If you encounter incomplete knowledge retrieval or inaccurate content while using the retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) feature in Alibaba Cloud Model Studio, this topic offers suggestions and examples to enhance RAG performance.
1. Introduction to the RAG workflow
RAG is a technique that combines information retrieval with text generation. It allows a model to use relevant information from an external knowledge base when generating answers.
Its workflow includes several key stages, including parsing and chunking, vector storage, retrieval and recall, and answer generation.
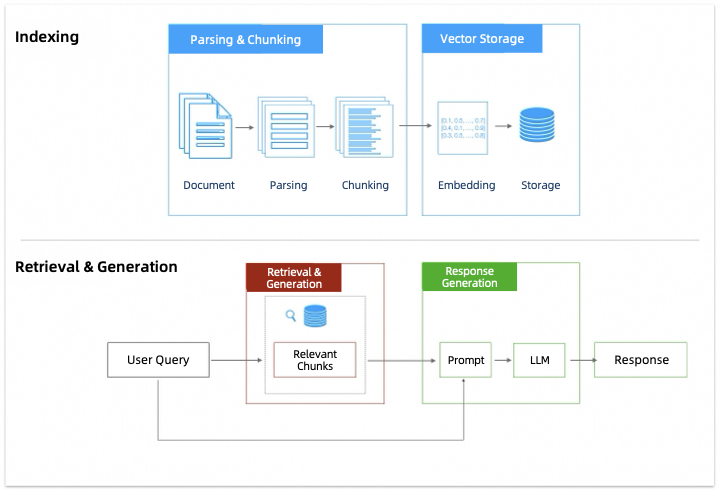
This topic discusses how to optimize RAG performance by focusing on the parsing & chunking, retrieval & recall, and answer generation stages.
2. Optimizing RAG performance
2.1 Preparations
First, ensure that the documents you import into the knowledge base meet the following requirements:
Include relevant knowledge: If the knowledge base lacks relevant information, the model will likely be unable to answer related questions. To solve this, update the knowledge base and add the necessary information.
Use Markdown format (recommended): PDF content has a complex format, and the parsing result may not be ideal. We recommend that you first convert PDFs to a text document format, such as Markdown, DOC, or DOCX. For example, you can use the DashScopeParse tool in Model Studio to convert a PDF to Markdown format, and then use a model to organize the format. This can also achieve good results. .
How should I handle illustrations in documents?
The knowledge base currently does not support parsing video or audio content in documents.
Clear content expression, reasonable structure, and no special styles: The content layout of the document also significantly affects RAG performance. For more information, see How should documents be formatted to benefit RAG?.
Match the prompt language: If user prompts are mostly in a language other than the source content, such as English, we recommend that your document content also be in that language. If necessary, for example, for professional terms in the document, you can use two or more languages.
Eliminate entity ambiguity: Standardize expressions for the same entity in the document. For example, you can standardize "ML", "Machine Learning", and "machine learning" to "machine learning".
You can input the document into a model to help you standardize it. If the document is long, you can split it into multiple parts and input them one by one.
These five preparations are the basis for ensuring the effectiveness of subsequent RAG optimization. After you complete them, you can start to understand and optimize each part of the RAG application in depth.
2.2 Parsing and chunking stage
This section introduces only the configuration items that Model Studio supports for optimization in the RAG chunking stage.
First, the documents you import into the knowledge base are parsed and chunked. The main purpose of chunking is to minimize the impact of interfering information during the subsequent vectorization process while maintaining semantic integrity. Therefore, the document chunking strategy you choose when you create a knowledge base has a significant impact on RAG performance. If the chunking method is inappropriate, it may lead to the following problems:
Text chunks are too short | Text chunks are too long | Obvious semantic truncation |
|
|
|
Chunks that are too short can have missing semantic information, leading to failed matches during retrieval. | Chunks that are too long can include irrelevant topics, causing unrelated information to be returned during recall. | Chunks with forced semantic truncation can cause content to be missing from the recall. |
Therefore, in practical applications, you should try to make the information in text chunks complete while avoiding excessive interfering information. Model Studio recommends that you perform the following actions:
When creating a knowledge base, select Smart chunking for the document chunking method.
After successfully importing the document into the knowledge base, manually check and correct the content of the text chunks.
2.2.1 Intelligent chunking
Choosing the right text chunk length for your knowledge base is not easy because you must consider multiple factors, such as:
Document type: For example, for professional literature, increasing the length usually helps to retain more contextual information. For social media posts, shortening the length can capture semantics more accurately.
Prompt complexity: Generally, if the user's prompt is complex and specific, you may need to increase the length. Otherwise, shortening the length is more appropriate.
These conclusions do not necessarily apply to all situations. You need to choose the right tools and experiment repeatedly to find the right text chunk length. For example, LlamaIndex provides evaluation functions for different chunking methods. However, this process can be difficult.
If you want to achieve good results quickly, we recommend that you select Intelligent Splitting for Document Splitting when you create a knowledge base.
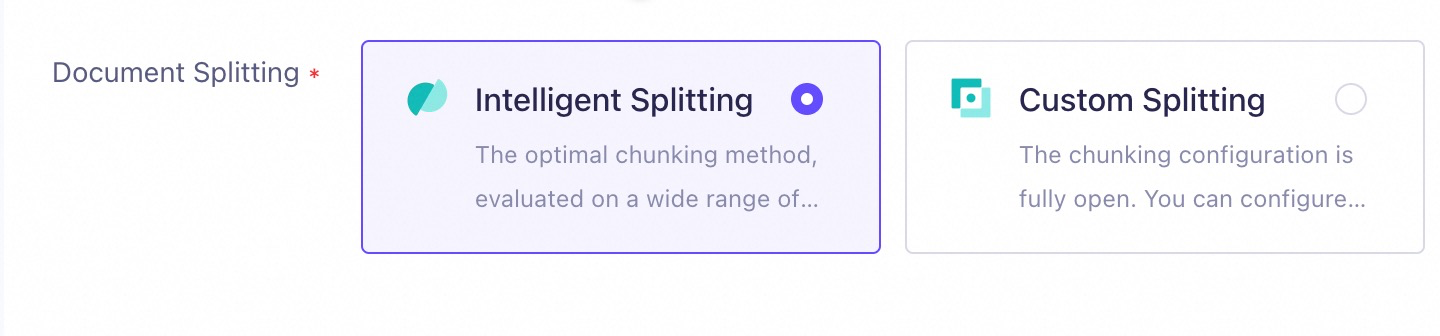
When this strategy is applied, the knowledge base performs the following steps:
First, use the system's built-in sentence delimiters to divide the document into several paragraphs.
Based on the divided paragraphs, adaptively select chunking points for chunking based on semantic relevance (semantic chunking), rather than chunking based on a fixed length.
During this process, the knowledge base strives to ensure the semantic integrity of each part of the document and tries to avoid unnecessary divisions and chunking. This strategy is applied to all documents in this knowledge base, including subsequently imported documents.
2.2.2 Correcting text chunk content
In the actual chunking process, unexpected chunking or other problems can still occur. For example, spaces in the text are sometimes parsed as %20 after chunking.

Therefore, Model Studio recommends that you perform a manual check after you import the document into the knowledge base to confirm the semantic integrity and correctness of the text chunk content. If you find unexpected chunking or other parsing errors, you can edit the text chunk directly to correct it. After you save your changes, the original content of the text chunk becomes invalid, and the new content is used for knowledge base retrieval.
Note that this action modifies only the text chunks in the knowledge base, not the original document or data table in your data management (temporary storage). Therefore, if you import it into the knowledge base again later, you must perform another manual check and correction.
2.3 Retrieval and recall stage
This section introduces only the configuration items that Model Studio supports for optimization in the retrieval and recall stage.
The main problem in the retrieval and recall stage is that it is difficult to find the text chunks that are most relevant to the prompt and contain the correct answer from the numerous text chunks in the knowledge base. This problem can be broken down into the following types:
Problem type | Improvement strategy |
In multi-round conversation scenarios, the user's prompt may be incomplete or ambiguous. | Enable multi-round conversation rewriting. The knowledge base automatically rewrites the user's prompt into a more complete form to better match the knowledge. |
The knowledge base contains documents from multiple categories. When you search in a document from Category A, the recall results include text chunks from other categories, such as Category B. | We recommend that you add tags to the documents. When the knowledge base retrieves information, it first filters relevant documents based on tags. Only document search knowledge bases support adding tags to documents. |
The knowledge base contains multiple documents with similar structures. For example, they all contain a "Function Overview" section. You want to search in the "Function Overview" section of Document A, but the recall results include information from other similar documents. | Extract metadata. The knowledge base uses metadata for a structured search before the vector search to accurately find the target document and extract relevant information. Only document search knowledge bases support creating document metadata. |
The recall results of the knowledge base are incomplete and do not include all relevant text chunks. | We recommend that you lower the similarity threshold and increase the number of recalled chunks to recall information that should have been retrieved. |
The recall results of the knowledge base contain a large amount of irrelevant text chunks. | We recommend that you increase the similarity threshold to exclude information with low similarity to the user's prompt. |
2.3.1 Multi-round conversation rewriting
In a multi-round conversation, a user might ask a question with a short prompt, such as "Bailian Phone X1". This prompt may cause the RAG system to lack the necessary context during retrieval for the following reasons:
A mobile phone product usually has multiple generations available for sale at the same time.
For the same generation of a product, the manufacturer usually offers multiple storage capacity options, such as 128 GB and 256 GB.
...
The user may have already provided this key information in previous turns of the conversation. Using this information effectively can help RAG retrieve more accurate information.
To address this situation, you can use the Multi-round Conversation Rewriting feature in Model Studio. The system automatically rewrites the user's prompt into a more complete form based on the conversation history.
For example, a user asks:
Bailian Phone X1.When the multi-round conversation rewriting feature is enabled, the system rewrites the user's prompt based on their conversation history before retrieval, as shown in the following example:
Provide all available versions of Bailian Phone X1 in the product library and their specific parameters.This rewritten prompt helps RAG better understand the user's intent and provide a more accurate response.
The figure below shows how to enable the multi-round conversation rewriting feature. This feature is also enabled when you select Recommended.
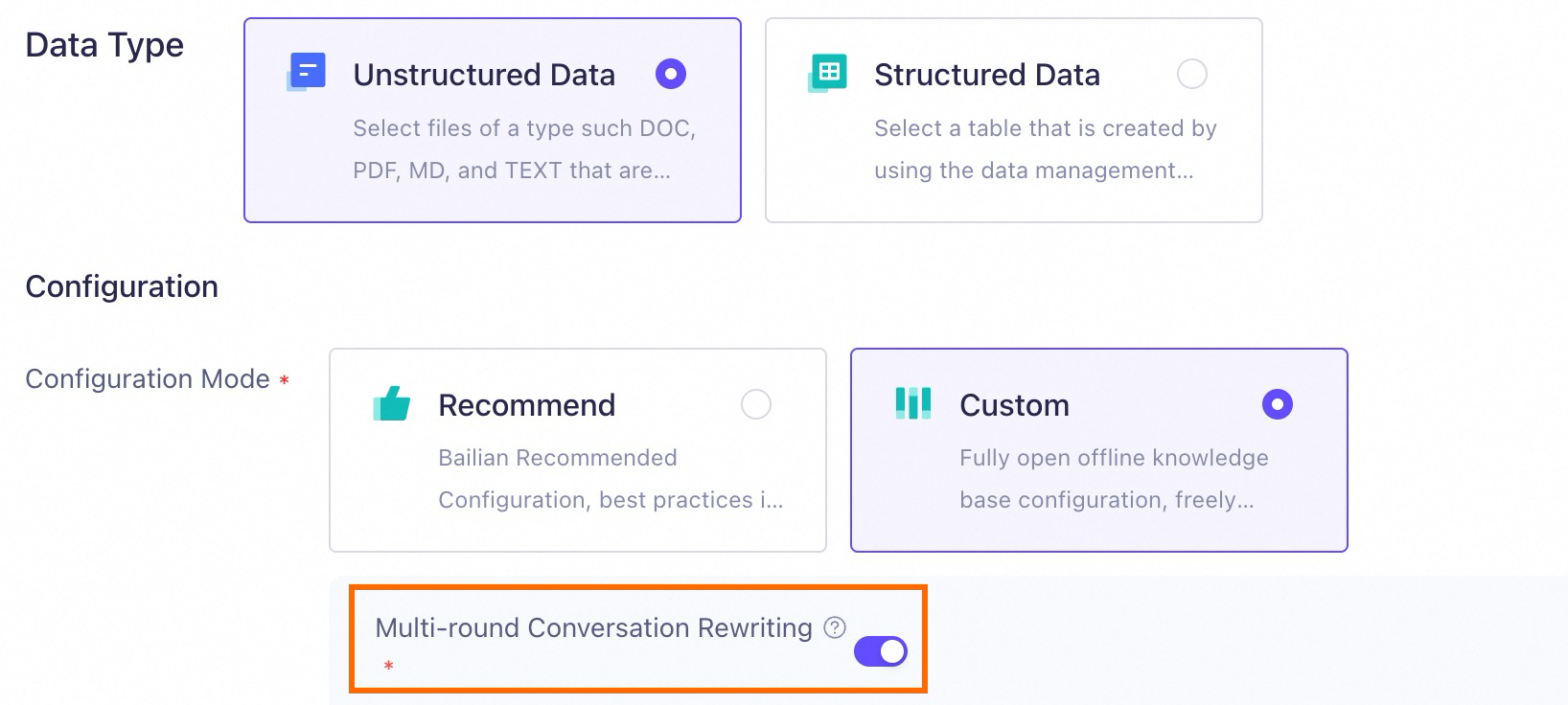
Note that the multi-round conversation rewriting feature is attached to the knowledge base. Once enabled, it applies only to queries related to the current knowledge base. If you do not enable this configuration when you create the knowledge base, you cannot enable it later unless you recreate the knowledge base.
2.3.2 Tag filtering
The content of this section applies only to document search knowledge bases.
When you use a music app, you might filter songs by the artist's name to quickly find songs from that artist.
Similarly, adding tags to your unstructured documents introduces additional structured information. This allows the application to filter documents based on tags when retrieving from the knowledge base, which improves retrieval accuracy and efficiency.
Model Studio supports two methods for setting tags:
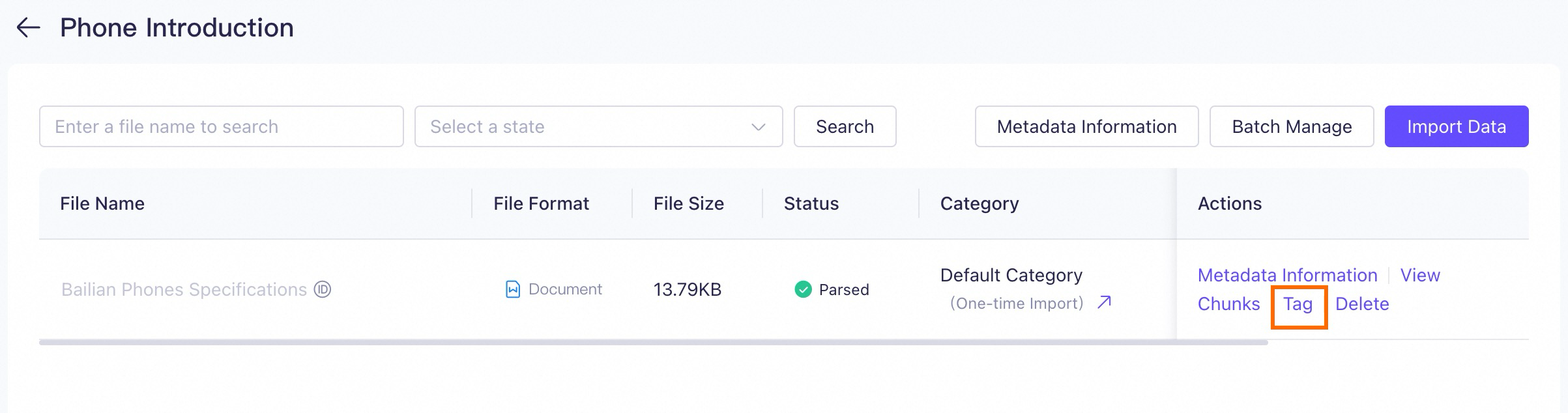
Set tags when uploading documents: For the steps in the console, see Import data.
Edit tags on the Data Management page: For uploaded documents, you can click Tag on the right of the document to edit.
Model Studio supports two methods for using tags:
When you call an application through an API, you can specify tags in the
tagsrequest parameter.Set tags when editing an application in the console. However, this method is applicable only to agent applications.
Note that this setting applies to all subsequent questions and answers for this agent application.
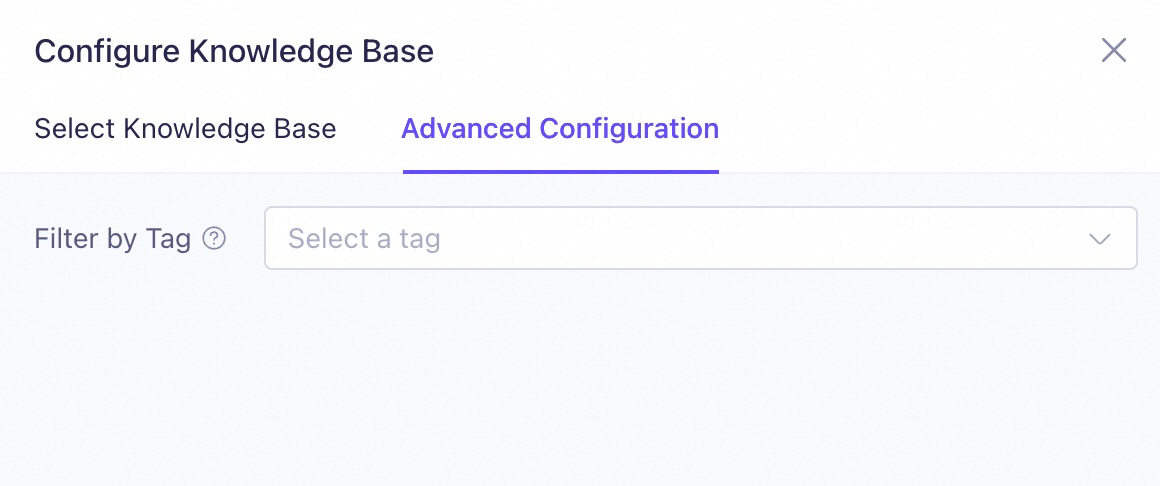
2.3.3 Extracting metadata
The content of this section applies only to document search knowledge bases.
Embedding metadata into text chunks can effectively enhance the contextual information of each chunk. In specific scenarios, this method can significantly improve the RAG performance of document search knowledge bases.
Consider the following scenario:
A knowledge base contains many mobile phone product description documents. The document names are the phone models (such as Bailian X1, Bailian Zephyr Z9, etc.), and all documents include a "Function Overview" chapter.
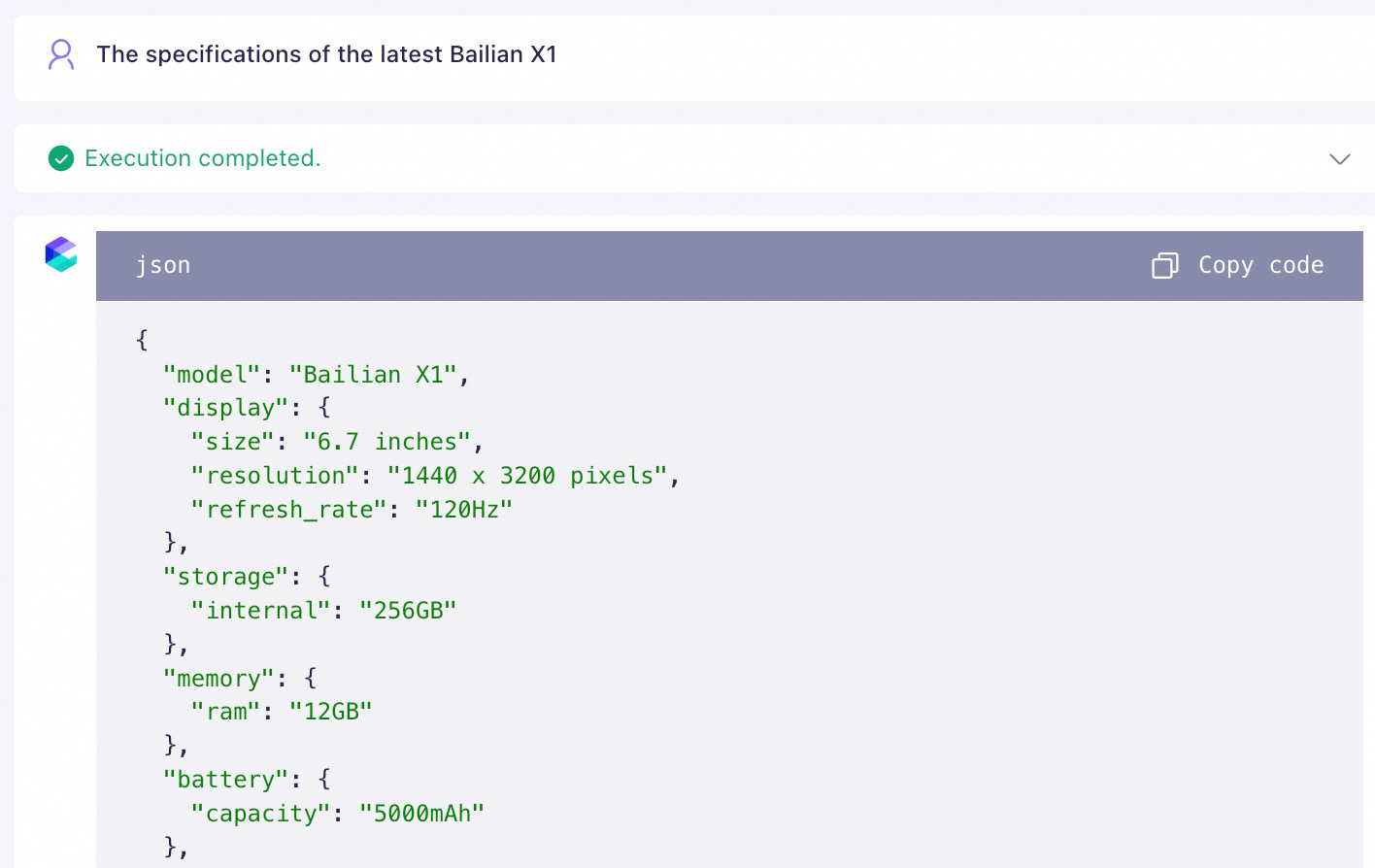
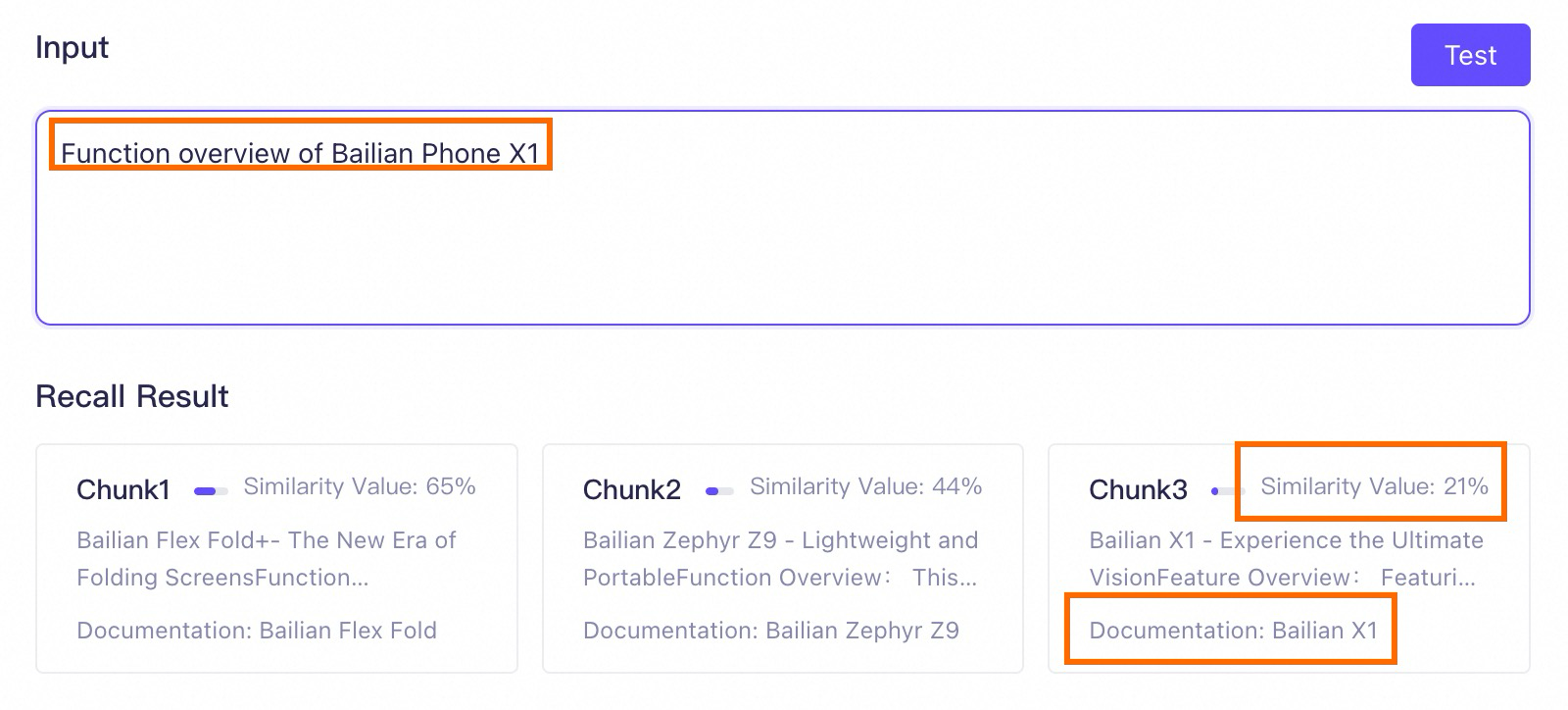
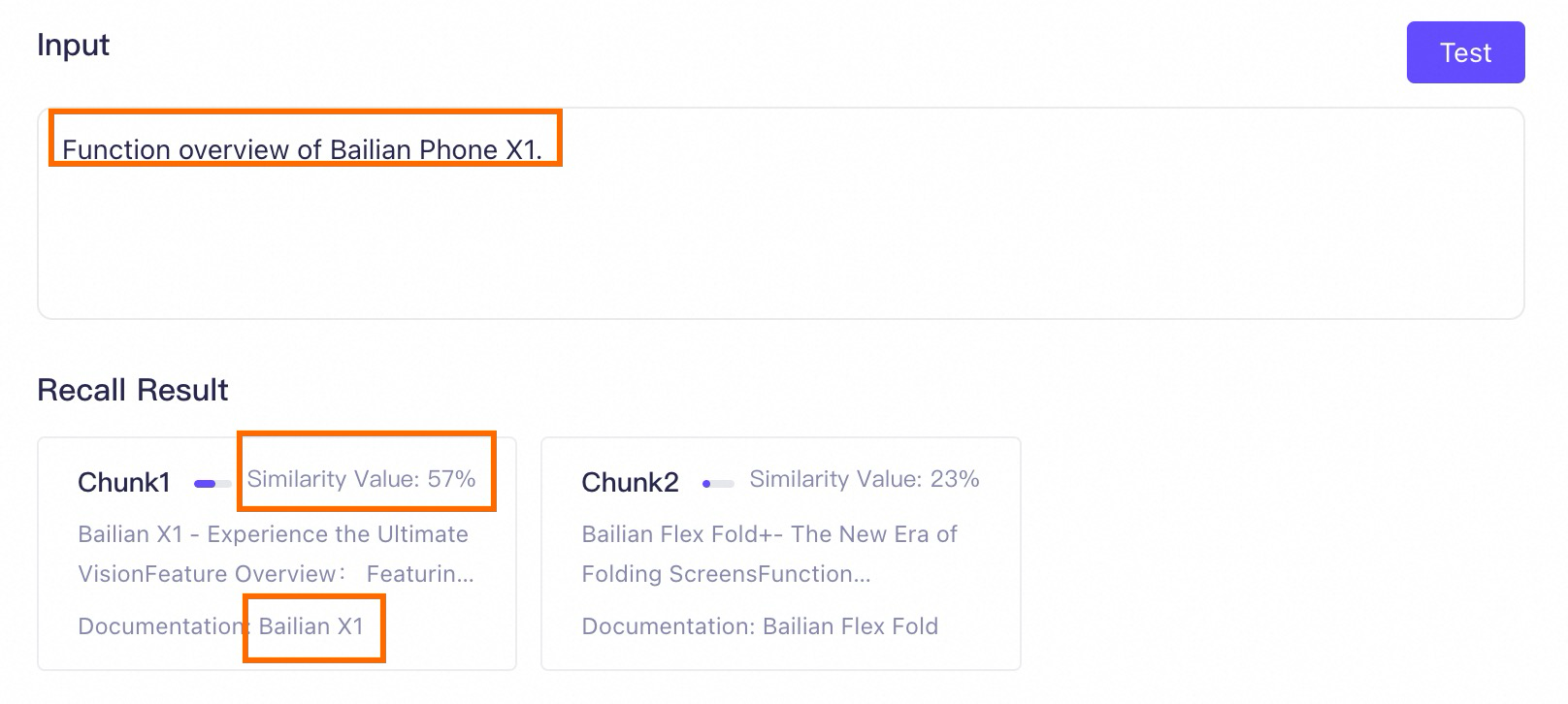
If metadata is not enabled for this knowledge base, a user might enter the following prompt for retrieval:
Function overview of Bailian Phone X1.A retrieval test shows which chunks were recalled, as shown in the following figure. Because all documents contain a "Function Overview" section, the knowledge base recalls some text chunks that are unrelated to the query entity (Bailian Phone X1) but are similar to the prompt, such as Chunk 1 and Chunk 2 in the figure. Their rankings are even higher than the text chunk that is actually needed. This clearly affects RAG performance.
The recall results of the retrieval test only guarantee the ranking. The absolute value of the similarity score is for reference only. When the difference in absolute values is small (within 5%), the recall probability can be considered the same.
Next, set the phone name as metadata. This is equivalent to adding the corresponding phone name information to the text chunks of each document. You can follow the steps in metadata extraction and then run the same test for comparison.
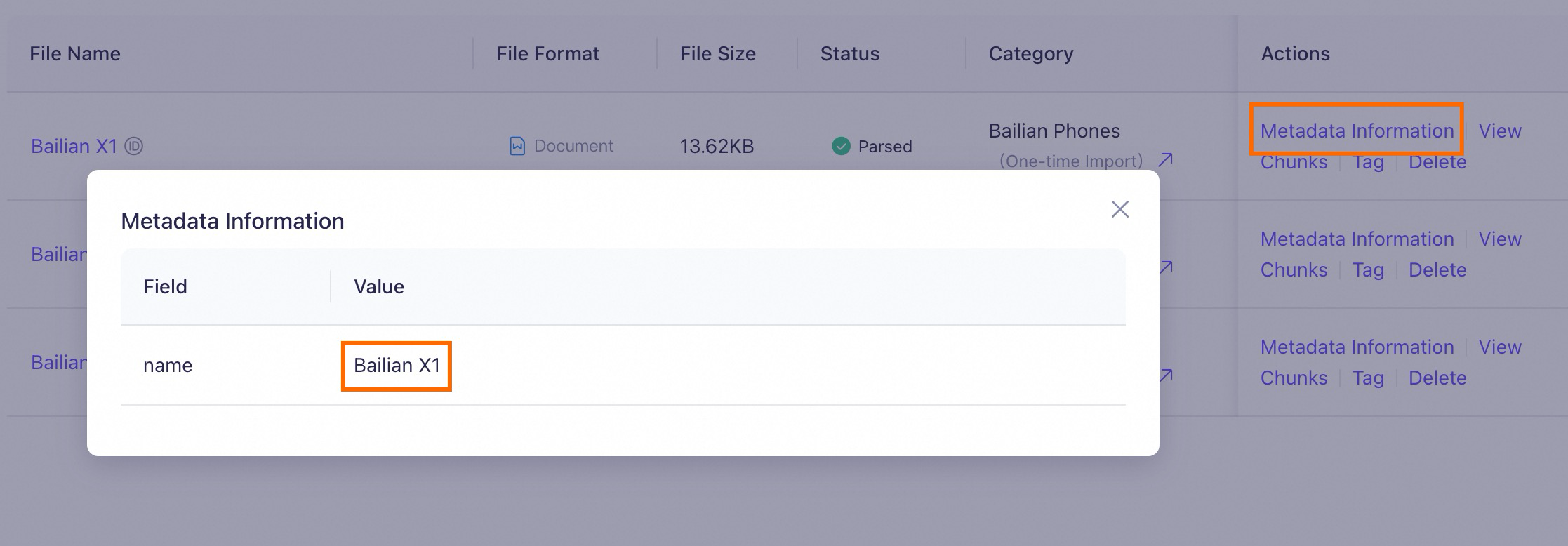
At this point, the knowledge base adds a layer of structured search before the vector search. The process is as follows:
Extract metadata {"key": "name", "value": "Bailian Phone X1"} from the prompt.
Based on the extracted metadata, find all text chunks that contain the "Bailian Phone X1" metadata.
Then, perform a vector (semantic) search to find the most relevant text chunks.
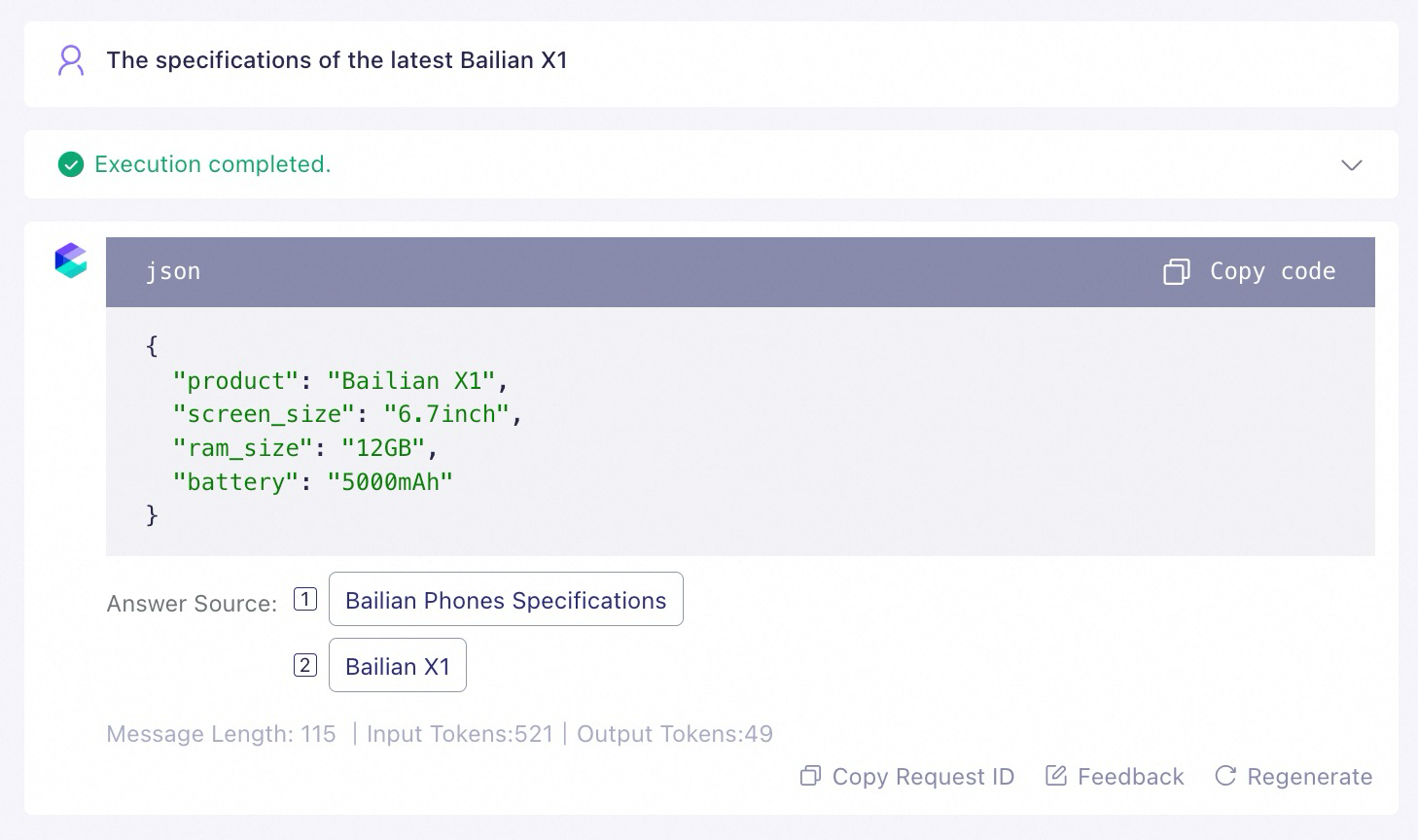
The actual recall effect of the retrieval test after enabling metadata is shown in the following figure. As you can see, the knowledge base can now accurately find the text chunk that is related to "Bailian Phone X1" and contains "Function Overview".
Another common application of metadata is to embed date information in text chunks to filter for recent content. For more information about metadata usage, see metadata extraction.
2.3.4 Adjusting the similarity threshold
When the knowledge base finds text chunks related to the user's prompt, it first sends them to the Rank model for reordering. You can configure this in the Custom parameter settings when you create the knowledge base. The similarity threshold is then used to filter the reordered text chunks. Only text chunks with a similarity score that exceeds this threshold are likely to be provided to the model.
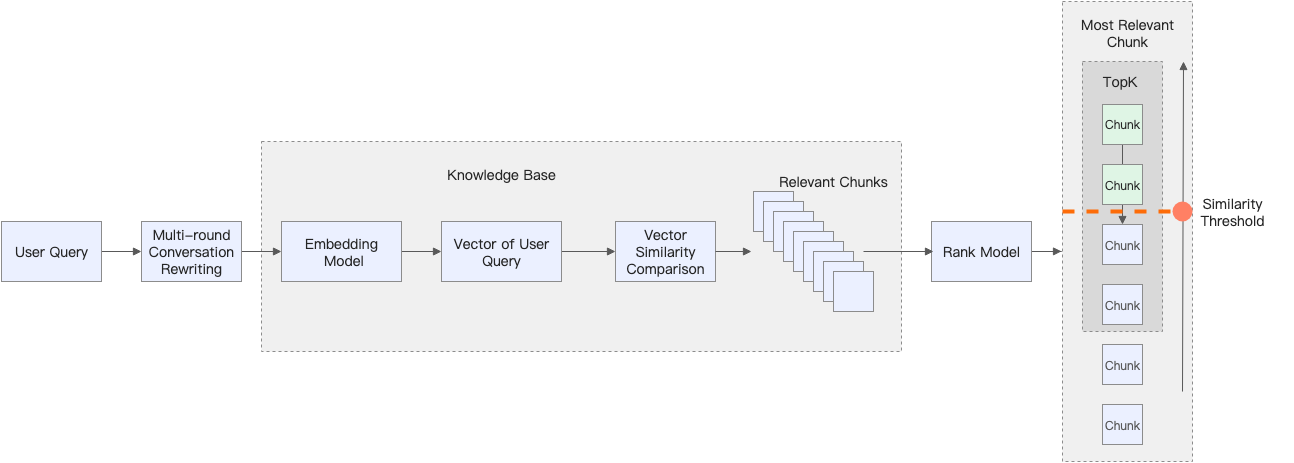
Lowering this threshold may recall more text chunks, but it may also cause some less relevant text chunks to be recalled. Increasing this threshold may reduce the number of recalled text chunks.
If it is set too high, as shown in the following figure, it may cause the knowledge base to discard all relevant text chunks. This limits the model's ability to obtain sufficient background information to generate an answer.
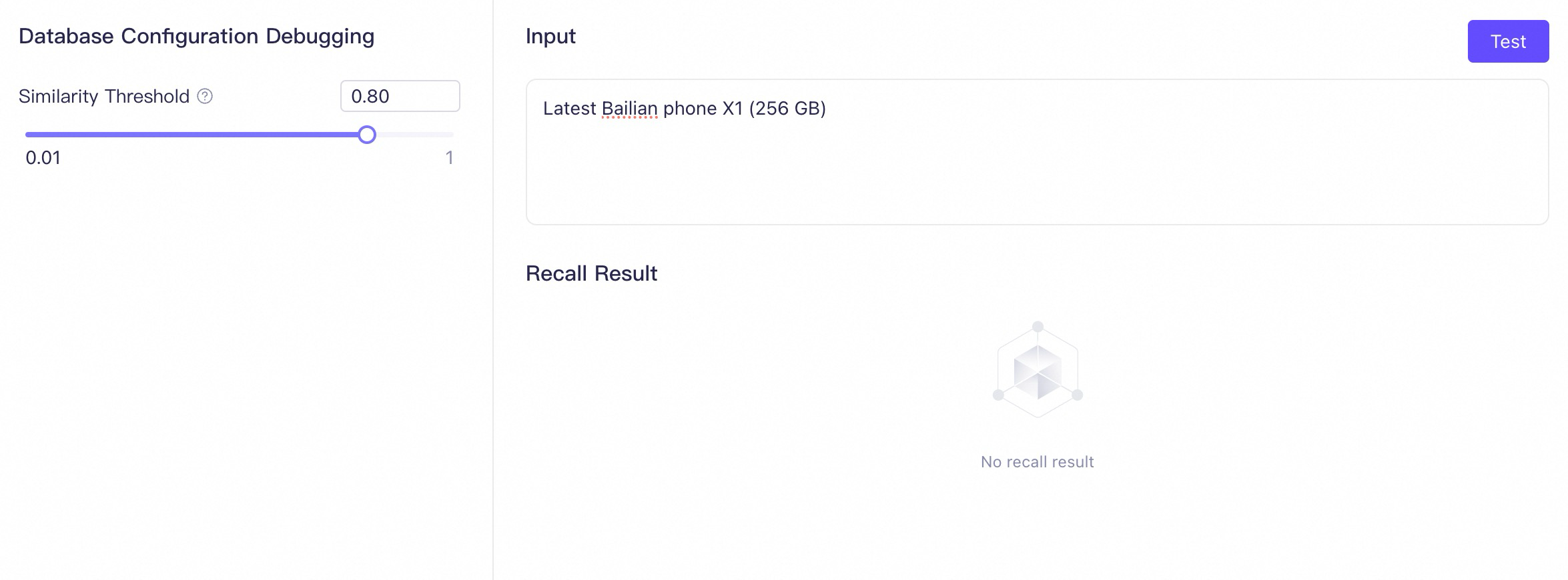
There is no single best threshold, only the one that is most suitable for your scenario. You need to experiment with different similarity thresholds through retrieval tests, observe the recall results, and find the solution that best suits your needs.
Recommended steps for retrieval testing | |
|
|
2.3.5 Increase the number of recalled chunks
The number of recalled chunks is the K value in the multi-channel recall strategy. After the similarity threshold filtering, if the number of text chunks exceeds K, the system selects the K text chunks with the highest similarity scores to provide to the model. Because of this, an inappropriate K value may cause RAG to miss the correct text chunks, which affects the model's ability to generate a complete answer.
For example, in the following case, the user retrieves with the following prompt:
What are the advantages of the Bailian X1 phone?As you can see in the following diagram, there are a total of 7 text chunks in the target knowledge base that are related to the user's prompt and should be returned. These are marked in green on the left. However, because this number exceeds the currently set maximum number of recalled chunks (K), the text chunks containing advantage 5 (ultra-long standby) and advantage 6 (clear photos) are discarded and not provided to the model.

Because RAG cannot determine how many text chunks are needed to provide a complete answer, the model will generate an answer based on the provided chunks, even if they are incomplete.
Many experiments show that in scenarios that require lists, summaries, or comparisons, providing more high-quality text chunks (for example, K=20) to the model is more effective than providing only the top 10 or top 5. Although this may introduce noise, if the text chunk quality is high, the model can usually offset the impact of the noise.
You can adjust the Number Of Recalled Chunks when you edit an application.
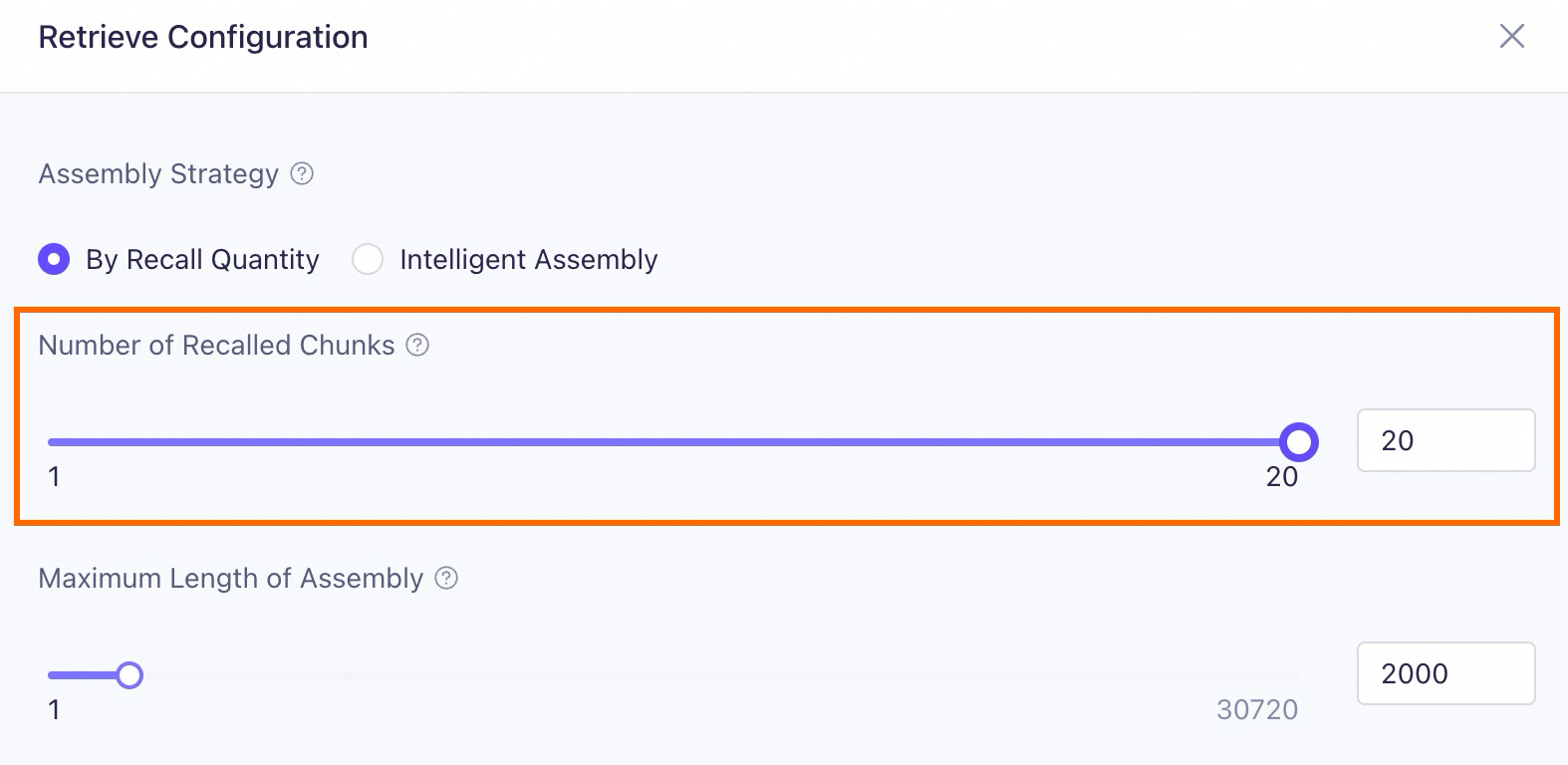
Note that a larger number of recalled chunks is not always better. Sometimes, after the recalled text chunks are assembled, their total length may exceed the input length limit of the model. This causes some text chunks to be truncated, which in turn affects RAG performance.
Therefore, we recommend that you select Intelligent Assembly. This strategy recalls as many relevant text chunks as possible without exceeding the maximum input length of the model.
2.4 Answer generation stage
This section introduces only the configuration items that Model Studio supports for optimization in the answer generation stage.
At this point, the model can generate the final answer based on the user's prompt and the content retrieved and recalled from the knowledge base. However, the returned result may still not meet your expectations.
Problem type | Improvement strategy |
The model does not understand the relationship between the knowledge and the user's prompt. The answer seems to be a clumsy combination of text. | We recommend that you choose a suitable model to effectively understand the relationship between the knowledge and the user's prompt. |
The returned result does not follow the instructions or is not comprehensive. | We recommend that you optimize the prompt template. |
The returned result is not accurate enough. It contains the model's own general knowledge and is not entirely based on the knowledge base. | We recommend that you enable rejection to restrict answers to only the knowledge retrieved from the knowledge base. |
For similar prompts, you want the results to be either consistent or varied. | We recommend that you adjust the model parameters. |
2.4.1 Choose a suitable model
Different models have different capabilities in areas such as instruction following, language support, long text, and knowledge understanding. This can lead to the following situation:
Model A fails to effectively understand the relationship between the retrieved knowledge and the prompt, so the generated answer cannot accurately respond to the user's prompt. Switching to Model B, which has more parameters or stronger professional capabilities, may solve this problem.
You can Select A Model when you edit an application based on your actual needs.
You can Select a Model when editing an application in Model Studio to meet your specific requirements. We recommend choosing a commercial model from the Qwen series, such as Qwen-Max, Qwen-Plus, or other models. These commercial models provide the latest capabilities and improvements compared to their open-source versions.
For simple information query and summarization, a model with a small number of parameters is sufficient, such as
Qwen-Turbo.If you want RAG to perform more complex logical reasoning, we recommend choosing a model with a larger number of parameters and stronger reasoning capabilities, such as
Qwen-Max.If your question requires consulting many document chunks, we recommend choosing a model with a longer context length, such as
Qwen-Plus.If the RAG application you are building is for a non-general domain, such as the legal field, we recommend using a model trained for that specific domain, such as
Qwen-Legal.
2.4.2 Optimizing the prompt template
A model predicts the next token based on the given text. This means you can influence the behavior of the model by adjusting the prompt, such as how it uses the retrieved knowledge. This can indirectly improve RAG performance.
The following are three common optimization methods:
Method 1: Constrain the output content
You can provide contextual information, instructions, and the expected output format in the prompt template to instruct the model. For example, you can add the following output instruction to require the model to:
If the information provided is not sufficient to answer the question, please state clearly, "Based on the existing information, I cannot answer this question." Do not invent an answer.This reduces the chance of the model generating hallucinations.
Method 2: Add examples
Use the Few-Shot Prompting method to add question-and-answer examples to the prompt for the model to imitate. This guides the model to correctly use the retrieved knowledge. The following example uses Qwen-Plus.
Prompt template | User prompt and the result returned by the application |
|
|
|
|
Method 3: Add content delimiters
If the retrieved text chunks are randomly mixed in the prompt template, it is difficult for the model to understand the structure of the entire prompt. Therefore, we recommend that you clearly separate the prompt and the ${documents} variable.
In addition, to ensure the best effect, make sure that the ${documents} variable appears only once in your prompt template. For more information, see the correct example on the left in the following table.
Correct example | Incorrect example |
| |
To learn more about prompt optimization methods, see Prompt engineering.
2.4.3 Enable rejection
If you want the results returned by your application to be based strictly on the knowledge retrieved from the knowledge base, and to exclude the influence of the model's own general knowledge, you can set the answer scope to Knowledge base only when you edit the application.
For cases where no relevant knowledge is found in the knowledge base, you can also set a fixed, automatic reply.
Answer scope: Knowledge Base + model Knowledge | Answer scope: Knowledge Base Only |
|
|
The result returned by the application will be a combination of knowledge retrieved from the knowledge base and the model's own general knowledge. | The result returned by the application will be strictly based on the knowledge retrieved from the knowledge base. |
To determine the knowledge scope, we recommend that you choose the Search Threshold + LLM Judgment method. This strategy first filters potential text chunks using a similarity threshold. Then, a model acts as a referee, using the Judgment Prompt that you set to conduct an in-depth analysis of the relevance. This further improves the accuracy of the judgment.

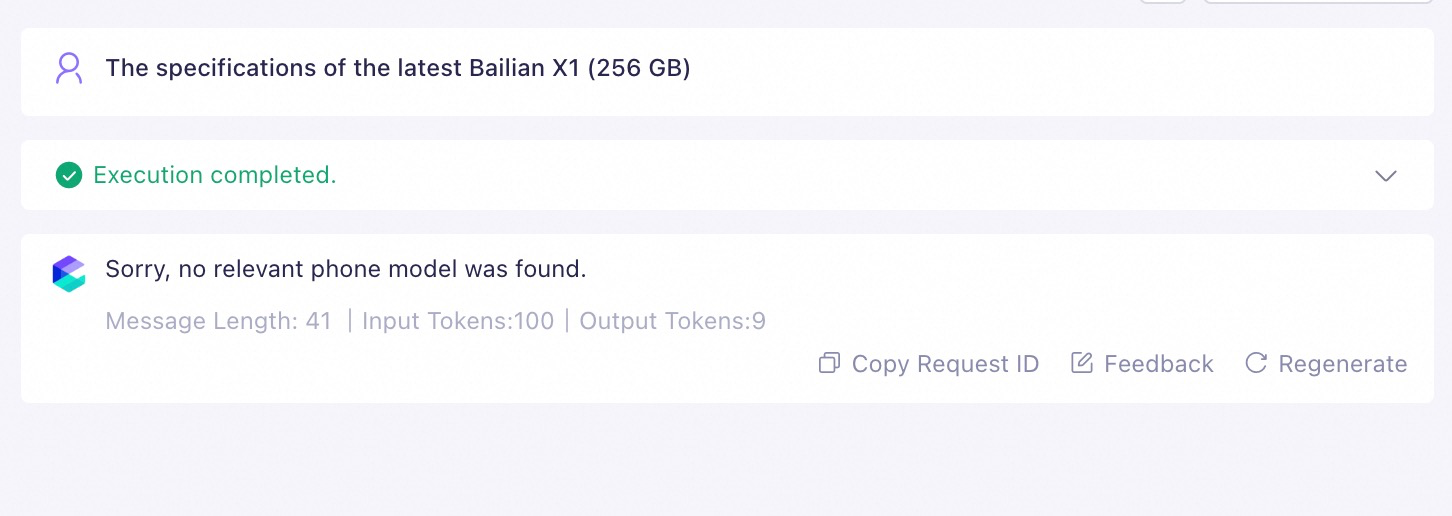
The following is an example of a judgment prompt for your reference. In this example, when no relevant knowledge is found in the knowledge base, a fixed reply is set: Sorry, no relevant phone model was found.
# Judgment rules:
- The premise for a match between the question and the document is that the entity involved in the question is exactly the same as the entity described in the document.
- The question is not mentioned at all in the document.User prompt and the result returned by the application (when knowledge is hit) | User prompt and the result returned by the application (when knowledge is not hit) |
|
|
2.4.4 Adjusting model parameters
For similar prompts, if you want the results to be consistent or varied each time, you can modify the Parameters to adjust the model parameters when you edit the application.
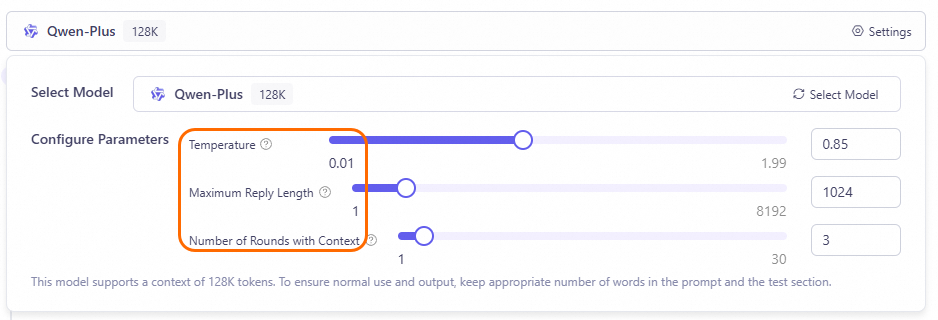
The temperature parameter in the preceding figure controls the randomness of the content generated by the model. The higher the temperature, the more diverse the generated text. Conversely, the more deterministic the generated text.
Diverse text is suitable for creative writing (such as novels, advertising copy), brainstorming, chat applications, and other scenarios.
Deterministic text is suitable for scenarios with clear answers (such as problem analysis, multiple-choice questions, fact-finding) or requiring precise wording (such as technical documents, legal texts, news reports, academic papers).
The other two parameters are:
Maximum response length: This parameter controls the maximum number of tokens generated by the model. You can increase this value to generate detailed descriptions or decrease it to generate short answers.
Number of context turns: This parameter controls the number of historical conversation turns that the model refers to. When set to 1, the model does not refer to historical conversation information when answering.