.txt. */
std::string GetobjectUrlName = "exampledir/exampleobject.txt";
/* Initialize resources, such as network resources. */
InitializeSdk();
ClientConfiguration conf;
conf.signatureVersion = SignatureVersionType::V4;
/* Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured. */
auto credentialsProvider = std::make_shared<EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider>();
OssClient client(Endpoint, credentialsProvider, conf);
client.SetRegion(Region);
/* Specify the validity period of the pre-signed URL. The maximum validity period is 32,400. Unit: seconds. */
std::time_t t = std::time(nullptr) + 1200;
/* Generate a pre-signed URL. */
auto genOutcome = client.GeneratePresignedUrl(BucketName, GetobjectUrlName, t, Http::Get);
if (genOutcome.isSuccess()) {
std::cout << "GeneratePresignedUrl success, Gen url:" << genOutcome.result().c_str() << std::endl;
}
else {
/* Handle exceptions. */
std::cout << "GeneratePresignedUrl fail" <<
",code:" << genOutcome.error().Code() <<
",message:" << genOutcome.error().Message() <<
",requestId:" << genOutcome.error().RequestId() << std::endl;
return -1;
}
/* Release resources, such as network resources. */
ShutdownSdk();
return 0;
}Ruby
For more SDK information, see Download files using presigned URLs in Ruby.
require 'aliyun/oss'
client = Aliyun::OSS::Client.new(
# In this example, the endpoint of the China (Hangzhou) region is used. Specify your actual endpoint.
endpoint: 'https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com',
# Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
access_key_id: ENV['OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID'],
access_key_secret: ENV['OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET']
)
# Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket.
bucket = client.get_bucket('examplebucket')
# Generate a presigned URL that is used to download the object and set its validity period to 3,600 seconds.
puts bucket.object_url('my-object', true, 3600)C
For more SDK information, see Download files using presigned URLs in C.
#include "oss_api.h"
#include "aos_http_io.h"
/* Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com. */
const char *endpoint = "yourEndpoint";
/* Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket. */
const char *bucket_name = "examplebucket";
/* Specify the full path of the object. Do not include the bucket name in the full path. Example: exampledir/exampleobject.txt. */
const char *object_name = "exampledir/exampleobject.txt";
/* Specify the full path of the local file. */
const char *local_filename = "yourLocalFilename";
void init_options(oss_request_options_t *options)
{
options->config = oss_config_create(options->pool);
/* Use a char* string to initialize aos_string_t. */
aos_str_set(&options->config->endpoint, endpoint);
/* Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured. */
aos_str_set(&options->config->access_key_id, getenv("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID"));
aos_str_set(&options->config->access_key_secret, getenv("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET"));
/* Specify whether to use CNAME. The value 0 indicates that CNAME is not used. */
options->config->is_cname = 0;
/* Configure network parameters, such as the timeout period. */
options->ctl = aos_http_controller_create(options->pool, 0);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
/* Call the aos_http_io_initialize method in main() to initialize global resources, such as network and memory resources. */
if (aos_http_io_initialize(NULL, 0) != AOSE_OK) {
exit(1);
}
/* Create a memory pool to manage memory. aos_pool_t is equivalent to apr_pool_t. The code that is used to create a memory pool is included in the APR library. */
aos_pool_t *pool;
/* Create a memory pool. The value of the second parameter is NULL. This value specifies that the pool does not inherit other memory pools. */
aos_pool_create(&pool, NULL);
/* Create and initialize options. This parameter includes global configuration information, such as endpoint, access_key_id, access_key_secret, is_cname, and curl. */
oss_request_options_t *oss_client_options;
/* Allocate memory resources in the memory pool to the options. */
oss_client_options = oss_request_options_create(pool);
/* Initialize oss_client_options. */
init_options(oss_client_options);
/* Initialize the parameters. */
aos_string_t bucket;
aos_string_t object;
aos_string_t file;
aos_http_request_t *req;
apr_time_t now;
char *url_str;
aos_string_t url;
int64_t expire_time;
int one_hour = 3600;
aos_str_set(&bucket, bucket_name);
aos_str_set(&object, object_name);
aos_str_set(&file, local_filename);
expire_time = now / 1000000 + one_hour;
req = aos_http_request_create(pool);
req->method = HTTP_GET;
now = apr_time_now();
/* Specify the validity period. Unit: microseconds * /
expire_time = now / 1000000 + one_hour;
/* Generate a presigned URL. */
url_str = oss_gen_signed_url(oss_client_options, &bucket, &object, expire_time, req);
aos_str_set(&url, url_str);
printf("Temporary download URL: %s\n", url_str);
/* Release the memory pool. This operation releases memory resources allocated for the request. */
aos_pool_destroy(pool);
/* Release the allocated global resources. */
aos_http_io_deinitialize();
return 0;
}The generated presigned URL example is as follows:
https://examplebucket.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/exampleobject.txt?x-oss-process=image%2Fresize%2Cp_10&x-oss-date=20241115T095058Z&x-oss-expires=3600&x-oss-signature-version=OSS4-HMAC-SHA256&x-oss-credential=LTAI****************%2F20241115%2Fcn-hangzhou%2Foss%2Faliyun_v4_request&x-oss-signature=6e7a*********************************************Using the command line tool ossutil
For the example.txt object in the examplebucket bucket, generate a file download link (presigned URL) with a default validity period of 15 minutes using the following command.
ossutil presign oss://examplebucket/example.txtFor more examples of using ossutil to generate presigned URLs, see presign (Generate presigned URLs).
Using the graphical management tool ossbrowser
ossbrowser supports object-level operations similar to those supported by the console. Follow the ossbrowser interface to complete the operation of obtaining a presigned URL. For information about how to use ossbrowser, see Common operations.
Get online preview links for files
To generate links that support online preview (presigned URLs), you must first attach a custom domain name. After attaching the custom domain name, use it to generate presigned URLs.
Use the OSS console
Log on to the OSS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Buckets. On the Buckets page, click the name of the bucket.
In the left-side navigation tree, choose .
On the Objects page, click the name of the object.
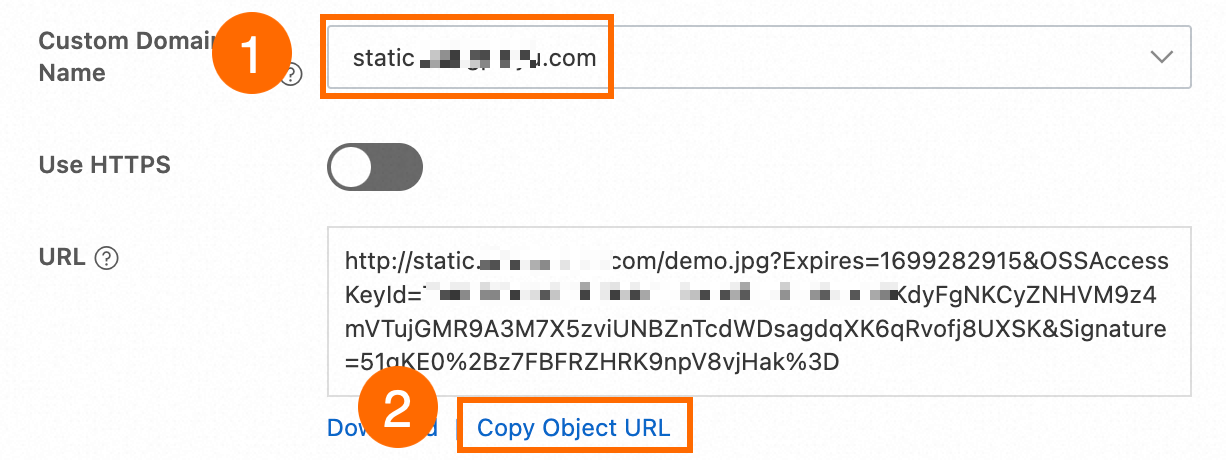
In the View Details panel, select the custom domain name that is mapped to the bucket in the Custom Domain Name field, retain the default settings for other parameters, and then click Copy Object URL.
Use ossbrowser
You can use ossbrowser to perform the same object-level operations that you can perform in the OSS console. You can follow the on-screen instructions in ossbrowser to obtain a presigned URL. For information about how to download ossbrowser, see Graphical management tool ossbrowser 1.0.
Use the custom domain name to log on to ossbrowser.
Obtain the URL of the object.
Use OSS SDKs
You can use the custom domain name to create an OssClient instance and generate a presigned URL.
Java
import com.aliyun.oss.*;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.*;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion;
import com.aliyun.oss.model.GeneratePresignedUrlRequest;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.Date;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
// Specify a custom domain name. Example: https://static.example.com.
String endpoint = "yourCustomEndpoint";
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. Example: cn-hangzhou.
String region = "cn-hangzhou";
// Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket.
String bucketName = "examplebucket";
// Specify the full path of the object. Do not include the bucket name in the full path. Example: exampledir/exampleobject.txt.
String objectName = "exampleobject.txt";
// Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, you must configure the environment variables.
EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = CredentialsProviderFactory.newEnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider();
// Create an OSSClient instance.
// Call the shutdown method to release resources when the OSSClient is no longer in use.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
// To enable CNAME, set this parameter to true.
clientBuilderConfiguration.setSupportCname(true);
// Explicitly declare the use of the V4 signature algorithm.
clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4);
OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create()
.endpoint(endpoint)
.credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
.region(region)
.build();
try {
// Specify the validity period of the presigned URL. Unit: milliseconds. In this example, the validity period is set to 1 hour.
Date expiration = new Date(new Date().getTime() + 3600 * 1000L);
// Generate a presigned URL.
GeneratePresignedUrlRequest request = new GeneratePresignedUrlRequest(bucketName, objectName, HttpMethod.GET);
// Set the validity period of the URL.
request.setExpiration(expiration);
// Generate the presigned URL that allows HTTP GET requests.
URL signedUrl = ossClient.generatePresignedUrl(request);
// Display the presigned URL.
System.out.println("signed url for getObject: " + signedUrl);
} catch (OSSException oe) {
System.out.println("Caught an OSSException, which means your request made it to OSS, "
+ "but was rejected with an error response for some reason.");
System.out.println("Error Message:" + oe.getErrorMessage());
System.out.println("Error Code:" + oe.getErrorCode());
System.out.println("Request ID:" + oe.getRequestId());
System.out.println("Host ID:" + oe.getHostId());
} catch (ClientException ce) {
System.out.println("Caught an ClientException, which means the client encountered "
+ "a serious internal problem while trying to communicate with OSS, "
+ "such as not being able to access the network.");
System.out.println("Error Message:" + ce.getMessage());
} finally {
if (ossClient != null) {
ossClient.shutdown();
}
}
}
}PHP
<?php
// Include the autoload file to ensure that dependency libraries are correctly loaded.
require_once __DIR__ . '/../vendor/autoload.php';
use AlibabaCloud\Oss\V2 as Oss;
// Define the descriptions of command-line parameters.
$optsdesc = [
"region" => ['help' => 'The region in which the bucket is located.', 'required' => True], // (Required) The region in which the bucket is located.
"endpoint" => ['help' => 'The domain names that other services can use to access OSS.', 'required' => False], // (Optional) The endpoint.
"bucket" => ['help' => 'The name of the bucket', 'required' => True], // (Required) The name of the bucket.
"key" => ['help' => 'The name of the object', 'required' => True], // (Required) The name of the object.
];
// Convert the parameter descriptions to the long options format required by getopt.
// Add a colon (:) after each parameter to indicate that a value is required.
$longopts = \array_map(function ($key) {
return "$key:";
}, array_keys($optsdesc));
// Parse the command-line arguments.
$options = getopt("", $longopts);
// Verify that all required parameters are provided.
foreach ($optsdesc as $key => $value) {
if ($value['required'] === True && empty($options[$key])) {
$help = $value['help']; // Obtain the help information for the parameter.
echo "Error: the following arguments are required: --$key, $help" . PHP_EOL;
exit(1); // If a required parameter is not provided, exit the program.
}
}
// Extract values from the parsed parameters.
$region = $options["region"]; // The region in which the bucket is located.
$bucket = $options["bucket"]; // The name of the bucket.
$key = $options["key"]; // The name of the object.
// Load the access credential from the environment variable.
// Use EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider to read the Access Key ID and Access Key Secret from environment variables.
$credentialsProvider = new Oss\Credentials\EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider();
// Use the default configurations of the SDK.
$cfg = Oss\Config::loadDefault();
$cfg->setCredentialsProvider($credentialsProvider); // Set the credential provider.
$cfg->setRegion($region); // Set the region in which the bucket is located.
$cfg->setEndpoint(endpoint: "http://static.example.com"); // Set this parameter to your custom endpoint.
$cfg->setUseCname(true); // Set this parameter to use a CNAME.
// Create an OSS client instance.
$client = new Oss\Client($cfg);
// Create a GetObjectRequest object to download an object.
$request = new Oss\Models\GetObjectRequest(bucket:$bucket, key:$key);
// Call the presign method to generate a signed URL.
$result = $client->presign($request);
// Print the presign result.
// Output the signed URL. Users can use this URL to perform download operations.
print(
'get object presign result:' . var_export($result, true) . PHP_EOL . // The details of the presign result.
'get object url:' . $result->url . PHP_EOL // The signed URL, which is used to directly download the object.
);
Node.js
const OSS = require("ali-oss");
// Specify a function used to generate a presigned URL.
async function generateSignatureUrl(fileName) {
// Obtain the presigned URL.
const client = await new OSS({
// Specify the custom domain name that you want to map to the bucket.
endpoint: 'http://static.example.com',
// Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
accessKeyId: process.env.OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID,
accessKeySecret: process.env.OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET,
bucket: 'examplebucket',
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if your bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to oss-cn-hangzhou.
region: 'oss-cn-hangzhou',
authorizationV4: true,
cname: true
});
return await client.signatureUrlV4('GET', 3600, {
headers: {} // Specify the request headers based on the actual request headers.
}, fileName);
}
// Call the function and pass in the name of the object.
generateSignatureUrl('yourFileName').then(url => {
console.log('Generated Signature URL:', url);
}).catch(err => {
console.error('Error generating signature URL:', err);
});Python
import argparse
import alibabacloud_oss_v2 as oss
# Create a command-line parameter parser and describe the purpose of the script.
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="presign get object sample")
# Specify the --region parameter to indicate the region in which the bucket is located. This parameter is required.
parser.add_argument('--region', help='The region in which the bucket is located.', required=True)
# Specify the --bucket parameter to indicate the name of the bucket in which the object is stored. This parameter is required.
parser.add_argument('--bucket', help='The name of the bucket.', required=True)
# Specify the --endpoint parameter to indicate the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. This parameter is optional.
parser.add_argument('--endpoint', help='The domain names that other services can use to access OSS')
# Specify the --key parameter to indicate the name of the object. This parameter is required.
parser.add_argument('--key', help='The name of the object.', required=True)
def main():
# Parse the command-line parameters to obtain the specified values.
args = parser.parse_args()
# From the environment variables, load the authentication information required to access OSS.
credentials_provider = oss.credentials.EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider()
# Use the default configuration to create a cfg object and specify the credential provider.
cfg = oss.config.load_default()
cfg.credentials_provider = credentials_provider
# Specify the region attribute of the configuration object based on the command line parameters specified by the user.
cfg.region = args.region
# Specify the custom endpoint. Example: http://static.example.com
cfg.endpoint = "http://static.example.com"
# Enable CNAME record resolution.
cfg.use_cname = True
# Use the preceding settings to initialize the OSSClient instance.
client = oss.Client(cfg)
# Initiate a request to generate a presigned URL.
pre_result = client.presign(
oss.GetObjectRequest(
bucket=args.bucket, # Specify the bucket name.
key=args.key, # Specify the object key.
)
)
# Display the HTTP method, expiration time, and presigned URL.
print(f'method: {pre_result.method},'
f' expiration: {pre_result.expiration.strftime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.000Z")},'
f' url: {pre_result.url}'
)
# Display the signed headers.
for key, value in pre_result.signed_headers.items():
print(f'signed headers key: {key}, signed headers value: {value}')
# Call the main function to start the processing logic when the script is directly run.
if __name__ == "__main__":
main() # Specify the entry point of the script. The control flow starts here.Go
package main
import (
"context"
"flag"
"log"
"time"
"github.com/aliyun/alibabacloud-oss-go-sdk-v2/oss"
"github.com/aliyun/alibabacloud-oss-go-sdk-v2/oss/credentials"
)
// Specify the global variables.
var (
region string // Region in which the bucket is located.
bucketName string // Name of the bucket.
objectName string // Name of the object.
)
// Specify the init function used to initialize command line parameters.
func init() {
flag.StringVar(®ion, "region", "", "The region in which the bucket is located.")
flag.StringVar(&bucketName, "bucket", "", "The name of the bucket.")
flag.StringVar(&objectName, "object", "", "The name of the object.")
}
func main() {
// Parse command line parameters.
flag.Parse()
// Check whether the name of the bucket is specified.
if len(bucketName) == 0 {
flag.PrintDefaults()
log.Fatalf("invalid parameters, bucket name required")
}
// Check whether the region is specified.
if len(region) == 0 {
flag.PrintDefaults()
log.Fatalf("invalid parameters, region required")
}
// Check whether the object is specified.
if len(objectName) == 0 {
flag.PrintDefaults()
log.Fatalf("invalid parameters, object name required")
}
// Load the default configurations and specify the credential provider and region.
cfg := oss.LoadDefaultConfig().
WithCredentialsProvider(credentials.NewEnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider()).
WithRegion(region).
WithEndpoint("http://static.example.com").
WithUseCName(true)
// Create an OSS client.
client := oss.NewClient(cfg)
// Generate a presigned URL for the GetObject request.
result, err := client.Presign(context.TODO(), &oss.GetObjectRequest{
Bucket: oss.Ptr(bucketName),
Key: oss.Ptr(objectName),
//RequestPayer: oss.Ptr("requester"), // Specify the identity of the requester.
},
oss.PresignExpires(10*time.Minute),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to get object presign %v", err)
}
log.Printf("request method:%v\n", result.Method)
log.Printf("request expiration:%v\n", result.Expiration)
log.Printf("request url:%v\n", result.URL)
if len(result.SignedHeaders) > 0 {
// If you specify request headers when you generate a presigned URL that allows HTTP GET requests, make sure that the request headers are included in the GET request initiated by using the presigned URL. This prevents request failures and signature errors.
log.Printf("signed headers:\n")
for k, v := range result.SignedHeaders {
log.Printf("%v: %v\n", k, v)
}
}
}Use ossutil
Use the custom domain name to generate a presigned URL for an object by running the presign command.
ossutil presign oss://examplebucket/exampleobject.txt --endpoint "http://static.example.com” --addressing-style "cname"To enable the ossutil command to automatically use a custom domain name, instead of manually specifying it each time, add the custom domain name to the configuration file.
If the link still cannot be previewed, check the following configurations.
Is the
Content-Typeset appropriately?If the file's
Content-Typedoes not match its actual type, the browser may not correctly identify and render the content, causing the file to be downloaded as an attachment. You can check How to set Content-Type (MIME)? to confirm whether the file name extension matches theContent-Type. If they do not match, refer to Manage object metadata for methods to modify the file'sContent-Type.Is
Content-Dispositionset toinline?If the file's
Content-Dispositionis set toattachment, the browser will force the file to download. Refer to Manage object metadata for methods to modify it toinlineto support preview.Has the CDN cache been refreshed?
If you are not using CDN acceleration, you can ignore this item.
If you use CDN to access OSS resources, you need to refresh the CDN cache after modifying file metadata. Otherwise, the old configuration may still be read, causing the preview to not take effect.
Get a forced download link for a file
If the current link (presigned URL) opens directly for preview in a browser, but you want it to download instead, you can use the following methods. Method 1 has higher priority than Method 2.
Method 1: One-time forced download
This only applies to the currently generated link. Implement this by setting the response-content-disposition parameter to attachment when generating the URL.
Java
Import the GeneratePresignedUrlRequest class.
import com.aliyun.oss.model.GeneratePresignedUrlRequest;Use the GeneratePresignedUrlRequest method and set the response-content-disposition response header to attachment.
// Build a presigned URL for GET request
GeneratePresignedUrlRequest request = new GeneratePresignedUrlRequest(
bucketName, objectName, HttpMethod.GET);
// Set forced download
request.getResponseHeaders().setContentDisposition("attachment");Python
Add the response_content_disposition parameter in GetObjectRequest and set its value to attachment.
# Generate a presigned GET request
pre_result = client.presign(
oss.GetObjectRequest(
bucket=args.bucket, # Specify the bucket name
key=args.key, # Specify the object key
response_content_disposition="attachment",# Set to forced download
)
)Go
Add the ResponseContentDisposition parameter in GetObjectRequest and set its value to attachment.
// Generate a presigned GET request with forced download behavior
result, err := client.Presign(context.TODO(), &oss.GetObjectRequest{
Bucket: oss.Ptr(bucketName),
Key: oss.Ptr(objectName),
ResponseContentDisposition: oss.Ptr("attachment"), // Set to forced download
})Method 2: Universal forced download setting (via metadata)
After setting this once, all access to the file will be forced to download. This is implemented by modifying the Content-Disposition field in the file metadata.
Using the OSS console
In the OSS Management Console, find the target file, click Set File Metadata in the file details panel, set Content-Disposition to attachment, and then click OK to save.
In addition to console operations, you can also refer to Manage file metadata to set this field using the SDK or the command line interface ossutil.
If you also want to customize the file name displayed during download, see Customize the file name during download.
Get links to specific versions of files
Generate links (presigned URLs) for specific versions of files, applicable to buckets with versioning enabled.
Using the OSS console
You can log on to the OSS Management Console, go to the Files tab of the target bucket, and switch Historical Version to Show in the upper-right corner of the page.

Find the target file, click the filename of the required historical version, and Copy the URL of this version file on the details page.

Using Alibaba Cloud SDK
Java
Add the following key code:
// 1. Define the version ID variable
String versionId = "CAEQARiBgID8rumR2hYiIGUyOTAyZGY2MzU5MjQ5ZjlhYzQzZjNlYTAyZDE3****";
// 2. Create a query parameter Map
Map<String, String> queryParam = new HashMap<String, String>();
queryParam.put("versionId", versionId);
// 3. Add the version ID parameter to the request
request.setQueryParameter(queryParam);Python
Add the version_id parameter to GetObjectRequest.
pre_result = client.presign(
oss.GetObjectRequest(
bucket=bucket_name,
key=object_name,
version_id='CAEQARiBgID8rumR2hYiIGUyOTAyZGY2MzU5MjQ5ZjlhYzQzZjNlYTAyZDE3****' # Set the VersionId parameter
)
)Go
Add the VersionId field to GetObjectRequest.
result, err := client.Presign(context.TODO(), &oss.GetObjectRequest{
Bucket: oss.Ptr(bucketName),
Key: oss.Ptr(objectName),
VersionId: oss.Ptr("CAEQARiBgID8rumR2hYiIGUyOTAyZGY2MzU5MjQ5ZjlhYzQzZjNlYTAyZDE7****"), // Set VersionId
}, oss.PresignExpires(10*time.Minute))Node.js
Add the queries parameter to signatureUrlV4.
const signedUrl = await client.signatureUrlV4('GET', 3600, {
queries: {
"versionId": 'CAEQARiBgID8rumR2hYiIGUyOTAyZGY2MzU5MjQ5ZjlhYzQzZjNlYTAyZDE7****' // Add versionId parameter
}
}, objectName);PHP
In GetObjectRequest, add the versionId parameter.
// Add specific version parameter
$versionId = "yourVersionId"; // Replace with actual version number
$request = new Oss\Models\GetObjectRequest(bucket:$bucket, key:$key, versionId:$versionId);Using ossutil
Generate a presigned URL for the example.txt object with version ID 123 in the examplebucket bucket.
ossutil presign oss://examplebucket/example.txt --version-id 123Batch generate file links
It is recommended to use the command line interface ossutil, which can batch generate links for files in an entire folder.
Use command line interface ossutil
Generate presigned URLs with a default validity period of 15 minutes for all files in the folder directory of the examplebucke bucket.
ossutil presign oss://examplebucket/folder/ -rGenerate presigned URLs with a default validity period of 15 minutes for files with the .txt extension in the folder directory of the examplebucket bucket.
ossutil presign oss://examplebucket/folder/ -r --include "*.txt"Generate presigned URLs with a default validity period of 15 minutes for all files in the examplebucket bucket.
ossutil presign oss://examplebucket/ -r
For more information about generating presigned URLs using ossutil, see presign (Generate presigned URLs).
Use OSS console
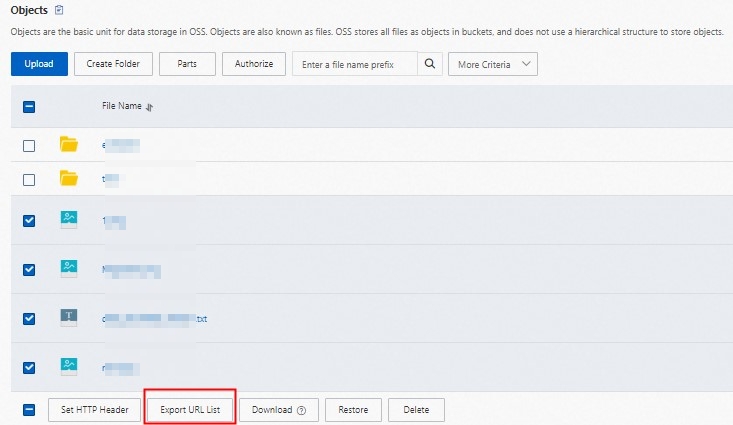
You can only export presigned URLs for files in the current directory. You cannot export presigned URLs for files in subdirectories.
Select the object file, and then click Export URL List below.
In the configuration panel that appears, the default parameters are suitable for most scenarios and can be used without modification.
Click OK to download and save the generated URL list file.
Use Alibaba Cloud SDK
Use the GetBucket(ListObjects) operation to obtain all object names, and then generate presigned URLs for each object.
Custom download file name
Based on forced downloads, you can further specify the file name that users see when saving files. Method 1 has higher priority than Method 2.
Method 1: Set download file name for a single request
Specify a download file name for a single signed URL. You only need to add the response-content-disposition parameter set to attachment and include the filename parameter.
Java
Set the response-content-disposition parameter.
// Set the file name displayed when the client downloads, using "test.txt" as an example
String filename = "test.txt";
request.getResponseHeaders().setContentDisposition("attachment;filename=" + URLEncoder.encode(filename,"UTF-8"));Python
Use the response_content_disposition parameter to customize the download file name as test.txt.
# Generate a presigned GET request
pre_result = client.presign(
oss.GetObjectRequest(
bucket=args.bucket, # Specify the bucket name
key=args.key, # Specify the object key
response_content_disposition="attachment;filename=test.txt",# Set the file name displayed when the client downloads, in this case "test.txt"
)
)Go
Use the ResponseContentDisposition parameter to customize the download file name as test.txt.
// Generate a presigned GET request with forced download behavior
result, err := client.Presign(context.TODO(), &oss.GetObjectRequest{
Bucket: oss.Ptr(bucketName),
Key: oss.Ptr(objectName),
ResponseContentDisposition: oss.Ptr("attachment;filename=test.txt"),//Set the file name displayed when the client downloads, in this case "test.txt"
})Method 2: Universal setting (through metadata)
Modify metadata to set a unified default download name for all access. This is implemented by modifying the Content-Disposition field in the file metadata to attachment; filename="yourFileName", where yourFileName is your custom file name, such as example.jpg.
Set the validity period of a link
The validity period of a link (presigned URL) is set when it is generated and cannot be modified afterward. The link can be accessed multiple times during its validity period and becomes invalid after expiration.
Different generation methods support different maximum validity periods. Exceeding the limit will cause generation failure or access exceptions.
Using the OSS console
You can log on to the OSS Management Console, go to the Files list of the target bucket, click the target file and set the link validity period in the Expiration Time in the details panel on the right.
Using Alibaba Cloud SDK
You need to have the oss:GetObject permission for third parties to successfully download files through the presigned URL. For specific authorization operations, see Grant custom permissions to RAM users. After generation, you can send the link to third parties who need to access the file.
You can set the expiration time of the presigned URL by modifying the expiration in the code.
Java
For more SDK information, see Download objects using presigned URLs in Java.
import com.aliyun.oss.*;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.auth.*;
import com.aliyun.oss.common.comm.SignVersion;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.Date;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
// In this example, the endpoint of the China (Hangzhou) region is used. Specify your actual endpoint.
String endpoint = "https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
// Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider credentialsProvider = CredentialsProviderFactory.newEnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider();
// Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket.
String bucketName = "examplebucket";
// Specify the full path of the object. Example: exampleobject.txt. Do not include the bucket name in the full path of the object.
String objectName = "exampleobject.txt";
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou.
String region = "cn-hangzhou";
// Create an OSSClient instance.
// Call the shutdown method to release resources when the OSSClient is no longer in use.
ClientBuilderConfiguration clientBuilderConfiguration = new ClientBuilderConfiguration();
clientBuilderConfiguration.setSignatureVersion(SignVersion.V4);
OSS ossClient = OSSClientBuilder.create()
.endpoint(endpoint)
.credentialsProvider(credentialsProvider)
.clientConfiguration(clientBuilderConfiguration)
.region(region)
.build();
try {
// Specify the validity period of the presigned URL. Unit: milliseconds. In this example, the validity period is 1 hour.
Date expiration = new Date(new Date().getTime() + 3600 * 1000L);
// Generate a presigned URL that allows HTTP GET requests. In this example, no additional request headers are specified. Other users can access the relevant content directly by using the browser.
URL url = ossClient.generatePresignedUrl(bucketName, objectName, expiration);
System.out.println(url);
} catch (OSSException oe) {
System.out.println("Caught an OSSException, which means your request made it to OSS, "
+ "but was rejected with an error response for some reason.");
System.out.println("Error Message:" + oe.getErrorMessage());
System.out.println("Error Code:" + oe.getErrorCode());
System.out.println("Request ID:" + oe.getRequestId());
System.out.println("Host ID:" + oe.getHostId());
} catch (ClientException ce) {
System.out.println("Caught an ClientException, which means the client encountered "
+ "a serious internal problem while trying to communicate with OSS, "
+ "such as not being able to access the network.");
System.out.println("Error Message:" + ce.getMessage());
} finally {
if (ossClient != null) {
ossClient.shutdown();
}
}
}
}Python
For more SDK information, see Download objects using presigned URLs in Python.
import argparse
import alibabacloud_oss_v2 as oss
# Create a command-line parameter parser and describe the purpose of the script.
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="presign get object sample")
# Specify the --region parameter to indicate the region in which the bucket is located. This parameter is required.
parser.add_argument('--region', help='The region in which the bucket is located.', required=True)
# Specify the --bucket parameter to indicate the name of the bucket in which the object is stored. This parameter is required.
parser.add_argument('--bucket', help='The name of the bucket.', required=True)
# Specify the --endpoint parameter to indicate the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. This parameter is optional.
parser.add_argument('--endpoint', help='The domain names that other services can use to access OSS')
# Specify the --key parameter to indicate the name of the object. This parameter is required.
parser.add_argument('--key', help='The name of the object.', required=True)
def main():
# Parse the command-line parameters to obtain the specified values.
args = parser.parse_args()
# From the environment variables, load the authentication information required to access OSS.
credentials_provider = oss.credentials.EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider()
# Use the default configuration to create a cfg object and specify the credential provider.
cfg = oss.config.load_default()
cfg.credentials_provider = credentials_provider
# Set the region attribute of the cfg object to the region provided in the command line.
cfg.region = args.region
# If a custom endpoint is provided, update the endpoint attribute of the cfg object with the provided endpoint.
if args.endpoint is not None:
cfg.endpoint = args.endpoint
# Use the preceding settings to initialize the OSSClient instance.
client = oss.Client(cfg)
# Initiate a request to generate a presigned URL.
pre_result = client.presign(
oss.GetObjectRequest(
bucket=args.bucket, # Specify the bucket name.
key=args.key, # Specify the object key.
)
)
# Display the HTTP method, expiration time, and presigned URL.
print(f'method: {pre_result.method},'
f' expiration: {pre_result.expiration.strftime("%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%S.000Z")},'
f' url: {pre_result.url}'
)
# Display the signed headers.
for key, value in pre_result.signed_headers.items():
print(f'signed headers key: {key}, signed headers value: {value}')
# Call the main function to start the processing logic when the script is directly run.
if __name__ == "__main__":
main() # Specify the entry point of the script. The control flow starts here.Go
For more SDK information, see Download objects using presigned URLs in Go.
package main
import (
"context"
"flag"
"log"
"time"
"github.com/aliyun/alibabacloud-oss-go-sdk-v2/oss"
"github.com/aliyun/alibabacloud-oss-go-sdk-v2/oss/credentials"
)
// Specify the global variables.
var (
region: string; // The region in which the bucket is located.
bucketName string // The name of the bucket.
objectName string // The name of the object.
)
// Specify the init function used to initialize command line parameters.
func init() {
flag.StringVar(®ion, "region", "", "The region in which the bucket is located.")
flag.StringVar(&bucketName, "bucket", "", "The name of the bucket.")
flag.StringVar(&objectName, "object", "", "The name of the object.")
}
func main() {
// Parse command line parameters.
flag.Parse()
// Check whether the bucket name is empty.
if len(bucketName) == 0 {
flag.PrintDefaults()
log.Fatalf("invalid parameters, bucket name required")
}
// Check whether the region is empty.
if len(region) == 0 {
flag.PrintDefaults()
log.Fatalf("invalid parameters, region required")
}
// Check whether the object name is empty.
if len(objectName) == 0 {
flag.PrintDefaults()
log.Fatalf("invalid parameters, object name required")
}
// Load the default configurations and specify the credential provider and region.
cfg := oss.LoadDefaultConfig().
WithCredentialsProvider(credentials.NewEnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider()).
WithRegion(region)
// Create an OSS client.
client := oss.NewClient(cfg)
// Generate a presigned URL for the GetObject request.
result, err := client.Presign(context.TODO(), &oss.GetObjectRequest{
Bucket: oss.Ptr(bucketName),
Key: oss.Ptr(objectName),
},
oss.PresignExpires(10*time.Minute),
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to get object presign %v", err)
}
log.Printf("request method:%v\n", result.Method)
log.Printf("request expiration:%v\n", result.Expiration)
log.Printf("request url:%v\n", result.URL)
if len(result.SignedHeaders) > 0 {
// If you specify request headers when you generate a presigned URL that allows HTTP GET requests, make sure that the request headers are included in the GET request initiated by using the presigned URL. This prevents request failures and signature errors.
log.Printf("signed headers:\n")
for k, v := range result.SignedHeaders {
log.Printf("%v: %v\n", k, v)
}
}
}
Node.js
For more SDK information, see Download objects using presigned URLs in Node.js.
const OSS = require("ali-oss");
// Specify a function used to generate a presigned URL.
async function generateSignatureUrl(fileName) {
// Obtain the presigned URL.
const client = await new OSS({
// Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
accessKeyId: process.env.OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID,
accessKeySecret: process.env.OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET,
bucket: 'examplebucket',
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if your bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to oss-cn-hangzhou.
region: 'oss-cn-hangzhou',
// Set secure to true and use HTTPS to prevent the generated download link from being blocked by the browser.
secure: true,
authorizationV4: true
});
return await client.signatureUrlV4('GET', 3600, {
headers: {} // Specify the request headers based on the actual request headers.
}, fileName);
}
// Call the function and pass in the name of the object.
generateSignatureUrl('yourFileName').then(url => {
console.log('Generated Signature URL:', url);
}).catch(err => {
console.error('Error generating signature URL:', err);
});PHP
For more SDK information, see Download objects using presigned URLs in PHP.
<?php
// Include the autoload file to ensure that dependency libraries are correctly loaded.
require_once __DIR__ . '/../vendor/autoload.php';
use AlibabaCloud\Oss\V2 as Oss;
// Define the descriptions of command-line parameters.
$optsdesc = [
"region" => ['help' => 'The region in which the bucket is located.', 'required' => True], // (Required) The region in which the bucket is located.
"endpoint" => ['help' => 'The domain names that other services can use to access OSS.', 'required' => False], // (Optional) The endpoint.
"bucket" => ['help' => 'The name of the bucket', 'required' => True], // (Required) The name of the bucket.
"key" => ['help' => 'The name of the object', 'required' => True], // (Required) The name of the object.
];
// Convert the parameter descriptions to the long options format required by getopt.
// Add a colon (:) after each parameter to indicate that a value is required.
$longopts = \array_map(function ($key) {
return "$key:";
}, array_keys($optsdesc));
// Parse the command-line arguments.
$options = getopt("", $longopts);
// Verify that all required parameters are provided.
foreach ($optsdesc as $key => $value) {
if ($value['required'] === True && empty($options[$key])) {
$help = $value['help']; // Obtain the help information for the parameter.
echo "Error: the following arguments are required: --$key, $help" . PHP_EOL;
exit(1); // If a required parameter is not provided, exit the program.
}
}
// Extract values from the parsed parameters.
$region = $options["region"]; // The region in which the bucket is located.
$bucket = $options["bucket"]; // The name of the bucket.
$key = $options["key"]; // The name of the object.
// Load the access credential from the environment variable.
// Use EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider to read the Access Key ID and Access Key Secret from environment variables.
$credentialsProvider = new Oss\Credentials\EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider();
// Use the default configurations of the SDK.
$cfg = Oss\Config::loadDefault();
$cfg->setCredentialsProvider($credentialsProvider); // Set the credential provider.
$cfg->setRegion($region); // Set the region in which the bucket is located.
if (isset($options["endpoint"])) {
$cfg->setEndpoint($options["endpoint"]); // If an endpoint is provided, set the endpoint.
}
// Create an OSS client instance.
$client = new Oss\Client($cfg);
// Create a GetObjectRequest object to download an object.
$request = new Oss\Models\GetObjectRequest(bucket:$bucket, key:$key);
// Call the presign method to generate a signed URL.
$result = $client->presign($request);
// Print the presign result.
// Output the signed URL. Users can use this URL to perform download operations.
print(
'get object presign result:' . var_export($result, true) . PHP_EOL . // The details of the presign result.
'get object url:' . $result->url . PHP_EOL // The signed URL, which is used to directly download the object.
);
.NET
For more SDK information, see Download objects using presigned URLs in .NET.
using Aliyun.OSS;
using Aliyun.OSS.Common;
// Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com.
var endpoint = "https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com";
// Obtain a credential from the environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
var accessKeyId = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID");
var accessKeySecret = Environment.GetEnvironmentVariable("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET");
// Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket.
var bucketName = "examplebucket";
// Specify the full path of the object. The full path cannot contain the bucket name. Example: exampledir/exampleobject.txt.
var objectName = "exampledir/exampleobject.txt";
// Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou.
const string region = "cn-hangzhou";
// Create a ClientConfiguration instance and modify the default parameters based on your requirements.
var conf = new ClientConfiguration();
// Specify the V4 signature.
conf.SignatureVersion = SignatureVersion.V4;
// Create an OSSClient instance.
var client = new OssClient(endpoint, accessKeyId, accessKeySecret, conf);
client.SetRegion(region);
try
{
var metadata = client.GetObjectMetadata(bucketName, objectName);
var etag = metadata.ETag;
// Generate a presigned URL.
var req = new GeneratePresignedUriRequest(bucketName, objectName, SignHttpMethod.Get)
{
// Set the validity period of the presigned URL. Default value: 3600. Unit: seconds.
Expiration = DateTime.UtcNow.AddHours(1),
};
var uri = client.GeneratePresignedUri(req);
// Print the generated presigned URL
Console.WriteLine("Generated Signed URL: " + uri);
}
catch (OssException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed with error code: {0}; Error info: {1}. \nRequestID:{2}\tHostID:{3}",
ex.ErrorCode, ex.Message, ex.RequestId, ex.HostId);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Failed with error info: {0}", ex.Message);
}Android
For more SDK information, see Download objects using presigned URLs in Android.
// Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket.
String bucketName = "examplebucket";
// Specify the full path of the source object. Do not include the bucket name in the full path. Example: exampleobject.txt.
String objectKey = "exampleobject.txt";
String url = null;
try {
// Generate a presigned URL to download the object.
GeneratePresignedUrlRequest request = new GeneratePresignedUrlRequest(bucketName, objectKey);
// Set the validity period of the presigned URL to 30 minutes.
request.setExpiration(30*60);
request.setMethod(HttpMethod.GET);
url = oss.presignConstrainedObjectURL(request);
Log.d("url", url);
} catch (ClientException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}iOS
For more SDK information, see Download objects using presigned URLs in iOS.
// Specify the name of the bucket.
NSString *bucketName = @"examplebucket";
// Specify the name of the object.
NSString *objectKey = @"exampleobject.txt";
__block NSString *urlString;
// Generate a presigned URL with a validity period for downloading the object. In this example, the validity period of the URL is 30 minutes.
OSSTask *task = [client presignConstrainURLWithBucketName:bucketName
withObjectKey:objectKey
httpMethod:@"GET"
withExpirationInterval:30 * 60
withParameters:@{}];
[task continueWithBlock:^id _Nullable(OSSTask * _Nonnull task) {
if (task.error) {
NSLog(@"presign error: %@", task.error);
} else {
urlString = task.result;
NSLog(@"url: %@", urlString);
}
return nil;
}];C++
For more SDK information, see Download objects using presigned URLs in C++.
#include <alibabacloud/oss/OssClient.h>
using namespace AlibabaCloud::OSS;
int main(void)
{
/* Initialize information about the account that is used to access OSS. */
/* Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com. */
std::string Endpoint = "yourEndpoint";
/* Specify the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the region to cn-hangzhou. * /
std::string Region = "yourRegion";
/* Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket. */
std::string BucketName = "examplebucket";
/* Specify the full path of the object. Do not include the bucket name in the full path. Example: exampledir/exampleobject.txt. */
std::string GetobjectUrlName = "exampledir/exampleobject.txt";
/* Initialize resources, such as network resources. */
InitializeSdk();
ClientConfiguration conf;
conf.signatureVersion = SignatureVersionType::V4;
/* Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured. */
auto credentialsProvider = std::make_shared<EnvironmentVariableCredentialsProvider>();
OssClient client(Endpoint, credentialsProvider, conf);
client.SetRegion(Region);
/* Specify the validity period of the pre-signed URL. The maximum validity period is 32,400. Unit: seconds. */
std::time_t t = std::time(nullptr) + 1200;
/* Generate a pre-signed URL. */
auto genOutcome = client.GeneratePresignedUrl(BucketName, GetobjectUrlName, t, Http::Get);
if (genOutcome.isSuccess()) {
std::cout << "GeneratePresignedUrl success, Gen url:" << genOutcome.result().c_str() << std::endl;
}
else {
/* Handle exceptions. */
std::cout << "GeneratePresignedUrl fail" <<
",code:" << genOutcome.error().Code() <<
",message:" << genOutcome.error().Message() <<
",requestId:" << genOutcome.error().RequestId() << std::endl;
return -1;
}
/* Release resources, such as network resources. */
ShutdownSdk();
return 0;
}Ruby
For more SDK information, see Download objects using presigned URLs in Ruby.
require 'aliyun/oss'
client = Aliyun::OSS::Client.new(
# In this example, the endpoint of the China (Hangzhou) region is used. Specify your actual endpoint.
endpoint: 'https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com',
# Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured.
access_key_id: ENV['OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID'],
access_key_secret: ENV['OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET']
)
# Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket.
bucket = client.get_bucket('examplebucket')
# Generate a presigned URL that is used to download the object and set its validity period to 3,600 seconds.
puts bucket.object_url('my-object', true, 3600)C
For more SDK information, see Download objects using presigned URLs in C.
#include "oss_api.h"
#include "aos_http_io.h"
/* Specify the endpoint of the region in which the bucket is located. For example, if the bucket is located in the China (Hangzhou) region, set the endpoint to https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com. */
const char *endpoint = "yourEndpoint";
/* Specify the name of the bucket. Example: examplebucket. */
const char *bucket_name = "examplebucket";
/* Specify the full path of the object. Do not include the bucket name in the full path. Example: exampledir/exampleobject.txt. */
const char *object_name = "exampledir/exampleobject.txt";
/* Specify the full path of the local file. */
const char *local_filename = "yourLocalFilename";
void init_options(oss_request_options_t *options)
{
options->config = oss_config_create(options->pool);
/* Use a char* string to initialize aos_string_t. */
aos_str_set(&options->config->endpoint, endpoint);
/* Obtain access credentials from environment variables. Before you run the sample code, make sure that the OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET environment variables are configured. */
aos_str_set(&options->config->access_key_id, getenv("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_ID"));
aos_str_set(&options->config->access_key_secret, getenv("OSS_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET"));
/* Specify whether to use CNAME. The value 0 indicates that CNAME is not used. */
options->config->is_cname = 0;
/* Configure network parameters, such as the timeout period. */
options->ctl = aos_http_controller_create(options->pool, 0);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
/* Call the aos_http_io_initialize method in main() to initialize global resources, such as network and memory resources. */
if (aos_http_io_initialize(NULL, 0) != AOSE_OK) {
exit(1);
}
/* Create a memory pool to manage memory. aos_pool_t is equivalent to apr_pool_t. The code that is used to create a memory pool is included in the APR library. */
aos_pool_t *pool;
/* Create a memory pool. The value of the second parameter is NULL. This value specifies that the pool does not inherit other memory pools. */
aos_pool_create(&pool, NULL);
/* Create and initialize options. This parameter includes global configuration information, such as endpoint, access_key_id, access_key_secret, is_cname, and curl. */
oss_request_options_t *oss_client_options;
/* Allocate memory resources in the memory pool to the options. */
oss_client_options = oss_request_options_create(pool);
/* Initialize oss_client_options. */
init_options(oss_client_options);
/* Initialize the parameters. */
aos_string_t bucket;
aos_string_t object;
aos_string_t file;
aos_http_request_t *req;
apr_time_t now;
char *url_str;
aos_string_t url;
int64_t expire_time;
int one_hour = 3600;
aos_str_set(&bucket, bucket_name);
aos_str_set(&object, object_name);
aos_str_set(&file, local_filename);
expire_time = now / 1000000 + one_hour;
req = aos_http_request_create(pool);
req->method = HTTP_GET;
now = apr_time_now();
/* Specify the validity period. Unit: microseconds * /
expire_time = now / 1000000 + one_hour;
/* Generate a presigned URL. */
url_str = oss_gen_signed_url(oss_client_options, &bucket, &object, expire_time, req);
aos_str_set(&url, url_str);
printf("Temporary download URL: %s\n", url_str);
/* Release the memory pool. This operation releases memory resources allocated for the request. */
aos_pool_destroy(pool);
/* Release the allocated global resources. */
aos_http_io_deinitialize();
return 0;
}Using the command line tool ossutil
Generate a presigned URL with a validity period of 1 hour for the example.txt object in the examplebucket bucket.
ossutil presign oss://examplebucket/example.txt --expires-duration 1hFor more examples of generating presigned URLs using ossutil, see presign (Generate a presigned URL).
Using the graphical management tool ossbrowser
ossbrowser supports object-level operations similar to those supported by the console. Follow the ossbrowser interface guide to complete the operation of obtaining a presigned URL. For more information about how to use ossbrowser, see Common operations.
Get long-term valid links
You can obtain file URLs (links) without signatures and expiration time limits through the following two methods.
Method 1: Set the file to public-read (not recommended)
Set the file ACL to "public-read" to obtain a permanently valid file URL. This configuration is simple and requires no additional tools. However, the file address is completely public, accessible by anyone, and vulnerable to malicious crawlers or traffic abuse. We recommend using this method with OSS hotlink protection (Referer whitelist), but there is still a risk of exposing the source.
Method 2: Provide public-read access through CDN (recommended)
Keep the file private and implement public access through CDN. After enabling the private OSS bucket back-to-origin feature for CDN, you can access all resources in the private bucket through the CDN-accelerated domain name. The private authentication method of the original URL will become invalid. Compared with Method 1, OSS is not directly exposed, providing higher security and supporting acceleration and access control features. We recommend enabling CDN's Referer hotlink protection and URL signing to prevent link abuse.
How to construct long-term valid file URLs
You can construct file access addresses based on the domain name type.
Domain name type | URL format | Example |
OSS default domain name |
| For example, in a bucket named examplebucket in the China (Hangzhou) region, there is a folder named example containing a file named example.jpg.
|
Custom domain name |
| For example, if you have attached a custom domain name |
CDN-accelerated domain name |
| For example, when the CDN-accelerated domain name is |
<BucketName>: The name of the bucket.<ObjectName>: The full path of the file (such asfolder/example.jpg).<Endpoint>: The endpoint of the region.<YourDomainName>: Your custom domain name. For more information, see Attach custom domain names to bucket default domain names.<CDN accelerated domain name>: Your CDN-accelerated domain name.
Configure HTTPS protocol
The link protocol is determined by the endpoint. The default endpoint requires no configuration and directly supports HTTPS. When using a custom domain name, you must first complete certificate hosting before you can enable the HTTPS protocol.
OSS console: When generating a link, you can select the protocol in the details panel. HTTPS is the default protocol.
ossutil/SDK: This depends on the endpoint you set. If it begins with
https://, HTTPS is used.
Garbled Chinese text when previewing .txt files
When previewing .txt files in a browser or OSS console, if Chinese characters appear as garbled text, it is usually because the file does not declare the correct encoding format. You can set the Content-Type field in the file metadata to text/plain;charset=utf-8, which forces the browser to display the content using the correct UTF-8 encoding.
Log on to the OSS Management Console.
Click Bucket List, and then click the name of the target bucket.
In the navigation pane on the left, choose .
To the right of the target object, choose .
In the HTTP Standard Properties area, set Content-Type to text/plain;charset=utf-8.
Click OK to save the settings.
Restrict access sources
Through configuring Referer hotlink protection, you can allow only specified websites to access OSS resources and reject requests from other sources.
For example, you can allow only access requests from your official website https://example.com, and requests from other sources will be denied.
Authorize third parties for more operations
In addition to signed URLs, Alibaba Cloud provides a more flexible temporary authorization method—STS temporary access credentials. If you want third parties to perform operations on OSS beyond downloading, such as listing and copying, we recommend that you learn about and use STS temporary access credentials. For more information, see Access OSS with STS temporary access credentials.
Process images
You can generate a presigned URL with image processing parameters to process images, such as resizing images and adding watermarks.