You can use canary release of frontend applications with monitoring and rollback policies to create a powerful mechanism that ensures system stability. The coordination of the three policies can help maintain high performance and high stability of frontend applications along with continuous iterations and updates of the applications. This topic describes how to configure a Microservices Engine (MSE) cloud-native gateway to implement a canary release on frontend applications.
Implement an end-to-end canary release
In microservices scenarios, calls among applications are random. If a new version is available for the Spring Cloud application or Dubbo application that you deploy, traffic that has specified characteristics may not be routed to the new version of the application. To implement an end-to-end canary release, you can use the canary release of frontend applications together with the end-to-end canary release based on cloud-native gateways provided by MSE.
Each request from a frontend user passes through a cloud-native gateway. After a request is authenticated by the permission system, its cookie includes a unique user identifier, such as userid: 001.
The gateway has a frontend-gray plugin attached. The plugin maps and forwards canary traffic based on configured plugin rules.
Prerequisites
A Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) managed cluster is created. For more information, see Create an ACK managed cluster.
An MSE cloud-native gateway is created. For more information, see Create an MSE cloud-native gateway.
Implement a canary release on frontend applications using MSE Ingress gateways
Install MSE Ingress Controller, and use an MSE Ingress gateway to access the ACK cluster. For more information, see Use MSE Ingress gateways to access services in ACK clusters and ACS clusters.
Step 1: Deploy applications in the ACK cluster
For more information about how to deploy an application, see Create a stateless application using a Deployment.
Step 2: Configure the canary release plug-in in the MSE console
Log on to the MSE console. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Cloud-native Gateway > Gateways. On the Gateways page, click the ID of the gateway.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Plug-in Marketplace.
On the Plug-in Marketplace page, search for the
frontend-graykeyword and click thefrontend-grayplugin card.Click the Plug-in Configuration tab, choose Domain-level plug-in rules, and then click Add Rule. In the Add Rule panel, configure the following rule. For more information about the configuration, see Configure rules.
grayKey: userid rules: - name: beta-user grayKeyValue: - "00000002" - "00000003" baseDeployment: version: base grayDeployments: - name: beta-user version: gray enabled: true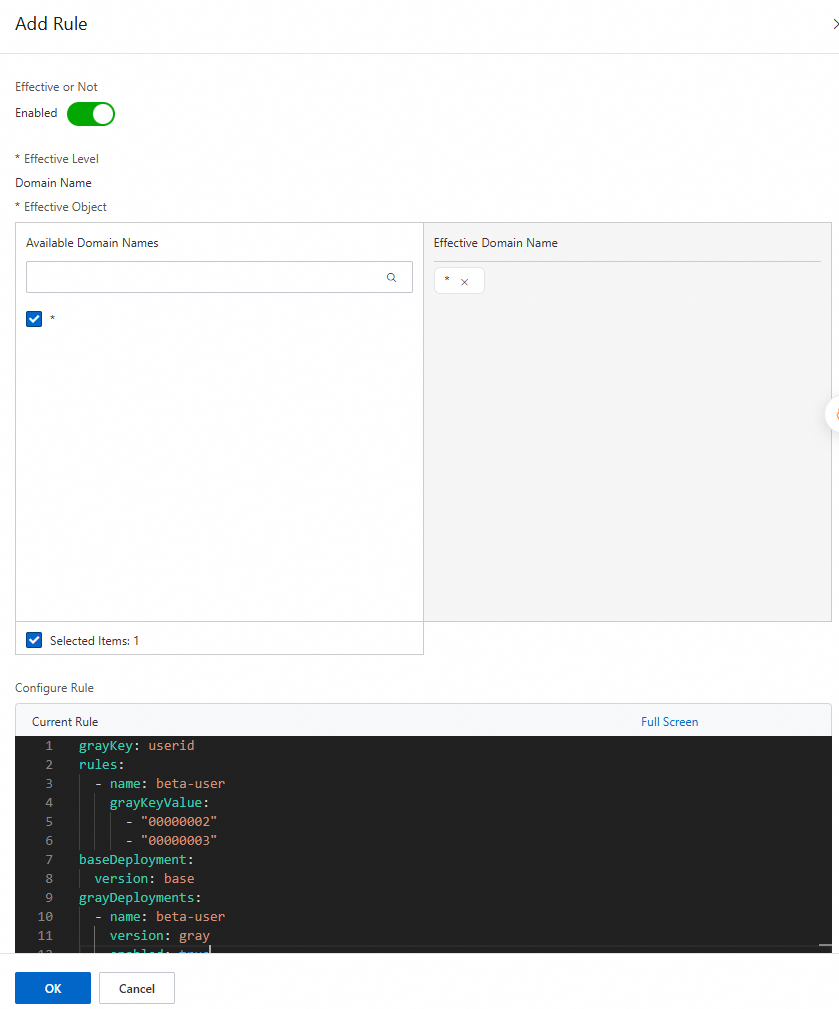
Step 3: Verify the result
Log on to the ACK console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Clusters. On the Clusters page, click the cluster that you created. On the cluster details page, choose Network > Ingresses from the navigation pane on the left to view the public endpoint.

Access the public endpoint
nlb-qv04p*******cn-hangzhou.nlb.aliyuncsslb.com, log on using theadmin/iceaccount, and access the base version. The user ID is 00000001.Access the public endpoint
nlb-qv04p*******cn-hangzhou.nlb.aliyuncsslb.com, log on as the regular user using theuser/iceaccount to access the canary release version, and verify that the user ID is 00000002.
Implement a canary release on frontend applications using ACK clusters
Step 1: Deploy applications in the ACK cluster
For more information about how to deploy an application, see Create a stateless application using a Deployment.
Step 2: Configure the canary release plug-in in the MSE console
Log on to the MSE console. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Cloud-native Gateway > Gateways. On the Gateways page, click the ID of the gateway.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Plug-in Marketplace.
On the Plug-in Marketplace page, search for the
frontend-graykeyword and click thefrontend-grayplugin card.Click the Plug-in Configuration tab, choose Domain-level plug-in rules, and then click Add Rule. In the Add Rule panel, configure the following rule. For more information about the configuration, see Configure rules.
grayKey: userid rules: - name: beta-user grayKeyValue: - "00000002" - "00000003" baseDeployment: version: base grayDeployments: - name: beta-user version: gray enabled: true
Step 3: Add a service source for the gateway
Log on to the MSE console. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Cloud-native Gateway > Gateways. On the Gateways page, click the ID of the gateway.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Routes. Then, click the Source tab.
Click Add Source. In the Add Source panel, select Container Service for Source Type, select the cluster that you created from the ACK/ASK/ACS Cluster drop-down list, and then click OK.
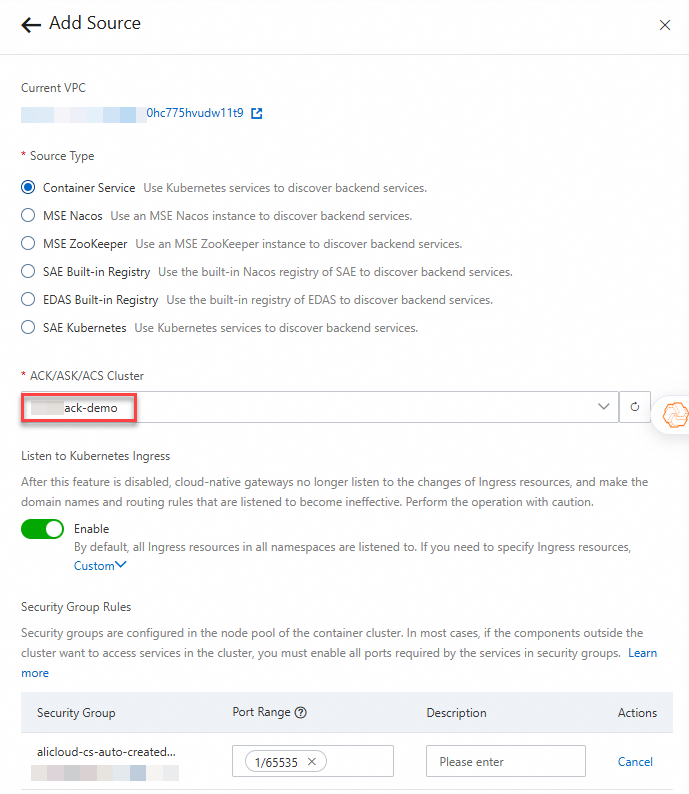
Step 4: Add a service
Log on to the MSE console. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Cloud-native Gateway > Gateways.
On the Gateways page, click the ID of the gateway.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Routes. Then, click the Services tab.
Click Add Service. In the Add Service panel, configure the parameters, and click OK.

Step 5: Add a base route
Log on to the MSE console. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Cloud-native Gateway > Gateways. On the Gateways page, click the ID of the gateway.
In the left-side navigation pane, click the Routes tab. On the Routes tab, click Add Route.
On the Add Route page, configure the parameters, and click Save and Advertise.

Step 6: Add a canary route
Log on to the MSE console. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Cloud-native Gateway > Gateways. On the Gateways page, click the ID of the gateway.
In the left-side navigation pane, click the Routes tab. On the Routes tab, click Add Route.
On the Add Route page, configure the parameters, and click Save and Advertise.
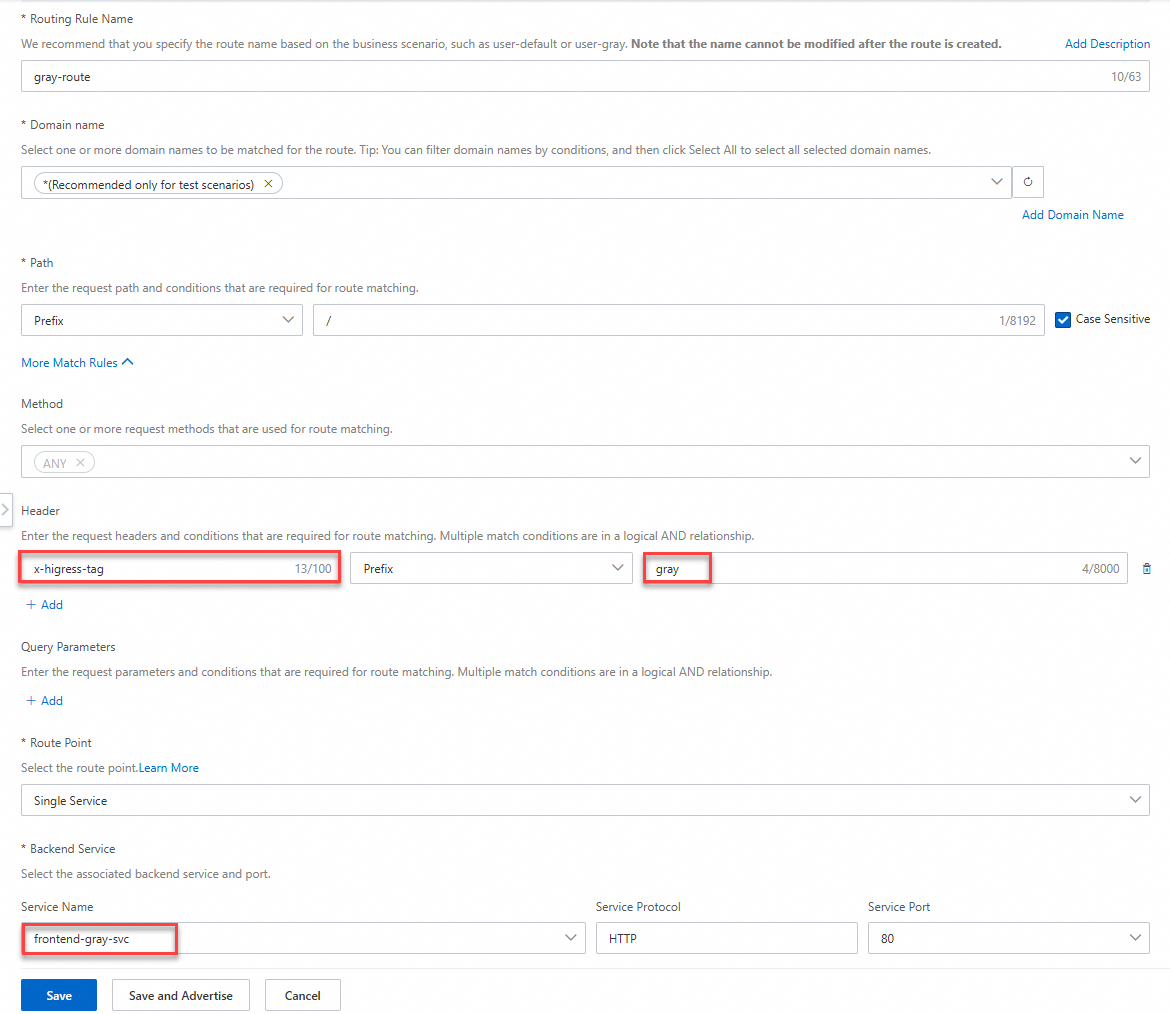 Note
Notegrayindicates the canary release version, which corresponds tograyDeployments.versionin the configuration of thefrontend-grayplugin.
Step 7: Verify the result
Log on to the MSE console. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Cloud-native Gateway > Gateways. On the Gateways page, click the ID of the gateway.
On the Overview page, click the Endpoint tab to view the public endpoint.
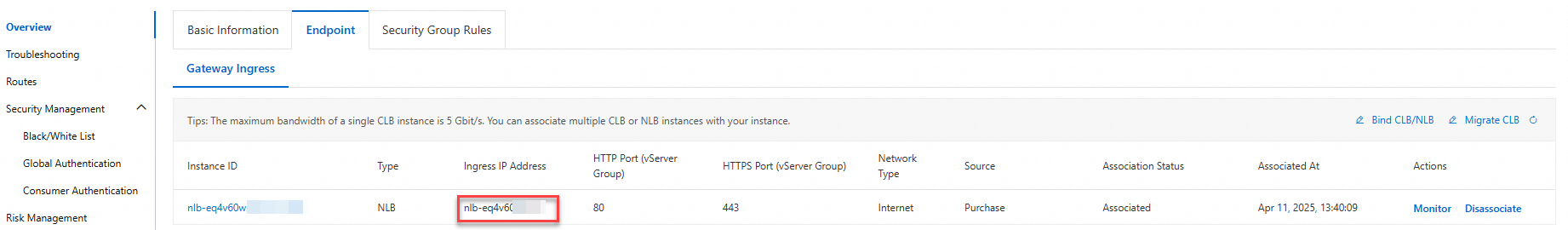
Access the public endpoint
nlb-qv04p*******cn-hangzhou.nlb.aliyuncsslb.com, log on using theadmin/iceaccount to access the base version, and verify that the user ID is 00000001.Access the public endpoint
nlb-qv04p*******cn-hangzhou.nlb.aliyuncsslb.com, log on as the regular user using theuser/iceaccount to access the canary release version, and verify that the user ID is 00000002.
Implement a canary release on frontend applications using ECS instances
Step 1: Deploy two frontend application versions on an ECS instance
Endpoint of the baseline application:
120.***.137.243:80Endpoint of the canary application version:
120.***.137.243:8081
Step 2: Add a service
Log on to the MSE console. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Cloud-native Gateway > Gateways.
On the Gateways page, click the ID of the gateway.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Routes. Then, click the Services tab.
Click Add Service. In the Add Service panel, select Fixed Address from the Service Source drop-down list, configure the parameters, and then click OK.
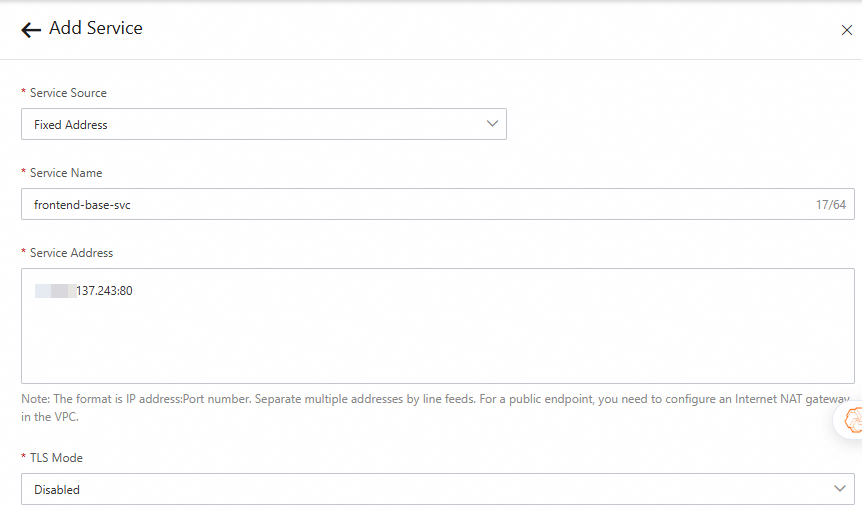
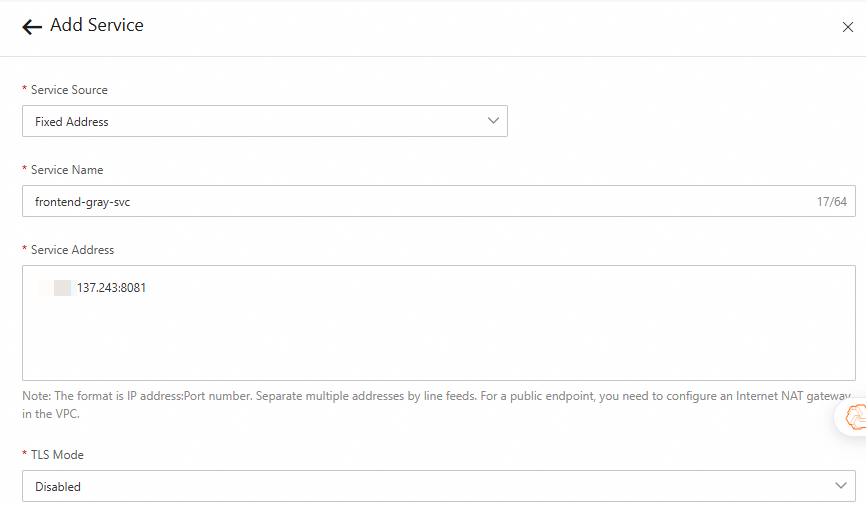
Step 3: Add a base route
Log on to the MSE console. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Cloud-native Gateway > Gateways.
On the Gateways page, click the ID of the gateway.
In the left-side navigation pane, click the Routes tab. On the Routes tab, click Add Route.
On the Add Route page, configure the parameters, and click Save and Advertise.

Step 4: Add a canary route
Log on to the MSE console. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Cloud-native Gateway > Gateways.
On the Gateways page, click the ID of the gateway.
In the left-side navigation pane, click the Routes tab. On the Routes tab, click Add Route.
On the Add Route page, configure the parameters, and click Save and Advertise.
Notegrayindicates the canary version, which corresponds tograyDeployments.versionin the configuration of thefrontend-grayplug-in.
Step 5: Configure the frontend-gray plug-in in the MSE console
Log on to the MSE console. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Cloud-native Gateway > Gateways.
On the Gateways page, click the ID of the gateway.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Plug-in Marketplace.
On the Plug-in Marketplace page, search for the
frontend-graykeyword and click thefrontend-grayplugin card.Click the Plug-in Configuration tab, choose Domain-level plug-in rules, and then click Add Rule. In the Add Rule panel, configure the following rule. For more information about the configuration, see Configure rules.
grayKey: userid rules: - name: beta-user grayKeyValue: - "00000002" - "00000003" baseDeployment: version: base grayDeployments: - name: beta-user version: gray enabled: true
Step 6: Verify the result
Log on to the MSE console. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Cloud-native Gateway > Gateways. On the Gateways page, click the ID of the gateway.
On the Overview page, click the Endpoint tab to view the public endpoint.

Access the public endpoint
nlb-qv04p*******cn-hangzhou.nlb.aliyuncsslb.com, log on using theadmin/iceaccount to access the base version, and verify that the user ID is 00000001.Access the public endpoint
nlb-qv04p*******cn-hangzhou.nlb.aliyuncsslb.com, log on as the regular user using theuser/iceaccount to access the canary release version, and verify that the user ID is 00000002.
Implement a canary release on frontend applications using CDN or OSS
Step 1: Prepare an OSS file
Step 2: Add a service
Log on to the MSE console. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Cloud-native Gateway > Gateways.
On the Gateways page, click the ID of the gateway.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Routes. Then, click the Services tab.
Click Add Service. In the Add Service panel, select DNS Domain Name from the Service Source drop-down list, enter the endpoints of OSS, and then click OK.
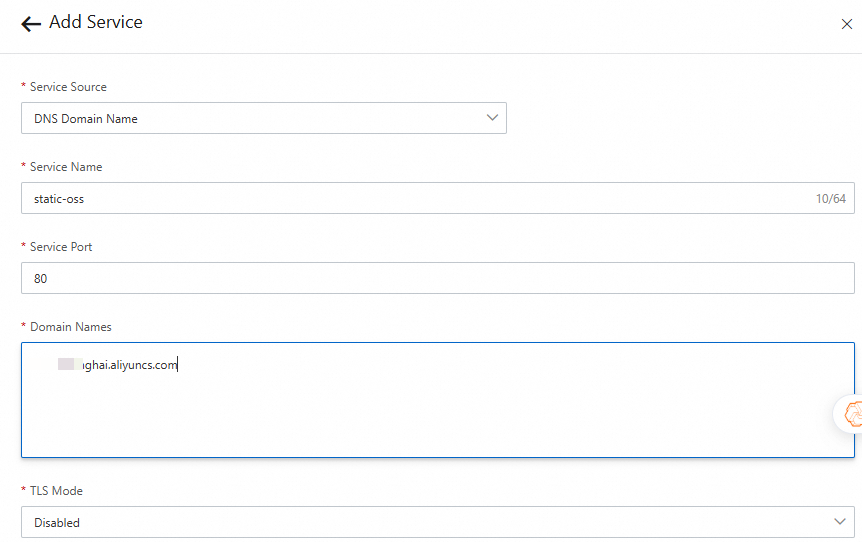 Important
ImportantIf OSS and the gateway are deployed in the same region, we recommend that you enter the internal endpoints of OSS. If OSS and the gateway are not deployed in the same region, enter the public endpoints.
Step 3: Add a route
Log on to the MSE console. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Cloud-native Gateway > Gateways.
On the Gateways page, click the ID of the gateway.
In the left-side navigation pane, click the Routes tab. On the Routes tab, click Add Route.
On the Add Route page, configure the parameters, and click Save and Advertise.

Step 4: Configure the frontend-gray plug-in in the MSE console
Log on to the MSE console. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Cloud-native Gateway > Gateways.
On the Gateways page, click the ID of the gateway.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Plug-in Marketplace.
On the Plug-in Marketplace page, search for the
frontend-graykeyword and click thefrontend-grayplugin card.On the page that appears, click the Plug-in Configuration tab, select Domain-level plug-in rules in the Rule Levels section, and then click Add Rule. In the Add Rule panel, configure the following rule. For configuration details, see Configure rules.
grayKey: userid rules: - name: beta-user grayKeyValue: - "00000002" - "00000003" rewrite: host: xx.oss-cn-shanghai.aliyuncs.com ## OSS endpoint indexRouting: "/app1": "/project-a/app1/{version}/index.html" # Path rewrite of the HTML home page fileRouting: "/app1": "/project-a/app1/{version}" # Path rewrite of resources such as CSS properties, JavaScript scripts, and images baseDeployment: version: dev grayDeployments: - name: beta-user version: 0.0.1 enabled: true
Step 5: Verify the result
Log on to the MSE console. In the top navigation bar, select a region.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Cloud-native Gateway > Gateways. On the Gateways page, click the ID of the gateway.
On the Overview page, click the Endpoint tab to view the public endpoint.

Access the public endpoint
nlb-qv04p*******cn-hangzhou.nlb.aliyuncsslb.com, log on using theadmin/iceaccount to access the base version, and verify that the user ID is 00000001.Access the public endpoint
nlb-qv04p*******cn-hangzhou.nlb.aliyuncsslb.com, log on as the regular user using theuser/iceaccount to access the canary release version, and verify that the user ID is 00000002.
FAQ
Can I configure rewrite policies and canary releases on frontend applications at the same time?
If the service source is not CDN or OSS, you can configure canary releases of frontend applications and rewrite policies at the same time and make them take effect.
If the service source is CDN or OSS, you cannot configure canary releases of frontend applications and rewrite policies at the same time. This is because the relevant rewrite policies are already implemented in the frontend-gray plug-in. If you configure a rewrite policy, conflicts may occur. As a result, errors such as the status code 403 are returned.
Can I inject some global variables into the HTML home page?
Inject some global JavaScript scripts into the <head> tag (usually properties such as CSS styles) of the HTML page, or into the first and last positions of the <body> tag of the HTML page.
Use injection to inject code into the HTML home page. You can inject code into the <head> tag, or into the first and last positions of the <body> tag.
grayKey: userid
rules:
- name: inner-user
grayKeyValue:
- '00000001'
- '00000005'
baseDeployment:
version: base
grayDeployments:
- name: beta-user
version: gray
enabled: true
weight: 80
injection:
head:
- <script>console.log('Header')</script>
body:
first:
- <script>console.log('hello world before')</script>
- <script>console.log('hello world before1')</script>
last:
- <script>console.log('hello world after')</script>
- <script>console.log('hello world after2')</script>When does a canary version take effect?
Suppose User A's current frontend version is 0.0.1 and you publish a new frontend version, 0.0.2. If User A hits a canary release rule, does the new version take effect immediately?
This is due to the following reasons:
If the canary version needs to take effect in real time, the backend needs to dynamically control the version. Frontend release cannot decouple from backend release. CDN acceleration cannot be performed because page stability strongly depends on the interface.
If the canary version takes effect in real time, when customers use a specific feature, a button in use may become unavailable at any time. This results in poor user experience.
When can I refresh a page?
In most cases, you need to re-log on to a website after a session times out.
You can log on to the application on the logon page.
When you log on to a page, refresh the page to obtain the latest canary release information. The following code shows an example for frontend application logon.
async function handleLogin(values: LoginParams) {
try {
const result = await login(values);
if (result.success) {
message.success ('Logon succeeded. ');
await updateUserInfo();
const urlParams = new URL(window.location.href).searchParams;
window.location.href = `${urlParams.get('redirect') || '/'}`;
return;
}
console.log(result);
// Configure an error message that is returned for logon failures. The following code shows a sample error message.
setLoginResult(result);
} catch (error) {
message.error('Logon failed. Try again. ');
console.log(error);
}
}