The Batch API is designed for scenarios that do not require real-time responses. It processes large volumes of data requests asynchronously, costs only 50% of the price of real-time responses, and is OpenAI compatible. This makes it ideal for batch jobs such evaluations and labeling large-scale data.
Workflow
Asynchronous batch inference:
Submit a task: Upload a file that contains multiple requests to create a batch task.
Asynchronous processing: The system processes tasks from a queue in the background. You can query the task progress and status in the console or using the API.
Download the results: After the task is complete, the system generates a result file with successful responses and an error file with details about any failures.
Scope
Mainland China
In the Mainland China deployment mode, endpoints and data storage are located in the Beijing region, and model inference compute resources are limited to Mainland China.
Supported models:
Text generation models: Stable and some
latestversions of Qwen-Max, Qwen-Plus, Qwen-Flash, and Qwen-Long. Also supports the QwQ series (qwq-plus) and third-party models such as deepseek-r1 and deepseek-v3.Multimodal models: Stable and some
latestversions of Qwen-VL-Max, Qwen-VL-Plus, and Qwen-VL-Flash. Also Qwen-OCR.Text embedding models: text-embedding-v4.
International
In the international deployment mode, endpoints and data storage are located in the Singapore region. Model inference compute resources are dynamically scheduled worldwide, excluding Mainland China.
Supported models: qwen-max, qwen-plus, qwen-flash, and qwen-turbo.
Getting started
Step 1: Prepare your batch file
Prepare a UTF-8 encoded .jsonl file that meets the following requirements:
Format: One JSON object per line, each describing an individual request.
Size limit: Up to 50,000 requests per file and no larger than 500 MB.
For files that exceed these limits, split them into smaller batches.
Line limit: Each JSON object up to 6 MB and within the model's context window.
Consistency: All requests in a file must target the same API endpoint (
url) and use the same model (body.model).Unique identifier: Each request requires a
custom_idunique within the file, which can be used to reference results after completion.
Request example
The following sample contains 2 requests sent to Qwen-Max:
{"custom_id":"1","method":"POST","url":"/v1/chat/completions","body":{"model":"qwen-max","messages":[{"role":"system","content":"You are a helpful assistant."},{"role":"user","content":"Hello!"}]}}
{"custom_id":"2","method":"POST","url":"/v1/chat/completions","body":{"model":"qwen-max","messages":[{"role":"system","content":"You are a helpful assistant."},{"role":"user","content":"What is 2+2?"}]}}JSONL batch generation tool
Use this tool to quickly generate JSONL files.
Step 2: Create the batch
Create and manage batch tasks through the console or the Batch API.
Console
(1) Create a batch
On the Batches page, click Create Batch Task.
In the dialog box that appears, enter a Task Name and Task Description. Set the Maximum Waiting Time (from 1 to 14 days) and upload the JSONL file.
Click Download Sample File for a template.
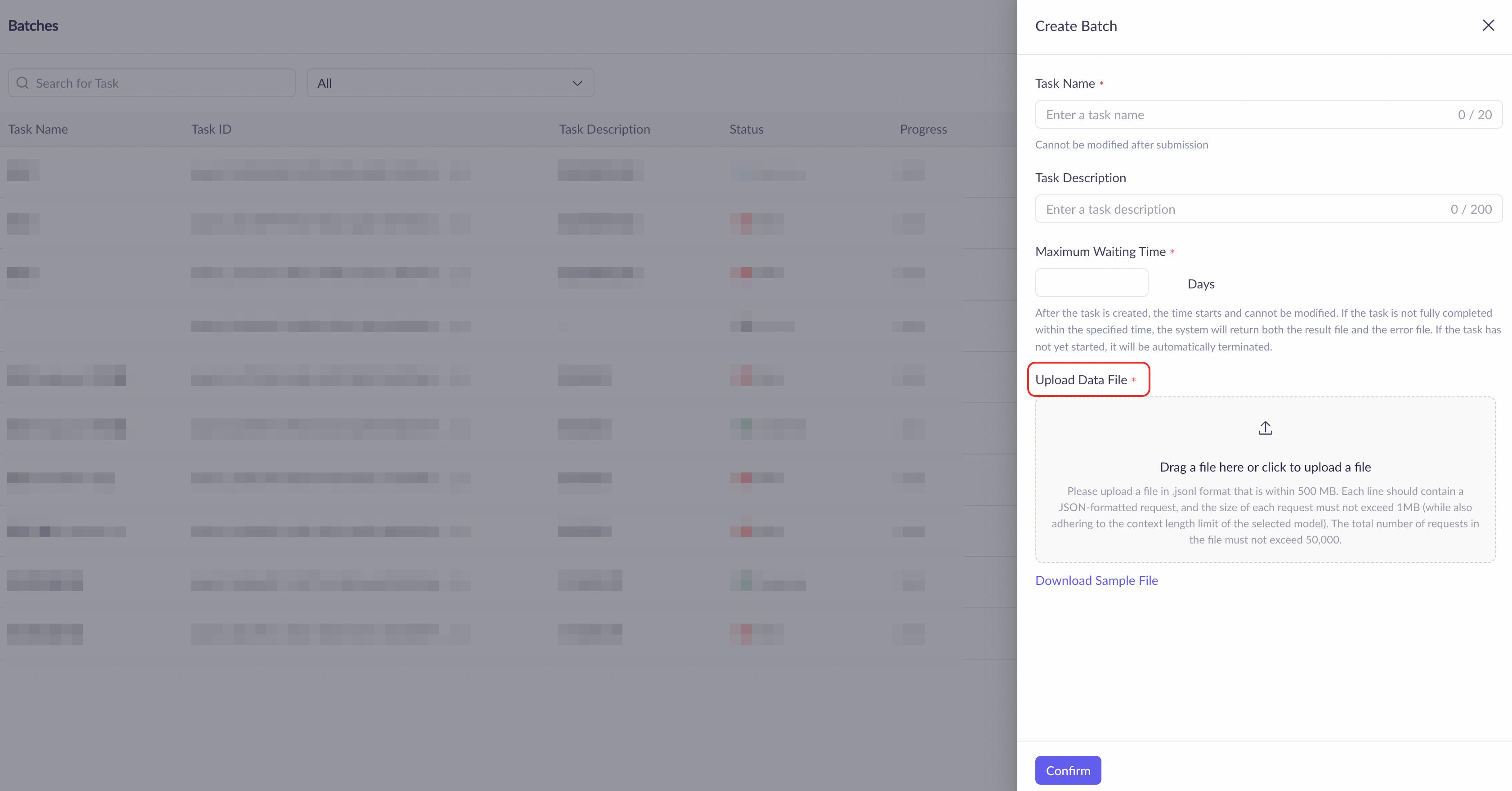
Click Confirm.
(2) View and manage batches
View:
The task list page show the Progress (processed requests/total requests) and Status of each batch.
To quickly find a batch, search by task name or ID, or filter by workspace.

Manage:
Cancel: Cancel tasks with the `in_progress` status in the Actions column.
Troubleshoot: For tasks with the `failed` status, hover over the status to view a summary. Download the error file to view the details.

(3) Download and analyze the results
After a task is complete, click View Results to download the output files:
Result file: Contains all successful requests and their
responseresults.Error file (if any): Contains all failed requests and their
errordetails.
Both files contain the custom_id field. Use it to match the results with the original input data to correlate results or locate errors.
API
For production environments that require automation and integration, use the OpenAI-compatible Batch API. Core workflow:
Create a batch
Call thePOST /v1/batchesendpoint to create a task and record the returnedbatch_id.Poll the status
Use thebatch_idto poll theGET /v1/batches/{batch_id}endpoint. When thestatusfield changes tocompleted, record the returnedoutput_file_idand stop polling.Download the results
Use theoutput_file_idto call theGET /v1/files/{output_file_id}/contentendpoint to download the result file.
For API definitions, parameters, and code examples, see Batch API reference.
Step 3: View statistics (optional)
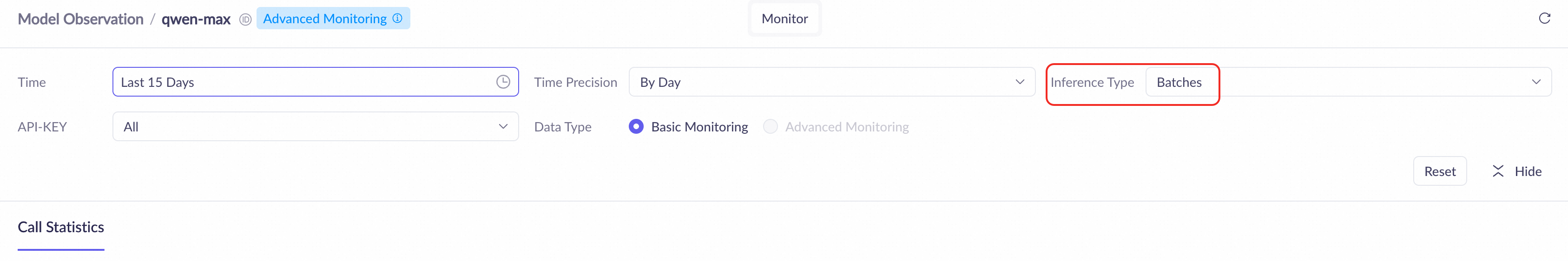
On the Model Monitoring page, filter and view usage statistics for batch inference.
View data overview: Select a Time range (up to 30 days) and set Inference Type to Batches:
Monitoring data: This section displays summary statistics for all models within the specified time period, such as the total number of calls and failures.
Model list: This section lists detailed data for each model, such as the total number of calls, failure rate, and average call duration.

To view inference data from more than 30 days ago, you can go to the Bills page.
View model details: In the Models list, click Monitor in the Actions column for a specific model to view its Call Statistics details, such as the call count and usage.
Batch inference call data is recorded based on the task end time. For tasks that are in progress, call information becomes available only after the task is complete.
Monitoring data may have a delay of 1 to 2 hours.
Status of a batch
validating: The batch file is being validated against the JSONL specification and the API format requirements.
in_progress: The batch file has been validated and is being processed.
completed: The batch has completed. The output and error files are ready for download.
failed: The batch file has failed the validation process. This is typically caused by file-level errors, such as an invalid JSONL format or an oversized file. No requests are processed, and no output file is generated.
expired: The batch was not able to be completed within the maximum waiting time set at creation. Set a longer waiting time.
cancelled: The batch has been cancelled. Unprocessed requests are terminated.
Billing
Unit price: The input and output tokens for successful requests are billed at 50% of the standard synchronous API for that model. Pricing details: Models.
Scope:
Only successfully executed requests in a task are billed.
File parsing failures, execution failures, or row-level request errors do not incur charges.
For canceled tasks, requests that successfully completed before the cancellation are still billed.
Batches are billed separately and does not support savings plan, new user free quotas, or features such as context cache.
FAQ
Do I need to purchase or enable anything extra to use batch inference?
No. Once Alibaba Cloud Model Studio is activated, you can call the Batch API with your API Key. Usage is billed pay-as-you-go and deducted from your account balance.
Why does my task fail immediately after submission (status changes to
failed)?This is usually caused by a file-level error. Check the following:
Format: The file must be in the strict JSONL format, with one complete JSON object per line.
Size: The file size and line count must not exceed the limits in Step 1: Prepare your batch file.
Model consistency:
body.modelmust identical for all requests in the file. The model and region must supported batches.
How long does it take to process a task?
It depends on system load. Under heavy load, batches may wait in a queue for resources. Results are returned within the maximum waiting time you set, no matter the batch succeeds or fails.
Error codes
If a call fails and returns an error message, see Error messages for solutions.