Cloud-native Gateway of Microservices Engine (MSE) is a managed service that works as an ingress and provides enormous traffic management capabilities. Cloud-native Gateway supports a variety of service sources, such as Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK), MSE Nacos, MSE ZooKeeper, Enterprise Distributed Application Service (EDAS) registry, Serverless App Engine (SAE) registry, fixed address, and Domain Name System (DNS). Cloud-native Gateway delivers a unified solution to support service versions and implement canary releases. This topic describes how to implement different service release strategies by using ACK clusters and Nacos instances for service discovery.
Prerequisites
You are familiar with the blue-green deployment, A/B testing, and canary release mechanisms. For more information, see Service release strategies.
An ACK managed cluster is created. For more information, see Create an ACK managed cluster.
An MSE cloud-native gateway is created. For more information, see Create a cloud-native gateway.
A Nacos engine is created. For more information, see Create a Nacos engine.
ACK
In this example, the ACK cluster is used for service discovery. The backend service is registered with CoreDNS by using annotation-based service APIs. The backend service provides an API operation that is used to query the version in use. The request path is /version and the version in use is v1. Cloud-native gateways are integrated with ACK clusters and can obtain service information from ACK clusters in real time. This way, cloud-native gateways can expose backend services to external users.
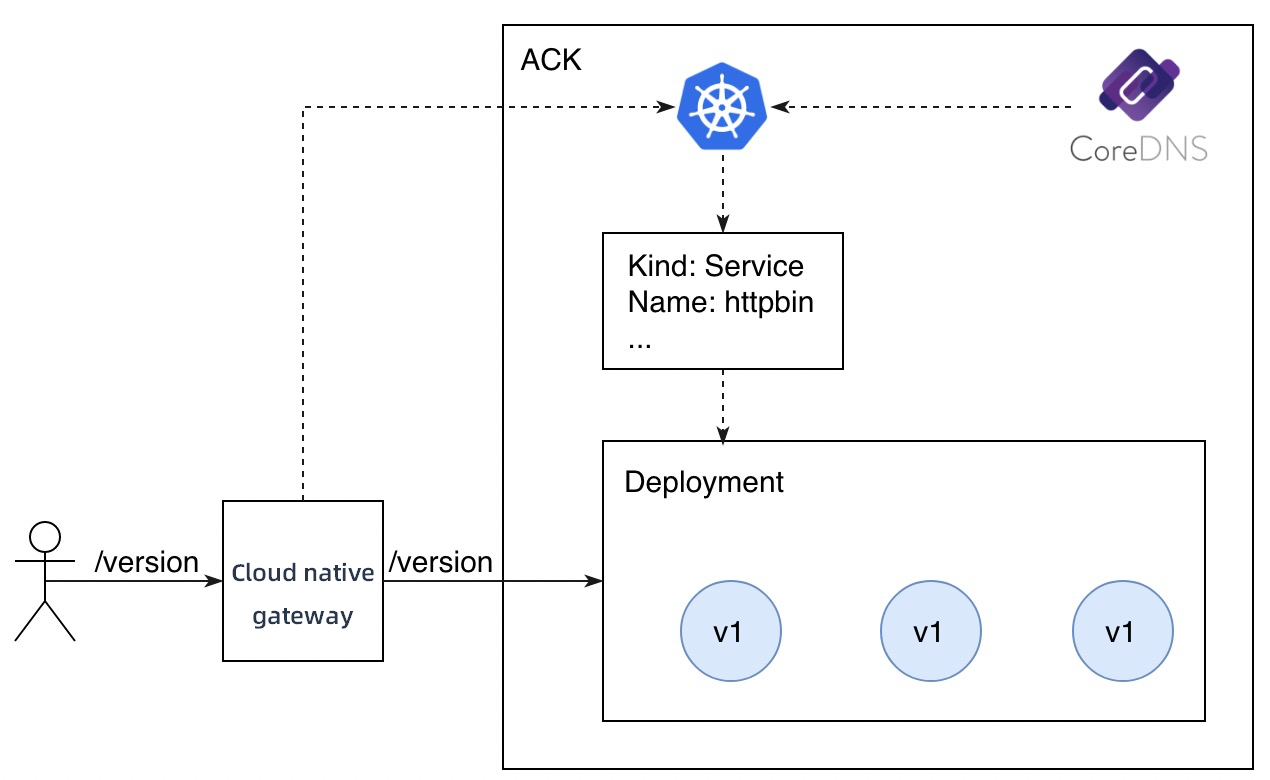
Deploy an application
Log on to the ACK console. Use the following YAML code to deploy an application with the version of v1.
For more information about how to deploy an application, see Create a stateless application by using a Deployment.
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: httpbin spec: ports: - port: 8080 protocol: TCP selector: app: httpbin --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: httpbin-v1 spec: replicas: 3 selector: matchLabels: app: httpbin version: v1 template: metadata: labels: app: httpbin version: v1 spec: containers: - image: specialyang/spring-cloud-httpbin-k8s:v1 imagePullPolicy: Always name: spring-cloud-httpbin-k8s ports: - containerPort: 8080Log on to the MSE console. On the Overview page of the desired gateway, click Routes in the left-side navigation pane. Then, click the Source tab. Click Add Source to add a container service as the service source.

In the left-side navigation pane, click Routes. Select the Service tab. Click Add Service. In the Add Service panel, add the httpbin service that you want to expose to the cloud-native gateway.
Add the v1 version to the httpbin service.
For more information about how to add a service version to a cloud-native gateway, see Manage service versions.
NoteYou must filter v1 nodes based on the tag for v1. Currently, only v1 is deployed. Therefore, v1 nodes take up 100% of instance nodes.

On the Route Settings page, create a route for the service to expose the service to external users. The route of the API operation used to expose the httpbin service is /version. The request is forwarded to the v1 version of the httpbin service.
Run the following command to send a test request:
for i in {1..10}; do curl "${GATEWAY_EXTERNAL_IP}/version"; echo ""; doneCommand output:
version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1
Perform a blue-green deployment
In a blue-green deployment, the new version of a service must take up the same amount of resources as the current version. After a blue-green deployment is complete, all traffic is switched over to the new version.
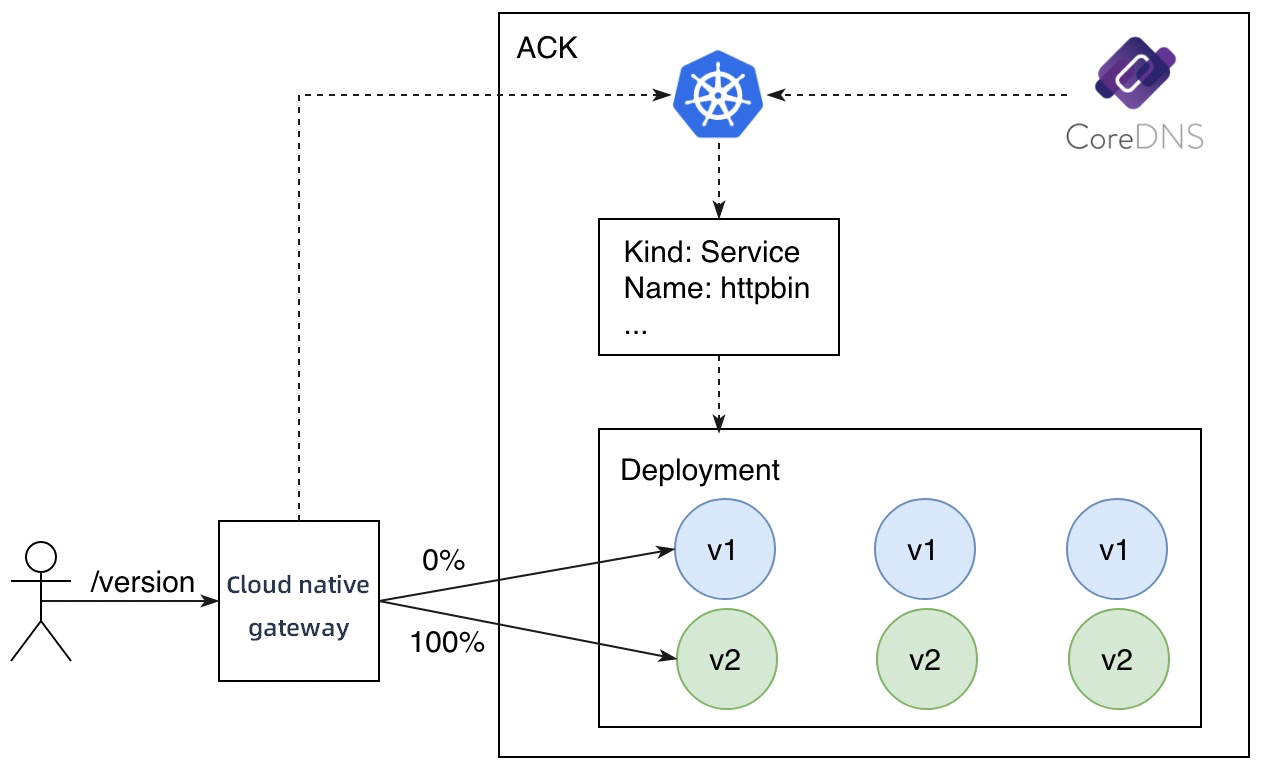
Deploy the v2 version for the httpbin service by using annotation-based API resources of ACK. The number of replicas is three.
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: httpbin-v2 spec: replicas: 3 selector: matchLabels: app: httpbin version: v2 template: metadata: labels: app: httpbin version: v2 spec: containers: - image: specialyang/spring-cloud-httpbin-k8s:v2 imagePullPolicy: Always name: spring-cloud-httpbin-k8s ports: - containerPort: 8080Add the v2 version to the httpbin service.
For more information about how to add a service version to a cloud-native gateway, see Manage service versions.
NoteYou must filter v2 nodes based on the tag for v2. Currently, the number of v1 nodes is the same as the number of v2 nodes in an instance. Therefore, v1 and v2 nodes each take up 50% of instance nodes.
Modify the service in the created route to switch traffic from v1 to v2 in the blue-green deployment.
For more information about how to modify a routing rule for a cloud-native gateway, see Modify a routing rule.

Run the following command to send a test request:
for i in {1..10}; do curl "${GATEWAY_EXTERNAL_IP}/version"; echo ""; doneCommand output:
version: v2 version: v2 version: v2 version: v2 version: v2 version: v2 version: v2 version: v2 version: v2 version: v2
Traffic that accesses API resources by using the /version request path has been switched from v1 to v2.
Perform A/B testing
A/B testing routes traffic to the new version of a service based on the metadata of a user request. A/B testing dynamically routes traffic based on request contents. In this example, the new version can be accessed only by requests whose User-Agent value is Android, and other requests are sent to the original version.
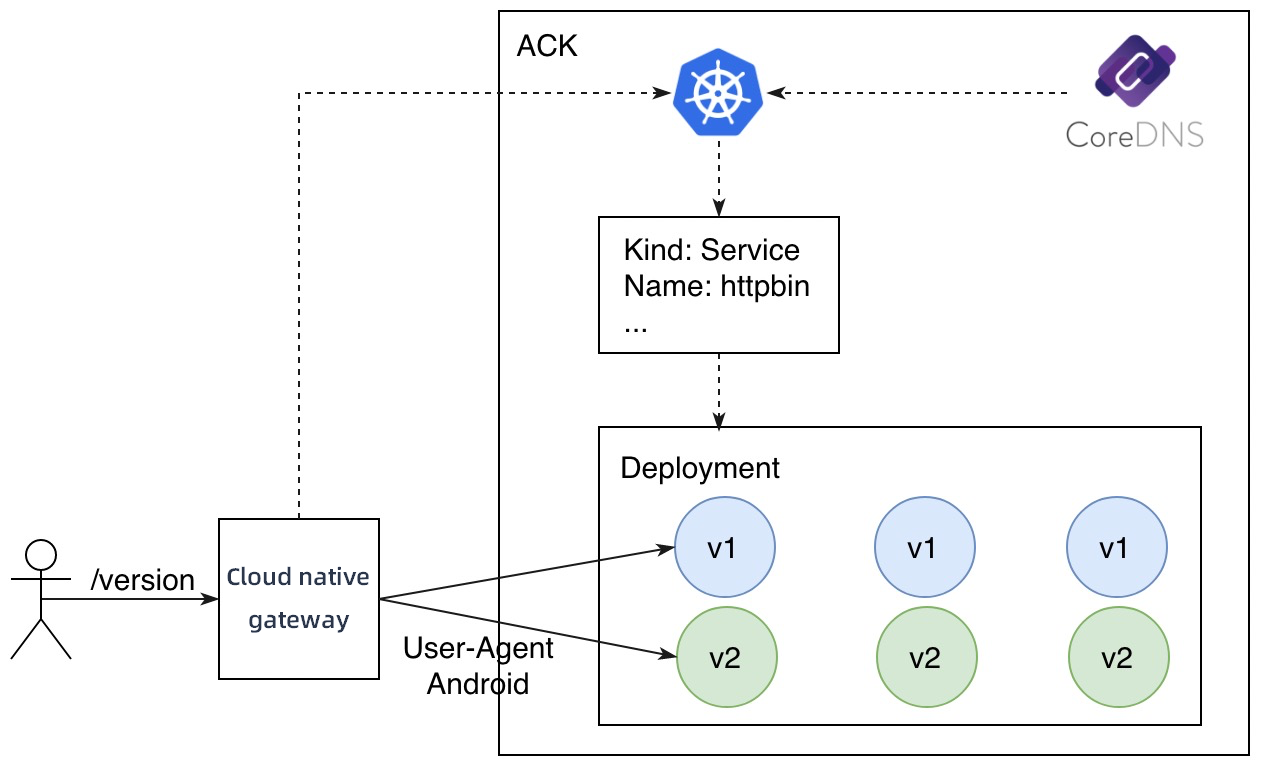
The v1 and v2 versions of the httpbin service are still used. In addition, two routing rules need to be created.
Requests that match the /version path are routed to the v1 version.
Requests that match the /version path and contain Android in the User-Agent header are routed to the v2 version.
NoteThe version-v2 route must be added with a request header that is used for matching.
Run the following command to send a test request that does not contain Android in the User-Agent header:
curl ${GATEWAY_EXTERNAL_IP}/versionCommand output:
version: v1Run the following command to send a test request that contains Android in the User-Agent header:
curl -H "User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 4.0.3)" ${GATEWAY_EXTERNAL_IP}/versionCommand output:
version: v2
Requests are distributed to different service versions based on operating systems from which the requests are sent.
Perform a canary release
The canary release feature allows a small amount of traffic to be routed to the new version of a service. After the new version is verified, more traffic is gradually routed to the new version until all traffic is routed to the new version. In this process, the new version is scaled out and the original version is scaled in to maximize the resource utilization.
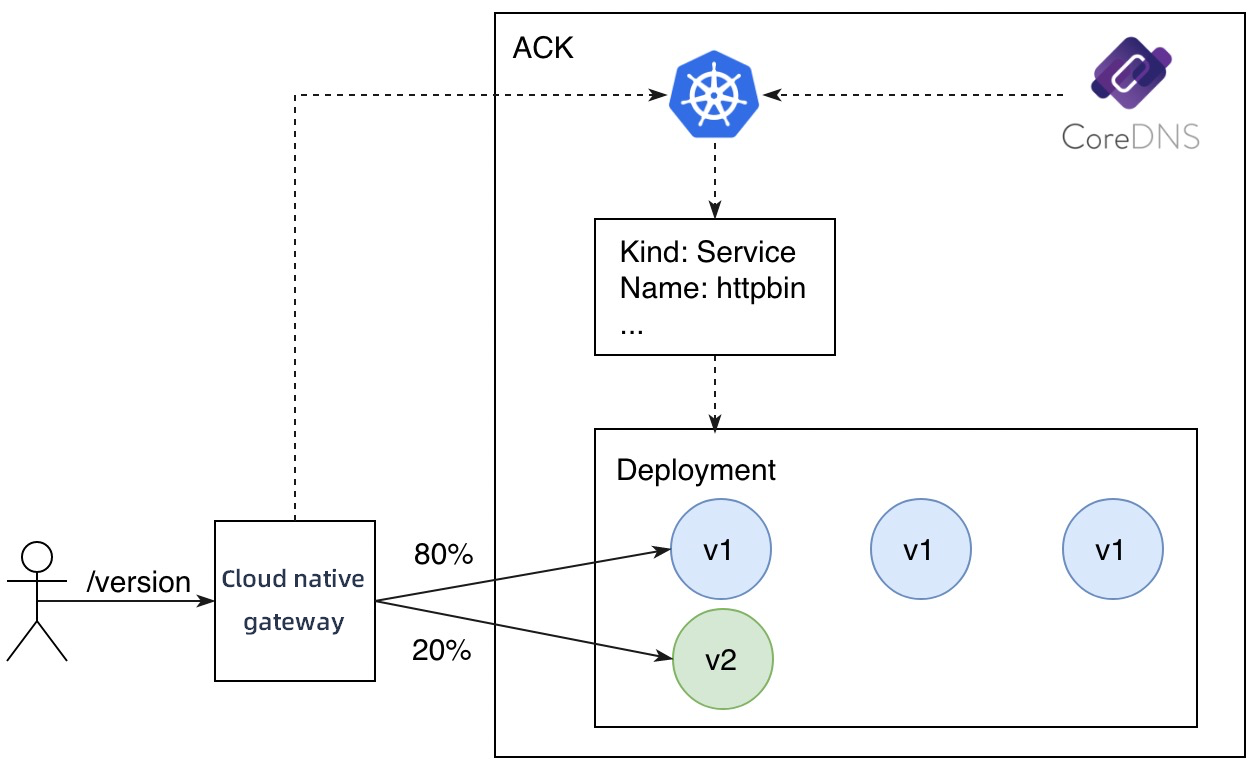
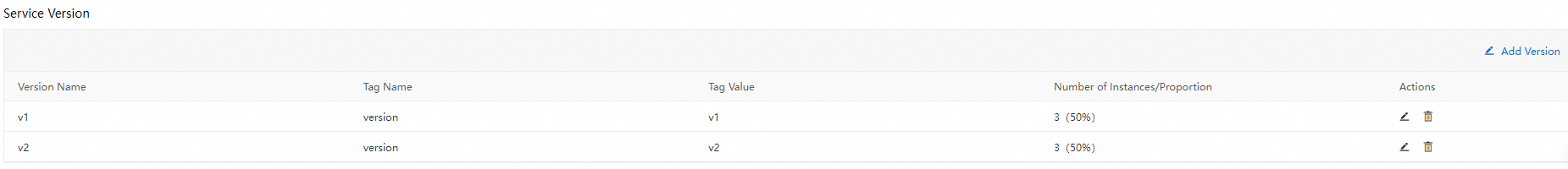
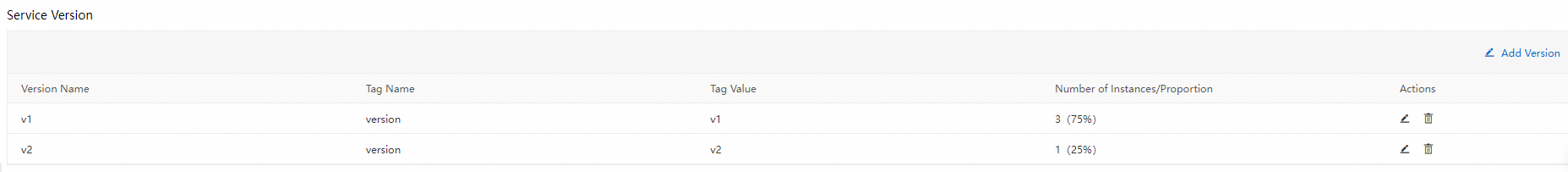
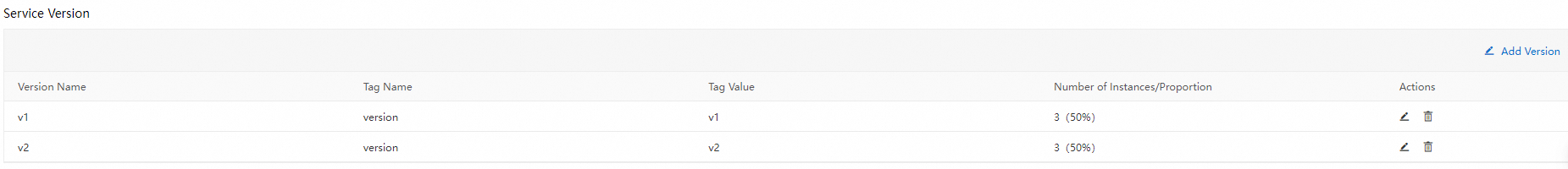
In a canary release, the number of replicas in the new version does not need to be consistent with that in the original version. The only requirement is that resources in the new version must be sufficient to handle canary traffic to the version. In this case, the number of replicas in the new version is set to 1. You can view the node distribution of versions in the Service Version section of the Services page.
Create a route to forward traffic to the new and original versions of the service based on node weights.
In the process, you must configure the v1 and v2 versions for the httpbin service and specify the weights based on which traffic is routed. For example, you can select Label Routing for Destination Service and set the weight of the v1 version to 80% and the weight of the v2 version to 20%.
Run the following command to send a test request:
for i in {1..10}; do curl "${GATEWAY_EXTERNAL_IP}/version"; echo ""; doneCommand output:
version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v2 version: v1 version: v2 version: v1 version: v1
Two out of ten requests access the v2 version. This traffic distribution ratio is the expected ratio.
In actual business scenarios, you can gradually increase the traffic percentage for the new version after the version is verified. When you increase the traffic percentage, you must scale out the new version and scale in the original version.
Nacos
In this example, the backend service provides an API operation that is used to query the version in use. The request path is /version and the version in use is v1. Cloud-native gateways are integrated with MSE Nacos instances and can obtain service information from MSE Nacos instances in real time. This way, cloud-native gateways can expose backend services to external users.
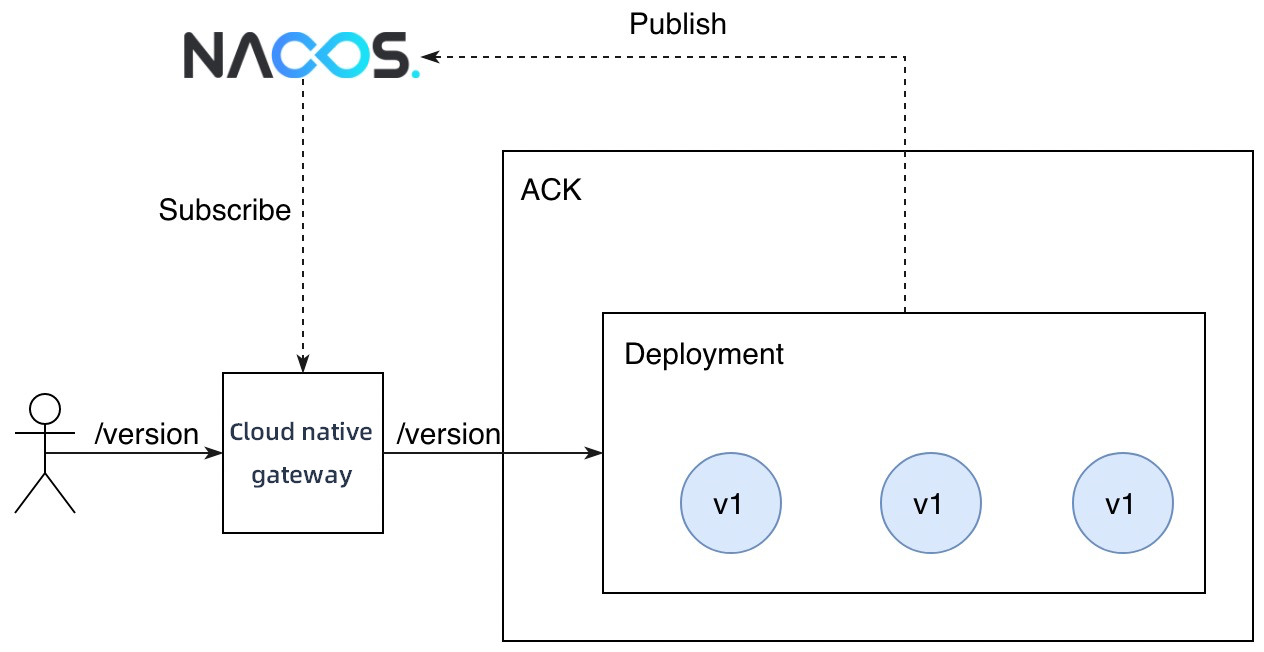
Deploy an application
Log on to the ACK console. Use the following YAML code to deploy an application with the version of v1.
For more information about how to deploy an application, see Create a stateless application by using a Deployment.
NoteThe
${NACOS_SERVER_ADDRESS}variable in the YAML file must be replaced with the address of your MSE Nacos instance. If your MSE Nacos instance resides in the same VPC as the gateway, you can replace the variable with the internal endpoint of the instance. Otherwise, replace the variable with the public endpoint of the instance.In ACK, data in labels of pods can be considered as node metadata. In Nacos, node metadata is determined by the data carried when a service is registered. In the Spring Cloud framework, you can use the
spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.metadata.xxxenvironment variable to add metadata for a node. In this example, theversionis used to distinguish nodes that have different versions. In this case, setspring.cloud.nacos.discovery.metadata.versionto v1 for applications.
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: httpbin-v1 spec: replicas: 3 selector: matchLabels: app: httpbin template: metadata: labels: app: httpbin spec: containers: - image: specialyang/spring-cloud-httpbin-nacos:v1 imagePullPolicy: Always name: spring-cloud-httpbin-nacos ports: - containerPort: 8080 env: - name: spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.server-addr value: ${NACOS_SERVER_ADDRESS} - name: spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.metadata.version value: v1Log on to the MSE console. On the Overview page of the desired gateway, click Routes in the left-side navigation pane. Then, click the Source tab to add an MSE Nacos instance as the service source.
In the left-side navigation pane, click Routes. Then, click the Service tab to import the httpbin service that you want to expose to the cloud-native gateway, and select MSE Nacos as the service source.
Add the v1 version to the httpbin service.
NoteYou must filter v1 nodes based on the tag for v1. Currently, only v1 is deployed. Therefore, v1 nodes take up 100% of instance nodes.

On the Route Settings page, create a route for the service to expose the service to external users. The route of the API operation used to expose the httpbin service is /version. The request is forwarded to the v1 version of the httpbin service.
Run the following command to send a test request:
for i in {1..10}; do curl "${GATEWAY_EXTERNAL_IP}/version"; echo ""; doneCommand output:
version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1
Perform a blue-green deployment
In a blue-green deployment, the new version of a service must take up the same amount of resources as the current version. After a blue-green deployment is complete, the traffic is switched over to the new version.
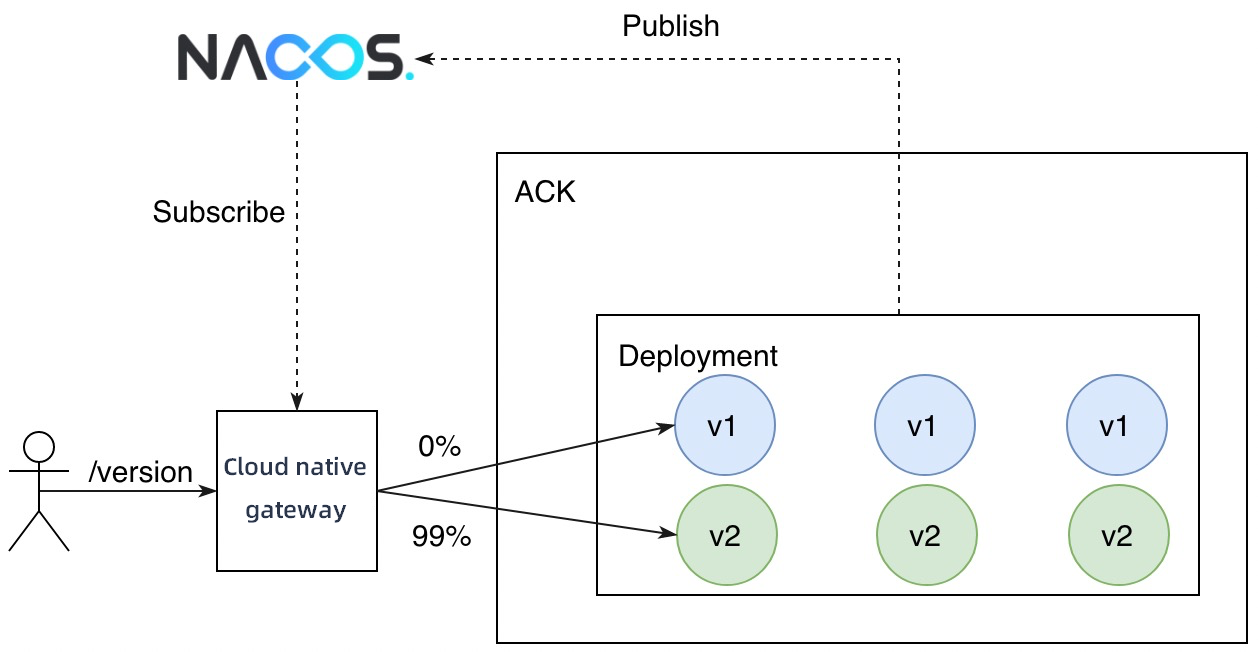
Deploy the new version v2 of the httpbin service.
NoteThe procedure for registering an application with a Nacos instance is the same as that for registering the service with an ACK cluster. Add the
spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.metadata.version=v2configuration for applications. When an application starts, the application is automatically registered with the Nacos instance and carries custom metadata. The cloud-native gateway can use the metadata to distinguish nodes of different versions.apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: httpbin-v2 spec: replicas: 3 selector: matchLabels: app: httpbin template: metadata: labels: app: httpbin spec: containers: - image: specialyang/spring-cloud-httpbin-nacos:v2 imagePullPolicy: Always name: spring-cloud-httpbin-nacos ports: - containerPort: 8080 env: - name: spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.server-addr value: ${NACOS_SERVER_ADDRESS} - name: spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.metadata.version value: v2Add the v2 version to the httpbin service.
For more information about how to add a service version to a cloud-native gateway, see Manage service versions.
NoteYou must filter v2 nodes based on the tag for v2. Currently, the number of v1 nodes is the same as the number of v2 nodes in an instance. Therefore, v1 and v2 nodes each take up 50% of instance nodes.
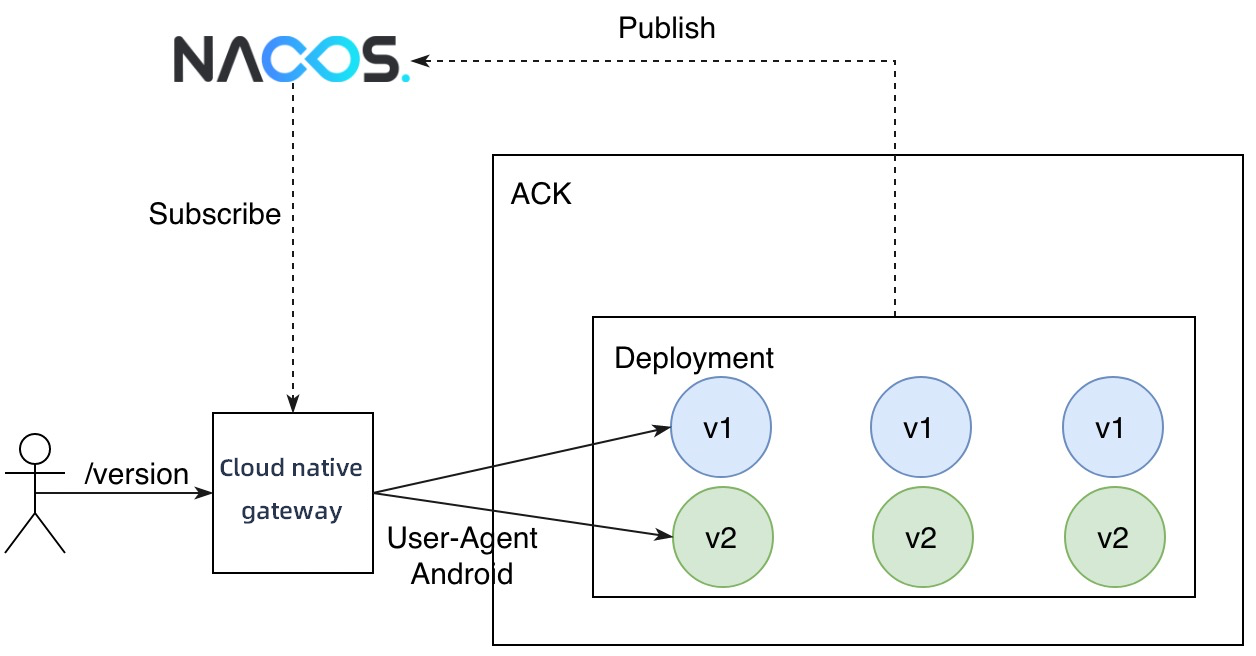
Modify the destination service in the created route to switch traffic from v1 to v2 in a blue-green deployment.
For more information about how to modify a routing rule for a cloud-native gateway, see Modify a routing rule.
Run the following command to send a test request:
for i in {1..10}; do curl "${GATEWAY_EXTERNAL_IP}/version"; echo ""; doneCommand output:
version: v2 version: v2 version: v2 version: v2 version: v2 version: v2 version: v2 version: v2 version: v2 version: v2
Traffic that accesses API resources by using the /version request path has been switched from v1 to v2.
Perform A/B testing
A/B testing routes traffic to the new version of a service based on the metadata of a user request. A/B testing dynamically routes traffic based on request contents. In this example, the new version can be accessed only by requests whose User-Agent value is Android, and other requests are sent to the original version.
The v1 and v2 versions of the httpbin service are still used. In addition, two routing rules need to be created.
Requests that match the /version path are routed to the v1 version.
Requests that match the /version path and contain Android in the User-Agent header are routed to the v2 version.
NoteThe version-v2 route must be added with a request header that is used for matching.
Run the following command to send a test request that does not contain Android in the User-Agent header:
curl ${GATEWAY_EXTERNAL_IP}/versionCommand output:
version: v1Run the following command to send a test request that contains Android in the User-Agent header:
curl -H "User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 4.0.3)" ${GATEWAY_EXTERNAL_IP}/versionCommand output:
version: v2
Requests are distributed to different service versions based on operating systems from which the requests are sent.
Perform a canary release
The canary release feature allows a small amount of traffic to be routed to the new version of a service. After the new version is verified, more traffic is gradually routed to the new version until all traffic is routed to the new version. In this process, the new version is scaled out and the original version is scaled in to maximize the resource utilization.
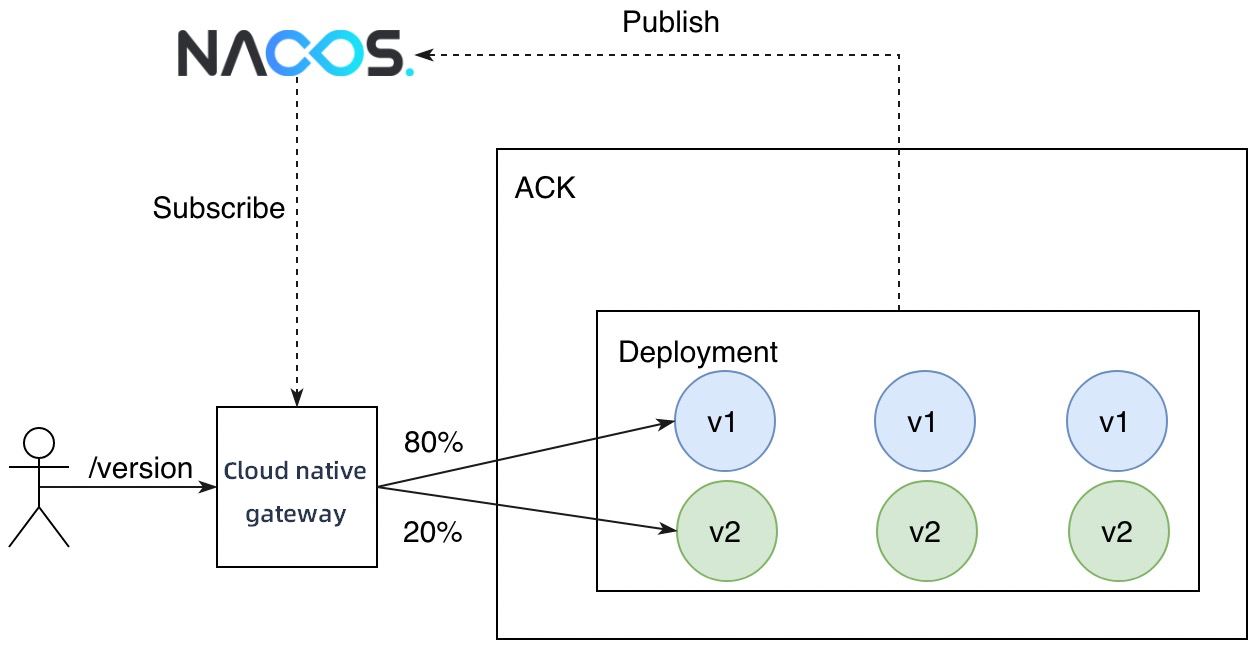
In a canary release, the number of replicas in the new version does not need to be consistent with that in the original version. The only requirement is that resources in the new version must be sufficient to handle canary traffic to the version. In this case, the number of replicas in the new version is set to 1. You can view the node distribution of versions in the Service Version section of the Services page.

Create a route to forward traffic to the new and original versions of the service based on node weights.
In the process, you must configure the v1 and v2 versions for the httpbin service and specify the weights based on which traffic is routed. For example, you can select Label Routing for Destination Service and set the weight of the v1 version to 80% and the weight of the v2 version to 20%.
Run the following command to send a test request:
for i in {1..10}; do curl "${GATEWAY_EXTERNAL_IP}/version"; echo ""; doneCommand output:
version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v1 version: v2 version: v1 version: v2 version: v1 version: v1
Two out of ten requests access the v2 version. This traffic distribution ratio is the expected ratio.
In actual business scenarios, you can gradually increase the traffic percentage for the new version after the version is verified. When you increase the traffic percentage, you must scale out the new version and scale in the original version.